Direct Reduced Iron Market Size and Growth 2025 to 2034
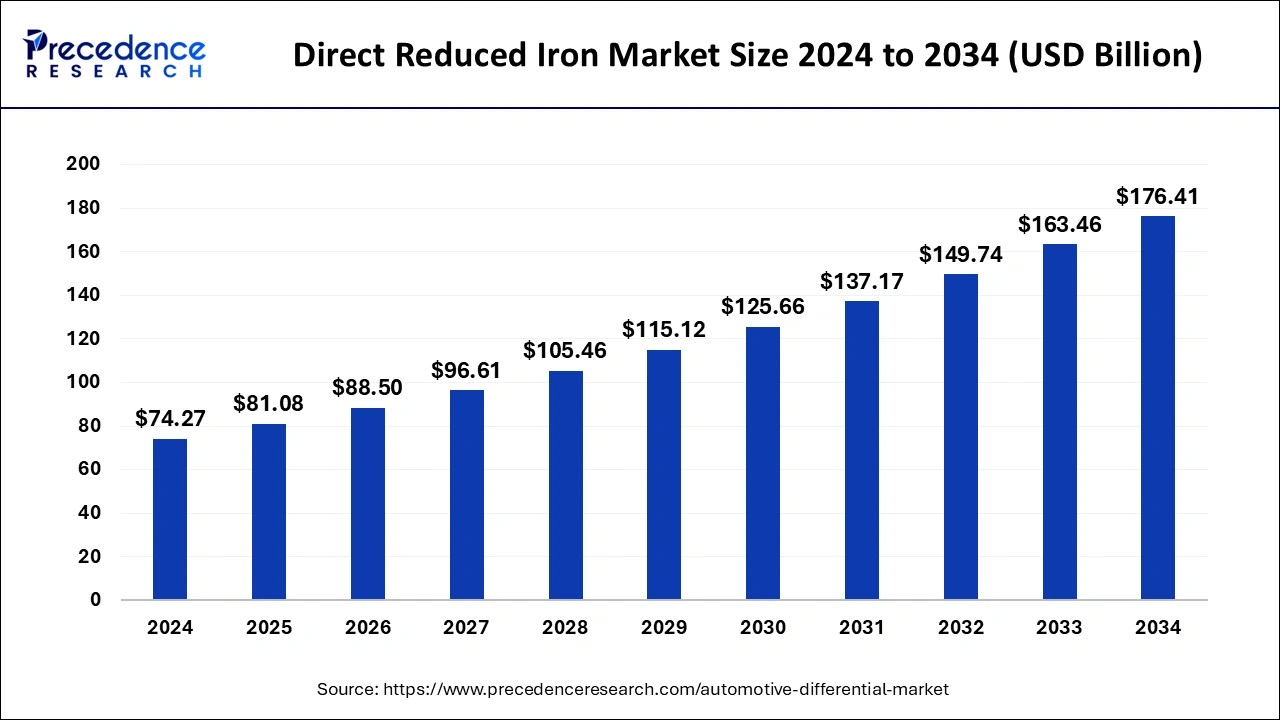
The global direct reduced iron market size was estimated at USD 74.27 billion in 2024 and is predicted to increase from USD 81.08 billion in 2025 to approximately USD 176.41billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 9.04% from 2025 to 2034. The primary reasons behind the growth of this market are a rise in demand for iron in industries and the need for sustainable solutions for extracting iron.
Direct Reduced Iron Market Key Takeaways
- The global direct reduced iron market was valued at USD 74.27 billion in 2024.
- It is projected to reach USD 176.41 billion by 2034.
- The direct reduced iron market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 9.04% from 2025 to 2034.
- Middle East and Africa held a significant share of the market in 2024.
- Asia Pacific is observed to be a significantly growing region during the forecast period.
