What is the HIV Drugs Market Size?
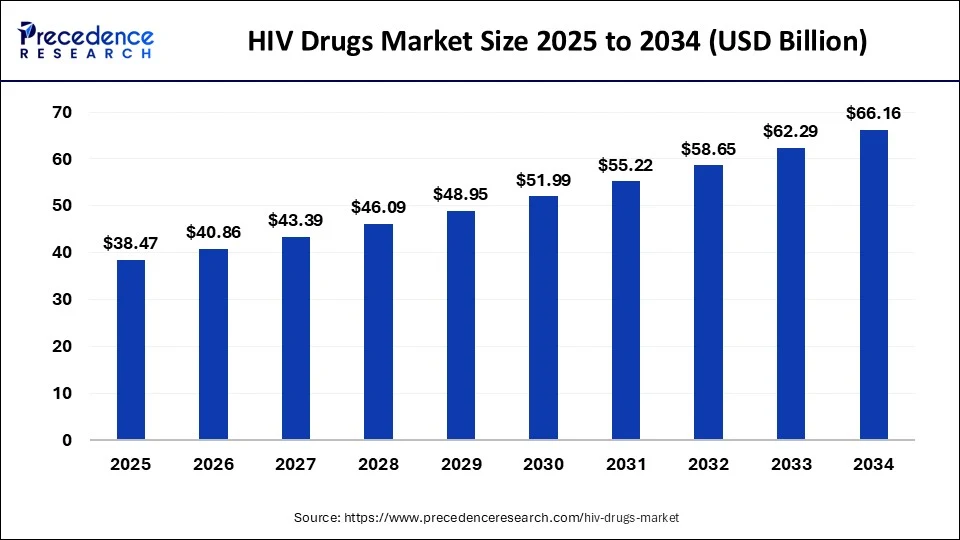
The global HIV drugs market size is calculated at USD 38.47 billion in 2025 and is predicted to increase from USD 40.86 billion in 2026 to approximately USD 66.16 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 6.21% from 2025 to 2034. The rising incidence of HIV cases and increasing resistance to existing therapies is pushing federal and private investment in the development of new therapies for HIV. These factors are driving growth in the HIV drugs market.
HIV Drugs Market Key Takeaways
- In terms of revenue, the global HIV drugs market was valued at USD 36.22 billion in 2024.
- It is projected to reach USD 66.16 billion by 2034.
- The market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 6.21% from 2025 to 2034.
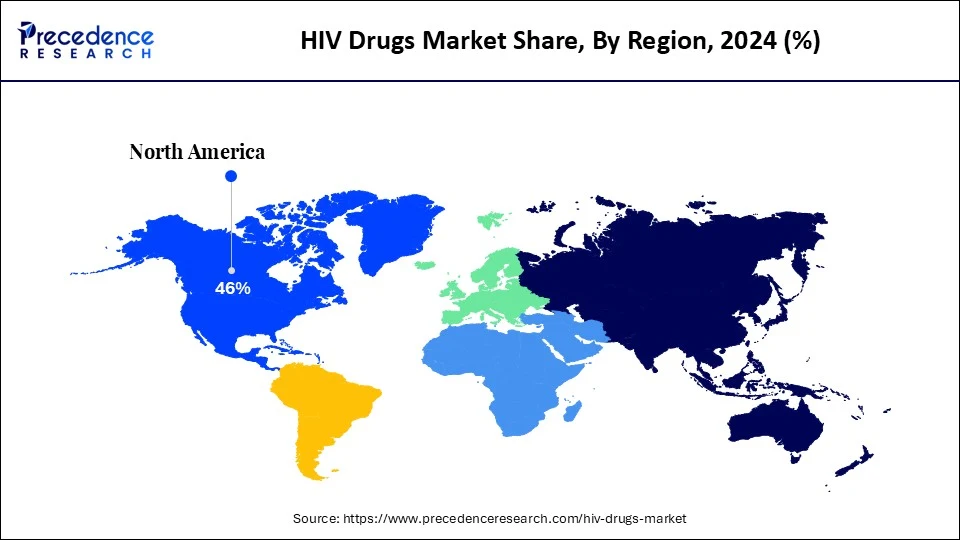
- America dominated the HIV drugs market with the highest market share of 46% in 2024.
