Deferiprone Market Size and Forecast 2025 to 2034
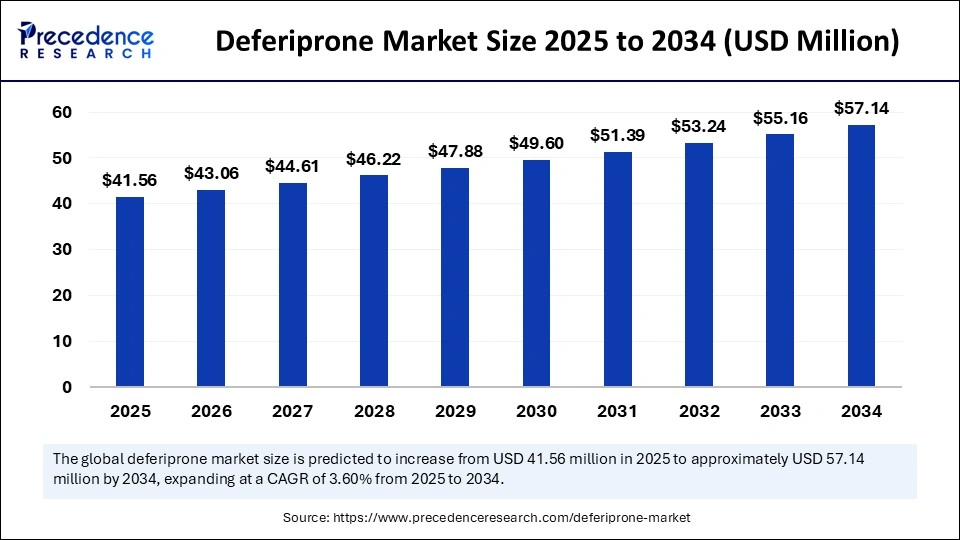
The global deferiprone market size was calculated at USD 40.12 million in 2024 and is predicted to increase from USD 41.56 million in 2025 to approximately USD 57.14 million by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 3.60% from 2025 to 2034. The market growth is attributed to the increasing prevalence of iron overload disorders, advancements in therapeutics, and growing awareness about the importance of early diagnosis and management.
Deferiprone Market Key Takeaways
- In terms of revenue, the deferiprone market is valued at $41.56 million in 2025.
- It is projected to reach $57.14 million by 2034.
- The market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 3.6% from 2025 to 2034.
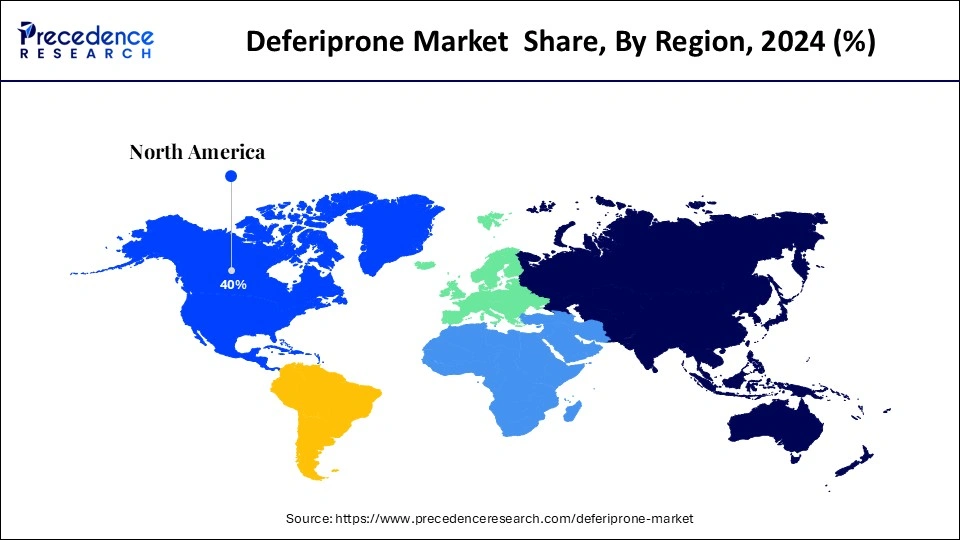
- North America accounted for the highest market share of 40% in 2024.
