Modern supply chains are shifting from manual, siloed operations to smart, connected networks powered by AI, automation, and real-time data. Businesses now focus on prediction, speed, and resilience instead of just cost and efficiency.
A New Era of Intelligent Supply Networks
The global supply chain is no longer a back-end operational function. It has become a strategic growth engine. Over the past decade, disruptions ranging from geopolitical tensions to pandemic-induced bottlenecks have exposed vulnerabilities in traditional supply models. In response, organizations worldwide are rethinking how supply chains are designed, managed, and optimized.
What is emerging is not merely a digital upgrade, but a structural reinvention. Today’s supply chain is increasingly intelligent, interconnected, predictive, and resilient. Artificial intelligence, automation, IoT, robotics, blockchain, and advanced analytics are collectively redefining how goods move from raw material sourcing to last-mile delivery.
From Linear Operations to Digital Ecosystems
Historically, supply chains operated in silos. Procurement, production, warehousing, and transportation functioned independently, often connected only by spreadsheets and manual coordination. Decision-making was reactive. Visibility was limited. Forecasting relied heavily on historical assumptions.
The modern supply chain now functions as an integrated digital ecosystem. Cloud platforms unify data streams across suppliers, manufacturers, logistics providers, and retailers. Real-time dashboards provide end-to-end visibility. Predictive models anticipate demand shifts before they occur.
This shift from linear execution to ecosystem orchestration represents one of the most significant operational evolutions of the 21st century.
Today’s digital supply chain is characterized by:
- Real-time data synchronization across nodes
Modern supply chains operate on interconnected digital platforms that synchronize data across suppliers, manufacturers, warehouses, logistics providers, and retailers in real time. Instead of waiting for periodic reports, stakeholders have instant visibility into inventory levels, shipment status, production schedules, and demand fluctuations. This synchronized flow of information reduces communication delays, minimizes manual intervention, and allows faster cross-functional decision-making. Real-time integration also improves collaboration between partners, creating a unified operational view rather than fragmented silos.
- Predictive planning instead of reactive correction
Traditional supply chains responded to disruptions after they occurred. Today’s digital networks rely on predictive analytics to anticipate demand spikes, supply shortages, and transportation bottlenecks before they escalate. Advanced forecasting models analyze historical data alongside live market signals, enabling organizations to adjust procurement, production, and distribution strategies proactively. This shift from reactive correction to predictive planning significantly reduces risk exposure and enhances overall operational stability.
- Automation embedded into operational workflows
Automation is no longer limited to isolated tasks. It is integrated throughout supply chain processes, from automated purchase order generation to robotic warehouse picking and intelligent shipment routing. Embedded automation reduces repetitive manual work, lowers error rates, and accelerates execution cycles. More importantly, it ensures consistent performance and scalability as operations expand. Employees are increasingly focused on strategic oversight and exception management rather than routine execution.
- Continuous optimization powered by machine learning
Machine learning algorithms enable supply chains to learn from patterns and improve continuously. Unlike static systems, these models refine themselves as new data becomes available. Whether optimizing inventory allocation, adjusting safety stock levels, or recalibrating transportation routes, machine learning ensures decisions evolve with changing conditions. This continuous optimization creates supply networks that are adaptive, responsive, and capable of maintaining efficiency even in volatile market environments.
