Strategic healthcare IT investments in AI, analytics, and EHRs are helping hospitals improve patient care, cut costs, boost efficiency, and make smarter decisions. Success depends not just on spending more, but on aligning technology with clear clinical and financial goals.
Healthcare systems globally are undergoing a profound digital transformation, driven by escalating cost pressures, workforce shortages, regulatory complexity, and rising patient expectations. Healthcare IT investments spanning electronic health records (EHRs), artificial intelligence (AI), cloud platforms, cybersecurity, and data interoperability have become central to institutional competitiveness and care delivery excellence.
However, while spending on healthcare IT continues to grow, value realization remains uneven. Winning organizations distinguish themselves not by the scale of investment alone, but by strategic alignment, execution discipline, and measurable clinical and economic outcomes. This whitepaper examines the critical success factors shaping high-impact healthcare IT investments and outlines a value-centric framework for sustainable returns.
The Urgent Call of Strategic Healthcare IT Investment.
Healthcare IT has come out to be more of a back-office facilitator to a strategic asset. Digital systems have changed the nature of clinical decision-making, the efficiency of operations, the interaction with patients, and the management of population health. The shift in the fifth stage of volume-based to value-based care models only increases the significance of the data-driven insights, real-time analytics, and coordinated care pathways.
Yet, healthcare remains one of the most complex environments for digital adoption. Fragmented legacy systems, heterogeneous data standards, clinician burnout, and regulatory constraints often dilute returns. As a result, the central question is no longer whether to invest in healthcare IT, but how to invest effectively to generate durable value.
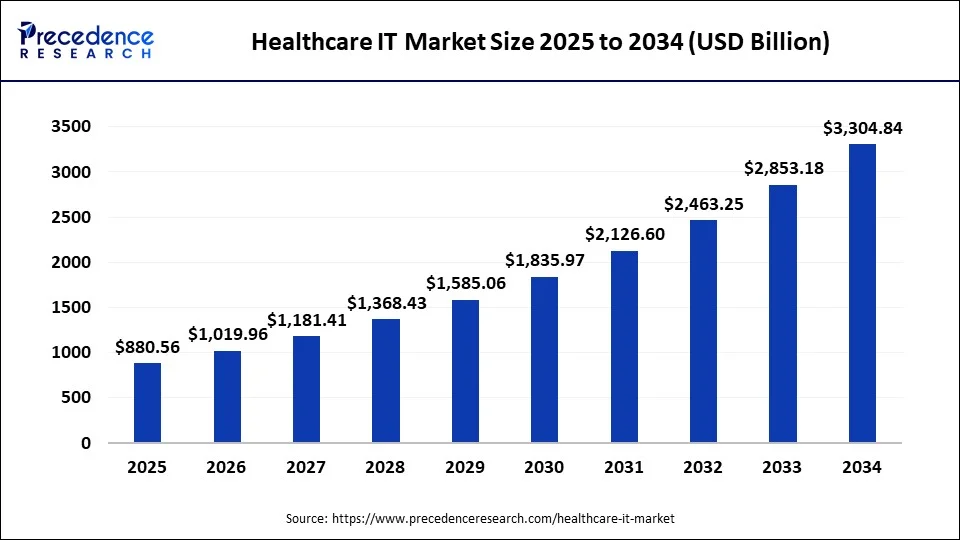
What is the Healthcare IT Market Size?
The global healthcare IT market size accounted for USD 880.56 billion in 2025 and is predicted to be worth around USD 3,715.34 billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of 15.48% from 2026 to 2035
Market Highlights
- North America dominated the market with revenue share of 41% in 2025.
- By region, Asia Pacific is expected to grow rapidly during the forecast period.
- By region, Asia Pacific is the fastest-growing in 2025.
- By product type, the healthcare provider solutions segment led the market in 2025.
