What is the Nuclear Power Market Size?
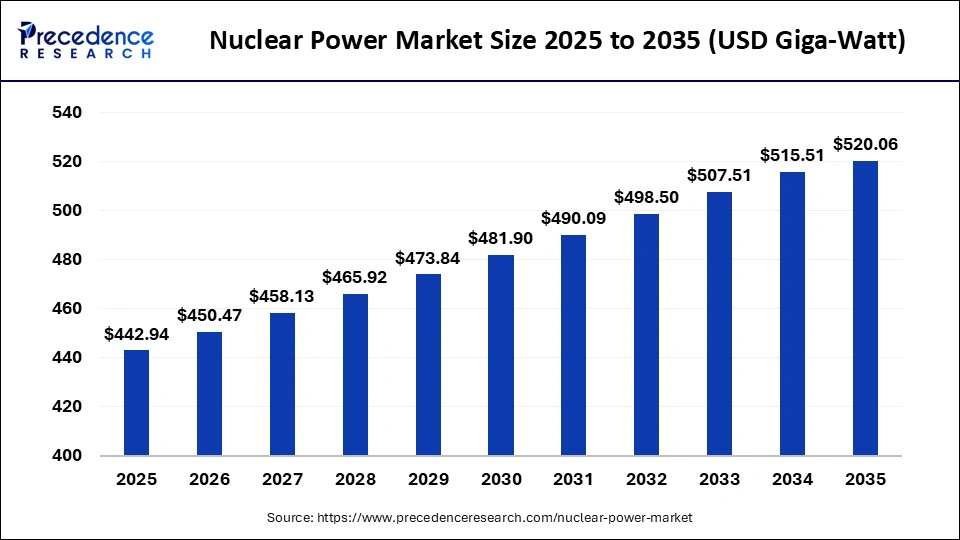
The global nuclear power market demand accounted for USD 442.94 giga-watt in 2025 and is anticipated to reach around USD 520.06 giga-watt by 2035, expanding at a CAGR of 1.62% between 2026 and 2035.
Nuclear Power Market Key Takeaways
- In terms of revenue, the market is valued at USD 442.94 giga-watt in 2025.
- It is projected to reach USD 520.06 giga-watt by 2035.
- The market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 1.62% from 2026 to 2035.
- North America has captured the maximum revenue share of around 39% in 2025.
- Asia-Pacific is expected to expand at the fastest CAGR between 2026 and 2035.
- By Reactor Type, the pressurized water reactors (PWRs) segment contributed the highest revenue share in 2025.
- By Application, the energy segment recorded the largest market share in 2025.
Market Overview
In order to achieve carbon neutrality, nuclear power is a crucial source of heat and electricity with low carbon emissions. New technologies that are currently being developed will allow nuclear power to continue to develop and will increase its integration with other low-carbon energy sources, such as variable renewables and fossil fuels with carbon capture and storage (CCS), in a future decarbonized energy mix. Modern nuclear power plants are thermal facilities that use heat to transform water into steam, which turns a turbine generator. Instead of using hydrocarbons as fuel, nuclear power plants use processed forms of uranium, plutonium, and (possibly) thorium. Inside a reactor, nuclear fission generates heat rather than hydrocarbon burning. About a million times more energy is released during the fission process than during combustion.
Nuclear Power Market Growth Factors
The increasing demand for electricity as the global population grows and becomes more urbanized is expected to augment the growth of the market during the forecast period. Nuclear power provides a reliable and efficient source of energy that can meet this growing demand. Unlike other sources of energy such as fossil fuels, nuclear power does not produce greenhouse gas emissions or air pollution, making it an attractive option for meeting energy needs while also reducing environmental impact.
Furthermore, with the increasing concern about climate change, reducing carbon emissions is a top priority for many countries. Nuclear power is a low-carbon energy source that can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and support the transition to a more sustainable energy system. Nuclear power is also a reliable source of energy that can help stabilize the grid, providing a secure source of energy that is not subject to the volatility of fossil fuel markets.
