Digital transformation reshapes organizations by aligning technology with strategy, people, and data to drive innovation, agility, and value creation, enabling sustainable growth, better experiences, smarter decisions, and resilience in a rapidly evolving digital world.
Digital transformation emerged as a defining paradigm shaping contemporary organizations, industries, and societies. Beyond the mere adoption of digital technologies, it represents a fundamental reconfiguration of organizational structures, processes, value creation mechanisms, and strategic orientations. This article presents a comprehensive conceptual analysis of digital transformation, examining its theoretical foundations, key drivers, strategic dimensions, and organizational implications. By synthesizing perspectives from information systems, strategic management, and organizational theory, the paper elucidates how digital transformation acts as both an enabler of innovation and a catalyst for systematic change. The article further highlights challenges, capability requirements, and further research directions, offering a structured understanding suitable for academic and managerial discourse.
Executive Summary
The article explores the profound impact of digital transformation on modern organizations and societies. It emphasizes that digital transformation is not merely about adopting digital technologies but entails a comprehensive reconfiguration of organizational structures, processes, and value creation mechanisms. The analysis presented in the article synthesizes perspectives from information systems, strategic management, and organizational theory, highlighting key drivers of digital transformation. It identifies how such a transformation serves as a dual force: an enabler of innovation and a catalyst for systemic change within organizations.
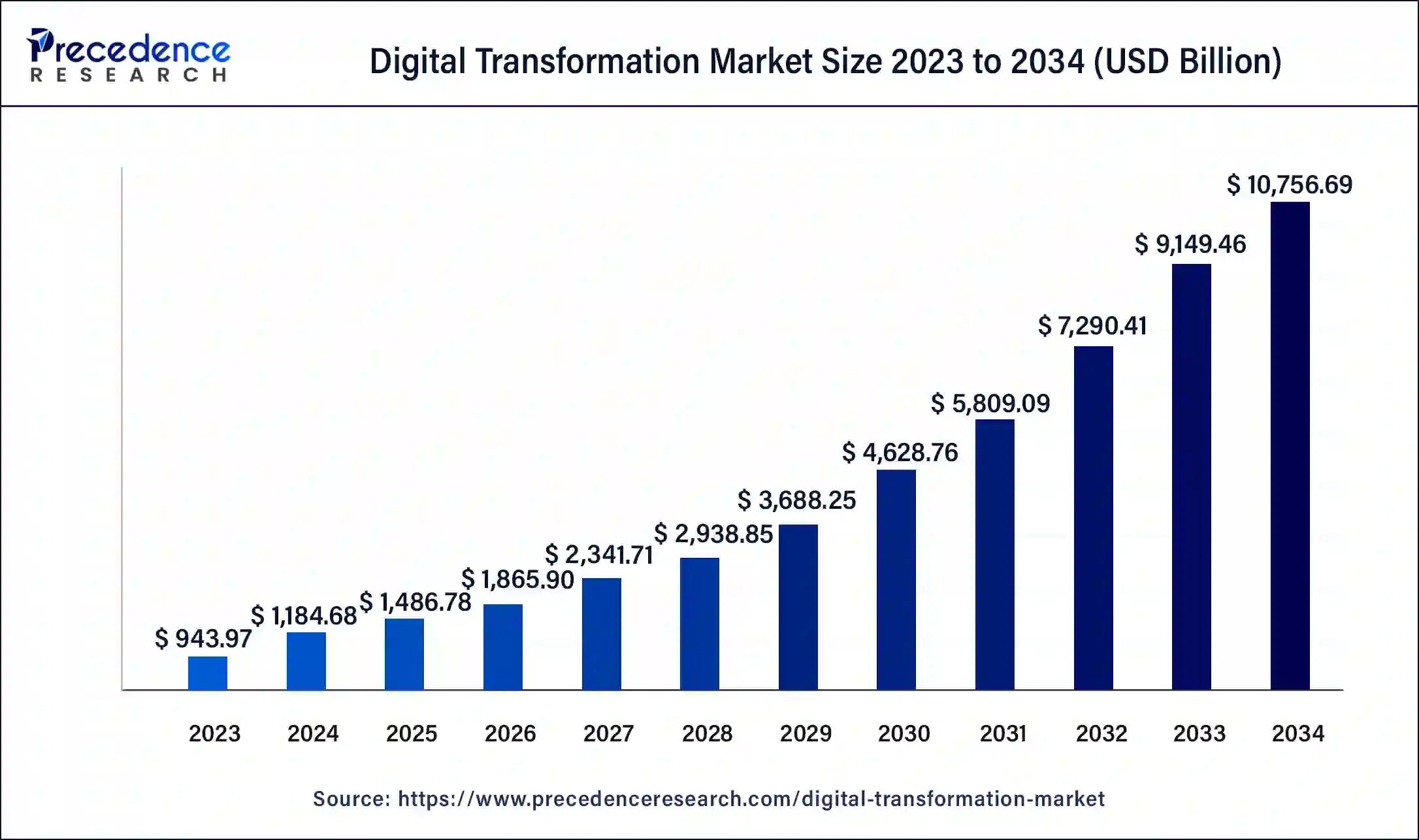
What is Digital Transformation Market Size?
