Sickle Cell Disease Treatment Market Size?
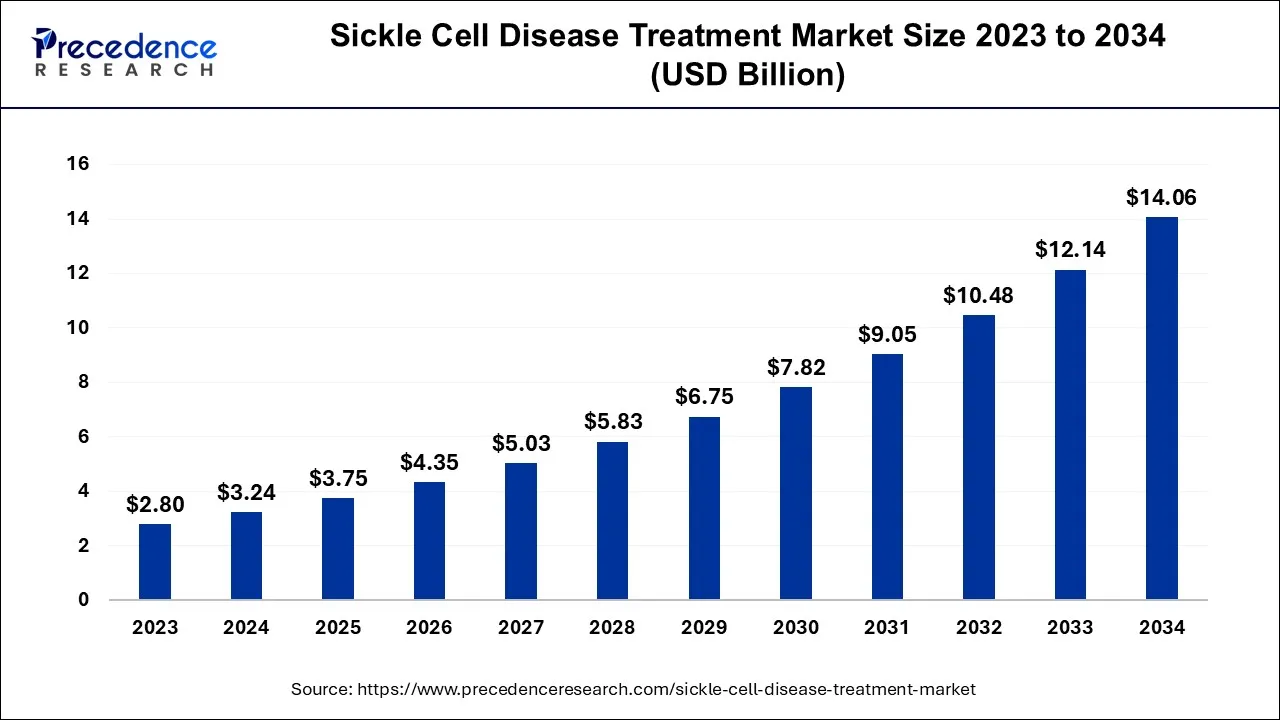
The global sickle cell disease treatment market size is valued at USD 3.75 billion in 2025 and is anticipated to reach around USD 14.06 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 15.81% over the forecast period from 2025 to 2034.