- Asia Pacific is expected to witness the fastest compound annual growth rate in the market in the forecast period from 2025 to 2034.
- By medication class, the multi-class combination drugs segment led the global market in 2024.
- By medication class, the nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors segment is set to grow at the fastest rate in the market during the forecast period.
- By distribution channel, the hospital pharmacies segment dominated the market in 2024.
- By distribution channel, the online pharmacies segment is expected to grow at the fastest rate in the market over the forecast period between 2024 and 2034.
Combating HIV: Treatment, Prevention, and Research
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a pathogen that attacks the body's immune system, resulting in the development of Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). The virus destroys CD4 T lymphocytes, also known as Helper T cells, required for most of the body's immune responses. This makes the patient highly susceptible to other infections, including hepatic diseases, renal disease, and respiratory diseases such as pneumonia. HIV is spread through the bodily fluids of an infected person, such as blood, breast milk, and semen. The disease has no cure, but AIDS is preventable and is treated with antiretroviral therapy.
Despite an improved understanding of HIV and advanced treatments, the accessibility of treatments and awareness is lacking in emerging economies. Social stigma around the disease still discourages regular testing and prevents affected individuals from seeking treatment. Breakthroughs in the development of new drug therapies for HIV and the development of a therapeutic HIV vaccine provide opportunities for growth in the HIV drugs market.
The growing incidence of HIV due to the prevalence of unprotected sexual intercourse, the use of contaminated needles, and a lack of awareness around the transmission of the virus has led to a push for developing treatments. Government and private investment in the research and development of disease testing and management protocols drives growth in the HIV drugs market. Africa holds a notable share of the HIV drugs market. The large presence of HIV in the region has led to continued research and development efforts since the advent of the disease.
- Sub-Saharan African countries have the highest rates of HIV, with an estimated 26.0 million people affected in the region. However, approximately 90% knew their status, and 82% were receiving treatment in 2023.
- Between 1986 and 2020, the Republic of South Africa, Uganda, Kenya, and Nigeria accounted for 54% of the total indexed publications and HIV research output in African countries. Africa's proportion of the world's total HIV publications reached 31.3% in 2020.
How is AI Transforming the HIV Drugs Market?
Artificial intelligence is making waves in the medical industry, demonstrating great potential in developing effective treatments for several prevalent diseases. In terms of treating AIDS, machine learning is being applied in HIV prevention intervention strategies. Artificial intelligence has sped up the development of automatic identification of individuals at risk, cluster detection, partner notification, and counseling. People can use pre-exposure prophylaxis when the risk of contracting HIV is high. Machine learning is being explored to identify persons who will benefit from pre-exposure prophylaxis more quickly using population health data, biomedical information, and informatics.
- In 2023, the University of Florida is using the HiPerGator 3.0, the university's artificial intelligence initiative, to work with a team of researchers, clinicians, public health professionals, and a community-based advisory panel. The team is using AI to analyze medical records to uncover patterns of risk and bias for patients in Florida, especially those with limited access to state-of-the-art, effective treatments.
Market Outlook
- Industry Growth Overview:
The HIV drugs market is growing, driven by a growing patient population, novel drug formulations such as integrase inhibitors, improvements in generic manufacturing, regulatory support, and increasing awareness campaigns - Global Expansion:
The HIV drugs market is increasing worldwide, driven by a growing patient population, novel drug formulations such as integrase inhibitors, development in generic drug production, government support, and increasing awareness campaigns. North America is dominant in the market due to the presence of modern healthcare infrastructure and R&D spending. - Major investors:
The significant commercial investors and developers in the HIV drug market are large, research-based healthcare companies. It involves Gilead Sciences, Inc., ViiV Healthcare, Merck & Co., Inc., Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, AbbVie Inc., and many others.
HIV Drugs Market Growth Factors
- Large prevalence of HIV/AIDS across the globe due to a lack of knowledge about transmission risks and reluctance to seek testing and treatment.