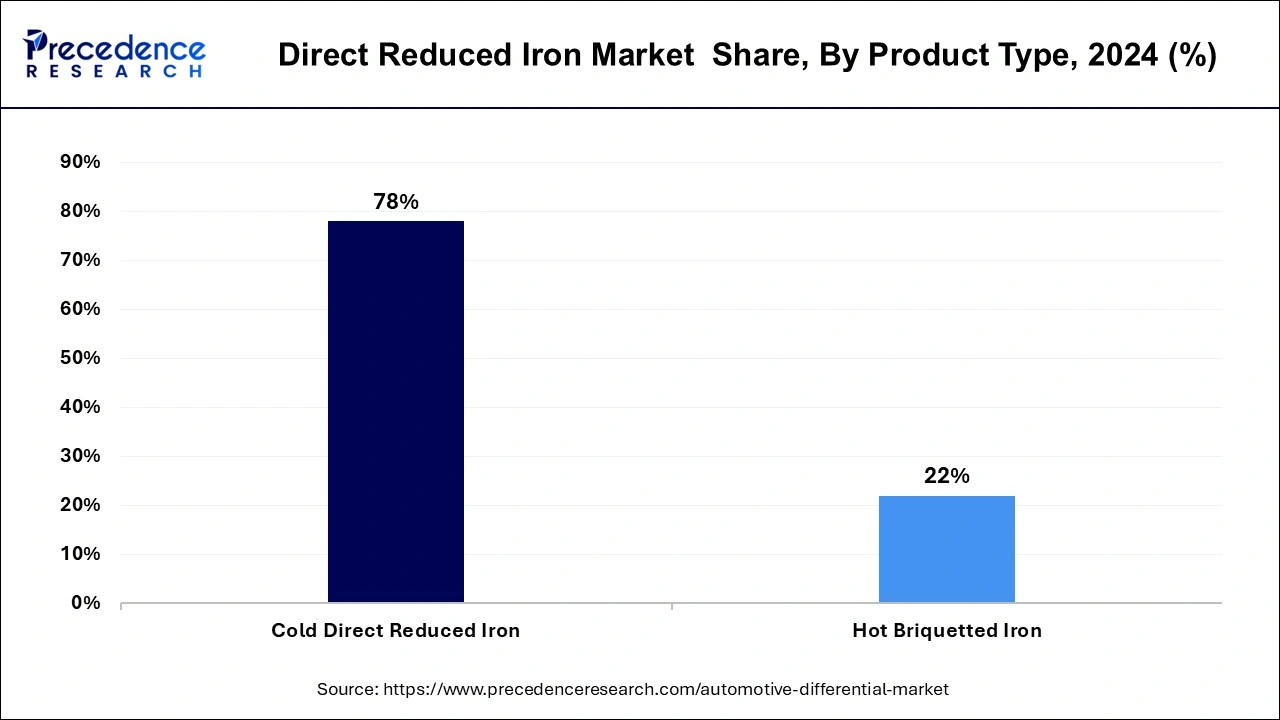
- By product, the cold direct reduced iron segment has generated more than 78% of the market share in 2024.