The global digital transformation market size accounted for USD 1.49 trillion in 2025 and is predicted to reach around USD 12.53 trillion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of 23.73% from 2026 to 2035.
Case Study of Digital Transformation
"Delivering superior quality in a digital landscape" is DHL's approach for 2025. The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the company's initiatives for digital transformation. Allocating more than $2 billion towards digital transformation initiatives from 2021 to 2025.
Disney introduced Disney+, bought significant entertainment properties, and focused extensively on personalization. An instance of digital personalization is the MyMagic+ wristbands given to park visitors. The wristbands feature integrated RFID chips that enable individuals to pay for services, reserve rides, unlock hotel rooms, and more. These data streams can then be utilized for tailored services. Caterpillar, known as CAT, is the top global producer of construction and mining machinery. Renowned for its loaders, dozers, excavators, and trucks. Recently, the multinational has transformed into a hardware-and-software firm, pioneering advancements in A.I. and digital twins.
Unlocking the Secrets of Digital Transformation
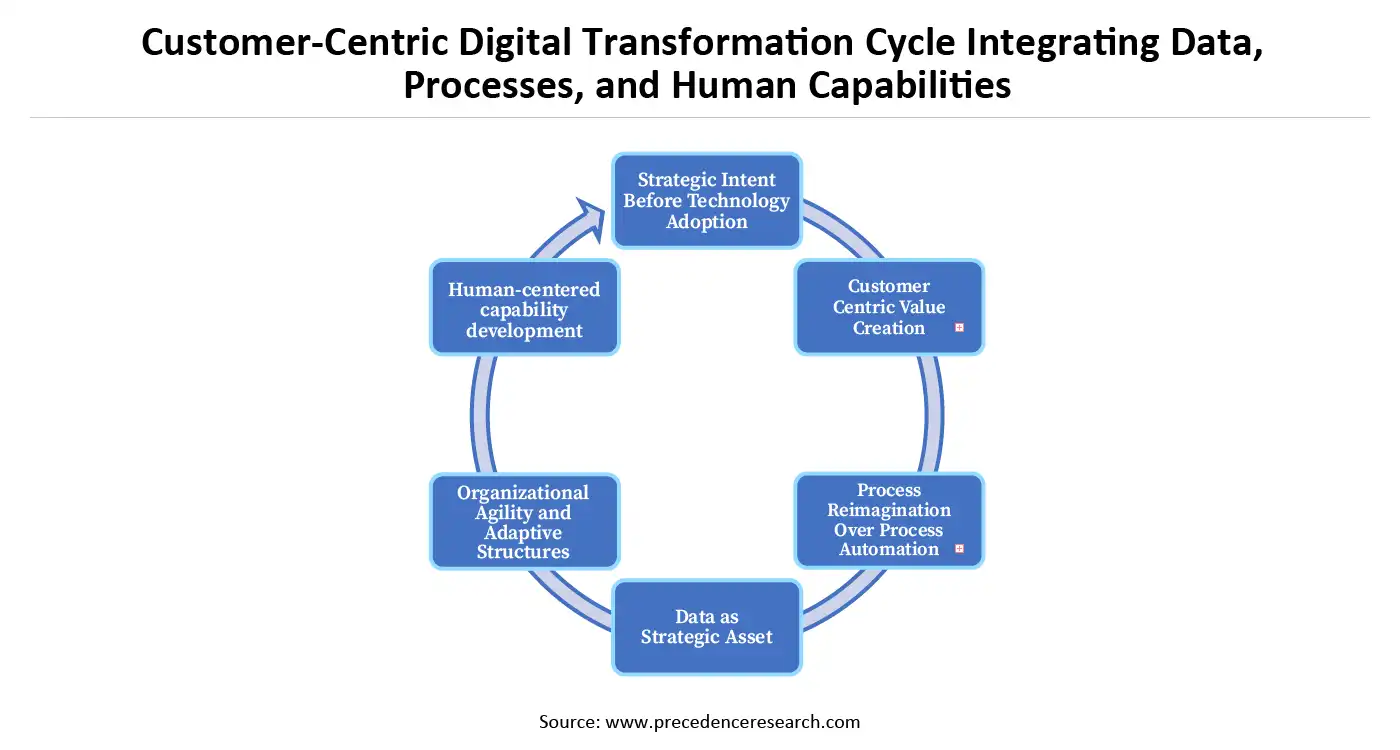
Digital transformation is not a technology-driven event but a strategically governed, human-centered, and continuously evolving organizational phenomenon. Its success depends on adherence to foundational principles that guide decision-making, capability development, and systematic change. The following principles articulate the core logic underpinning effective digital transformation across organizations and sectors.