- Research breakthroughs in new biotechnologies and the demand for pre-exposure prophylaxis regimens.
- Research and development spending for combating HIV as part of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals.
Market Scope
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 66.16 Billion |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 38.47 Billion |
| Market Size in 2026 | USD 40.86 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate from 2025 to 2034 | CAGR of 6.21% |
| Largest Market | North America |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | Medication Class, Drug Type, and Regions |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America and Middle East & Africa |
Market Dynamics
Drivers
Increasing prevalence of HIV/AIDS globally
The prevalence of HIV among the world's population is due to a lack of knowledge about transmission risks and the prevalence of unprotected sexual intercourse across Africa, the Americas, and Southeast Asia. In the HIV drugs market, factors like the opioid epidemic in the United States have led to growing concern about how injection drug-related opioid use might fuel the transmission of infectious diseases. Significant investment in developing global HIV strategies, with organizations such as the WHO, the Global Fund, and UNAIDS focusing on sustainable development goal 3.3 of ending the HIV epidemic by 2030.
- According to the World Health Organisation, in 2023, an estimated 630,000 people died from HIV-related causes, and an estimated 1.3 million people acquired HIV. HIV continues to be a major global public health issue, having claimed the lives of 42.3 million people so far.
Development of new treatment protocols for HIV-affected individuals
The pharmaceutical industry has continued to invest in research and development for the HIV drugs market. The goal is to achieve HIV remission or a functional cure. The current treatment protocols for HIV involve antiretroviral therapy, which includes taking a combination of HIV medicines daily that keeps the viral load low. The expanded use of pre-exposure prophylaxis, such as long-acting injectable cabotegravir, a demand for antiretroviral drugs, and generic equivalents to branded, expensive medication, is driving growth in the HIV drug industry. Innovations in the field, such as the development of long-lasting injectables and implants, have enhanced the effectiveness of HIV therapeutics.
- In 2023, Zyon Pharmaceutical company signed an exclusive agreement with the Hebrew University in Jerusalem for the development of peptides (short chains of amino acid monomers) which cause many copies of the HIV DNA to enter the cell instead of the usual one copy, triggering the cell's self-destruction mechanism, preventing a spread of the virus in the carrier's body.
Restraints
Slow regulatory approval and lack of awareness
Growth in the HIV drugs market is limited by a lack of awareness in emerging nations about the transmission methods of the virus. Lack of regular testing, especially among at-risk, leads to the risk of undetected transmission. According to the Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS), about 5.4 million people did not know that they were living with HIV in 2023. The lack of proper infrastructure, limited facilities for screening, and social stigma around the disease in emerging economies are hindering proper treatment. The regulatory processes involved in the approval of HIV injections involve rigorous evaluations for safety and quality standards, slowing down the adoption of new treatments.
- As the HIV epidemic waned off its peak in 2004, funding for research has seen a downward trend. According to UNAIDS, funding for HIV research in the United States dropped by 5% from 2022 to 2023 and by 7.9% between 2020 and 2023.
Opportunities
HIV drug resistance
The increased use of antiretroviral therapy over the past decade has saved the lives of millions. However, the widespread use of antiretroviral therapy has led to the emergence of HIV drug resistance. As treatments for HIV have evolved, so has the virus, with the emergence of resistance to Dolutegravir, a popular antiretroviral drug. HIV drug resistance occurs due to mutations in the genetic structure of HIV that affect its ability to replicate. HIV drug resistance needs to be countered with the development of new classes of antiretroviral drugs. Future growth in the HIV drugs market depends upon the unmet diagnostic and treatment needs present in African and Asian countries.
- According to the World Health Organisation, at the end of 2021, 28.7 million people, out of an estimated 38.4 million people living with HIV, were receiving ART globally.
- According to the WHO 2024 HIV drug resistance report and studies supported by the United States President's Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief, estimates show that resistance among individuals receiving Dolutegravir-based antiretroviral therapy with detectable viremia ranges from 3.9% in people without viral suppression for at least nine months to 19.6% in people with heavy prior treatment experience.
