Generative AI is reshaping life sciences, with potential economic benefits of up to USD110 billion annually. It boosts efficiency in manufacturing, R&D, and clinical processes, driving productivity and innovation in the industry.
The life sciences sector is undergoing a complete reinvention thanks to generative AI, which is moving from small-scale digital upgrades. McKinsey estimates that scalable Gen AI could yield an annual value of between $60 billion and $110 billion. It maximizes manufacturing efficiency, reduces clinical cycles, increases R&D productivity, and customizes engagement. Scaling and integrating Gen AI across research, clinical, commercial, and operational domains is the true challenge, though.
Our analysis suggests that organizations treating Gen AI as a strategic transformation rather than as scattered pilots capture measurable financial and innovation benefits within the first two years of adoption. Success demands domain-driven strategies, unified data platforms, agile operating models, and rigorous governance.
In addition, up to 45% faster pipeline execution and 30% lower operating costs are reported by companies that have integrated Gen AI into their core business models. This demonstrates that Gen AI is a catalyst for change rather than merely a tool. Leading experts in the field are developing AI-driven value chains across manufacturing, clinical, and discovery processes, going beyond proof of concept.
Why Gen AI Matters for Life Sciences?
A shift to value-based care has increased regulatory demands; cost constraints, and faster innovation are all putting tremendous pressure on the life sciences sector, which includes pharmaceuticals, biotech, medical devices, and diagnostics. A set of potent levers is provided by Gen AI in this context.
Three issues facing the industry are complex data, high R&D costs, and a long time to market. Gen AI plays a strategic role in addressing these issues. Through the use of AI-powered predictive analytics, businesses can now prioritize promising drug targets early on and optimize clinical trial designs, saving years of development time.
- Speed and innovation in R&D/Discovery: Gen AI speeds up compound design, creates hypotheses, synthesizes large amounts of scientific literature, and may shorten time to market.According to our analysis by combining multi-omics data with predictive modeling, Gen AI can shorten the time needed for preclinical drug development from five years to less than two years. Companies that have already reported early-stage success using these strategies include Insilico Medicine and Recursion Pharmaceuticals.
- Better commercial & medical engagement: Gen AI can increase businesses productivity by producing personalized content insights for field teams and more intelligent stakeholder engagement workflows.Furthermore, in certain pilot projects, chatbot-based HCP interaction platforms and AI-assisted medical content generation have increased customer satisfaction levels by more than 50%. These tools allow medical receptionists and salespeople to respond to clinical inquiries in real time with data-backed answers.
- Operational Efficiency: Gen AI can eliminate repetitive tasks, enhance quality, and free up higher-value labor in a variety of industries, including manufacturing supply chain, regulatory documentation, and internal knowledge generation.AI-generated manufacturing records that cut human error by 70% and automated regulatory submission drafting that cuts down on documentation time by half are two examples. Across the value chain, these enhancements result in tangible operational gains.
- Strategic Differentiation: Effective use of Gen AI can become a differentiator in a highly competitive environment.As investors favor companies exhibiting digital leadership, our analysis shows that companies implementing AI-led R&D platforms can increase their market capitalization by 10 to 15 percent in just three years.
Our analysis suggests that most organizations struggle because they underestimate the complexity of data integration and culture change required for scaling. Businesses must create AI centers of excellence (COEs) that link research technology and business operations to overcome this. These kinds of structures guarantee data consistency, speed up adoption, and produce a long-term competitive edge.
