Microfinance Market Size and Forecast 2025 to 2034
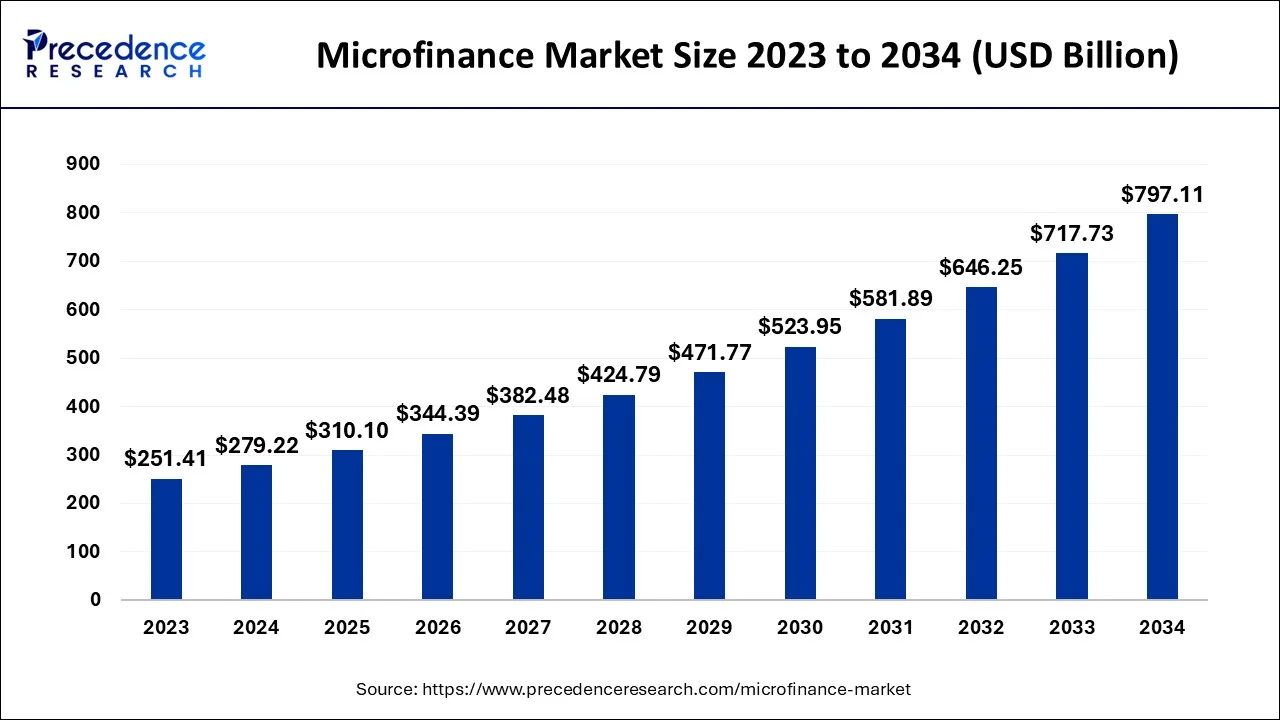
The global microfinance market size accounted for USD 279.22 billion in 2024, and is anticipated to hit around USD 310.10 billion by 2025, and is predicted to surpass around USD 797.11 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 11.06% between 2025 and 2034.
Microfinance Market Key Takeaways
- In terms of revenue, the market is valued at $310.1 billion in 2025.
- It is projected to reach $797.11 billion by 2034.
- The market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 11.06% from 2025 to 2034.
- Asia Pacific dominated microfinance market share in 2024.
- North America is expected to expand at the fastest CAGR between 2025 and 2034.
- By type, the bank segment captured the largest market share in 2024.
- Based on type, the microfinance institutes (MFI) segment is observed as fastest growing in the market.
- By purpose, the manufacturing/production segment contributed the largest market share in 2024.
- By purpose, the agriculture segment signifies as the fastest growing in global microfinance market.