- Strategic Intent Before Technology Adoption: Digital transformation should be a consequence of a well-defined strategic intent rather than a result of an opportunistic adoption of emerging technologies. The role of technology is that of an enabler, not a driver, of the transformation. Organizations that start with tools instead of purpose bear the risk of fragmentation, misalignment, and underutilization of digital investments. Strategic intent, thus, acts as a glue by aligning digital initiatives with long-term value creation, competitive positioning, and organizational mission.
- Customer-Centric Value Creation: Digital transformation is about redefining the value creation, delivery, and experience mechanisms for all the stakeholders, mainly customers. This principle underlines the importance of designing processes, products, and services based on customer needs, behaviours, and expectations. While digital technologies allow for personalization, responsiveness, and continuous engagement, their effectiveness is predicated on a thorough understanding of customer journeys and pain points. Transformation takes place when customer value becomes the central organizing logic of digital initiatives.
- Process Reimagination Over Process Automation: One of the fundamental principles of digital transformation is the reimagination of processes instead of their mere automation. Implementing inefficient or obsolete workflows, even if they are digitized, perpetuates structural inefficiencies. A genuine transformation is about questioning the underlying assumptions, abolishing redundancies, and redesigning processes to take full advantage of digital capabilities such as real-time data, intelligent automation, and system integration. This principal advocates for a shift of focus from merely achieving efficiency.
- Data as Strategic Asset: Data is the foundational resource of digital transformation. Organizations must treat data not as a by-product of operations but as a strategic asset that informs decision-making, enables prediction, and supports innovation. This principle involves establishing robust data governance, ensuring data quality, and fostering analytical capabilities across organizational levels.