Market Highlights
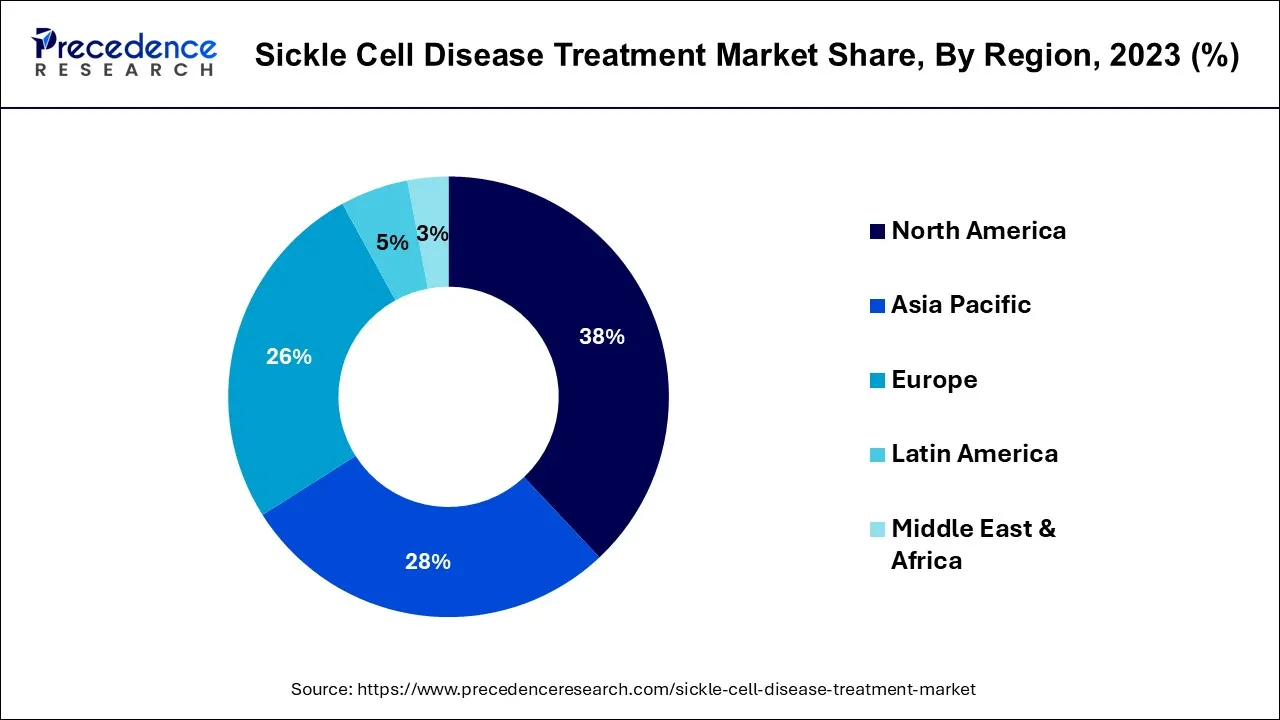
- North America led the global market with the highest market share of 38% in 2024.
- Asia-Pacific is projected to expand at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period.
- By Treatment, the blood transfusion segment registered the maximum market share of 49.5% in 2024.
- By Treatment, the bone marrow transplant segment is expected to grow at a remarkable CAGR of 42.8% during the forecast period.
- By End-use, the hospital segment recorded more than 61% of revenue share in 2024.
- By End-use, the Specialty clinics segment is estimated to expand at the fastest CAGR over the projected period.
Sickle Cell Disease Treatment Market Overview: Highlighting the Market Insights
Sickle cell disease is a genetic blood disorder that causes misshapen red blood cells, leading to pain, anemia, and organ damage. Treatment aims to manage symptoms and complications. Common interventions include pain relief with analgesics, hydration, and blood transfusions to improve oxygen levels. Hydroxyurea, a medication, can help reduce the frequency of painful crises. For severe cases, a bone marrow transplant is a potentially curative option. Patients also derive benefits from routine check-ups, vaccinations, and antibiotics to prevent infections. Education on self-care, including managing triggers such as dehydration and extreme temperatures, is vital for enhancing the quality of life for individuals with sickle cell disease.
Sickle Cell Disease Treatment Market Growth Factors
The sickle cell disease (SCD) treatment market is experiencing notable growth, driven by various factors and industry trends. Sickle cell disease is a genetic blood disorder characterized by misshapen red blood cells, leading to pain, anemia, and organ damage. One of the significant growth drivers is the continuous advancement in therapies. The emergence of gene-editing techniques like CRISPR-Cas9 holds promise for potential cures, stimulating increased research and development activities in the field. Increased awareness of sickle cell disease is a significant catalyst driving market growth. This growing recognition of sickle cell disease's prevalence, particularly in specific regions, has generated a heightened emphasis on early diagnosis and treatment.
Consequently, this increased awareness has triggered greater investments and initiatives geared towards improving the quality of life for individuals affected by the disease. Government support plays a pivotal role in driving the industry. Many governments have initiated programs and provided incentives to boost research efforts, enhance access to treatment, and address the challenges associated with SCD. These governmental efforts are particularly prominent in regions where the burden of sickle cell disease is substantial.