Segment Insights
Medication Class Insights
The multi-class combination drugs segment led the global HIV drugs market in 2024. Multi-class combination drugs combine different subtypes of HIV medication into one regimen based on the presentation of HIV, possible side effects, and ease of adherence to treatment plans. Treatment also varies depending on the type of HIV virus: wild-type virus (naturally occurring virus) or a drug-resistant one (mutated virus). These multi-class combinations combine various types of nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors, non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors, integrase strand transfer inhibitors, and more. The high comorbidity of HIV and Hepatitis and the common medication pool between the two diseases also contribute to the usage of multi-class combination drugs.
- According to the WHO guidelines on the use of antiretroviral drugs for treating and preventing HIV infection, Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate and Emtricitabine combination medicines are the preferred backbone regimen for HIV post-exposure prophylaxis in adults and adolescents. Other multi-combination drugs, such as Atripla and Genvoya, are commonly prescribed.
The nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors segment is set to grow at the fastest rate in the HIV drugs market during the forecast period. Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors block an HIV enzyme called reverse transcriptase, preventing the conversion of its RNA into DNA and preventing the virus from replicating. According to a study published by the Creighton University School of Pharmacy & Health Professions, among various FDA-approved treatments, nucleoside/nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors were most effective in limiting HIV-1 infection. Further research and development efforts into nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors have led to the development of new medication in this subtype. The newer generation of reverse transcriptase inhibitors have longer half-lives, more favorable adverse effect profiles, and fewer drug interactions.
Distribution Channel Insights
The hospital pharmacies segment dominated the HIV drugs market in 2024. The number of people currently receiving antiretroviral therapy in hospitals leads to high sales of HIV drugs in hospital pharmacies. In regions like Saharan Africa, people with HIV-related diseases occupy more than half of all hospital beds.
The online pharmacies segment is expected to grow at the fastest rate in the HIV drugs market over the forecast period between 2024 and 2033. The digitization of healthcare with telemedicine and the rise of medical e-commerce have spurred online sales of HIV drugs in high-income economies. Improvements in logistics and the rise of online payment platforms have improved accessibility in emerging economies where federal healthcare expenditure and disposable incomes continue to rise.
Implement Type Insights
The tillage/soil preparation implement segment accounted for the dominating share of 34.60% in 2024. The segment includes ploughs (moldboard, disc, chisel), harrows (disc, tine), cultivators (field, rotary), rotavators / rotary tillers, and subsoilers. Tillage implements play a vital role in numerous primary tasks such as breaking up soil, preparing a seedbed, controlling weeds, and others. The growth of the segment is mainly driven by the growing demand for efficient and sustainable agricultural practices, which require efficient use of water resources and minimal use of chemicals.
Power Source Insights
The powered segment held a dominant presence in the coronary stents market in 2024, with 61.30%. The powered segment includes PTO-powered and hydraulically powered. Powered equipment is more efficient and productive, which allows farmers to accomplish more in less time and with reduced labor. Powered equipment allows for precise and consistent results, which is crucial for modern farming operations. Moreover, the increasing trend towards mechanization in agriculture is driving the demand for powered tractor implements.
Mounting Type Insights
The three-point hitch-mounted segment held the major market share of 47.90% in 2024. The growth of the segment is attributed to the increasing agricultural mechanization and the global shortage of agricultural labor is making mechanized tools more essential. Additionally, the strong focus on precision agriculture is significantly boosting the adoption of more sophisticated hitch systems. The market is experiencing a shift toward quick-hitch systems, which reduce implement attachment time by nearly 70%.
Application Insights
The land preparation segment registered its dominance with 33.50% over the global tractor implements market in 2024. The land preparation is segmented into plowing, tilling, and harrowing, which are all important for tasks like breaking up soil, preparing seedbeds, leveling, and others. Land preparation is a crucial step for successful crop cultivation. The growth of the segment is driven by the growing need for improved soil health and the increasing demand for precision agriculture techniques.