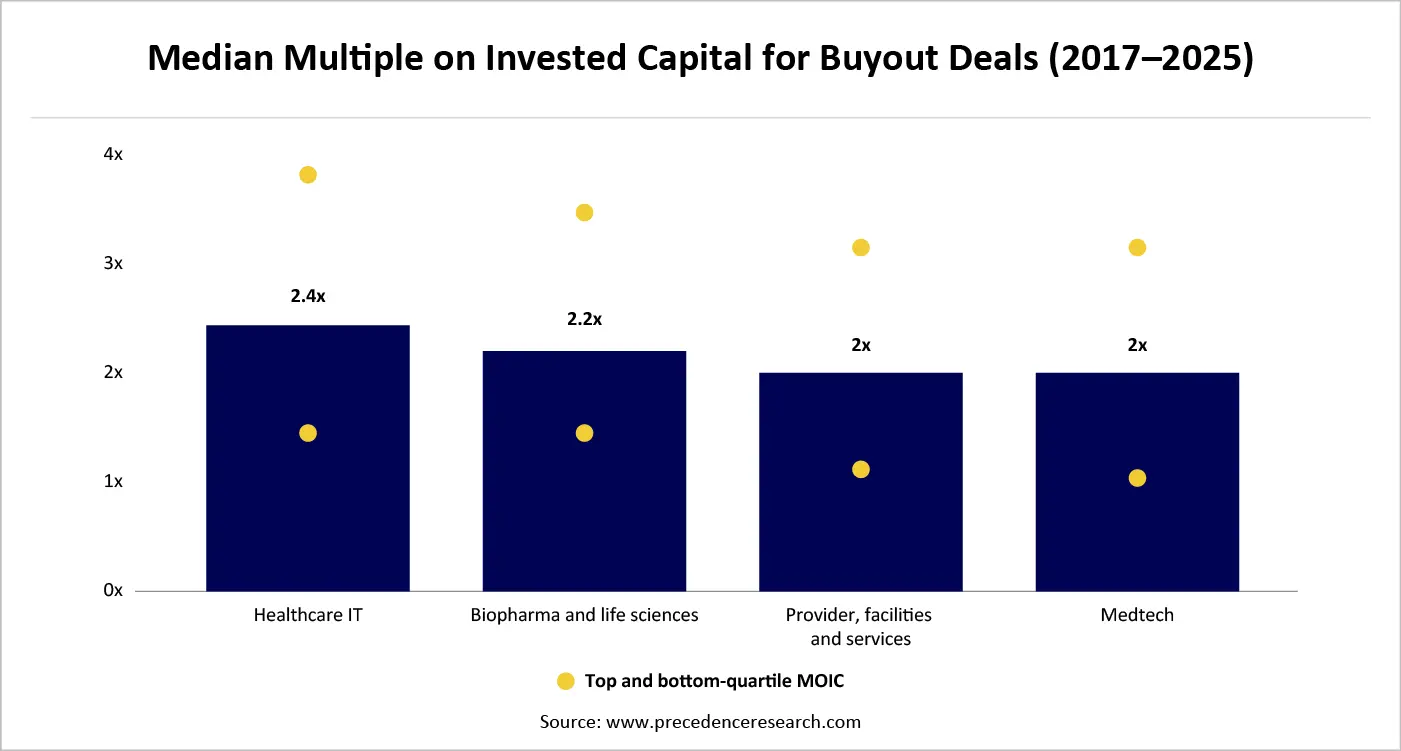
Median Multiple on Investment Capital (MOIC)
Multiple on Invested Capital (MOIC) is a base measure that is applied to assess the overall value generated by an investment in comparison with the invested capital. Unlike the return measures, which look at the time value, MOIC offers a pure value-creation prism, explaining one of the key questions of the investor: How many times did we make our money back? The median MOIC is a central value of MOIC values of a portfolio, a cohort, or a benchmark universe. This measure balances the effects of non-representative successes or failures of outliers by looking at the median, rather than the average, and provides a better approximation of the overall performance of investments.
In a healthcare IT context
Median MOIC is often used to benchmark returns across subsegments such as EHR platforms, revenue cycle management software, digital health analytics, and AI-enabled clinical tools. It helps investors and strategists identify which technology categories consistently deliver scalable and defensible returns rather than relying on a small number of exceptional exits
| Metric | What it measures | Key limitations |
| MOIC | Absolute value creation | Ignores time value |
| Median MOIC | Typical value creation | No timing sensitivity |
| IRR | Annualized return | Can be distorted by early exist |
| DPI | Cash returned | Ignores unrealized value |
| TVPI | Total portfolio value | Sensitive to valuation assumptions |
Median MOIC complements IRR by emphasizing capital efficiency and durability of value, particularly important in longer duration IT investments.