- Organizational Agility and Adaptive Structures: Digital transformation demands organizational agility, the capacity to sense change, respond rapidly, and continuously adapt. Rigid hierarchies and soiled functions inhibit transformation by slowing decision-making and innovation. The principal advocates for flexible structures, cross-functional collaborations, and iterative execution models. Agility enables organizations to experiment, learn from failure, and recalibrate strategies in a dynamic digital environment.
- Human-centered capability development: Digital transformation is a people-centred concept just as much as it is a technology-centred one. Accordingly, this principle highlights the importance of digital skills, analytical literacy, and change readiness for the entire workforce. Digital transformation, instead of displacing human roles, reshapes those roles and thus calls for new competencies and mindsets. Ongoing learning, reskilling, and a sense of empowerment are the conditions without which transformation cannot be sustained, and employees cannot be fully engaged.
Customer-Centric Digital Transformation Cycle Integrating Data, Processes, and Human Capabilities
The Evolution of Digital Transformation and the Question of Return
Traditional digital transformation predates formal science. Ancient civilizations harnessed biological processes through observation and experience rather than molecular understanding. Practices such as fermentation of food and beverages, selective breeding of crops, and the use of microorganisms for preservation represent early biotechnological interventions. These methods were slow, artisanal, and highly dependent on environmental conditions, yet remarkably sustainable and resilient. What defined this era was biological intuition rather than control. Processes worked because they aligned with natural biological rhythms, even though the underlying mechanisms were not yet understood.
The identification of microorganisms, enzymes, and metabolic pathways changed the approach from reliance on intuition to that of experimentation. The advent of microscopes, sterilization procedures, and fermenters allowed reproducibility and scaling up to be achieved. This age saw the birth of antibiotics, vaccines, and industrial enzyme production. Biotechnology was here, moving from the realm of the handmade to that of the industry.
Modern Biotechnology: Digital Transformation as a Programmable System
Modern biotechnology is a different story altogether; it is not just a matter of observing or manipulating biology, but of engineering it. The combination of molecular biology, genomics, proteomics, and bioinformatics has given scientists the ability to create biological systems in a deliberate and predictable way. This change cannot be separated from the rise of modern tools and equipment, which have completely changed the way biological research and production are done.
How Modern Equipment Is Transforming the Biotechnology Industry?
Modern biotechnology relies not only on scientific discovery but also on technological infrastructure. Sophisticated equipment has changed the speed, scale, accuracy, and economic viability. Precision and Control Automated bioreactors, high-throughput screening systems, and real-time monitoring devices enable very accurate control of biological parameters such as temperature, pH, oxygen concentrations, and nutrient supply. Such accuracy reduces variability and thus confirms reproducibility for pharmaceutical and clinical applications. Acceleration of Discovery
Now, the Very Major Question Remains: Will Traditional Methods Return Soon?
Traditional methods, characterized by simplicity, robustness, and ecological alignment, are increasingly being revisited in contexts such as sustainable agriculture, natural product extraction, and decentralized manufacturing. These approaches offer advantages in low-resource settings and in applications where minimal intervention is required. Most likely future is not a return to traditional methods in their original form, but a hybrid model. Traditional biological wisdom, such as natural fermentation, microbial consortium, and holistic process design. The future of digital technology lies not in choosing between tradition and modernity, but in harmonizing them where ancient biological wisdom is guided by modern technological intelligence.
The Evolutionary Tree of Biotechnology from Traditional Roots to Future Innovations (2007–2050)
(Note: The picture can be edited by clicking on this link. Please visit the given link, which is kept editable for all. The link is mentioned below;
Beyond Technology: Digital Resources, Structures, and Strategies Powering Transformation
Digital transformation is not maintained by isolated technologies, but rather it is a structured network of digital resources, adaptive organization, and considered growth strategies. Those organizations that are successful at transformation consider digitalization as a strategic competence, an asset, people, and processes that align with ongoing value creation. This section discusses the underlying digital resources, organizational structures that facilitate transformation, as well as the strategies that promote digital growth. Human knowledge is one of the most invaluable digital assets.