Market Overview
In May 2024, the Accion Digital provided a $152.5 million funds to financial institutes in order to encourage micro, small and medium enterprises globally, which were looking for financial support in the year. The goal of this investment was to connect millions of MSMEs and people toward digital economy, to reduce poverty and develop future for underserved communities.
Microfinance and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
- Microfinance and SDGs are linked as microfinance financial services are spectacularly to achieving the SDGs, some SDGs relevant to microfinance organizations as:
- No poverty: microfinance help poor people to manage their households by providing financial services.
- Zero hunger: microfinance enhance economic status of poor farmers by providing low-interest loans to improve agriculture productivity, food security, and to achieve goal of zero hunger rates.
- Industry, innovation, and infrastructure: microfinance provides financial access to small, micro and medium infrastructure projects.
- reduced inequalities: microfinance encourages to minimize financial exclusion and enhance social inclusions.
- Gender equality: microfinance promoting women's empowerment and boosting it by helping economically with gender equality and modern livelihood.
- employments and economic growth: microfinance plays crucial role to create job opportunities, entrepreneurships and financial growth.
Market Scope
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 797.11 Billion |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 310.10 Billion |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 279.22 Billion |
| Growth Rate from 2025 to 2034 | CAGR of 11.06% |
| Largest Market | Asia Pacific |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | Provider Type, Purpose and Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Market Dynamics
Drivers
Increasing demand for financial inclusion to brighten the market prospect
Financial inclusion aims to provide individuals and communities, especially those underserved by traditional banking services, access to affordable and inclusive financial products. Microfinance institutions (MFIs) play a vital role in meeting this demand by offering small loans, savings accounts, insurance, and other financial services tailored to the specific needs of underserved populations. The demand for financial inclusion arises from recognizing that access to financial services is a fundamental right and an enabler of economic growth and poverty reduction. Many individuals and small businesses, particularly in developing countries, lack access to formal banking services due to low income, limited collateral, or remote locations. Microfinance addresses these barriers by providing flexible and accessible financial solutions that empower individuals to improve their livelihoods and create economic opportunities.
The microfinance market is driven by its transformative impact on individuals and communities. By receiving microloans, individuals can invest in income-generating activities, education, healthcare, and housing, leading to increased economic stability and improved living standards. Microfinance-supported small businesses can expand operations, create jobs, and stimulate local economies. Technological advancements have further accelerated the demand for microfinance. Mobile banking, digital payments, and innovative financial technologies have facilitated the delivery of microfinance services, making them more efficient, cost-effective, and scalable. These digital solutions have enabled MFIs to reach remote areas where traditional banking infrastructure is limited and provide financial services to previously excluded populations. Thus, the increasing demand for financial inclusion has driven the growth of the microfinance market.
Growing adoption of entrepreneurship and small business development
Microfinance institutions provide access to credit, savings, and other financial services that enable aspiring entrepreneurs to start or expand existing businesses. By empowering individuals with financial resources, microfinance contributes to job creation, income generation, and overall economic development. It significantly impacts women's empowerment, allowing them to overcome traditional barriers and take control of their financial lives. Many programs specifically target women borrowers, recognizing their entrepreneurial potential and the multiplier effect of empowering women. By offering financial services, business training, and support, microfinance empowers women to start and manage their businesses, leading to greater gender equality and economic independence. For instance, in April 2023, FINCA Microfinance Bank Limited announced a collaboration with CIRCLE Women, a social enterprise dedicated to women's economic empowerment and leadership development. The collaboration aims to empower women from low-income strata by promoting digital literacy and financial inclusion under CIRCLE Women's Digital Literacy Programme (DLP).
As the adoption of entrepreneurship and small business development increases, the demand for microfinance is expected to grow. This enables individuals to generate sustainable incomes, build assets, and lift themselves out of poverty. Microfinance institutions often target marginalized and low-income populations, providing them with financial services to increase their living standards and break the cycle of poverty. Furthermore, governments and industries worldwide are investing heavily in developing entrepreneurship and small business development, which is anticipated to drive the growth of the microfinance market.