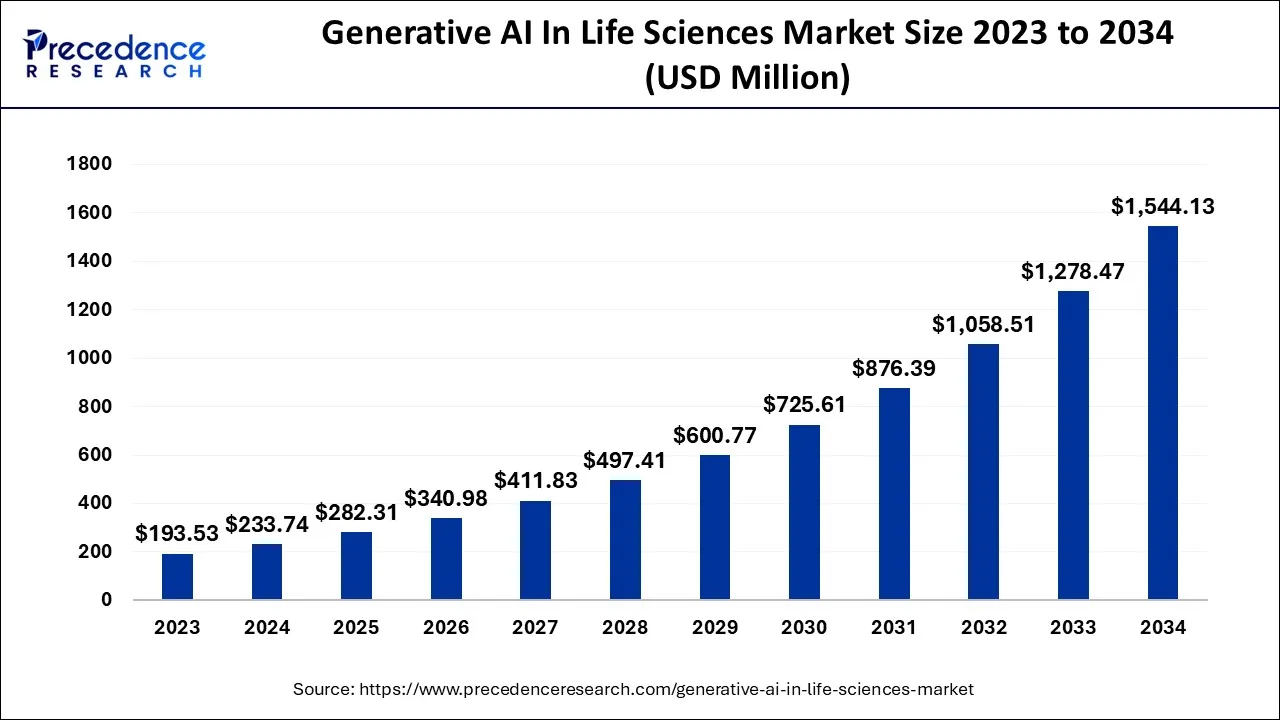
What is Generative AI in Life Sciences Market Size in 2023 to 2034
The global generative AI in life sciences market size is worth around USD 233.74 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 1,544.13 million by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 20.78% over the forecast period from 2024 to 2034.
The Competitive Edge of Gen AI in Life Sciences
New complexities in patient safety and compliance are introduced by Gen AI. Currently, regulatory bodies such as the FDA and EMA are issuing guidelines on transparency, traceability, and validation of AI models. According to our analysis, companies with internal governance systems such as continuous model monitoring and human-in-the-loop validation have higher approval success rates.
Transparency and fairness are also important aspects of ethical AI in addition to regulatory compliance. To examine data sources, model outputs, and potential bias in patient interactions, life science companies are forming internal AI ethics boards. Organizations that exhibit both performance and responsibility in their AI deployments will be favored in the future.
Furthermore, black-box AI models are giving way to explainable AI (XAI) frameworks that provide clarity on the prediction process. In clinical settings where decision traceability can have a direct impact on patient safety, this is especially important.
Internal AI oversight boards have already been established by companies like Johnson and Johnson and Roche to guarantee responsible deployment. According to our analysis, the next stage of AI-driven life science innovation will be dominated by organizations that align performance goals with ethical governance.
The Economics of Scaling: Roi Framework for Gen Ai
Implementing Gen AI on a large scale requires a balanced understanding of costs and value creation. Priority areas where AI investment translates into quantifiable returns can be identified with the aid of a well-defined ROI framework. By using the three-stage ROI model (direct cost savings, productivity improvement, and strategic value creation), organizations can expect a return multiplier of four to five times in three years, according to our analysis.
Our analysis also shows that businesses can speed up board approval for new AI projects by up to 60% by using a structured ROI framework. The reason for this is that unambiguous metrics such as cost savings and innovation speed give executives tangible proof of value creation. AI Performance Dashboards have been implemented by companies like Merck and Novartis, which directly link ROI to business results.
|
ROI Category |
Examples |
Expected Return |
|
Direct Savings |
Automation of documentation reduced trial costs |
15.25% cost reduction |
|
Productivity Gains |
R&D speed, AI-assisted manufacturing |
20-40% cycle time improvement |
|
Strategic Value |
Faster innovation pipeline, improved market positioning |
30-50% increase in ROI over 3 years |
Furthermore, real-time tracking of value creation can be done continuously by AI-based monitoring systems, which can notify leaders when performance veers off course. This makes it possible to make decisions based on data and to quickly correct courses, ensuring that every generation of AI initiatives supports the expansion of businesses.