The necessary skills in the field of technology-to-value translation include analytics, digital design, cybersecurity, and systems thinking. Another aspect is a significant one: organizational knowledge, i.e., documented processes, digital know-how, as well as experience of learning, make it possible to continue transformation efforts and to make them scalable. Digital transformation redefines jobs and functions throughout the company. The business of leadership is becoming more about orchestration, setting up visions, and building capabilities as opposed to being command-and-control. The new positions are dedicated to the coordination of digital integration and innovation to reconcile the areas of business and technology.
Digital expansion is increasingly based on platform approaches that facilitate network effects. Organizations build self-reinforcing ecosystems through attracting partners, developers, and users, which scale fast and diversify revenue streams. Experimentation Data-driven experimentation helps organizations test new offerings, optimize procedures, and refine strategies with low risk. Constant testing encourages innovation and streamlines growth efforts to meet evidence-based findings. Digital growth plans are also concerned with the growth of operations that are efficient. Automation, smart systems, and digital supply chains lower the marginal costs and facilitate growth even without a corresponding growth in resources.
Strategic alignment of digital resources, dynamic organizational structures, and intentional growth strategies is what helps to maintain digital transformation. The capabilities, which appear as the building blocks of digital endeavours, the pace and efficiency of execution, which are defined by organizational structures, and the growth schemes that transform the digital potential into real results. Companies that unify these aspects come out of digital adoption and attain digital maturity. Finally, technology alone is not a successful parameter of digital transformation, but rather, the level of smartness with which it is incorporated into the organizational fabric.
From Screens to Shared Realities: The Metaverse as a Catalyst for Digital Transformation
The digital transformation has continued to transform the way organisations interact, operate, and create value. The rise of the metaverse is an important inflection point in this process- it is the place where digital transformation is applied not only to process and platform optimization but also to the immersive, experiential, and spatial realms. The metaverse is not an independent technological trend but a more sophisticated version of digital change, as it transforms the nature of engagement, collaboration, and value creation in industries.
The metaverse may be thought of as a permanent, communal, and immersive virtual world in which there is an overlap between physical and virtual realities. It combines the use of technologies like extended reality (XR), digital twins, real-time systems of data, and virtual economies to produce interactive digital spaces. The initial digital transformation was concerned with process automation and better efficiency. The metaverse brings forth the concept of immersion, where individuals can engage with the digital systems in a manner that reflects or complements the experiences in the physical world. This change alters the way organizations create workflows, training, and models of customer engagement.
Does the Metaverse Redefine Digital Transformation?
The metaverse indicates a shift in the digital efficacy to the digital embodiment. Although not every organization can implement metaverse technologies as fast and on the same scale, its conceptual power already defines the way the digital transformation is perceived and imagined. The metaverse is a strategic choice, not a universal destination, which is most valuable when experience, simulation, and interaction are at the heart of value creation. The digital transformation will probably be hybrid in the future: strong digital platforms with selective use of immersive environments that can help improve learning, collaboration, and engagement.
The metaverse is a logical next step in the digital transformation process to optimize the systems to transform the experiences. It evolves the impact of digital transformation on efficiency and automation to those of immersion, interaction, and co-creation. Companies that do not view the metaverse as a new development but as a continuation of the digital transformation will be better placed to innovate in a responsible way, engage positively, and stay afloat in an ever-more digital world.
Why Are Key Drivers Important for Digital Transformation and What Are They?
Technological Advancements: Rapid innovation in digital technologies lowers barriers to experimentation and scalability. The modularity and interoperability of digital systems enable organizations to reconfigure processes and offerings with unprecedented flexibility.
Changing Customer Expectations: Digitally empowered customers demand personalized, seamless, and real-time experiences. These expectations compel organizations to redesign customer journeys and adopt data-driven decision-making frameworks.
Competitive Pressures: Digital native firms and platform-based business models disrupt traditional industries by leveraging network effects and data-centric strategies. Incumbent organizations must transform to remain relevant in increasingly digitized markets.