The interpretation framework
In healthcare IT, median MOICs are often lower than top-quartile outcomes due to regulatory friction, extended sales cycles, and adoption complexity making the median a critical realism anchor.
| Meadian MOIC | Investment Interpretation |
| <1.0x | Systematic value destruction |
| 1.0-1.5x | Capital preservation/ modest uplift |
| 1.5-2.0x | Healthy value creation |
| 2.0-3.0x | Strong investment performance |
| >3.0 x | Exceptional, scalable value |
The median multiple on invested capital is a critical indicator of sustainable value creation, particularly in complex, innovation-driven sectors such as healthcare IT. By emphasizing typical outcomes rather than exceptional cases, it provides a grounded, decision-useful measure of investment effectiveness. For investors seeking resilient, repeatable returns, median MOIC serves not merely as a performance metric but as a strategic compass guiding capital allocation, portfolio design, and long-term value creation.
AI and analytics as Top Investment Priority
- Strategic Context: Artificial intelligence (AI) and sophisticated analytics have become no longer an overly experimental asset but a strategic asset in the healthcare systems. The increasing clinical complexity and ongoing cost-inflation, staffing gaps, and a shift to value-based care, have made data-driven decision-making increasingly a tactical competence, but an enterprise-wide necessity. As a result, AI and analytics have already become one of the top-priority areas of investment in healthcare IT portfolios. Compared to the previous generations of digitization, where the emphasis was on capturing data and automating systems, the technology of AI-enabled analytics transforms fragmented clinical, operational, and financial data into actionable intelligence. This transformation essentially reinvents the way healthcare organizations direct their resources, risk management, and outcome improvement.
- Clinical Decision Support and Outcomes: AI-based clinical analytics supplement physician judgment, processing massive data sets of structured and unstructured data, such as imaging, genomics, and electronic health records. These systems minimize variations in patient diagnosis, facilitate the early identification of diseases, and enable precision medicine. Companies that have invested in clinically embedded AI are consistently reporting not only improvements in care quality, patient safety, and predictability of outcomes, but also in their own quality.
- Workforce Optimization and Operational Efficiency: Resource inefficiency is one of the most urgent problems in healthcare that can be tackled with the help of operational analytics that is driven by AI. Predictive models enhance demand management, operating room management, bed management, and staff scheduling. Analytics investments eliminate burnout and boost system throughput by automating administrative and non-clinical workflows.
-  Financial Performance and Revenue Integrity: The use of advanced analytics can improve performance in the revenue cycle in the form of denial prediction, automated coding, and fraud detection. Financial insights powered by AI increase cash flow insight and margin cover, especially in complicated payer settings. With the introduction of new reimbursement models, investments in analytics are becoming the key to financial sustainability. The management of population health and risk is a crucial component of the prevention management process.
- Future of AI and analytics in healthcare: In the future, AI and analytics will become more of a decision support and less of an autonomous organization of healthcare processes. Generative AI, systems of real-time learning, and data sharing across the ecosystem will continue to increase the value creation scope. In the long run, the maturity of analytics will be one of the key features of well-performing healthcare systems.
The primary healthcare IT investment priority has become AI and analytics, which are the most significant. Their capability to extract the intelligence out of the data, to boost the outcomes, to make the processes more efficient and to create the financial strength makes them the center of the healthcare transformation. Companies that invest early, operate in a responsible way and size decisively will transform the edge of information benefits into sustained clinical and economic leadership.
Beyond the Digital Record: How EHRS Power End-to-End Healthcare
Transformation
- The development of Electronic Records to Digital Foundations: Electronic Health Records (EHRs) have been firstly implemented as a set of systems that were adopted to complete the compliance element and remodel the paper chart substitution by electronic documentation of patient records. However, over time, EHRs have developed to become the fundamental digital foundation of healthcare organizations, which allows not only storing data but also transforming enterprises on a global scale. The current EHRs are used as the developmental platforms around which analytics, AI, interoperability, and patient engagement solutions are developed. Digital transformation in healthcare has ceased to be on individual technology implementations and has become the redesigning of care delivery, operations and decision making around digitally enabled workflows. Here, EHRs serve as the sole provider of clinical reality, which grounds the change processes throughout the healthcare value chain.