Moreover, the market's expansion is propelled by emerging economies that have historically faced constraints in accessing comprehensive healthcare services. In these regions, there is currently an upswing in investments in healthcare infrastructure and the diversification of treatment options, which is playing a substantial role in driving the overall expansion of the market. However, the industry faces its share of challenges. High treatment costs associated with novel therapies can limit access for some patients and strain healthcare systems.
Furthermore, the challenge of ensuring equal access to healthcare and addressing the unique requirements of diverse patient demographics persists as a hurdle in the quest for effective sickle cell disease treatment. Nonetheless, the industry is well-positioned for ongoing growth and innovation, dedicated to enhancing the well-being of individuals afflicted by SCD.
Major Key Trends in Sickle Cell Disease Treatment Market:
- Emergence of Curative Gene Therapies: Advancements in gene-editing technologies, such as CRISPR and lentiviral vectors, present curative possibilities for SCD, decreasing reliance on ongoing treatments and greatly enhancing long-term patient outcomes.
- Focus on Early Diagnosis and Screening: Innovative newborn screening initiatives and diagnostic advancements are facilitating earlier interventions for SCD cases, thus improving prognoses and fine-tuning treatment approaches from an early age.
- Increase in Public-Private Partnerships: Collaborations among government entities, pharmaceutical companies, and nonprofit organizations are expediting drug development, enhancing access, and broadening the scope of clinical trials for innovative SCD treatments.
Sickle Cell Disease Treatment Market Outlook: The Future Trends
- Industry Growth Overview: The growing incidence of diseases, advancements in gene therapies, and growing investments are driving the industrial growth in the market.
- Major Investors: Large pharmaceutical corporations, leading biotech firms, government bodies, and venture capital firms are the major investors in the market.
- Startup Ecosystem: To develop curative and one-time treatment for sickle cell disease with the use of advanced technologies is the focus of the startup ecosystems.
Market Scope
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 3.75 Billion |
| Market Size in 2026 | USD 4.35 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 14.06 Billion |
| Growth Rate from 2025 to 2034 | CAGR of 15.81% |
| Largest Market | North America |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | By Treatment and By End-use, and region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Market Dynamics
Drivers
Expanded access to healthcare and advancements in therapies
Expanded access to healthcare has significantly surged the demand for sickle cell disease treatment. Improved healthcare infrastructure, increased availability of medical facilities, and enhanced accessibility to specialized care have led to earlier diagnoses and more comprehensive management of sickle cell disease.
As a result, a larger patient population seeks treatment, driving up demand for therapies, medications, and supportive care services. This expansion in the patient base not only benefits affected individuals but also boosts market growth as pharmaceutical companies and healthcare providers respond to the rising need for effective treatments and therapies for sickle cell disease.
Moreover, Advancements in therapies, particularly the development of innovative treatments such as gene therapies and disease-modifying drugs, have ignited significant demand in the sickle cell disease treatment market. These breakthroughs promise enhanced symptom management, reduced complications, and potential cures, driving patient and physician interest.
As these therapies demonstrate effectiveness and safety, they instill greater confidence among healthcare providers and patients, leading to increased adoption and market growth. Moreover, ongoing research and development efforts further fuel the market's expansion as the pursuit of improved treatments remains at the forefront of addressing the challenges associated with sickle cell disease.
Restraints
Limited treatment options and limited awareness
The limited treatment options available for sickle cell disease restrain market demand by restricting the range of therapeutic choices for both patients and healthcare providers. With only a handful of treatments, especially curative options, patients often face a lack of comprehensive care. This limitation also hinders healthcare systems' ability to address the diverse needs of individuals with the disease. Consequently, the market's growth potential is hampered with the challenge of addressing the complex and varied requirements of sickle cell disease management.
Moreover, limited awareness poses a significant restraint on the sickle cell disease treatment market. Insufficient awareness also hinders research funding and public health initiatives, impeding progress in treatment development and the overall growth of the market. Addressing this awareness gap is crucial to ensuring that patients receive timely and appropriate care.