Additionally, nuclear power provides a secure source of energy that is not subject to the geopolitical risks associated with fossil fuel imports. This can help reduce the dependence on foreign energy sources and enhance energy security. Also, globally, the electrification of the transportation and heating industries accelerated, with record sales of electric cars and heat pumps in 2022 fueling the expansion.
Market Outlook
- Industry Growth Overview: The nuclear power market is experiencing steady global growth, driven by rising electricity demand, government commitments to decarbonization, and the need for stable, low-carbon energy to complement renewables.
- Major investors: Major investors in the nuclear power industry include a mix of public and private entities, investment firms, and technology companies such as Microsoft, Google (Alphabet), BlackRock, and several state-owned corporations and development banks.
- Global Expansion: Governments in over 40 countries are providing incentives, subsidies, and regulatory frameworks to support new projects and lifetime extensions of existing plants.
Market Scope
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Demand in 2025 | USD 442.94 Giga-Watt |
| Market Demand in 2026 | USD 450.47 Giga-Watt |
| Market Demand by 2035 | USD 520.06 Giga-Watt |
| Growth Rate from 2026 to 2035 | CAGR of 1.62% |
| Largest Market | North America |
| fastest Growing Market | Asia Pacific |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 to 2035 |
| Segments Covered | By Reactor Type, By Reactor Size, and By Application |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America and Middle East & Africa |
Market Dynamics
Driver
Increasing demand for electricity
According to the 2023 Electricity Market Report by IEA, over the next three years, China, India, and Southeast Asia will collectively account for more than 70% of the increase in the world's electricity demand. The growth of emerging and developing economies is mirrored by an increase in the demand for power. Advanced economies are promoting electrification at the same time to decarbonize their industrial, heating, and transportation sectors. As a result, compared to the growth rate in 2022, the worldwide demand for energy is anticipated to increase by 3% annually between 2023 and 2025. More than twice as much power will be consumed globally between now and 2025—a total increase in demand of nearly 2,500 terawatt-hours (TWh).
- In May 2025, Electricité de France (EDF) and asset management firm Siparex announced the launch of a second investment fund dedicated to the nuclear sector, as disclosed. Named Fonds France nucléaire 2 (FFN2), the fund targets a capitalization of € 300 million (USD 324 million) to support the growth of subcontractors and suppliers involved in future nuclear projects in France.
Nuclear power facilities generate steam by heating water. Steam is used to power enormous turbines, which create energy. Nuclear power now accounts for 20% of electricity generated in the UNECE region, as well as 43% of low-carbon generation. However, fossil fuels continue to dominate supply, accounting for more than half of the region's electricity. Many UNECE nations, including Bulgaria, Belgium, Croatia, the Czech Republic, France, Finland, Hungary, Slovenia, Slovakia, Spain, Ukraine, Sweden, and the United States, rely heavily on nuclear power to generate low-carbon electricity. Twenty UNECE Member States now operate nuclear power facilities, and 15 countries are either building or preparing to build new reactors. Furthermore, for the first time, nuclear power programs are being developed in 7 UNECE Member States. Nuclear power is expanding outside of the UNECE region in Asia, the Middle East, South America, and Africa. Additionally, developing nations, which are looking into ways to fulfill their pledges to sustainable development, have a keen interest in nuclear power.
Restraints
High cost of nuclear power
Nuclear power expenses are frequently divided into capital costs and operating costs. Site preparation, engineering, construction, manufacture, commissioning, and financing are all capital expenses. Fuel expenditures, decommissioning, maintenance, and waste disposal are all part of operating expenses. Nuclear power plants have far higher beginning costs than other energy sources like coal and natural gas, and their annual repayment expenses are much greater than their annual operating costs.
This is due to the technical complexity of nuclear power facilities and the severe licensing and design standards they must meet. A new nuclear power plant's design and construction require a large number of highly skilled specialists and frequently take many years, compounding finance expenses that can grow significantly. Design modifications or legal disputes may result in delays that raise the finance expenses, which in certain situations are higher than the actual building costs.