- EHRs as Integrated Care Delivery Catalysts: The current EHR systems can support longitudinal patient records that combine data between inpatient, outpatient, laboratory, imaging, and pharmacy data. The integration helps maintain continuity of care, eliminate information asymmetry, and facilitate multidisciplinary cooperation. The integration of clinical guidelines, alerts, and care pathways into workflow transforms healthcare into an attentive treatment system into proactive and coordinated care models. Interoperable EHR ecosystems also allow sharing data among providers, payers, and public health agencies, which has become essential during population health management and value-based care efforts.
- Workflow-based Operational Transformation with EHR: In addition to clinical documentation, EHRs are also potent motivation factors of operational efficiency. The computer-based scheduling, order management, billing, and discharge activities help to lessen manual intervention and administrative load. EHR workflow automation enhances throughput, error reduction, and decreases care cycles. Together with analytics, EHR data can be used to do proactive operational planning- bed utilization, staffing levels, and supply chain operations. Consequently, EHR-driven change has a direct impact on cost pressure and increased workforce productivity and resilience.
- Improving Clinical Quality, Patient Safety: EHRs are at the center of clinical quality and safety improvement through standardized documentation, decreased variability, and decision support based on evidence. EHRs with clinical decision support systems (CDSS) can help clinicians with their diagnostic, medication management, and risk notifications at the point of care. The digital transformation based on EHRs also makes the safety of patients stronger by using medication reconciliation, allergy alerts, and real-time monitoring of adverse events. It is these capabilities that place digital maturity in terms of quantifiable outcome improvements.
- Digital Transformation in the Patient: EHRs are becoming increasingly provider-directed into patient-control. The mobile health integrations, patient portals, and digital consent tools allow people to retrieve their records, make appointments, and interact with care teams. Such change increases transparency, involvement, and mutual decision-making. With the expansion of healthcare consumerism, digital front-end powered by EHR turns out to be a key ingredient of a smooth, individualized patient experience. Companies that use EHR data to customize communication channels and pathways to care earn a competitive edge on patient loyalty and satisfaction.
- EHRs as AI and Higher Analytics Facilitators: The major source of data that drives AI and analytics programs is EHRs. Predictive modeling and real-time insights are possible with structured clinical data and unstructured notes that are processed using natural language processing. The digital transformation can be hastened by designing EHRs to have cloud integration, open APIs, and analytics platforms.
- Adoption, Change Management and Governance: Digital transformation that is successful and led by EHR necessitates that technology is implemented. The alignment of clinical leadership, IT, and operations through governance frameworks is necessary to guarantee usability, quality of data, and regulatory compliance. Clinician involvement and education are also essential to address the resistance and introduce digital tools into the everyday practice. The higher the adoption and better long-term payoff of EHR transformation occurs in organizations that view EHR change as a cultural and operational change and not as a technical update.
- Difficulties in EHR-Based Transformation: Although such systems have the potential to transform, they also introduce challenges such as documentation burden, interoperability, and inflexibility of the legacy system. These problems must be overcome by investing in usability design, automation, and integration.
- The Future of EHRs in Digital Healthcare: The subsequent stage in the development of EHR will be an increase in the level of intelligence of systems, interoperability, and invisibility. Voice-based documentation, generative artificial intelligence, real-time analytics, and interoperable health data networks will further cause an administrative load, thereby improving clinical understanding.
The Development of Electronic Records to Digital Foundations.
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) have been firstly implemented as a set of systems that were adopted to complete the compliance element and remodel the paper chart substitution by electronic documentation of patient records. However, over time, EHRs have developed to become the fundamental digital foundation of healthcare organizations, which allows not only storing data but also transforming enterprises on a global scale. The current EHRs are used as the developmental platforms around which analytics, AI, interoperability and patient engagement solutions are developed.
Digital transformation in healthcare has ceased to be on individual technology implementations and has become the redesigning of care delivery, operations and decision making around digitally enabled workflows. Here, EHRs serve as the sole provider of clinical reality, which grounds the change processes throughout the healthcare value chain.