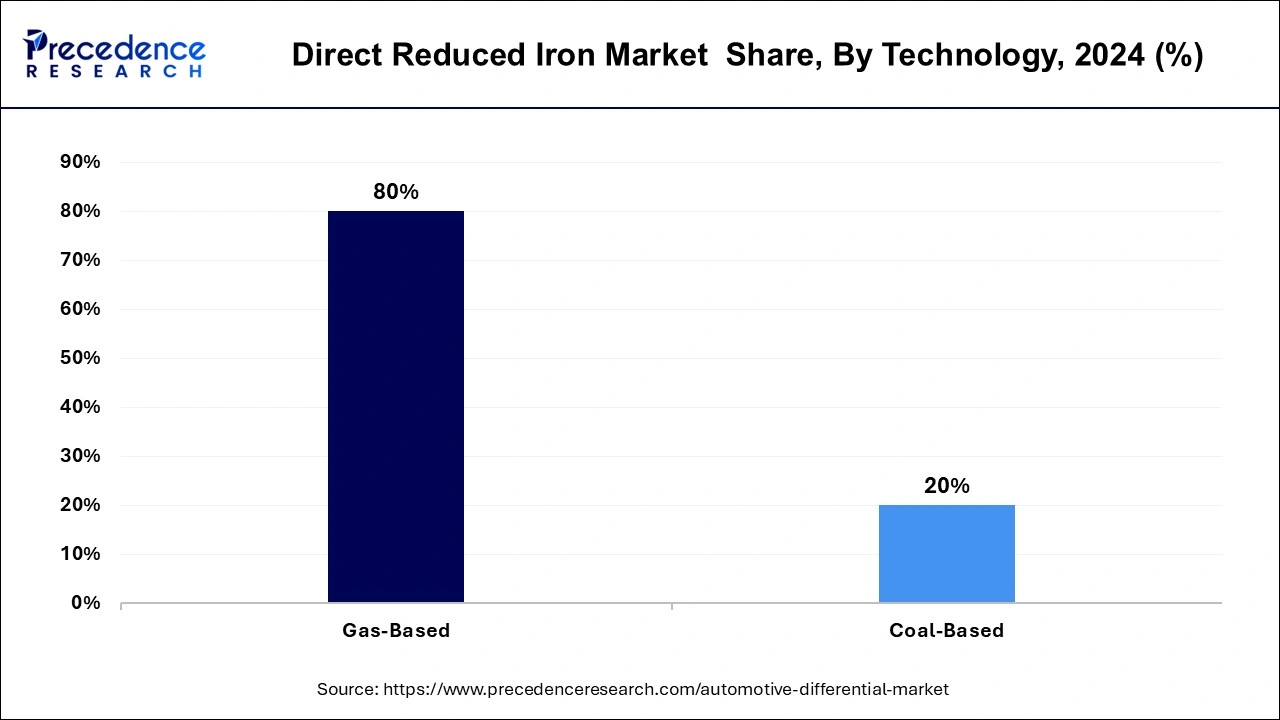
- By technology, the gas-based segment led the market with the largest market share of 80% in 2024.
- By application, the basic oxygen furnace segment is observed to grow at a notable rate during the forecast period.
- By end use, the construction segment dominated the market in 2024.
Market Overview
The direct reduced iron market refers to the global industry involved in the production, distribution, and consumption of direct reduced iron, also known as sponge iron. DRI is a high-purity, solid iron product obtained by reducing iron ore (typically in the form of pellets or lump ore) using a reducing gas or solid reductant at elevated temperatures in a direct reduction process.
The direct reduction process occurs in specialized reactors such as rotary kilns, fluidized bed reactors, or shaft furnaces, where iron oxide is converted into metallic iron without melting. The reduction is typically achieved using natural gas, coal, or syngas (derived from natural gas or coal) as the reducing agent.
- India was the largest producer of direct reduced iron in January 2021-December 2021. It produced 39.04 million tonnes of sponge iron. This was with a growth rate of 16.2%.
Direct Reduced Iron Market Growth Factors
- Rising need of iron in different industries, and its use in electronics, infrastructure, etc.
- Sustainable solutions provided by the direct reduced iron extraction and processing.
- Global trade patterns, tariffs, and trade agreements affect the flow of DRI products and raw materials between regions and influence market trends and pricing.
- Innovations in direct reduction technology, process efficiency, and environmental performance shape the evolution of the DRI market and drive adoption by steel producers.
Market Scope
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Growth Rate from 2025 to 2034 | CAGR of 9.04% |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 81.08 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 176.41 Billion |
| Largest Market | Middle East & Africa |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | By Product Type, By Technology, By Application and By End-use |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Market Dynamics
Drivers
Rising industrial application
Iron has many uses in industries, and for electric appliances, construction, etc. For overcoming the difficulties of conventional blast furnaces, direct reduction processes were developed. Unlike blast furnaces, they don't need to be a part of a steel plant. DRI plants require lesser capital investments, and the operating costs are low as well. Such plants are beneficial in countries where there is a lot of steel scrap to recycle. Direct reduced iron has a high iron content, that can be around 90 to 94 percent. It is good for mini mills. Hot briquetted iron is designed for easy shipping and storage. Considering the rising industrial application of such is observed to promote the market's expansion.