Regulatory and Societal Influences: Governments and institutions promote digital adoption to enhance transparency, efficiency, and sustainability. Simultaneously, societal shifts toward digital engagement reinforce the urgency of transformation.
| 20th Waseda University World Digital Government Rankings 2025 | |||||||||||
| Rank | Country | Score | Rank | Country | Score | Rank | Country | Score | Rank | Country | Score |
| 1 | UK | 95.5353 | 18 | Norway | 81.5416 | 35 | SouthAfrica | 72.7346 | 52 | Bahrain | 63.1591 |
| 2 | Denmark | 94.8924 | 19 | Iceland | 80.3447 | 36 | CzechRepublic | 71.8405 | 53 | Paraguay | 62.9098 |
| 3 | Singapore | 94.7332 | 20 | United Arab Emirates | 80.0000 | 37 | Israel | 71.5105 | 54 | Chile | 62.7289 |
| 4 | Estonia | 94.4940 | 21 | Taiwan | 78.5491 | 38 | China | 70.6782 | 55 | Columbia | 62.6006 |
| 5 | South Korea | 93.2292 | 22 | Australia | 77.7832 | 39 | Poland | 70.3537 | 56 | Peru | 62.4887 |
| 6 | Netherlands | 90.0041 | 23 | Indonesia | 76.8192 | 40 | HongKong | 70.0965 | 57 | Pakistan | 58.7617 |
| 7 | USA | 88.9118 | 24 | India | 76.2653 | 41 | Uruguay | 68.6246 | 58 | Egypt | 58.5005 |
| 8 | Saudi Arabia | 88.0054 | 25 | Spain | 75.6524 | 42 | Turkey | 67.4754 | 59 | Tunisia | 57.5974 |
| 9 | Japan | 87.4509 | 26 | Italy | 75.4399 | 43 | Vietnam | 67.0794 | 60 | Morocco | 57.4197 |
| 10 | Finland | 85.6950 | 27 | France | 75.4016 | 44 | Russia | 66.6144 | 61 | Argentina | 56.7737 |
| 11 | Canada | 85.5729 | 28 | Austria | 75.1211 | 45 | Lithuania | 66.3245 | 62 | Fiji | 55.6310 |
| 12 | Germany | 85.3774 | 29 | Philippines | 75.0914 | 46 | Brunei | 66.2118 | 63 | Nigeria | 55.3305 |
| 13 | Ireland | 83.8640 | 30 | Malaysia | 74.6291 | 47 | Brazil | 66.0921 | 64 | Bangladesh | 54.7317 |
| 14 | New Zealand | 82.3740 | 31 | Belgium | 73.6713 | 48 | Mexico | 65.7952 | 65 | CostaRica | 53.3757 |
| 15 | Switzerland | 82.3158 | 32 | Portugal | 73.5837 | 49 | Romania | 65.7006 | 66 | Ghana | 52.6494 |
| 16 | Sweden | 81.6764 | 33 | Kazakhstan | 73.0981 | 50 | Uzbekistan | 64.2491 | |||
| 17 | Thailand | 81.6245 | 34 | Oman | 72.8363 | 51 | Kenya | 63.6843 | |||
Between Adoption and Alignment: The Strategy Approach to Digital Technologies.
To approach digital technologies successfully, it is necessary to go beyond the energy towards innovation or rapid integration of tools. An attentive, systematic, and intentional strategy will mean that digital technologies create sustainable value instead of operational complexity. This guide provides a strategic roadmap that should be followed by organizations and individuals to embrace digital technologies with clarity, confidence, and long-term consequences.
- Begin with Purpose, Not Tools: The primary and most important step in the approach to digital technologies would be to define the reason why they are required. Digital mechanisms must support well-defined goals, which may include better customer experience, greater efficiency, innovative opportunities, and growth. Beginning with purpose eliminates the technology-based decisions that are not strategic and aligns them with the overall goals.