The digital transformation based on EHRs also makes the safety of patients stronger by using medication reconciliation, allergy alerts, and real-time monitoring of adverse events. It is these capabilities that place digital maturity in terms of quantifiable outcome improvements EHRs are becoming increasingly provider-directed into patient-control. The mobile health integrations, patient portals, and digital consent tools allow people to retrieve their records, make appointments, and interact with care teams. Such change increases transparency, involvement, and mutual decision-making. With the expansion of healthcare consumerism, digital front-end powered by EHR turns out to be a key ingredient of a smooth, individualized patient experience. Companies that use EHR data to customize communication channels and pathways to care earn a competitive edge on patient loyalty and satisfaction.
The major source of data that drives AI and analytics programs is EHRs. Predictive modeling and real-time insights are possible with structured clinical data and unstructured notes that are processed using natural language processing. The digital transformation can be hastened by designing EHRs to have cloud integration, open APIs, and analytics platforms. By modernizing EHR infrastructures, healthcare organizations open the potential to use AI to support clinical decisions, operations optimization, and population health management-driving the scale of data volumes into intelligence. Digital transformation that is successful and led by EHR necessitates that technology is implemented. The alignment of clinical leadership, IT, and operations through governance frameworks is necessary to guarantee usability, quality of data, and regulatory compliance. Clinician involvement and education are also essential to address the resistance and introduce digital tools into the everyday practice. The higher the adoption and better long-term payoff of EHR transformation occurs in organizations that view EHR change as a cultural and operational change and not as a technical update.
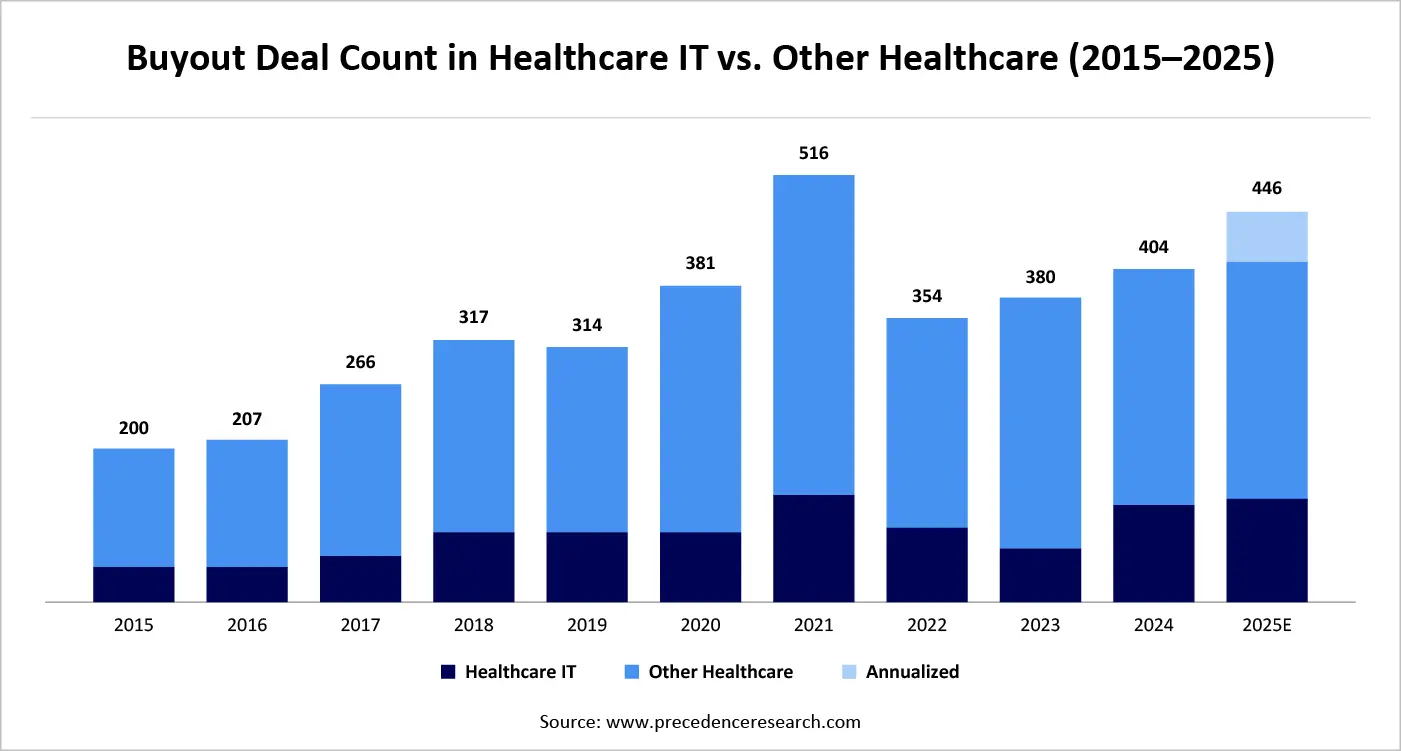
Deal Momentum as an Indicator of Health: The Strength of the Healthcare IT is Made Durable through the Activity of Transactions.