Environmental regulations
An advantage offered by direct reduced iron market is that the processes emit lower greenhouse gases and pollutants as compared to the conventional methods. Direct reduced iron is cost effective, and when there are fluctuations in the prices of iron, direct reduced iron can be the saviour. There are constant developments happening, for example, the development of better reducing agents, this is making the direct reduced iron production even more prominent in multiple industries. The demand for steel is growing too, as steel is used in kitchenware, hardware, electronics, automotives, etc.
Restraint
Intensive production method
Direct reduced iron market has several restraints that are responsible for hindering the growth of this market. Direct reduced iron can catch rust easily in open air. During the process of oxidation, a lot of heat is produced, and this happens in a large amount in bulk DRI cargos. Due to a sponge like structure, the direct reduced iron prevents heat dissipation, and isolated pockets of direct reduced iron can hence get heated up. When coming in contact with water, the direct reduced iron may emit hydrogen gas. Hydrogen is combustible, and it can lead to fires too. The process of making direct reduced iron is energy intensive and might consume gas or coal in a large amount. Production costs and profits are impacted because of the fluctuations shown in the energy resources.
Opportunity
Emphasis on sustainable practices
Direct reduced iron (DRI) plants have the flexibility to integrate renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydropower into their production processes. Renewable energy integration can further reduce the carbon footprint of DRI production and enhance its environmental sustainability credentials. By utilizing renewable energy for DRI production, stakeholders can capitalize on incentives, subsidies, and favorable market conditions for clean energy investments. DRI production generates less waste and by-products compared to traditional ironmaking processes. The direct reduction process produces primarily iron metal as the main product, with minimal slag and emissions of pollutants such as sulfur dioxide. This results in reduced waste disposal requirements and environmental pollution, supporting sustainable waste management practices and regulatory compliance.
Product Type Insights
According to product, the cold direct reduced iron market is dominated by the hot briquetted iron segment. It is considered ideal for electric arc furnace steelmaking and has become popular because of the flexibility and energy efficiency it offers.
Using hot briquetted iron, high quality steel products can be produced. It uses low grade scrap to make good quality steel products. It is used in combination with scrap or an alternative to scrap and used for ironmaking applications. Made directly from iron oxides, it does not contain any impurity. It has low residual element contents like copper, nickel, tin, sulphur or phosphorous. Hot briquetted iron has a high thermal and electrical conductivity. It is easy to handle and store.
Technology Insight
According to technology, the gas-based segment dominated the direct reduced iron market in 2024 by accounting for the largest market share. Gas-based direct reduction processes, such as the Midrex and HYL technologies, are known for their high energy efficiency compared to coal-based processes. Gas-based DRI plants typically use natural gas or syngas derived from natural gas as the reducing agent, resulting in lower energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions per ton of DRI produced. This energy efficiency is advantageous from both economic and environmental perspectives, driving the preference for gas-based technologies in the direct reduced iron market.
Application Insights
The basic oxygen furnace segment held a significant share of the direct reduced iron market and is observed to grow at a notable rate during the forecast period. Oxygen furnace technology offers high efficiency and flexibility in the production of DRI. Oxygen is injected into the furnace to react with carbon and other impurities, resulting in rapid and controlled reduction of iron ore pellets or fines. This process allows for precise control of temperature, gas composition, and residence time, leading to consistent quality and yield of DRI.
Oxygen furnace technology is energy efficient compared to traditional blast furnace methods for producing iron and steel. By using pure oxygen instead of air for the reduction reaction, oxygen furnaces minimize the energy required to heat and maintain the process temperature, resulting in lower fuel consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. The energy efficiency of oxygen furnaces makes them a preferred choice for environmentally conscious manufacturers seeking to reduce their carbon footprint.