- Asia Pacific is anticipated to grow at a significant rate during the forecast period.
- By type, the tablets segment held the largest share of 79% in 2024.
- By type, the oral solutions segment is expected to grow at the fastest rate between 2025 and 2034.
- By therapeutic use, the iron overload disorders segment held the highest market share of 40% in 2024.
- By therapeutic use, the thalassemia treatment segment is anticipated to grow at a significant CAGR during the studied years.
- By indication, the transfusional iron overload segment contributed the biggest market share of 62% in 2024.
- By indication, the NTDT caused overload segment is projected to expand rapidly in the coming years.
Impact of Artificial Intelligence on the Deferiprone Market
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rebuilding the strategies of development and distribution of deferiprone through the improved precision and efficiency at several stages. AI-based models implemented in pharmaceutical companies' operations allow the detecting of optimal formulations and optimization of the dosing strategies for a particular group of patients. Furthermore, AI allows quick data processing from trials where deferiprone was applied, thus enabling researchers to find lines and make appropriate decisions in real time.
U.S. Deferiprone Market Size and Growth 2025 to 2034
The U.S. deferiprone market size was exhibited at USD 12.04 million in 2024 and is projected to be worth around USD 17.47 million by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 3.79% from 2025 to 2034.
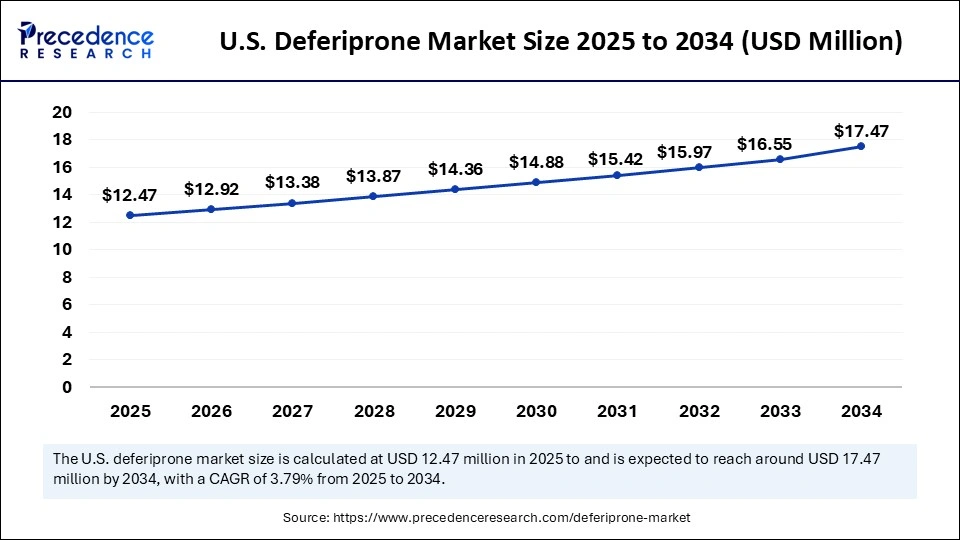
North America led the deferiprone market by capturing the highest market share of 40% in 2024. This is mainly due to the increased awareness of iron overload disorders. The region's well-developed healthcare infrastructure further bolstered the regional market growth. The U.S. is well known for having a well-developed healthcare system to facilitate rare disease treatments, such as thalassemia and sickle cell diseases.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), sickle cell disease (SCD) affects about 100,000 people in the U.S. This creates the need for effective iron chelation therapies such as deferiprone. Moreover, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved deferiprone for iron overload management, sustaining the long-term growth of the market in the region.
Asia Pacific is anticipated to witness the fastest growth during the forecast period, owing to the rising prevalence of thalassemia and iron overload disorders, especially in countries such as India, China, and Thailand. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that the incidence rate of thalassemia is very high in Southeast Asia. This, in turn, boosts the demand for iron chelation therapies. Governments around the region are making efforts to improve accessibility to improve accessibility to healthcare services. In 2024, the Indian government put in place a national screening program that would help in the early detection of thalassemia and prompt the demand for deferiprone.