A strong flow of transactions in the healthcare IT still reflects the structural resilience of the sector and its sustainability in investments over the long-term. The high rate of mergers, acquisitions, and strategic investments over a period clearly indicates that there is a firm belief that healthcare IT would create strong cash flows, scale in care settings and be responsive to changing regulatory and reimbursement landscapes. Compared to cyclical industries, changes, and technological resources in healthcare IT, most of which are integrated into clinical processes (including EHR systems, revenue cycle, analytics, and digital health infrastructure) exhibit high switching costs and recurring revenue patterns, making them appealing to target even during macroeconomic uncertainty. A convergence between healthcare delivery and technology also supports transaction momentum by pushing both financial sponsors and strategic acquirers toward consolidating platforms, increasing capabilities, and using data to differentiate. Notably, the deal activity is moving beyond opportunistic acquisition moves and commencing long-term value creation plans, which portends market optimism about healthcare IT as an undercarriage, mission-critical component of contemporary healthcare systems.
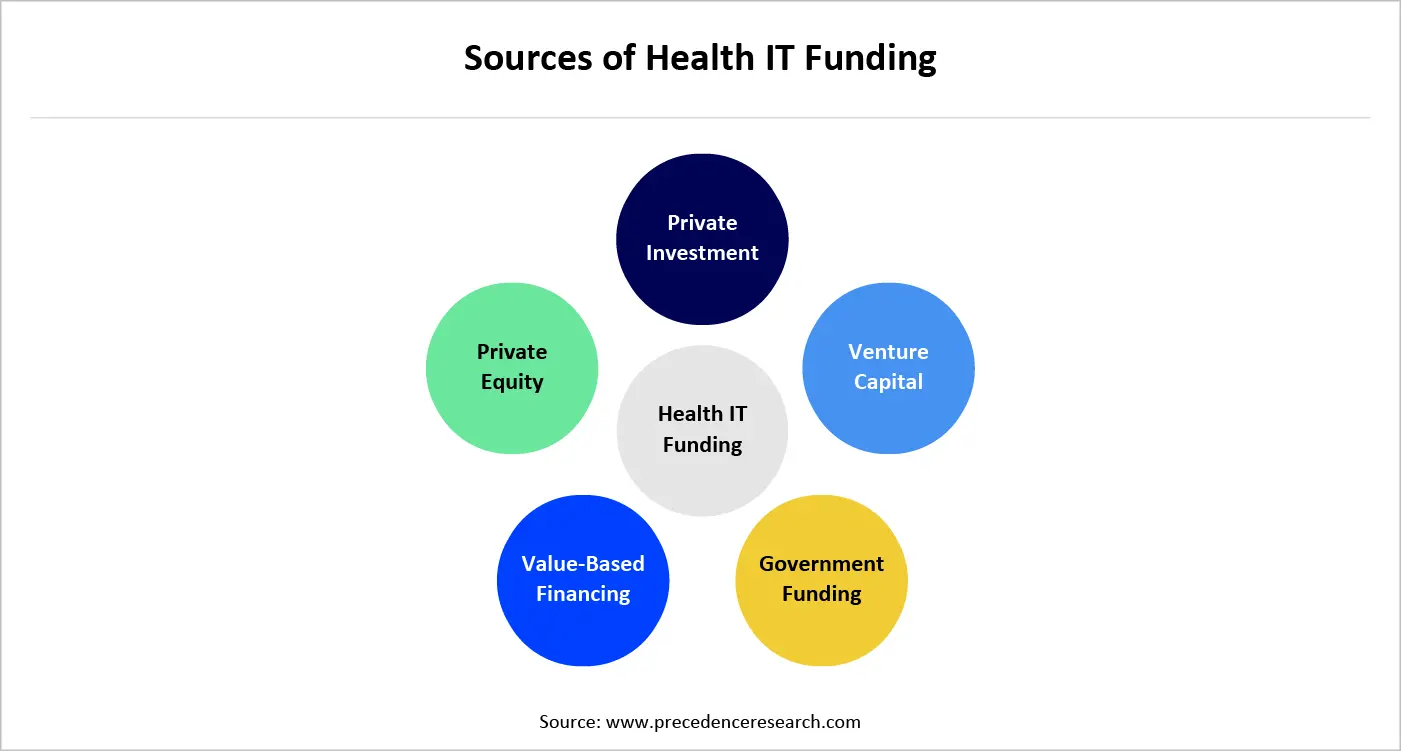
Catalyzing Innovation at Scale: Government Funding as a Growth Engine for Healthcare IT
Government funding opportunities play a pivotal role in accelerating healthcare IT adoption and innovation, acting as both a catalyst for digital transformation and a stabilizing force during periods of market uncertainty. Across developed and emerging economies, public sector investments are increasingly directed toward strengthening digital health infrastructure, expanding access to care, improving data interoperability, and enhancing system resilience. These funding mechanisms ranging from grants and subsidies to public–private partnerships and outcome-based financing signal strong policy alignment with long-term healthcare digitization goals.
A significant share of government funding is focused on core health IT modernization, including electronic health records, health information exchanges, cybersecurity, and cloud-based data platforms. By underwriting foundational infrastructure, governments reduce financial barriers for providers, particularly small hospitals, and rural healthcare systems, enabling broader and more equitable digital adoption. This, in turn, creates downstream opportunities for advanced analytics, AI integration, and population health initiatives built on standardized digital foundations.
Governments are also prioritizing AI-enabled digital health and data analytics, recognizing their potential to improve clinical outcomes, optimize resource utilization, and support value-based care models. Funding programs increasingly emphasize real-world impact, such as reduced hospital readmissions, improved chronic disease management, and enhanced public health surveillance, encouraging solution providers to align innovation with measurable outcomes rather than experimental deployments. This outcome-oriented approach improves capital efficiency and accelerates the commercialization of scalable technologies.