End-use insights
Construction segment dominated the direct reduced iron market in 2024. Construction industry has a heavy demand of steel products and iron in order to provide strength to the structures. Due to a rising population, there is an increased need for better infrastructure. The construction industry is a major consumer of steel, which is essential for building infrastructure, residential and commercial buildings, bridges, roads, and other construction projects. Direct reduced iron (DRI) is a primary feedstock for steelmaking in electric arc furnaces (EAFs), which are commonly used in the construction industry to produce steel products. The high demand for steel in construction applications drives the consumption of DRI as a raw material.
Regional Insights
The Middle East and Africa held a significant share of the direct reduced iron market in 2024. Governments in the Middle East and Africa have implemented supportive policies and incentives to promote domestic steel production, attract foreign investment, and foster industrial development. These policies may include tax incentives, subsidies, import tariffs, and preferential access to energy resources, which create a conducive business environment for DRI producers and encourage investment in the sector. The Middle East and Africa are experiencing robust economic growth, urbanization, and industrialization, driving increasing demand for steel and steel products across various sectors, including construction, infrastructure, automotive, and manufacturing. The growing demand for steel in these regions creates opportunities for DRI producers to expand their production capacities and capture a larger share of the market.
Asia Pacific is observed to grow at a significant share in the direct reduced iron market during the forecast period. There is a rising awareness about carbon emissions and steps are being taken to develop sustainable solutions. There are carbon emissions from steel plants polluting the environment, however, direct reduced iron plants show lower carbon emissions, and don't make a serious impact on the environment. Hydrogen based technology for producing iron will further reduce the carbon emissions in the region.
North America is observed to grow at a notable rate during the forecast period in the direct reduced iron market. North America is a large hub for research and development. Constant research is taking place to develop sustainable solutions in all fields, and reduced iron market is one of them. As direct reduction involves reduction of iron ore in its solid-state using carbon monoxide and hydrogen, this is considered to be a sustainable way of producing iron, as hydrogen and carbon monoxide are extracted from natural gas. Direct reduced iron is also finding its uses in construction. Hydrogen based reduction is gaining popularity, because it shows lesser emissions.
Direct Reduced Iron Market Companies
- MIDREX technologies
- Hylsa SA
- de CV
- Kobe steel
- Jindal steel and power
- Metinvest Holding LLC
- Tenova HYL SA
- JSW Steel Limited
- Qatar Steel Company FZE
- Nucor Corporation
- Essar Steel India Limited
- JFE Steel India Limited
- Iron Dynamics
- LLC
- Tata Steel Limited
- NLMK Group
Recent Developments
- In January 2024, Baosteel Zhangjhing, a Chinese iron and steel plant launched a direct reduced iron plant having a production capacity if 1 million tons per year. For the production, natural gas, coke oven gas, and hydrogen will be used. It is the largest operating direct reduced iron plant in the world.
- In October 2023, the Hebel Bishi group in China got an approval for green hydrogen-2 million mt green electric furnace zero carbon short process casting project. The project is planned to be located in Naiman Banner, Tongliao city, Inner Mongolia. Scheduled period of construction is October 2023 to September 2025. Approximately 5 billion yuan is the budget for the project.
Segments covered in the report
By Product Type
- Hot Briquetted Iron
- Cold Direct Reduced Iron
By Technology
- Gas Based
- Coal based
By Application
- Steelmaking
- Electric Arc furnace
- Basic Oxygen furnace
- Foundries
- Other
By End-use
- Construction
- Automotive
- Aerospace
- Machinery and equipment
- Electrical and Electronic
- Renewable Energy
- Others
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Ask For Sample
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
 Get a Sample
Get a Sample
 Table Of Content
Table Of Content
 sales@precedenceresearch.com
sales@precedenceresearch.com
 +1 804-441-9344
+1 804-441-9344
 Schedule a Meeting
Schedule a Meeting