- Evaluate Preparedness and Situation: An analysis of the present capabilities, processes, and culture should be done before adoption. This involves awareness of current systems, digital capability, maturity of data, and the degree of the organization's openness to change. Through an assessment of reality, organizations can focus on the technologies that are appropriate to them and not focus on disruptive change too soon.
- Reason in Terms of Value Creation: The digital technologies are to be treated as the facilitators of value as opposed to cost centers. Every initiative needs a well-formulated value proposition, either in the increase of revenue, cost reduction, risk mitigation, or improved experience. The value focus will help to make sure that the investments in technology will yield quantifiable and significant results.
- Take an Incremental and Iterative Attitude: Instead of massive, single-implementation strategies, successful digital strategies focus on testing and learning. Learning is possible through action, through pilot projects, prototypes, and minimum viable solutions. This minimizes risk, develops trust, and facilitates the sustained improvement through feedback in the real world.
- Establish Powerful Data Precursors: Digital technologies are based mostly on data. The effectiveness of digital tools using untrusted, unavailable, and poorly governed data is restricted. Setting standards in data, data quality, and providing analytic capabilities are fundamental steps to scaling digital solutions.
Beyond the Numbers: Measuring ROI in the Age of Digital Transformation
Digital transformation has become a strategic imperative rather than a discretionary investment. Organizations across industries are allocating substantial resources to digital initiatives ranging from advanced analytics and automation to platform modernization and immersive technologies. Yet, measuring return on investment in digital initiatives ranging from advanced analytics and automation to platform modernization and immersive technologies. Unlike traditional capital investments, digital transformation delivers value in multidimensional, non-linear, and often intangible ways. This article explores how organizations can meaningfully measure ROI in digital transformation without reducing it to short-term financial metrics alone.
Why Digital ROI is Different?
The classical ROI computations are based on the obvious cost-benefit factors: capital investment and revenue increase or cost decrease. Digital transformation is, however, system, behaviour, and capability-based. Its results are typically better agility, customer experience, accelerating innovation cycles, and better data intelligence, benefits that are not directly converted into quarterly financial performances. Besides, digital efforts are generally connected. The worth of a data platform, such as, can be realized only when analytics, skills, and decision processes develop simultaneously. The digital investments have a strategic impact that would be underrated when measured alone as ROI.
Moving towards Project ROI to Portfolio ROI
The single most efficient solution to digital ROI is to no longer evaluate projects on a case-by-case basis but view them as a portfolio. Digital transformation is a process made up of several initiatives, which are capability building. Certain projects can produce cash flows in the short term, whereas others serve as a catalyst for value generation in the long term. Portfolio level ROI considers the cumulative effects of efficiency, growth, reduction of risk, and strategic preparedness. This method correlates ROI measurement with intent to transform as opposed to short-term performance constraints.
With Leading Indicators and Lagging Indicators
The best ROI models are a combination of leading and lagging indicators. Lagging indicators- Lagging indicators are ones that validate value-realized, e.g., revenue growth or cost-saving, but often come later in the transformation cycle. Leading indicators, like the rates of adoption, the degree of process digitization, or the use of data, indicate the possibility of value appearing. As an example, the greater the use of a digital platform, the more likely that revenue will not grow at once but will significantly forecast the efficiency and gains in innovations in the future. Measuring both kinds of indicators allows making the right decision during transformation.
Attribution within A Multifaceted Digital Ecosystem
It is intrinsically hard to assign results to definite digital investments because of interdependence. Instead of pursuing accurate attribution, an organization should be contribution-oriented. This is the knowledge of how the digital initiatives can impact the results, along with the organizational change, market conditions, and human behavior. Contribution-based measurement is cognizant of complexity and yet more accountable; the ROI discussion is more realistic and constructive.