End-User Sector Insights
The agriculture segment contributed the biggest market share of 89.20% in 2024. The agriculture segment includes farm-level (large, medium, small) and commercial farming. Agriculture is a significant and growing industry. The industry is seeking improved farming productivity, enhanced efficiency, and reduced labor dependency through advanced mechanization and precision farming technologies. In addition, the rising global food demand necessitates more efficient and productive farming equipment, along with the increasing integration of smart and precision farming technologies, leading to improved resource efficiency and higher yields in the agriculture industry. Individual Farmers are increasingly adopting advanced mechanization, owing to the labor shortages and increasing need to boost yield. Large Commercial farming is the early adopter of advanced technology, like GPS-guided machinery, autonomous equipment, and others, to optimize resource utilization and increase productivity.
Regional Insights
North America: Increasing Pharmaceutical Production
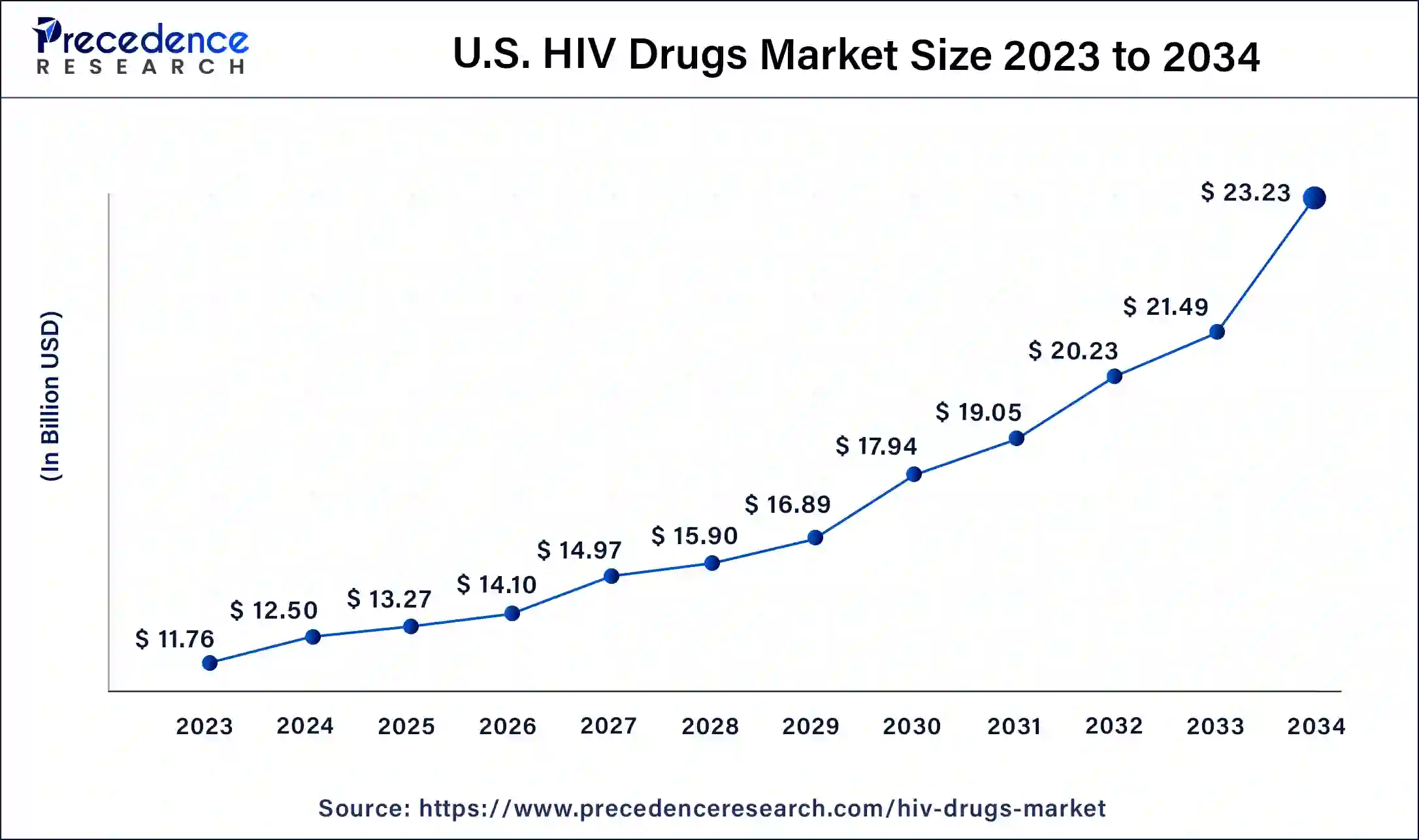
The U.S. HIV drugs market size is exhibited at USD13.27 billion in 2025 and is projected to be worth around USD 23.23 billion by 2034, poised to grow at a CAGR of 6.39% from 2025 to 2034.