In addition, public funding plays a critical role in stimulating ecosystem development. Innovation grants, research funding, and startup accelerators supported by government agencies help early-stage health IT companies bridge the gap between research and market entry. These initiatives de-risk innovation, attract private capital, and foster collaboration between healthcare providers, technology firms, and academic institutions. For investors and industry participants, government-backed programs often serve as early validation signals for emerging technologies and business models.
From a strategic perspective, government funding opportunities enhance the overall durability of the healthcare IT sector. By anchoring demand, shaping standards, and supporting long-term digital roadmaps, public investment reduces volatility and reinforces healthcare IT’s status as mission-critical infrastructure. Organizations that proactively align their product strategies, compliance frameworks, and impact metrics with government funding priorities are better positioned to secure non-dilutive capital, accelerate growth, and achieve sustainable competitive advantage.
From Spend to Impact: Assessing the ROI of Health IT Investments
IT investments is now a strategic requirement as healthcare organizations juggle increased technology expenses with increasing demands to prove value on the balance sheet. In contrast to the traditional capital projects, health IT initiatives affect several aspects of performance, namely clinical outcomes, operational efficiency, workforce productivity, patient experience, and financial sustainability, and ROI assessment is inherently multidimensional. Consequently, top institutions are no longer focusing on the limited cost-cutting measures but have shifted to overall value models that address both qualitative and quantitative irradiation. The fundamental pillar of successful ROI evaluation is a strict correspondence between investments on technology and business goals. Complex analytics and AI are now playing a key role in reinforcing the ROI analysis. Dashboards of real-time performance, predictive modeling as well as benchmark comparisons allow an organization to monitor value realization as it comes as opposed to conducting retrospective reviews. Such a change can enable adaptive investment choices to enable leaders to re tune deployment, scale successful use cases, and wind down poor-Cinitiatives. Notably, change management and adoption are equally important to the successful ROI realization as is technology capability. Health IT investments without a smooth transition into clinical and operational processes tend to perform poorly even if their technical performance is high. It is found that organizations with greater investment in clinician engagement, training, and process redesign always have greater realized ROI as compared to organizations that engage in system implementation only. Given that the world is becoming an ever more capital-constrained market, the ROI of health IT investments ceases to be a finance endeavor, but a discipline of governance. Having a holistic and outcome-driven ROI model enables healthcare organizations in a better position to focus on investments, develop stakeholder trust, and make digital transformation reflect itself in tangible and sustainable value.