Opportunities
Improving access to care and developing curative therapies
Improving access to care in the sickle cell disease treatment market significantly boosts demand. Enhanced access means more patients can receive timely diagnosis and treatment, increasing the patient pool. This, in turn, drives greater demand for therapies, medications, and healthcare services. As accessibility expands, healthcare providers and institutions are more likely to invest in treating sickle cell disease, while pharmaceutical companies are incentivized to develop and market new treatments.
Ultimately, improving access to care not only benefits patients but also fuels market growth by addressing an underserved healthcare need. Moreover, the development of curative therapies has significantly surged the demand in the sickle cell disease treatment market. These innovative treatments hold the promise of not just managing symptoms but offering potential cures, transforming the outlook for patients.
The prospect of a definitive solution has intensified patient and physician interest, driving the market's growth. As these therapies prove their effectiveness and safety, they foster greater confidence, prompting increased adoption and market expansion. The pursuit of curative options represents a critical turning point in addressing the longstanding challenges of sickle cell disease treatment.
Segment Insights
Treatment Insights
According to the Treatment, the blood transfusion segment has held 49.5% revenue share in 2024. Blood transfusion, a crucial treatment for sickle cell disease (SCD), involves the infusion of healthy red blood cells to replace the abnormal sickle-shaped ones. In the SCD treatment market, a trend toward more targeted and less frequent transfusions has emerged. This approach aims to reduce iron overload, a common complication of regular transfusions, by using erythrocytapheresis, a specialized technique. Additionally, efforts are underway to enhance donor diversity and improve blood compatibility for better patient outcomes, reflecting ongoing advancements in SCD care.
The bone marrow transplant segment is anticipated to expand at a significant CAGR of 42.8% during the projected period. A bone marrow transplant, also known as a hematopoietic stem cell transplant, is a medical procedure where damaged or abnormal bone marrow is replaced with healthy stem cells. In the sickle cell disease (SCD) treatment market, this curative therapy has gained prominence as it offers the potential for a definitive cure. Recent trends show an increasing focus on optimizing the transplant process, including developing less toxic conditioning regimens, improving donor matching, and enhancing post-transplant care. These trends aim to make bone marrow transplantation safer and more accessible to a broader range of SCD patients.