Europe is considered to be a significantly growing area. The growth of the deferiprone market in Europe is attributed to the rising demand for deferiprone due to the increased awareness about the iron overload diseases. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) has recommended deferiprone for the iron overload disorders, making it more available and accessible among member states. Furthermore, government support and patient advocacy groups aiming to enhance rare disease treatments will likely drive the market.
Market Overview
The rapidly growing rate of iron overloading disorders worldwide is one of the key factors boosting the growth of the deferiprone market. Iron overload, caused by chronic blood transfusions or poor erythropoiesis, may cause critical conditions, such as heart failure, liver cirrhosis, and endocrine disorders. Deferiprone is an oral iron chelator, which is well studied and effectively used to maintain transfusional iron overload, especially in patients with thalassemia major and sickle cell disease. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) report published in 2024, sickle cell disease affects about 100,000 Americans, with 1 in 365 Black or African-American children born being diagnosed with the condition. Furthermore, the increasing knowledge and awareness of the presence of iron overload disorders and the continuity of research and development in the field of iron overload chelation therapies are expected to fuel the market.
Deferiprone Market Growth Factors
- Rising Incidence of Iron Overload Disorders: The increasing number of patients with iron overload disorders due to frequent blood transfusions is expected to contribute significantly to the market's growth.
- Advancements in Drug Formulations: Ongoing research and improvements in deferiprone formulations, including reduced side effects, are anticipated to enhance patient compliance and drive market expansion.
- Growing Awareness and Diagnosis Programs: Expanding global awareness and early diagnosis initiatives will likely improve treatment outcomes, further driving the demand for deferiprone-based therapies.
- Government Initiatives for Rare Disease Treatment: Increased governmental support and funding for rare diseases like thalassemia are projected to foster the growth of deferiprone treatment options.
- Rising Geriatric Population: The growing geriatric population, more susceptible to iron overload due to chronic conditions, is expected to contribute to the growing demand for effective chelation therapies.
- Shift Towards Oral Chelation Therapy: The growing preference for non-invasive, oral iron chelation therapies like deferiprone over injectable options is likely to accelerate market growth.
- Technological Advancements in Drug Delivery Systems: Ongoing innovations in controlled-release and sustained-release formulations of deferiprone are projected to enhance treatment efficiency and adherence.
Market Scope
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 57.14 Million |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 41.56 Million |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 40.12 Million |
| Market Growth Rate from 2025 to 2034 | CAGR of 3.60% |
| Dominating Region | North America |
| Fastest Growing Region | Asia Pacific |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | Type, Therapeutic Use, Indication, and Regions |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Market Dynamics
Drivers
Increasing Thalassemia Burden Driving the Demand for Effective Chelation Therapies
The increasing prevalence of thalassemia is expected to drive the growth of the deferiprone market. With the rising incidence of thalassemia, the demand for therapies using deferiprone is on the rise. A genetic blood disorder that entails excess iron build-up as a result of continued blood transfusions called thalassemia, requires efficient iron chelation treatment. Deferiprone, an oral chelator of iron, provides an easy and efficient solution for iron overload, particularly in resistance to other treatments. Countries in Southeast Asia, the Middle East, as well as Africa have been reported by the World Health Organization to have increased incidence rates that lead to the constant demand for treatment. CDC also reported in 2024 that thalassemia patients dependent on regular blood transfusions are at risk of chronic iron overload, which requires long-term chelation options such as deferiprone. Furthermore, thousands of newborns develop severe forms of thalassemia every year, largely in low- and middle-income countries, which hinders the growth of the market.
Restraint
Adverse Effects of Long-Term Use
Adverse effects associated with long-term use of deferiprone are expected to limit patient adherence, hampering the growth of the deferiprone market. Deferiprone treatment is associated with many side effects, including gastrointestinal disruptions, joint pain, and neutropenia. Agranulocytosis calls for constant monitoring of blood, which burdens the patients and healthcare systems. Clinical guidelines suggest weekly absolute neutrophil count (ANC) testing. However, patients in a low-resource environment cannot access regular lab services, and this delays the treatment decision. These clinical challenges reduce the acceptance of deferiprone by a patient as the first-line chelator.