Opportunities
Government initiatives to promote product diversification.
Growing government initiatives for individual economy developments holding great market potential. Promoting supporting financial inclusions like Financial Literacy programs, Microfinance Infrastructure Developments (MID), and regulatory agencies for microfinance are developing new way for the microfinance success among developing regions. Encouraging innovations in agriculture finance, saving products, microinsurance, mobile financing, and digital payment options are supporting growth of market. government has supported to allow financial services access to population to enhance economical stability. Growing participation by government and regulatory frameworks are likely to boost microloan distributions, young employments, and novel entrepreneurships.
Growing awareness of the sustainable development goals
Awareness of climate risks, opportunities, concerns about water, soil conservation, and energy storage has increased rapidly since from past few years. Farmers has been aware about risk managements of environmental changes, which has increased participation of social and governess factors to reduce risk and improve productivity. SDG-enable microfinance products like green microloans for renewable energy, microinsurance for climate resilience, Women's empowerment loas, education loans, agriculture microfinance for eco-friendly farming has impacting market expansion. Future of microfinance market is highly depended on SDG-aligned microfinance, promotion of sustainable financial products, cutting-edge technology innovations, increased climate and weather action focus and global cooperations. Adoption of SDGs and promotion of sustainability developments and economical inclusion for rural populations are the key trends of microfinance adoption in upcoming period.
Key Market Challenges
The high cost of microfinance is causing hindrances to the market:
Serving marginalized and low-income populations involves inherent operational costs, including outreach, loan administration, and client education. These costs, combined with the perceived risks of lending to such clients, can result in higher interest rates. Balancing the need for affordability with sustainable interest rates is a constant challenge for microfinance institutions. High-interest rates and fees associated with microfinance loans make it difficult for low-income individuals and small businesses to afford and repay the borrowed funds. The high cost can limit the number of people who can access these services, defeating the purpose of financial inclusion. It creates a barrier for those who require credit but cannot afford the high borrowing costs.
However, with technological advancements, microfinance costs are expected to decrease over time. It can explore innovative practices and technologies to reduce operational costs and enhance efficiency. Governments can also play a vital role by providing helpful policies and regulatory frameworks encouraging competition, transparency, and responsible lending practices.
Key Market Opportunities
- Government initiatives to promote product diversification.
- Development of advanced technologies in microfinance.
- Growing awareness of the sustainable development goals.
Provider Type Insights
The microfinance institutes (MFI) segment is the fastest growing segment of market. region with less banking infrastructures are majorly adopting microfinance institutes. Asia pacific is the largest region for MFI adoption due to increased population and urbanizations. Growth in digitalization and technologies are boosting the segment to success. Rasing small-scale business are under leaderships of women empowerment are driving need of microfinance institutes. Economical growth, social awareness, need of tailored financial products like saving accounts and microloans, as well as increased digitalization are likely to empower segment to highest success in upcoming years.