End-use Insights
Based on the End-use, the hospital segment held the largest market share of 61% in 2024. Hospitals play a central role in the sickle cell disease (SCD) treatment market as key end-users. These healthcare institutions provide comprehensive care for SCD patients, ranging from diagnosis and acute crisis management to long-term disease management and specialized treatments. In recent trends, hospitals are increasingly adopting telemedicine solutions to improve accessibility for SCD patients, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Furthermore, some hospitals are participating in clinical trials for advanced therapies, contributing to ongoing research and the development of potential cures for SCD. Hospitals remain pivotal in addressing the evolving needs of SCD patients and driving advancements in treatment options.
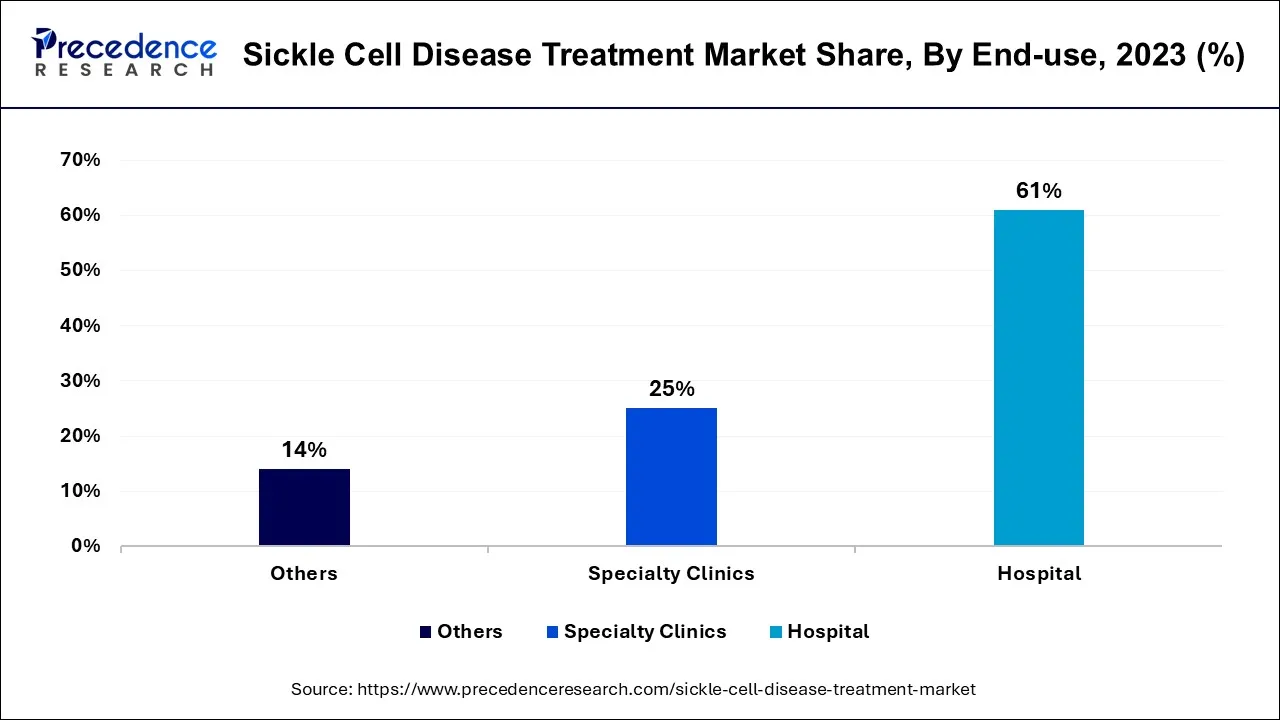
On the other hand, the Specialty clinics segment is projected to grow at the fastest rate over the projected period. Specialty clinics are healthcare facilities that exclusively focus on diagnosing, managing, and providing specialized care for individuals with SCD. These clinics offer comprehensive services, including regular check-ups, pain management, transfusions, and access to clinical trials. Trends in the SCD treatment market indicate a growing emphasis on the establishment of specialized SCD clinics. These clinics aim to centralize expertise, improve patient outcomes, and enhance the quality of care. They also facilitate easier access to emerging treatments and therapies, contributing to a more holistic and patient-centric approach to managing this genetic blood disorder.
Regional Insights
U.S. Sickle Cell Disease Treatment Market Size and Growth 2025 to 2034
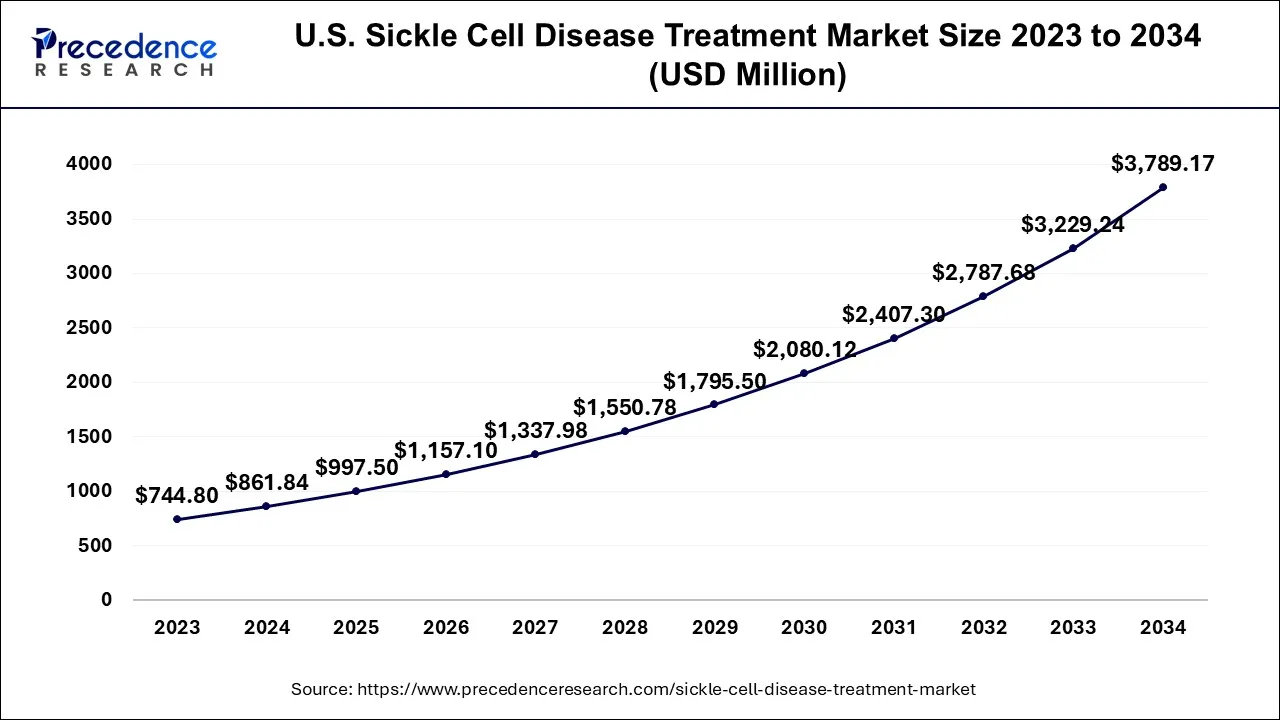
The U.S. sickle cell disease treatment market size accounted at USD 997.50 million in 2025 and is projected to be worth around USD 3,789.17 million by 2034, poised to grow at a CAGR of 15.96% from 2025 to 2034.
Increasing Comprehensive Care Drives North America
North America has held the largest revenue share 36% in 2024. This region has seen an increasing emphasis on comprehensive care and improved access to treatments. Specialized SCD clinics and centers of excellence have become more prevalent, providing multidisciplinary care to patients. Moreover, Participation in clinical trials and research is increasing, with an emphasis on creating curative remedies such as gene editing. Telemedicine has gained traction, enhancing access to care, particularly in remote or underserved areas. These trends reflect a commitment to advancing SCD treatment, addressing disparities, and improving the overall quality of life for patients in North America.