Organizations that embrace this model are not just improving efficiency. They are building structural resilience.
AI in Supply Chain Market Size and Forecast 2025 to 2034
The global AI in supply chain market size accounted for USD 7.15 billion in 2024 and is predicted to increase from USD 9.94 billion in 2025 to approximately USD 192.51 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 39.00% from 2025 to 2034. The market growth is attributed to the increasing adoption of AI-driven automation and real-time monitoring solutions to enhance supply chain efficiency and resilience.
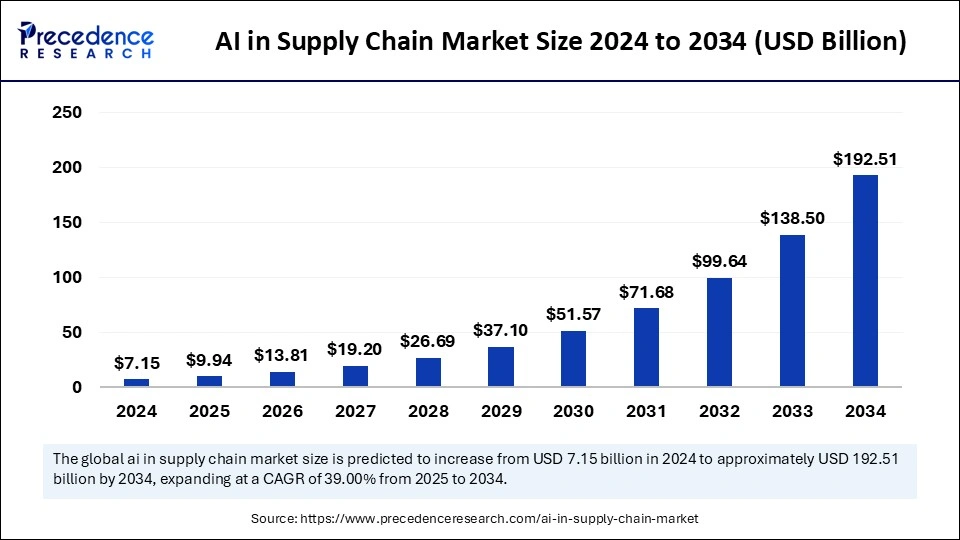
AI in Supply Chain Market Key Takeaways
- In terms of revenue, the market is valued at $9.94 billion in 2025.
- It is projected to reach $192.51 billion by 2034.
- The market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 39% from 2025 to 2034.
Artificial Intelligence as the Strategic Core of Modern Supply Chains
AI has moved beyond pilot programs and innovation labs. It is now embedded within core supply chain processes, driving measurable improvements in forecasting accuracy, inventory efficiency, logistics optimization, and risk management.
Recent industry trends indicate:
- Over 70 percent of supply chain leaders prioritize AI investments
- AI-driven demand forecasting can improve accuracy by up to 70 percent
- Intelligent inventory systems can reduce stock-outs by as much as 40 percent
- Warehouse automation can increase operational efficiency by 25 to 35 percent
These figures reflect a fundamental truth. AI is not simply automating tasks. It is enhancing decision intelligence.
An experienced supply chain executive recently summarized this shift clearly:
“The future supply chain is not managed manually. It is continuously optimized by algorithms that learn faster than any human team.”
Demand Forecasting: From Historical Guesswork to Predictive Intelligence
Forecasting has traditionally been one of the most challenging aspects of supply chain management. Inaccurate predictions result in excess inventory, lost sales, and unnecessary capital lock-in.
AI transforms forecasting by incorporating multiple data layers simultaneously, including historical sales patterns, consumer behavior signals, macroeconomic indicators, promotional campaign data, and seasonal variations.
Instead of relying on periodic reviews, predictive models update continuously. They learn from new inputs and refine projections dynamically.
Inventory Optimization in Real Time
Inventory management has shifted from manual stock checks to real-time algorithmic control. Modern AI systems track inventory across multiple warehouses, retail outlets, and distribution centers while adjusting reorder points dynamically.
This approach enables balanced stock allocation across regions, reduced warehousing costs, improved working capital utilization, and lower risk of overstock or obsolescence.
Inventory is no longer treated as a static asset. It is a fluid resource optimized continuously based on demand signals and operational conditions.
Logistics and Route Optimization at Scale
Transportation represents a substantial portion of supply chain costs. Traditional route planning relied on fixed schedules and manual oversight. AI has introduced dynamic routing models that adjust based on traffic patterns, fuel costs, delivery urgency, and vehicle availability.
Companies deploying AI-based logistics solutions often report:
- 10 to 15 percent transportation cost reductions
- Improved on-time delivery performance
- Lower fuel consumption and reduced emissions
This combination of cost efficiency and sustainability makes AI-driven logistics especially valuable in today’s business environment.
AI-Powered Supply Chains: Performance Gains at a Glance