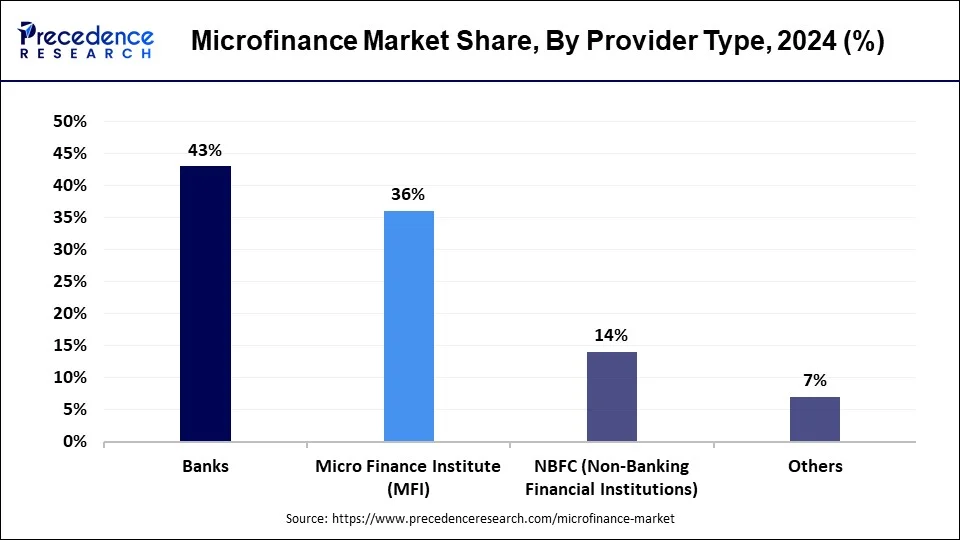
However, in some regions, MFIs and NBFCs might play a more prominent role in the microfinance market, particularly in areas with limited banking infrastructure or where specialized institutions have been established to cater specifically to the needs of underserved populations
Purpose Insights
The manufacturing/production segment dominated the global microfinance market. Growing population are encouraging the small-scale manufacturers to develop their organizations. Rapid growth of microfinance institutes is helping manufacturers and producers for training and mentorship also offers the economical help for supply of raw materials and equipment's. Microfinance products like Working Capital Loans, Inventory financing, Equipment Financing, Supply Chian Financing, and Business Loans are supporting small-scall businesses developments. This segment is expected to boost with growth in employment, enhance productivity and competitiveness of market.
The agriculture segment held the largest share of the microfinance market in 2023, due to its focuses on providing financial services and support to farmers, agricultural enterprises, and rural communities engaged in agricultural activities. Agriculture is a vital sector in many developing countries, and access to finance is crucial for smallholder farmers and agricultural businesses to invest in equipment, seeds, fertilizers, and other inputs necessary for production. Microfinance institutions targeting the agriculture segment offer tailored financial products, such as crop loans, livestock loans, agricultural equipment financing, and value chain financing, to support the entire agricultural ecosystem.
Regional Insights
Asia-Pacific dominates the market. This growth can be attributed to the surge in government initiatives aimed at poverty reduction and improving the standard of living for the population, which has become a significant trend in the microfinance market. Furthermore, much of the population resides in rural areas with limited access to traditional banking services. As a result, microfinance plays a crucial role in providing financial services to this underserved population.
According to data released by the Microfinance Industry Network (MFIN), the Indian microfinance industry experienced a substantial expansion in its loan portfolio during the financial year 2023-24. As of March 31, 2024, the sector's gross loan portfolio (GLP) or portfolio outstanding surged by 24.5 percent to Rs 4.33 lakh crore, up from Rs 3.48 lakh crore on March 31, 2023. This growth demonstrates the sector's resilience and its crucial role in providing financial access to underserved segments of the population.
- In February 2025, Pakistani fintech ABHI, which expanded its operations to the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, launched ABHI Microfinance Bank in collaboration with TPL Corp. ABHI is serving customers in Pakistan, UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Bangladesh through its credit-bridging products such as the Earned Wage Access (EWA) facility.
India is the major country supporting microfinance market with its vast population and growth of micro, small, and medium business, growing awareness of women empowerment driving government initiatives to support emerging institutes and enterprises of the country.
- India has emerged to 48% growth in credit linkage gap and 46% growth in loan distribution during FY 2022 to 2023.
- Government stakeholders, Banks, MFIs, NGOs and Federations are focusing on addressing the challenges of SHGs in order to gain flexible and inclusive growth of countries economics.
- Microfinance has promoted the Self-Help Group Bank Linkage Program (SHG-BLP), during 2022-2023, which is the largest microfinance program globally. This programme witnesses significant growth in some areas of country, however, there is still room for development and awareness of this program beneficial to clients and outreach.