Furthermore, due to the high cost of developing plants, nuclear energy finds it difficult to compete with alternative energy sources, particularly natural gas. The high price of nuclear energy has led to a major decline in the construction of new nuclear power stations. For instance, two South Carolina utility dropped two incomplete Westinghouse AP1000 reactors in 2017, left just two other AP1000 reactors under development in Georgia as a result of difficulties in equipment production, significant construction delays, and cost overruns. These reactors have likewise experienced delays and cost overruns. Construction is ongoing spite the reality that the initial price estimated at $14 billion was raised to $23 billion by 2019, given the assurance of government financial support for these reactors.
Opportunities
Development of advanced reactor systems
Move over, millennials; a new generation is set to emerge by 2030. 14 countries, including the United States, are working together to create Generation IV nuclear reactors. These advances will provide enormous potential prospects for the market in the next years. Currently, the United States Department of Energy and its national laboratories are funding research and development on a wide range of new advanced reactor technologies that potentially revolutionize the nuclear sector.
These cutting-edge solutions will be cleaner, safer, and more efficient than earlier generations. Sodium-cooled fast reactors (SFR), extremely high-temperature reactors, and molten salt reactors are among the emerging advanced reactor technologies. These technologies are projected to meet future energy needs at a reasonable cost. Furthermore, advanced small modular reactors (SMRs) could revolutionize the way we think about reliable, clean, and economical nuclear power within the next decade.
Rather than going big, scientists and engineers developed microreactors that are around one-third the size of a typical nuclear power station. As a result, the largest clean energy source may be entering the market, making nuclear more scalable and versatile than ever before.
- In February 2025, UK-based maritime nuclear innovation company Core Power launched a U.S.-anchored maritime civil nuclear program, titled Liberty, that aims to bring floating nuclear power to market by the mid-2030s. The program will lay the foundation for the use of nuclear power in the civil maritime sector.
Reactor Type Insights
On the basis of reactor type, the pressurized water reactors (PWRs) segment held the largest revenue share in 2025. Approximately 300 of these reactors are now operational for power generation, and several hundred more are used for naval propulsion, making them the most prevalent type. PWRs were originally intended to be submarine power plants. Ordinary water is used by PWRs as a coolant and a moderator. Since less electricity is produced as the heat rises, operating this reactor is simple. The reactor is also safer and easier to operate since its core contains less fissile material, which lowers the likelihood of more fission events. Also, the PWR's turbine cycle is its most advantageous component. Water cannot ever be polluted by radioactive material in the main system loop because the primary and secondary loops are distinct. In conclusion, contamination is impossible because the water from the primary and secondary loops will never come into contact or mix. These factors are expected to present enormous prospects for the segmental growth of the market.
Application Insights
Based on the application, the energy segment held the largest market share in 2025. The increasing energy and water demand, coupled with strained supply sources is expected to support the segmental growth of the market. By 2034, global power consumption is expected to have doubled due to population increase, industrialization, and expectations of improved living standards. Additionally, due to these pressures, there is a growing demand for energy-intensive desalination plants and are further leading in lack of fresh water. Significant prospects exist to use nuclear energy to produce clean water on an industrial scale and meet the growing need for base-load electricity.
Regional Insights
U.S. Nuclear Power Market Size and Growth 2026 to 2035
The global nuclear power market demand reached USD 120.92 giga-watt in 2025 and is expected to be worth around USD 148.74 giga-watt by 2035, expanding at a CAGR of 2.09% from 2026 to 2035.