By integrating performance dashboards that track these metrics in real time, leaders can justify further scaling and secure board-level buy-in.
Future Roadmap: Integrating Gen AI with Quantum and Omics Data
The convergence of multi-omics data, quantum computing, and genetic intelligence will be the next frontier of artificial intelligence in life sciences. Quantum-enabled models are capable of processing intricate molecular interactions and structures at speeds that are not achievable with traditional computing. According to our analysis, by 2030, quantum-gen AI hybrid systems could cut costs by up to 60% and cut drug discovery time in half.
Additionally, the integration of AI and quantum mechanics is anticipated to open up new avenues for personalized medicine. With the ability to simulate millions of molecular interactions in a matter of seconds, quantum-gen AI enables extremely accurate drug targeting and patient-specific dosage strategies.
The collaboration between Boehringer Ingelheim and IBM Quantum to predict chemical reactions with greater accuracy and the partnership between Roche and Google Quantum AI to model protein folding dynamics are examples of early initiatives.
The Evolutionary Path of Gen AI in Life Science
|
Phase |
Capability |
Industry impact |
|
2020-2023 |
AI Assistive Tools |
Automating documentation and literature review |
|
2024-2027 |
Autonomous Agentic Systems |
End-to-end workflow automation in R&D and clinical ops |
|
2028-2030 |
Quantum gen AI integration |
Accelerated molecular modeling and predictive therapies |
To create platforms that are ready for the future, this transition necessitates collaboration between pharmaceutical giants, AI startups, and quantity technology firms.
Building AI-Ready Organizations
As much as it is about technology scaling, Generation AI is also about people. Businesses that invest in rapid engineering, agile AI culture, and cross-functional skill development see two times higher adoption rates. Organizations that support experimentation and knowledge sharing through internal AI labs are more resilient to technological change, according to our analysis.
|
Pillar |
Description |
Outcome |
|
Empowerment |
Upskill employees in AI literacy and prompt design |
Increased adoption and innovation |
|
Collaboration |
Foster interdisciplinary teams |
Reduce implementation friction |
|
Governance |
Define clear accountability for AI ethics and compliance |
Sustainable, responsible scaling |
Why It’s Hard to Scale Gen AI?
Despite the promise, many life sciences firms are stuck in pilots. McKinsey identifies five major scaling barriers:
- Strategy & Domain Alignment: Too many businesses operate disparate use-cases without connecting them to a domain or business objective. Instead of using the scattergun of pilot McKinsey advocates for a domain-driven approach. Example: 38% of life sciences organizations surveyed cite research as their leading strategic focus for Gen AI, followed by commercial at 28%.
- Talent, Culture & Operating Model- Gen AI isn’t simply an IT project: Rethink the operating model, the talent mix (including positions like business translators, AI engineers, and prompt engineers), and integrating change management are all necessary for organizations. If you don't, you might finish a pilot but not be able to incorporate it into ongoing operations.
- Platform, Data, and Technology Foundations: Clean, governed data (both structured and unstructured), reusable platform components for workflow integration, model management, etc., are all necessary. You won't be able to scale if you use a case created from the ground up by every business unit.
- Ecosystem, Partnership & Workflow Integration: Academic institutions, technology suppliers, cloud/hyperscale partners, and regulatory agencies are all important to life sciences companies. Integration into real workflows is essential; it (not just nice to have) is critical.
Our analysis suggests that a domain-driven approach supported by cross-functional collaboration can expedite gen AI implementation.
A Practical Framework to Scale Gen AI
The global life sciences sector is turning into a testbed for innovation driven by artificial intelligence. Businesses are witnessing a shift from manual research to data-driven discovery as they incorporate Gen AI into core strategies. According to our analysis, early adopters outperform traditional operators in terms of patient outcomes and time-to-market. The competitive advantage stems from the capacity to instantly synthesize unstructured data from clinical trials, genomics, and market feedback. AI-generated models are being used by companies like Pfizer and Novartis to reduce drug development cycles by as much as 30%.