ROI Measurement leadership and Governance
The leadership is critical in defining the way ROI is measured and understood. When leaders consider digital ROI solely as a financial justification exercise, efforts to transform are likely to be limited. Mature organizations integrate ROI measurement within governance structures that focus on strategic alignment, learning, and adaptation. Open boards, frequent value appraisals, and interdepartmental responsibility keep ROI a management variable and not a post-hoc calculation.
The ROI of digital transformation cannot be measured with exactness and is more strategic. It entails transcending the financial indices to a multidimensional concept of value that portrays the reconstitution of organizations by digital capabilities. ROI measurement can be a potent driver of long-term digital success when its measurement is consistent with its purpose, portfolio thinking, and long-term vision. The highest returns in digital transformation are not necessarily those that are reflected in the balance sheets, but those that enable an organization to be adaptable, innovative, and ahead of the pack in a constantly changing digital environment.
| Customers | Employees | Operations | Safety | infrastructure | disruption |
| Crafting compelling experiences | Engaging employees | Digitalization of business processes | Protecting digital asset | Implementing and running new assets. | Prototyping and testing. |
| Net promotors | Engagement score | Manufacturing | Number of threats | Speed of new technology | Percentage of budget allocation |
What is Establishing the Future of Digital Transformation?
The future of the industry is being increasingly shaped by digital transformation and technological advancements. As organizations adapt to the evolving landscape, several key trends and factors will define the trajectory of various sectors:
- Increased Automation: Industries will continue to embrace automation to enhance efficiency and reduce operational costs. Robotics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning will play pivotal roles in automating repetitive tasks, allowing human workers to focus on more strategic and creative endeavors.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Organizations will leverage big data and analytics to make more informed decisions. The ability to gather, analyze, and interpret vast amounts of data will enable companies to better understand market trends, customer preferences, and operational efficiencies, driving competitive advantage.
- Customer Experience Revolution: Businesses will prioritize customer-centric strategies, utilizing technology to deliver personalized experiences. Through tailored products and services, real-time engagement, and improved customer service channels, companies will seek to enhance customer loyalty and satisfaction.
- Sustainability and Ethical Practices: The focus on sustainability will intensify as consumers and stakeholders demand environmentally responsible practices. Industries will adopt green technologies and sustainable practices to minimize their ecological footprint, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards while meeting consumer expectations for ethical operations.
- Remote Work and Collaborative Tools: The shift towards remote work, accelerated by the global pandemic, will become a lasting trend. Companies will continue to invest in collaborative digital tools and platforms that facilitate communication and teamwork, leading to flexible work environments that enhance productivity and work-life balance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the future of the industry is set to be dynamic and transformative. Embracing digital transformation with a strategic focus will be essential for organizations looking to thrive in the face of rapid technological change and evolving market demands.
About the Authors

Aditi Shivarkar
Aditi, Vice President at Precedence Research, brings over 15 years of expertise at the intersection of technology, innovation, and strategic market intelligence. A visionary leader, she excels in transforming complex data into actionable insights that empower businesses to thrive in dynamic markets. Her leadership combines analytical precision with forward-thinking strategy, driving measurable growth, competitive advantage, and lasting impact across industries.

Aman Singh
Aman Singh with over 13 years of progressive expertise at the intersection of technology, innovation, and strategic market intelligence, Aman Singh stands as a leading authority in global research and consulting. Renowned for his ability to decode complex technological transformations, he provides forward-looking insights that drive strategic decision-making. At Precedence Research, Aman leads a global team of analysts, fostering a culture of research excellence, analytical precision, and visionary thinking.

Piyush Pawar
Piyush Pawar brings over a decade of experience as Senior Manager, Sales & Business Growth, acting as the essential liaison between clients and our research authors. He translates sophisticated insights into practical strategies, ensuring client objectives are met with precision. Piyush’s expertise in market dynamics, relationship management, and strategic execution enables organizations to leverage intelligence effectively, achieving operational excellence, innovation, and sustained growth.





 Request Consultation
Request Consultation