Warehouse Automation and Intelligent Fulfillment
Warehouses have evolved into high-speed, technology-driven hubs. Autonomous mobile robots, robotic picking systems, and AI-enabled computer vision systems now streamline operations.
Instead of human-dependent picking lines, many facilities operate with robotic fleets that navigate dynamically, identify products through vision recognition, and optimize picking sequences.
This automation does not eliminate human roles. Instead, it shifts workforce focus toward supervision, analytics, and system optimization. Operational gains include improved throughput, enhanced worker safety, and significantly reduced order processing times.
Autonomous Systems and Agentic AI
A major advancement in supply chain innovation is the emergence of agentic AI. These autonomous systems make contextual decisions with minimal human oversight.
They can reallocate inventory during demand spikes, identify supplier risk signals early, automatically reroute shipments during disruptions, and optimize coordination across multi-tier suppliers.
This level of autonomy moves supply chains toward self-orchestrating ecosystems. The objective is to augment human capability with continuous, intelligent decision-making at scale.
IoT and End-to-End Visibility
Artificial intelligence depends on reliable data. IoT devices provide that data in real time. Connected sensors and RFID systems allow companies to monitor shipments, warehouse conditions, equipment performance, and asset locations instantly.
For temperature-sensitive industries such as pharmaceuticals and food processing, IoT ensures regulatory compliance and quality control. Real-time visibility also enhances customer trust by enabling precise delivery tracking and proactive issue resolution.
The Future of Supply Chains
Looking ahead, supply chains will continue evolving toward fully autonomous, predictive, and self-optimizing networks. The next phase of transformation will not simply enhance operational efficiency but redefine how decisions are made across global ecosystems. Intelligence will move from dashboards to execution layers, where systems act in real time with minimal manual intervention.
Generative AI assistants will increasingly support procurement and supplier management. These systems will analyze supplier performance history, pricing trends, risk indicators, contract clauses, and market volatility before recommending optimal sourcing strategies. Instead of static negotiations conducted periodically, procurement will become data-driven, dynamic, and continuously optimized.
Predictive maintenance will become standard across logistics fleets, warehouse equipment, and manufacturing assets. AI models will analyze vibration data, temperature readings, usage cycles, and historical breakdown patterns to forecast failures before they occur. This will significantly reduce downtime, extend asset lifespan, and improve service reliability.
Digital twins will mature into essential strategic planning tools. Organizations will create real-time virtual replicas of their entire supply networks, including suppliers, transportation routes, distribution centers, and demand nodes. These digital environments will allow leaders to simulate disruptions such as port congestion, geopolitical conflicts, raw material shortages, or demand spikes. Instead of reacting after damage occurs, companies will test mitigation strategies in advance and deploy the most effective solution instantly.
In the coming years, supply chains will also become increasingly interconnected across tiers. Multi-tier supplier visibility will reduce blind spots and enable early detection of systemic risks. Autonomous decision engines will rebalance inventory, reroute shipments, and adjust production schedules within seconds of detecting anomalies.
The transformation can be summarized across key dimensions:
| Dimension | Current State | Future State |
| Decision-Making | Human-led with system support | AI-led with human oversight |
| Forecasting | Periodic predictive models | Continuous real-time learning models |
| Procurement | Reactive sourcing cycles | AI-assisted dynamic negotiation |
| Maintenance | Scheduled inspections | Predictive and condition-based monitoring |
| Risk Management | Event-driven response | Scenario-based anticipation using digital twins |
| Network Visibility | Tier 1 supplier visibility | Multi-tier end-to-end transparency |
| Sustainability | Emission tracking reports | Real-time carbon optimization |
The ultimate objective is clear. The future supply chain will not merely respond to disruption. It will anticipate shifts in demand, supplier risk, regulatory changes, and transportation bottlenecks before they escalate into crises.
Organizations that build anticipatory capabilities today will operate with greater resilience tomorrow. They will move faster, allocate resources more intelligently, and maintain service continuity even under volatile conditions.
Sustainability as a Core Strategy
Sustainability has become central to supply chain design. AI supports carbon footprint tracking, route optimization to reduce emissions, and energy-efficient warehouse management. Organizations implementing intelligent logistics report fuel savings between 10 and 20 percent. Smart warehouse systems can reduce energy consumption by up to 25 percent.
The Evolution of Supply Chain Intelligence
| Function | Traditional Model | Intelligent Model |
| Forecasting | Periodic review | Continuous prediction |
| Inventory | Static buffer stock | Dynamic optimization |
| Logistics | Fixed routes | Real-time routing |
| Maintenance | Reactive repairs | Predictive alerts |
| Decision Making | Manual reporting | Manual reporting |
The supply chain industry stands at a transformative moment. AI integration, automation, real-time visibility, and advanced analytics represent a fundamental shift in how global commerce operates. Organizations leading this transformation understand that supply chain performance directly influences profitability, resilience, customer experience, and sustainability outcomes.
In the coming decade, supply chains will be evaluated not only by cost efficiency but also by intelligence, adaptability, and foresight. The question is not whether AI will shape the future of supply chains. The question is how quickly organizations are prepared to lead that transformation.
About the Authors

Aditi Shivarkar
Aditi, Vice President at Precedence Research, brings over 15 years of expertise at the intersection of technology, innovation, and strategic market intelligence. A visionary leader, she excels in transforming complex data into actionable insights that empower businesses to thrive in dynamic markets. Her leadership combines analytical precision with forward-thinking strategy, driving measurable growth, competitive advantage, and lasting impact across industries.

Aman Singh
Aman Singh with over 13 years of progressive expertise at the intersection of technology, innovation, and strategic market intelligence, Aman Singh stands as a leading authority in global research and consulting. Renowned for his ability to decode complex technological transformations, he provides forward-looking insights that drive strategic decision-making. At Precedence Research, Aman leads a global team of analysts, fostering a culture of research excellence, analytical precision, and visionary thinking.

Piyush Pawar
Piyush Pawar brings over a decade of experience as Senior Manager, Sales & Business Growth, acting as the essential liaison between clients and our research authors. He translates sophisticated insights into practical strategies, ensuring client objectives are met with precision. Piyush’s expertise in market dynamics, relationship management, and strategic execution enables organizations to leverage intelligence effectively, achieving operational excellence, innovation, and sustained growth.





 Request Consultation
Request Consultation