AI-as-a-service for clinical data or predictive diagnostics, for example, helps organizations unlock new business models and create diversified revenue streams. Long-term competitive differentiation is made possible by the ability to directly link AI results to commercial impact, which offers a tangible ROI.
Real-world Success Stories: Pharma Leaders Using Gen AI
Gen AI is being piloted by businesses worldwide to address particular pain points in drug discovery and manufacturing. To improve molecular target identification, for example, Sanofi used genetic AI, which resulted in a nearly 40% reduction in the screening phase. Using AI-generated insight tools, Astazenecca increased efficiency by 25% by automating clinical data analysis. According to our analysis, such projects successfully transition from pilots to enterprise deployment when they are in line with the domain strategy.
|
Company |
Gen AI use case |
Impact |
|
Pfizer |
AI-driven compound screening |
30% reduction in discovery cycle |
|
Sanofi |
Predictive target identification |
40% faster R&D throughput |
|
Novartis |
Automated clinical report drafting |
50% reduction in manual documentation time |
|
GSK |
Virtual patient simulations |
Enhanced trial accuracy and patient safety |
|
Roche |
Knowledge synthesis from unstructured data |
Improved R&D collaboration across departments |
Regulatory Readiness and Ethical AI in Healthcare
Domain-Driven Strategy
Pick one or two important business functions or domains (e.g., R&D at an early stage, commercial field force, manufacturing operations) rather than dispersing too widely.
Align Gen AI efforts with the business strategy (e.g., “reduce time-to-market by 20%”, “increase field-force productivity by 30%”).
Get C-suite sponsorship and establish a cross-domain governance body.
Sequence your efforts: start with use-cases that are high-value and feasible; then build the platform for reuse.
Platform & Data Foundation
Create a build once/deploy many platforms using prompt frameworks, vector stores, shared data ingestion pipelines, and retrieval augmented generation (RAG) architecture.
Assure data governance and preparedness, including lineage privacy/compliance quality checks, and structured and unstructured data.
Put human-in-the-loop controls for auditability, security, and model monitoring right away.
Avoid custom one-off silos; if you treat each use case as a separate project, you’ll duplicate effort and slow scaling.
Talent, Operating Model & Culture
Modify your talent mix by adding domain experts, business translators, AI engineers, and prompt engineers.
Organise cross-functional teams (business+tech+domain) in agile squads.
Incorporate change management through workflow redesign, ambassadors' user training, and asking how Gen AI changes the way we work.
Develop a reuse mindset by rewarding component reuse, creating internally visible success stories, and refraining from having each unit start from scratch.
Ecosystem & Partnerships
Engage outside partners such as startups, cloud/hyperscale academic institutions, and AI vendors.
Define clear criteria/triggers for when to scale a use case into full rollout.
To guarantee a smooth launch and prevent unpleasant surprises, the launch should involve regulatory and compliance teams early in the ecosystem.
Risk, Governance & Value Capture
Establish clear governance from the outset, including bias/hallucination guards, audit logs model monitoring, and human-in-the-loop rules.
Integrate risk functions early; do not treat risk as an afterthought.
Set KPT early time saved, cost reduced, productivity uplift, and probability of success improvements.
Track adoption, reuse, results, and make the business case for further investment.
Roadmap: From Pilot to Enterprise Scale
|
Phase |
Key Activities |
Expected Outcome |
|
Readiness & planning |
Assess current state, define strategy, domains, and sponsorship |
Clear baseline, leadership aligned |
|
Pilot/Proof of Value |
Select 1.3 high-value use cases, build MVP, define KPI begin small rollout |
Early wins, lessons learned |
|
Platform & Operating Model Build |
Build a reusable platform, set up cross-functional squads embed governance data pipelines |
Foundation for scale |
|
Enterprise Scale & Sustain |
Roll out across domains, monitor value capture, manage portfolio of use cases, optimize reuse. |
Gen AI is integral to business |
Use Case Snapshots
Here are some representative use cases to illustrate what Gen AI can do in life sciences.
- R&D & Discovery: Gen AI creates potential molecules, scans scientific literature, and suggests experiments.
- Clinical Development: Improving enrollment, choosing sites, automating data query resolution, and drafting protocols.