North America is observed to grow at a considerable growth rate in the upcoming?period because of rising awareness, a robust healthcare system, and a dense presence of pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies. Supportive regulatory environments, including fast-track approvals from the FDA, enhance innovation and the availability of new therapies, such as gene-editing treatments. Increased government funding, collaborations between public and private sectors, and advocacy from communities have improved screening practices and early diagnosis. Additionally, the growing use of advanced therapies and personalized medicine is leading to better patient outcomes, driving substantial market growth in the region.
Robust Research and Development Propels U.S.
The SCD treatment market in the United States is at the forefront of North America, bolstered by robust research and development efforts, access to innovative therapies, and supportive reimbursement frameworks. Institutions like the NIH and CDC play crucial roles in funding and raising awareness. With the recent approvals of gene-editing therapies and a rise in clinical trials, the U.S. is setting standards for treatment advancement, significantly enhancing the quality of life for those with sickle cell disease.
Growing Diagnosis and Treatment Boost Asia Pacific
Asia-Pacific is estimated to observe the fastest expansion. In this region, trends in the sickle cell disease (SCD) treatment market are evolving. While the prevalence of SCD is lower compared to some other regions, there is a growing recognition of the need for improved diagnosis and treatment. Advancements in healthcare infrastructure and increased awareness of SCD are driving early diagnosis efforts.
However, access to specialized care and curative therapies remains a challenge in many parts of the region. Telemedicine adoption, bolstered by the COVID-19 pandemic, is helping bridge some of these gaps. Additionally, collaborations between healthcare providers, governments, and pharmaceutical companies are contributing to research and the development of more effective treatments tailored to the Asia-Pacific population.
Advanced Healthcare Transforms China
The presence of advanced healthcare infrastructures is increasing the diagnosis and treatment of the sickle cell diseases in China. The growing government initiatives are also increasing their awareness and early diagnosis. Moreover, the companies are developing advanced therapies, driving their adoption rates.
Europe Driven by Growing Disease Incidences
Europe is expected to grow significantly in the sickle cell disease treatment market during the forecast period, due to its growing incidence. This is accelerating the R&D driving the development of novel treatment options. Additionally, the growing government policies and screening programs are increasing the demand for the same, promoting the market growth.