Europe is a significant market for microfinance, with Germany, the United Kingdom, and France being the major contributors to the market's growth. This is due to the rising importance of microfinance in promoting financial inclusion and supporting entrepreneurship, leading to the establishment of microfinance institutions and supportive regulatory frameworks. Various institutions, including microfinance banks, non-governmental organizations, cooperatives, and social enterprises, provide financial services to individuals and small businesses, focusing on social impact and sustainable development.
- In February 2025, the Hellenic Development Bank established the Microfinance Fund, with the aim of providing funding for small businesses with up to 10 employees. This initiative aims to support 3,300 businesses, including 1,000 focused on promoting female entrepreneurship. According to a European Commission study for the 2021-2027 period, the financing gap in the microloan market in Greece is estimated at a minimum of 578.1 million euros per year, with the figure potentially reaching up to 750 million euros.
North America has numerous microfinance institutions, including community development financial institutions, credit unions, and non-profit organizations. These institutions provide microloans, business training, and other financial resources to small businesses and low-income individuals. The United States and Canada are the major countries driving the demand for microfinance in the North American region. The sector has grown steadily over the years, with the establishment of microfinance institutions and the participation of various stakeholders. Moreover, these countries invest heavily to empower underserved communities, reduce poverty, and support economic development. The focus extends beyond providing access to credit, including capacity-building programs, financial education, and mentorship.
North America to be significant growth
- In April 2023, for the promotion of mobile money for microfinance use, The United Nations Capital Development Fund (UNCDF) has introduced its some novel initiatives for developing countries. UNCDF is key player for two development sectors including Inclusive Finance and Local Development Finance.
Microfinance Market Companies
- Annapurna Finance Pvt Ltd
- Bank Rakyat Indonesia (BRI)
- Bandhan Bank
- CDC Small Business Finance
- Grameen America
- Cashpor Micro Credit
- Grameen Bank
- Kiva
- Madura Microfinance Ltd.
- Pacific Community Ventures Inc.
Recent Developments
- In April 2025, Belstar Microfinance Limited, a subsidiary of Muthoot Finance Limited, launched its Gold Loan services. This new offering is backed by the expertise and guidance of its promoter, Muthoot Finance Limited, ensuring the same high level of service and 7-layer security for its customers. With the launch of its Gold Loan services, Belstar Microfinance Limited aims to reach untapped markets and provide them with secure gold loan services.
- In December 2024, Nagaland Chief Minister's Micro Finance Initiative 2.0 was unveiled, opened a gateway of opportunities for aspiring entrepreneurs and farmers across the state. It is designed to provide holistic financial support, The initiative offers subsidies, tailored financial solutions, and innovative project support to turn ideas into reality.
- In April 2025, SBS, a global fintech company, announced the expansion of its SBP Core Amplitude technology for microfinance operations across Africa. Nearly 220 large retail groups, including greenfield banks and microfinances across Africa, such as KCB Group, BGFI Bank, Orabank, Coris Bank, and Advans Nigeria, already use SBP Core Amplitude to optimise their operations.
- In April 2024, in order to support small-scale organizations to scale up their economic inequity till next decade, Grameen America, a leading organization of microfinance has promoted the campaign to raise $600 millions in next five years.
- In September 2024, India's leading Non-Banking Financial Company and Microfinance Institute (NBFC-MFI), Annapurna Finance Pvt. Ltd., has made collaboration with British International Investment (BII), which is the UK's development finance institution and impact investor, and FinReach Solutions. The partnership was arranged with goal of enhancing India's Micro and Small Enterprises (MSEs) to empower nation's economy.
Segments Covered in the Report
By Provider Type
- Banks
- Micro Finance Institute (MFI)
- NBFC (Non-Banking Financial Institutions)
- Others
By Purpose
- Agriculture
- Manufacturing/Production
- Trade & Services
- Household
- Others
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Ask For Sample
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
 Get a Sample
Get a Sample
 Table Of Content
Table Of Content
 sales@precedenceresearch.com
sales@precedenceresearch.com
 +1 804-441-9344
+1 804-441-9344
 Schedule a Meeting
Schedule a Meeting