North America dominated the HIV drugs market in 2024. The prevalence of HIV in the region, combined with the presence of large pharmaceutical companies investing in the research and development of HIV medication, is driving growth in the region. North America also has a robust healthcare infrastructure and a strong regulatory framework for the expedient testing of new HIV treatment regimens.
U.S.: Growing pharmaceutical innovation
In the U.S. a high prevalence of viral diseases, a massive and experienced patient population, a classy healthcare infrastructure, and predominant spending in development and research. Increased awareness about HIV and the importance of testing and treatment supports. Strong presence of pharmaceutical companies in the US is at the lead of developing novel treatments, including single-tablet regimens and long-lasting injectables.
- According to the World Health Organisation, an estimated 4.0 million people were living with HIV in 2023 in the Americas. According to data released by the United States National HIV/AIDS Strategy, approximately 1.2 million people in the U.S. have HIV, with about 13% being unaware of their condition.
Asia Pacific: Increasing government funding
Asia Pacific is expected to witness the fastest compound annual growth rate in the HIV drugs market in the forecast period from 2025 to 2034 due to the growing incidence of HIV infections in the region. Public awareness campaigns run by several governments in the region have increased awareness around HIV along with the frequency of testing.
- According to the World Health Organisation, an estimated 4.0 million people were living with HIV in 2023 in southeast Asia, of which 78% knew their status and 66% were receiving treatment. Emerging economies like India and China have seen a rise in government spending on programs to combat the spread of HIV.
India: Robust Research and Development (R&D)
Indian manufacturers such as Hetero Labs, Cipla, and Mylan produce a massive majority of the world's generic antiretroviral (ARV) drugs, accounting for more than 80% of donor-funded purchases for emerging countries. India has advanced medical research institutions and a large pool of physicians and skilled professionals, which drives the growth of the market.
Europe: Increasing government support and healthcare infrastructure
Europe is significantly growing in the market with growing government-driven healthcare programs, which confirm advanced infrastructure and a stable sector for innovative and generic HIV drugs. Increasing rates of treatment acceptance and viral suppression in Western Europe demonstrate the efficiency of these systems. European organizations engage in international collaboration with NGOs and other organizations to enhance the accessibility and cost-effectiveness of HIV medications in low- and middle-income countries, which contributes to the growth of the market.
UK: Strong public health initiatives
The UK's National Health Service (NHS) plays a significant role in the advancement and adoption of HIV actions. Rapid adoption of novel, efficient treatments and prevention processes, such as PrEP (pre-exposure prophylaxis). This creates a promising environment for healthcare innovation and confirms patient access to modern therapies.
HIV Drugs Market- Value Chain Analysis
- R&D:
R&D processes of HIV drugs include multi-stage processes such as discovery and development, target identification, compound screening, and incremental innovation.
Key Players: Cipla Ltd and Boehringer Ingelheim GmbH - Clinical Trials:
The clinical trial process for HIV drugs is conducted by structured, multi-stage strategies to ensure the safety and efficacy of novel treatments, from initial discovery to post-market monitoring.
Key Players: Merck Sharp & Dohme - Patient Services:
The HIV drugs market is offering medication to include an inclusive, integrated system of care designed to enhance treatment results, adherence, and quality of life for patients living with HIV (PLHIV).