Screening Programs Stimulate the UK
The growing screening programs are increasing the early diagnosis and treatment of sickle cell disease. Their growing incidence is increasing patient awareness, which is backed by government support. This is increasing the development and adoption of advanced therapies, accelerating their clinical trials and approvals.
Government Initiatives Shape MEA
MEA is expected to grow in the sickle cell disease treatment market during the forecast period, due to growing government initiatives to tackle the increasing incidence of the disease. This is increasing the demand and adoption of novel treatment options. Their growing innovations are further supported by the investments from various sources, which are enhancing the market growth.
Growth of the Sickle Cell Disease Market in the UAE
The sickle cell disease market in the UAE is expanding due to an increasing patient population, substantial government support for healthcare, and a rising focus on innovative treatments, including gene therapies. This growth is also driven by enhanced public awareness and improved diagnostic capabilities through newborn screening programs.
Value Chain Analysis
- R&D
The R&D of the sickle cell disease treatments involves the development of potential curative gene therapies and novel small-molecule drugs.
Key players: Vertex Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, CRISPR Therapeutics. - Clinical Trials and Regulatory Approvals
Clinical trials and regulatory approvals of sickle cell disease treatments require the evaluation of their safety and long-term efficacy.
Key players: Vertex Pharmaceuticals, CRISPR Therapeutics. - Patient Support and Services
Patient support programs and services like financial assistance, education resources, and insurance navigation support are provided in the patient support and services of the sickle cell disease treatments.
Key players: Vertex Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, CRISPR Therapeutics.
Key Players in Sickle Cell Disease Treatment Market and their Offerings
- Novartis: Adakveo is provided by the company.
- Vertex Pharmaceuticals: The company provides Casgevy.
- Bluebird bio: The company provides Lyfgenia.
- Emmaus Medical: Endari is the product provided by the company.
- Pfizer: Oxbryta is provided by the company.
Recent Developments
- In December 2023, Vertex Pharmaceuticals and CRISPR Therapeutics launched Casgevy, a gene therapy utilizing CRISPR/Cas9 technology for sickle cell disease, following FDA approval. This represents the first gene-editing therapy for SCD to be commercially available in the U.S., presenting a potential one-time cure.
- In January 2024, Pfizer has completed the acquisition of Global Blood Therapeutics' assets pertaining to sickle cell disease, thereby enhancing its foothold in hematology. This acquisition bolsters Pfizer's portfolio with Oxbryta and other promising therapies currently under investigation that focus on minimizing complications related to SCD.
- In March 2024, Bluebird Bio has officially launched Lyfgenia, its lentiviral-based gene therapy for sickle cell disease, after securing FDA approval in late 2023. The company intends to make this one-time treatment accessible through specialized treatment centers throughout the U.S.
- In 2023, Bluebird a bio gene therapy developer, submitted a long-awaited application to the Food and Drug Administration to approve its drug for sickle cell disease, setting up competition with Vertex Pharmaceuticals and CRISPR Therapeutics.
- In 2023, Editas Medicine received FDA Orphan Drug Designation for EDIT-301 in the Treatment of Sickle Cell Disease. The FDA previously granted Orphan Drug Designation to EDIT-301 for the treatment of beta-thalassemia and Rare Pediatric Disease designation to EDIT-301 for the treatment of beta-thalassemia and sickle cell disease.
- In 2022, Pfizer completed the acquisition of Global Blood Therapeutics, Inc. (GBT), a biopharmaceutical company dedicated to the discovery, development and delivery of life-changing treatments that provide hope to underserved patient communities starting with sickle cell disease (SCD).
- In 2021, Vertex Pharmaceuticals and CRISPR Therapeutics established a collaboration agreement to develop, manufacture, and commercialize CTX001, an investigational CRISPR/Cas9-based gene editing therapy that is being developed as a potentially curative therapy for sickle cell disease (SCD) and transfusion-dependent beta-thalassemia (TDT).
Segments Covered in the Report
By Treatment
- Blood Transfusion
- Pharmacotherapy
- Bone Marrow Transplant
By End-use
- Hospital
- Specialty Clinics
- Others
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa
 Get a Sample
Get a Sample
 Table Of Content
Table Of Content