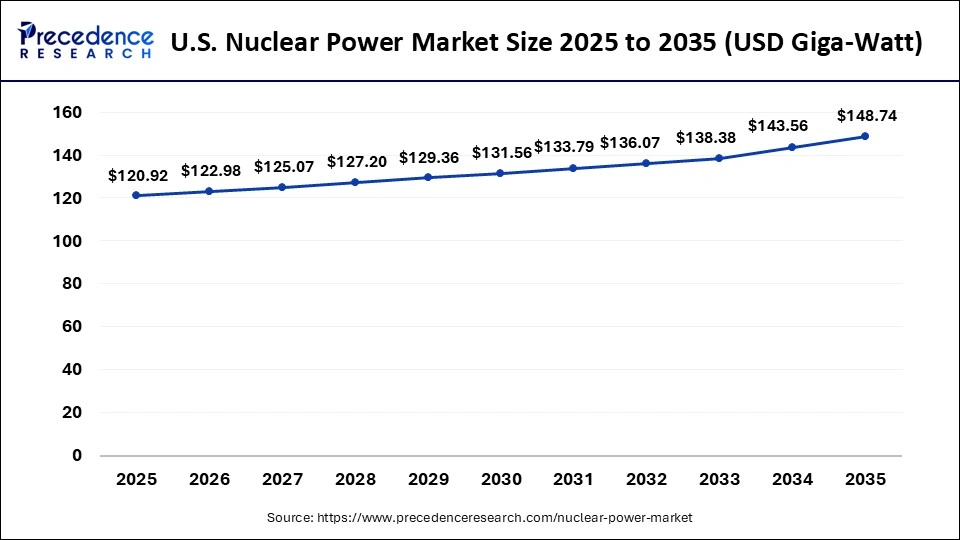
North America has held the largest revenue share in 2025 This is owing to the availability of large-production nuclear reactors along with rising energy demand in the region. As per the World Nuclear Association, the 92 nuclear reactors that are currently in operation in the USA have a net capacity of 94.7 GWe. 19.6% of the nation's electricity was produced by nuclear power in 2021. With a total net capacity of 13.6 GWe, Canada has 19 operational nuclear reactors. 14.3% of the nation's electricity was produced by nuclear power in 2021. With a total net capacity of 1.6 GWe, Mexico has two nuclear reactors that are currently in operation. 5.3% of the nation's electricity was produced by nuclear power in 2021. Thus, with so many nuclear reactors, the market in the region is expected to grow within the estimated timeframe.
United States Medical Disposable Market Trends
The United States is growing in the medical disposable market. The increasing prevalence of chronic diseases like cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and many more increases demand for medical disposables like catheters, syringes, and dressings. The aging population and increasing focus on infection control fuel demand for medical disposables like drapes, masks, and gowns. The advancements in disposable medical devices, like innovations in sterilization and smart sensors, help the market growth. The increasing private and public healthcare spending and government initiatives for the prevention of infection & hygiene drive the overall growth of the market.
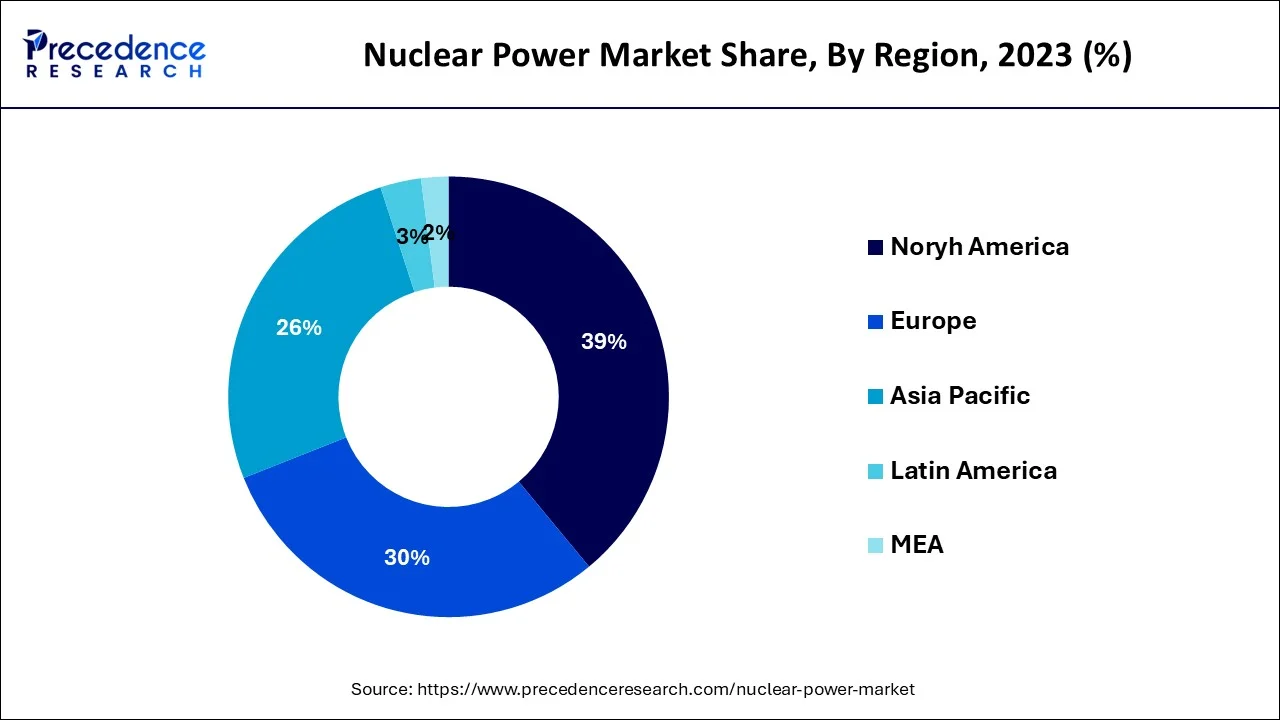
Asia-Pacific is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period.This is attributable to the increasing urbanization and increasing electricity demand due to the growing population across the region. China has held the largest share in the APAC region. According to the World Nuclear Association, with a total net capacity of 53.3 GWe, China has 55 nuclear reactors that are currently in operation. Nuclear power produced 5.0% of the nation's electricity in 2021. With 21 reactors planned to be completed by the end of July 2022, the nation continued to lead the new nuclear build market.
- In March 2025, Union Minister Jitendra Singh announced that the goal to generate 100 GW of nuclear power by 2047 is ambitious and achievable, and state-run Nuclear Power Corporation of India Limited (NPCIL) and its subsidiaries aim to fulfil nearly half of that target. Addressing a post-budget webinar organised by NITI Aayog, Singh.