Opportunity
Rising Research into Deferiprone's Applications in Neurological Disorders
Growing research on deferiprone to explore applications beyond thalassemia is expected to create immense opportunities for key players competing in the market. Researchers are exploring the application of deferiprone in neurological disorders, further creating high demand for this type of medicine. A 2024 phase 2 trial study published in the New England Journal of Medicine highlighted the effects of deferiprone in early-stage Parkinson's disease victims. During the study, deferiprone was not found to significantly improve the motor symptoms but the iron content in substantia nigra brain region involved in Parkinson's pathology was reduced. Moreover, the emerging applications of deferiprone point to the capacity of this drug to deal with iron-associated pathologies in neurological conditions.
Type Insights
The tablets segment dominated the deferiprone market with the largest market share of 79% in 2024 due to the convenience and ease of administration and patient preference for oral solid preparations. Tablets are widely used in the treatment of thalassemia for their potential for reliable dosing. Healthcare providers and patients prefer tablets since they do not require much preparation time as compared to injectables or liquid products. Furthermore, the tablet form facilitates the preparation into regimens, particularly in outpatient settings.
The oral solutions segment is expected to grow at the fastest rate, driven by their suitability for pediatric and geriatric patients. Oral solutions are widely preferred for patients who have difficulty swallowing. The freehand in the dosing for oral solutions gives an advantage when dealing with treatment regimens in young patients and those who have a problem with tablet formulations. Moreover, increased awareness among patients about the advantages of liquid formulations is likely to boost the acceptance of oral solutions.
Therapeutic Use Insights
The iron overload disorders segment held a considerable share of 40% market in 2024 due to the high demand for active chelation treatments for dealing with iron build-up, which typically occurs when multiple blood transfusions are required. These disorders harm organs if not monitored closely. The efficacy of deferiprone in managing these conditions, especially in patients who do not respond to other therapies, has made it a preferred treatment.
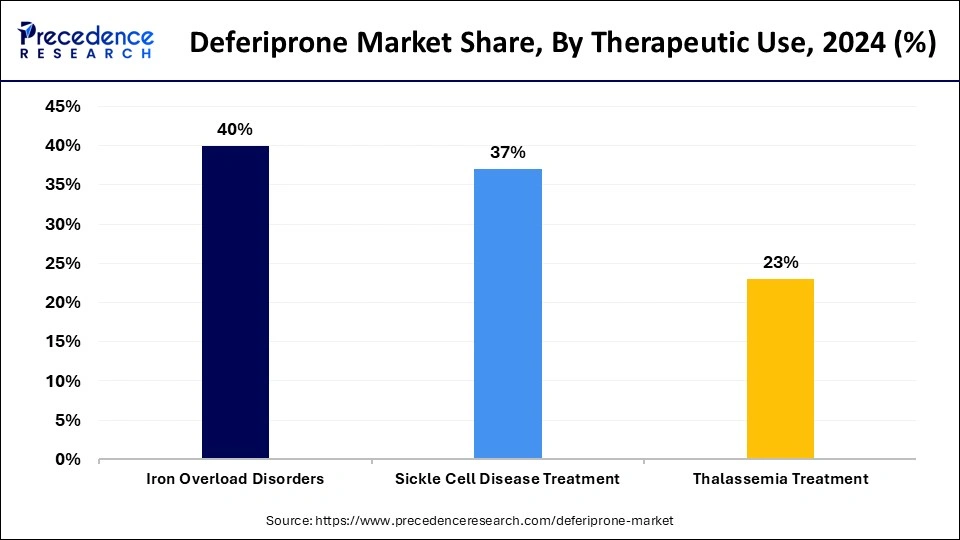
The thalassemia treatment segment is anticipated to grow at a significant CAGR during the studied years, owing to the rising incidence of thalassemia, particularly in Southeast Asia, the Middle East, and Africa. Thalassemia is a genetic blood disorder that causes abnormal hemoglobin production, leading to frequent blood transfusions and iron overload. Deferiprone, as an oral iron chelator, has demonstrated efficacy in reducing iron levels in thalassemia patients, making it a crucial part of the treatment regimens. Furthermore, health authorities are making efforts to enhance awareness and expand programs of early diagnosis, which contributes to the growth of the segment.