| Stakeholder | Role |
| Clinicians | Provide input on clinical benefits and workflow implications |
| Administrators | Provide input on operational and financial implications |
| Financial Leaders | Provide input on financial analysis and ROI |
The Future of the Healthcare IT Industry: From Digital Enablement to Intelligent Health Systems
The future of the healthcare IT industry will be defined by its transition from foundational digitization to intelligence-driven, adaptive health systems that continuously learn, predict, and optimize outcomes across the care continuum. As healthcare faces sustained pressure from aging populations, chronic disease burden, workforce shortages, and cost inflation, technology will move beyond supporting operations to actively orchestrating care delivery and system performance. Healthcare IT will increasingly function as mission-critical infrastructure, embedded deeply into clinical decision-making, financial management, and population health strategies.
Artificial intelligence, advanced analytics, and generative technologies will sit at the core of this evolution. EHRs and digital platforms will evolve into intelligent ecosystems that automate documentation, surface real-time clinical insights, and enable predictive and prescriptive decision support. Interoperability will mature from data exchange to data liquidity, allowing seamless movement of information across providers, payers, life sciences companies, and public health agencies. This shift will enable longitudinal, person-centric care models and unlock new value from integrated datasets.
The industry will also see a structural shift toward platformization and consolidation. Point solutions will increasingly be absorbed into broader platforms offering end-to-end capabilities spanning clinical care, operations, revenue management, and patient engagement. This consolidation will be driven by buyer demand for simplicity, integration, and measurable ROI, favouring vendors with scalable architectures, embedded workflows, and recurring revenue models. As a result, healthcare IT leaders will compete less on features and more on outcomes, usability, and ecosystem reach.
Regulation and governance will play a central role in shaping the industry’s trajectory. As AI-driven decision-making becomes more prevalent, trust, transparency, and explainability will emerge as key differentiators. Vendors and providers that embed ethical AI frameworks, cybersecurity resilience, and regulatory alignment into their offerings will gain long-term credibility and market advantage. Government funding and policy incentives will continue to accelerate adoption, particularly in areas such as interoperability, cybersecurity, and population health infrastructure.
Finally, the future healthcare IT industry will be increasingly consumer-centric and preventive in orientation. Digital front doors, remote monitoring, and AI-enabled personalization will extend care beyond hospital walls, shifting the focus from episodic treatment to continuous health management. In this future state, healthcare IT will not merely support the system it will actively shape how care is delivered, financed, and experienced. Organizations that invest today in intelligence, interoperability, and outcomes-driven design will define the next generation of healthcare leadership.
About the Authors

Aditi Shivarkar
Aditi, Vice President at Precedence Research, brings over 15 years of expertise at the intersection of technology, innovation, and strategic market intelligence. A visionary leader, she excels in transforming complex data into actionable insights that empower businesses to thrive in dynamic markets. Her leadership combines analytical precision with forward-thinking strategy, driving measurable growth, competitive advantage, and lasting impact across industries.

Aman Singh
Aman Singh with over 13 years of progressive expertise at the intersection of technology, innovation, and strategic market intelligence, Aman Singh stands as a leading authority in global research and consulting. Renowned for his ability to decode complex technological transformations, he provides forward-looking insights that drive strategic decision-making. At Precedence Research, Aman leads a global team of analysts, fostering a culture of research excellence, analytical precision, and visionary thinking.

Piyush Pawar
Piyush Pawar brings over a decade of experience as Senior Manager, Sales & Business Growth, acting as the essential liaison between clients and our research authors. He translates sophisticated insights into practical strategies, ensuring client objectives are met with precision. Piyush’s expertise in market dynamics, relationship management, and strategic execution enables organizations to leverage intelligence effectively, achieving operational excellence, innovation, and sustained growth.





 Request Consultation
Request Consultation