China Nuclear Power Market Trends
In the Asia Pacific, China dominated the market owing to robust government support for energy security and extensive domestic investment in cutting-edge reactor tech such as Hualong One & SMRs.Also, the country is commercializing SMRs for more flexible deployment, including industrial desalination and heating, driving market growth further.
The urgent need to enhance urban air quality and lower greenhouse gas emissions is a major driving force behind the development of new nuclear power in China. India currently has 22 nuclear reactors that are operational, with a total net capacity of 6.8 GWe. Nuclear power produced 3.2% of the nation's electricity in 2021. As part of its extensive infrastructure development program, the Indian government is committed to increasing nuclear power capacity. The government set the lofty goal of having 14.6 GWe of nuclear capacity online by 2024 in 2010. With a total capacity of 6.7 GWe, eight reactors were being built in India as of the end of July 2022. These initiatives are likely to encourage the adoption of nuclear power solutions, which is driving market growth in the region.
Europe is significantly growing in the medical disposable market. The aging population and growing chronic diseases like respiratory disorders, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases increase demand for medical disposables like wound care items, syringes, and catheters. The growing demand for infection control increases the adoption of medical disposables. The increasing number of minimally invasive surgeries increases demand for medical disposables like gowns, procedure kits, gloves, and drapes. The growing surgical procedures in ambulatory surgical centers and hospitals support the overall growth of the market.
India Nuclear Power Market Trends
India's market is poised for significant expansion as the government positions nuclear energy as a core component of its long-term clean energy and energy security strategy, with plans to substantially increase installed capacity over the coming decades. Growth is supported by policy reforms aimed at attracting private investment and expanding international cooperation in the civil nuclear sector.
Germany Nuclear Power Market Trends
The growth of the market in the country can be driven by the ongoing growth of cost-effective solar and wind energy, optimised by regulatory frameworks and government subsidies. In addition, nuclear power provides stable and uninterrupted electricity, which can benefit many states in the country, leading to market growth soon.