- Commercial/Medical Affairs: Creating customized content, interacting with HCPs, evaluating stakeholder sentiment, and customizing messaging.
- Operations/Manufacturing/Supply Chain: Forecasting demand, improving technology transfer, creating batch records, and optimizing process parameters.
Key Metrics & KPIs to Track for Gen AI Value
|
Metric Category |
Example Metrics |
|
Time to Value |
Days/months saved in document drafting cycle time reduction |
|
Productivity |
% reduction in manual hours, number of repetitive tasks automated |
|
Cost/Efficiency |
Cost savings in operations/ manufacturing, input/material cost reduction |
|
Probability of Success |
Uplift in the success rate of R&D/clinical projects |
|
Adoption/Usage |
% of eligible users actively using the Gen AI tool, frequency |
|
Reuse & Scale |
Number of domains, business units re-using platform components |
|
Risk & Compliance |
Number of model-related incidents/hallucinations audit findings |
Our analysis suggests that strategic alignment and strong governance are crucial to avoiding wasted resources in pilot projects.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls
Even with the best of intentions, a lot of organizations fall into well-known pitfalls. One of the most prevalent is pilot it is which is conducting an excessive number of unrelated experiments without a well-thought-out business plan. Another is a technology-first mentality in which business alignment is subordinated to enthusiasm for new tools. Some businesses undervalue the work involved in data preparation or fail to modify their operating models and cultures. Others ignore risk and adherence until the authority steps in. Lastly, unclear ROI is frequently the consequence of not defining value tracking mechanisms early on. It takes discipline to avoid these traps: begin with a strategic roadmap, establish solid data and governance foundations, involve risk partners early, and measure everything.
Why Now: The Strategic Imperative
Converging forces are changing the life sciences today, which makes scaling Gen AI urgent. As new modalities like gene and cell therapies expand the parameters of treatment, innovation cycles are getting shorter. Evidence is valued, and more transparency is being demanded by regulators and payers. As the healthcare industry undergoes rapid digital transformation, patients anticipate quicker, more individualized responses.
In the meantime, operational expenses keep going up, and growth is constrained by a lack of skilled workers in data science and clinical roles. Gen AI offers a way to simultaneously address these demands. Businesses that adopt it early on can build adaptable learning organizations that can quickly discover new things, develop quickly, and engage with customers in a timely manner. In an industry that is moving toward intelligent automation, those who put things off run the risk of falling behind.
Our analysis suggests that future generation AI agents will be able to operate autonomously, integrating multimodal data for insightful decision-making.
The Emerging Future of Gen AI in Life Sciences
In the future, agentic AI autonomous systems able to handle intricate workflows from clinical trial coordination to regulatory submission generation will surpass assistive Gen AI. Holistic insights can be obtained through multiple multi-models that incorporate text images, molecular structures, and omics data. Academic institutions, AI vendors, and life sciences companies will work together to develop domain-specific models as ecosystem collaboration increases. As frameworks like the EU, AI Act set standards for accountability, transparency, and safety regulations will also develop.
By embracing Gen AI early on, emerging markets, particularly those in the Asia Pacific and India, may surpass established players. These areas can act as testbeds for scalable, economical Gen AI deployments due to their wealth of technical talent and expanding digital infrastructure. For example, local AI startups could drive innovation partnerships with international pharmaceutical companies while multilingual generative models could transform how businesses interact with diverse healthcare professionals and patients in India.
Recommendations for Life-Sciences Leaders
A few principles stand out for executives navigating this shift. Consider general artificial intelligence as a strategic shift rather than a test project. Every initiative should be firmly rooted in a business plan that is driven by domains and has obvious leadership support. Make significant investments in talent platforms and data; these are the cornerstones that allow for scalability. Integrate risk management and governance early on to turn compliance into a differentiator rather than a limitation. Pay attention to change management and adoption, making sure staff members are aware of and have faith in the tools. Continue to monitor business impact and share success stories to keep the momentum going. Lastly, cultivate an ecosystem mentality by working with regulators, startups, and academic institutions to responsibly influence the direction of AI-enabled healthcare.