Indication Insights
The transfusional iron overload segment led the deferiprone market by holding more than 62% in 2024 due to the high incidence of iron accumulation in patients who received chronic blood transfusions. Such conditions, including thalassemia major and sickle cell disease, require frequent donations of blood, therefore accumulating much iron in the body. This overload leads to extreme suffering, such as heart failure, liver and endocrine failure. Deferiprone is very effective in the treatment of transfusional iron overload. It chelates excess iron, especially when other iron chelation therapy is ineffective. Furthermore, with prevalence rates of transfusion-dependent anemia being high in regions such as Southeast Asia, the Middle East, and Africa, there is a continued demand for effective chelation therapies.
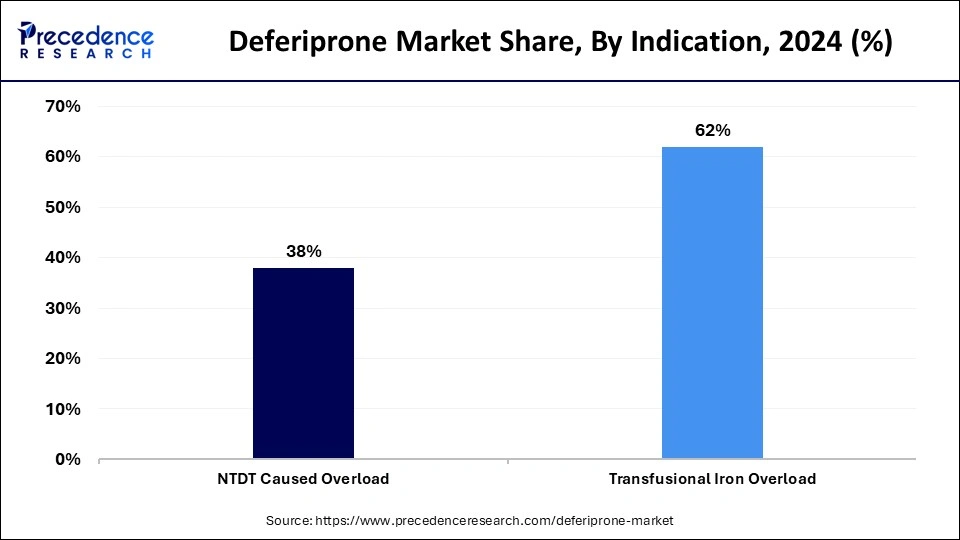
The NTDT caused overload segment is projected to expand rapidly in the coming years. Although there is no need for frequent blood exchange in patients with NTDT, iron overload is inevitable with ineffective erythropoiesis and enhanced gastrointestinal iron absorption. A promising treatment for excess iron overload in patients suffering from NTDT, deferiprone is an iron chelator known for its strength. Conventional methods may not be as effective in these patients. Furthermore, the increased familiarity with NTDT and its complications, coupled with improvements in the techniques for diagnosing, leads to increased uptake of deferiprone for controlling the NTDT-induced iron overload.
Deferiprone Market Companies

- Apotex Inc.
- Chiesi Farmaceutici S.p.A.
- Cipla Limited
- Novartis International AG
- Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
- Taro Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
- VHB Life Sciences Limited
- Zydus Cadila
Recent Development
- In April 2023, Chiesi Global Rare Diseases, a division of the Chiesi Group, announced that Health Canada approved Ferriprox MR (deferiprone extended-release tablets, 1000 mg) for the treatment of transfusional iron overload in patients with thalassemia syndromes when existing chelation therapies are inadequate. This extended-release version of deferiprone aims to improve treatment compliance by offering a more convenient dosing schedule. The approval highlights continued efforts to enhance therapeutic options for individuals living with rare blood disorders in Canada.
Segments Covered in the Report
By Type
- Capsule
- Oral Solutions
- Tablets
By Therapeutic Use
- Iron Overload Disorders
- Sickle Cell Disease Treatment
- Thalassemia Treatment
By Indication
- NTDT Caused Overload
- Transfusional Iron Overload
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Ask For Sample
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
 Get a Sample
Get a Sample
 Table Of Content
Table Of Content
 sales@precedenceresearch.com
sales@precedenceresearch.com
 +1 804-441-9344
+1 804-441-9344
 Schedule a Meeting
Schedule a Meeting