Top Companies in the Nuclear Power Market & Their Offerings
- RWE AG: Offers services for the decommissioning and safe dismantling of nuclear power plants at sites including Biblis, Emsland, and Gundremmingen. The company is also heavily investing in renewable energy, such as developing battery storage and hydrogen-capable power plants on former nuclear sites.
- Energiewerke Nord GmbH (EWN): A federally owned company responsible for the decommissioning and dismantling of the former East German Soviet-designed reactors and managing related radioactive waste.
Nuclear Power Market Companies
- GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy
- China National Nuclear Corporation
- Westinghouse Electric Company LLC
- Centrus Energy
- Electricite de France
- Cameco Corp.
- Nuscale Power
- Rosatom
- Energy Harbor Nuclear Generation LLC
- Orano SA
- Constellation Energy Corporation
- Korea Hydro & Nuclear Power Co., Ltd.
- FirstEnergy Corp.
- Engie SA
Recent Developments
- In April 2025, Intco Medical launched new Syntex synthetic disposable latex gloves. The gloves are fully compliant with EU CE and FDA standards. Syntex gloves are available for use in various industries like industrial protection, healthcare, and food processing. The gloves have strong chemical & puncture resistance and provide high elasticity. (Source: https://www.biospectrumasia.com)
- In July 2025, Johnson & Johnson launched a disposable multifocal toric contact lens, ACUVUE OASYS MAX 1-Day MULTIFOCAL. The lens is useful for a person suffering from presbyopia and astigmatism. The lens offers stable, crisp, and clear vision across all distances. (Source: https://www.mpo-mag.com)
- In December 2024, ConTIPI Medical launched the ProVate disposable device for pelvic organ prolapse in the United States. The patients can easily use the device at home, and it is available in six sizes. The device can be used up to 7 days and is available for physicians. (Source:https://femtechinsider.com/contipi-medical-launches-provate-device-for-pelvic-organ-prolapse-in-the-u-s/)
- In April 2025, China launched five new nuclear power projects to meet surging AI energy demand. As China's homegrown AI models, such as DeepSeek, expand into manufacturing, healthcare, education, and infrastructure, particularly power supply, has become crucial for sustaining large-scale AI deployments.
- In March 2025, BNP Paribas' THEAM Quant platform, in partnership with BNP Paribas Exane Research, launched the THEAM Quant Nuclear Opportunities fund, seeking exposure to companies involved in the nuclear energy value chain.
- In February 2025, CORE POWER, the world's leading developer of maritime sector nuclear technologies, announced that it would develop a U.S.-anchored maritime civil nuclear program that would bring floating nuclear power to market by the mid-2030s. The program, titled Liberty, will lay the foundation for the use of nuclear power in the civil maritime sector.
- In April 2023,Saskatchewan and New Brunswick signed a formal agreement to construct small modular reactors (SMRs). This revitalized relationship will benefit both provinces by capitalizing on opportunities arising from nuclear energy development efforts in Canada and around the world, as well as accelerating progress towards decarbonizing power networks and industrial facilities using SMR technologies.
- In December 2022,the administration told the Lok Sabha that India is expected to commission 20 nuclear power stations by 2031, adding roughly 15,000 MW of power generating capacity. The first of these 20 nuclear power plants, a 700 MW unit, is scheduled to be completed in 2023 at Kakrapar in Gujarat, which already has three active nuclear power plants.
Segments Covered in the Report
By Reactor Type
- Pressurized Water Reactors (PWRs)
- Boiling Water Reactors (BWRs)
- Pressurized Heavy Water Reactors (PHWRs)
- Others
By Reactor Size
- Large Reactors
- Small Modular Reactors (SMRs)
By Application
- Energy
- Hydrogen Production
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Ask For Sample
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
 Get a Sample
Get a Sample
 Table Of Content
Table Of Content
 sales@precedenceresearch.com
sales@precedenceresearch.com
 +1 804-441-9344
+1 804-441-9344
 Schedule a Meeting
Schedule a Meeting