Key Players: Gilead Sciences and AbbVie
Top Vendors in the HIV Drugs Market & Their Offerings
|
Company |
Headquarters |
Key Strengths |
Latest Info (2025) |
|
AbbVie Inc. |
United States |
Diverse and robust product portfolio. |
In June 2025, the FDA approved an expanded indication for AbbVie's MAVYRET as the first and only treatment for people with acute hepatitis C |
|
Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH |
Germany |
High investment in research & development |
Boehringer Ingelheim's human pharma research majorly focuses on the therapeutic areas of cardiovascular and metabolic health, mental health, cancer, eye health, and inflammatory diseases. |
|
Bristol-Myers Squibb Company |
United States |
Strong R&D focus |
Bristol Myers Squibb mainly focuses on advancing novel medicines to address the unmet medical needs of patients with severe diseases. |
|
Cipla Inc. |
India |
Diversified Product Portfolio and Pipeline |
Cipla's core approach is offering high-quality, affordability medicines globally. |
|
Genentech, Inc. |
United States |
Robust and innovative R&D pipeline |
In October 2025, Genentech, a member of the Roche Group, announced the company's first Direct-to-Patient (DTP) program. |
Other HIV Drugs Market Companies
- Gilead Sciences, Inc.
- Merck & Co., Inc.
- ViiV Healthcare
Recent Developments
- In July 2024, results of clinical trials conducted by Gilead Sciences were published for lenacapavir. The participants who received either of the oral PrEP options, Truvada and Descovy, had infection rates of about 2%, consistent with the infection rates of oral PrEP in earlier clinical trials. LEN is an HIV-1 capsid inhibitor that is delivered by subcutaneous injection twice a year for HIV prevention.
- In July 2024, a multinational team led by Weill Cornell Medicine investigators announced the development of a test that will help measure the persistence of HIV in people affected by viral strains found predominantly in Africa. The team developed a new assay by modifying existing laboratory tests that identify HIV subtype B proviruses to detect proviruses that are subtypes A1 and D.
- In March 2024, a team from the University of Amsterdam developed a proof of concept for eliminating HIV from infected cells using Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR-Cas9) gene-editing technology. The team presented their synopsis at ECCMID 2024.
Segments Covered in the Report
By Implement Type (Revenue: US$ Bn & Volume: Mn Units)
- Tillage / Soil Preparation Implement
- Ploughs (Moldboard, Disc, Chisel)
- Harrows (Disc, Tine)
- Cultivators (Field, Rotary)
- Rotavators / Rotary Tillers
- Subsoilers
- Sowing & Planting Implement:
- Seed Drills
- Planters (Precision Planters)
- Transplanters
- Crop Maintenance & Protection Implement
- Weeders
- Inter-row Cultivators
- Sprayers (Boom, Airblast)
- Fertilizer Spreaders / Applicators
- Harvesting & Post-Harvest Implement
- Reapers
- Combine Harvesters
- Forage Harvesters
- Potato Diggers
- Balers (Round, Square)
- Material Handling, Transport & Other Implement
- Front-End Loaders
- Bale Grabbers / Spears
- Pallet Forks
- Tractor Trailers / Trolleys
- Post-Hole Diggers
- Landscaping & Earthmoving (Dozer Blades, Box Scrapers, Land Graders)
By Power Source
- Powered:
- PTO-Powered
- Hydraulically Powered
- Unpowered:
- Ground-Engaging
By Mounting Type
- Three-Point Hitch Mounted
- Drawbar / Trailed
- Front-Mounted
- Semi-Mounted
By Application
- Land Preparation
- Plowing
- Tilling
- Harrowing
- Sowing & Planting
- Crop Protection & Fertilizing
- Harvesting & Threshing
- Post-Harvest & Agro-Processing
By End-User Sector
- Agriculture
- Farm-level (Large, Medium, Small)
- Commercial Farming
- Non-Agriculture:
- Forestry
- Construction & Landscaping
- Municipal Services (e.g., snow removal, groundskeeping)
By Geography
- North America
- Asia Pacific
- Europe
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Tags
Ask For Sample
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
 Get a Sample
Get a Sample
 Table Of Content
Table Of Content




 sales@precedenceresearch.com
sales@precedenceresearch.com
 +1 804-441-9344
+1 804-441-9344
 Schedule a Meeting
Schedule a Meeting