Trust, Ethics, and Responsible Acceleration of GenAI in Life Sciences
As Generative AI becomes interwoven with the life sciences value chain from molecule ideation and in-silico assays to protocol drafting and supply-chain orchestration, the industry’s foremost obligation is to anchor innovation in trust, ethics, and responsible governance. GenAI possesses unprecedented capacity to accelerate discovery, compress experimentation timelines, and democratize complex scientific reasoning, yet its potency demands a commensurate moral architecture. Trust must be engineered into every layer: transparent model behavior, auditable data lineage, bias mitigation, and robust validation frameworks that withstand regulatory scrutiny. Ethical stewardship requires that GenAI becomes an enhancer of scientific integrity, not a shortcut that jeopardizes reproducibility or inflates false positives. Equally vital is the protection of proprietary datasets, patient-derived information, and pre-clinical insights that form the intellectual lifeblood of biopharma. Responsible acceleration thus becomes a delicate choreography: embracing AI’s transformative velocity while maintaining rigorous oversight, preserving human interpretive authority, and ensuring that decisions affecting patient outcomes remain grounded in evidence-based, ethically aligned judgement. In this new paradigm, GenAI must not simply be powerful; it must be principled, predictable, and profoundly respectful of the human lives its innovations ultimately serve.
Conclusion
In the biological sciences, Gen AI is expanding the possibilities. It has the potential to improve operational efficiency at a never-before-seen scale, expedite clinical timelines to personalize engagement, and transform drug discovery. However, going beyond experimentation to enterprise transformation is necessary to realize that vision. Scaling Gen AI is more about discipline, design, and leadership than it is about technology, as McKinsey's analysis shows. In addition to seizing the current $100 billion opportunity, businesses that align strategy, establish solid data foundations, cultivate interdisciplinary talent, and maintain ethical governance will also influence the direction of intelligent healthcare in the future.
Success in this new era will be determined by how well intelligence is integrated into a company's DNA, changing decisions, speeding up research, and ultimately improving lives all around the world, rather than just how many models it produces.
 Figure 1: Gen AI’s estimated value potential across life sciences domains, based on McKinsey analysis
Figure 1: Gen AI’s estimated value potential across life sciences domains, based on McKinsey analysis
Table 1: Five Major Barriers to Scaling Gen AI
|
Barrier |
Description |
|
Strategy & domain alignment |
Disjointed pilots without a strategic focus limit scalability |
|
Talent & Culture |
Lack of cross-functional teams and AI-ready skills slows adoption |
|
Platform & data foundation |
Fragmented data systems hinder reuse and model deployment |
|
Ecosystem & partnership |
Limited collaboration with tech, regulatory, and academic partners. |
|
Risk & value governance |
Insufficient governance frameworks and unclear value metrics. |
Table 2: Key Metrics for Tracking Gen AI Impact
|
Metric Category |
Example Metrics |
|
Productivity |
Reduction in manual hours, tasks automated per month |
|
Time Efficiency |
Cycle time reduction in R&D, clinical, or documentation |
|
Cost Savings |
Operational cost reduction, efficiency per dollar spent |
|
Success Rate |
Improved R&D or clinical success probabilities |
|
Adoption & Usage |
Percentage of workforces actively using Gen AI tools |
|
Compliance & governance |
Rate of model validation, number of AI-related incidents |
About the Authors

Aditi Shivarkar
Aditi, Vice President at Precedence Research, brings over 15 years of expertise at the intersection of technology, innovation, and strategic market intelligence. A visionary leader, she excels in transforming complex data into actionable insights that empower businesses to thrive in dynamic markets. Her leadership combines analytical precision with forward-thinking strategy, driving measurable growth, competitive advantage, and lasting impact across industries.

Aman Singh
Aman Singh with over 13 years of progressive expertise at the intersection of technology, innovation, and strategic market intelligence, Aman Singh stands as a leading authority in global research and consulting. Renowned for his ability to decode complex technological transformations, he provides forward-looking insights that drive strategic decision-making. At Precedence Research, Aman leads a global team of analysts, fostering a culture of research excellence, analytical precision, and visionary thinking.

Piyush Pawar
Piyush Pawar brings over a decade of experience as Senior Manager, Sales & Business Growth, acting as the essential liaison between clients and our research authors. He translates sophisticated insights into practical strategies, ensuring client objectives are met with precision. Piyush’s expertise in market dynamics, relationship management, and strategic execution enables organizations to leverage intelligence effectively, achieving operational excellence, innovation, and sustained growth.





 Request Consultation
Request Consultation

