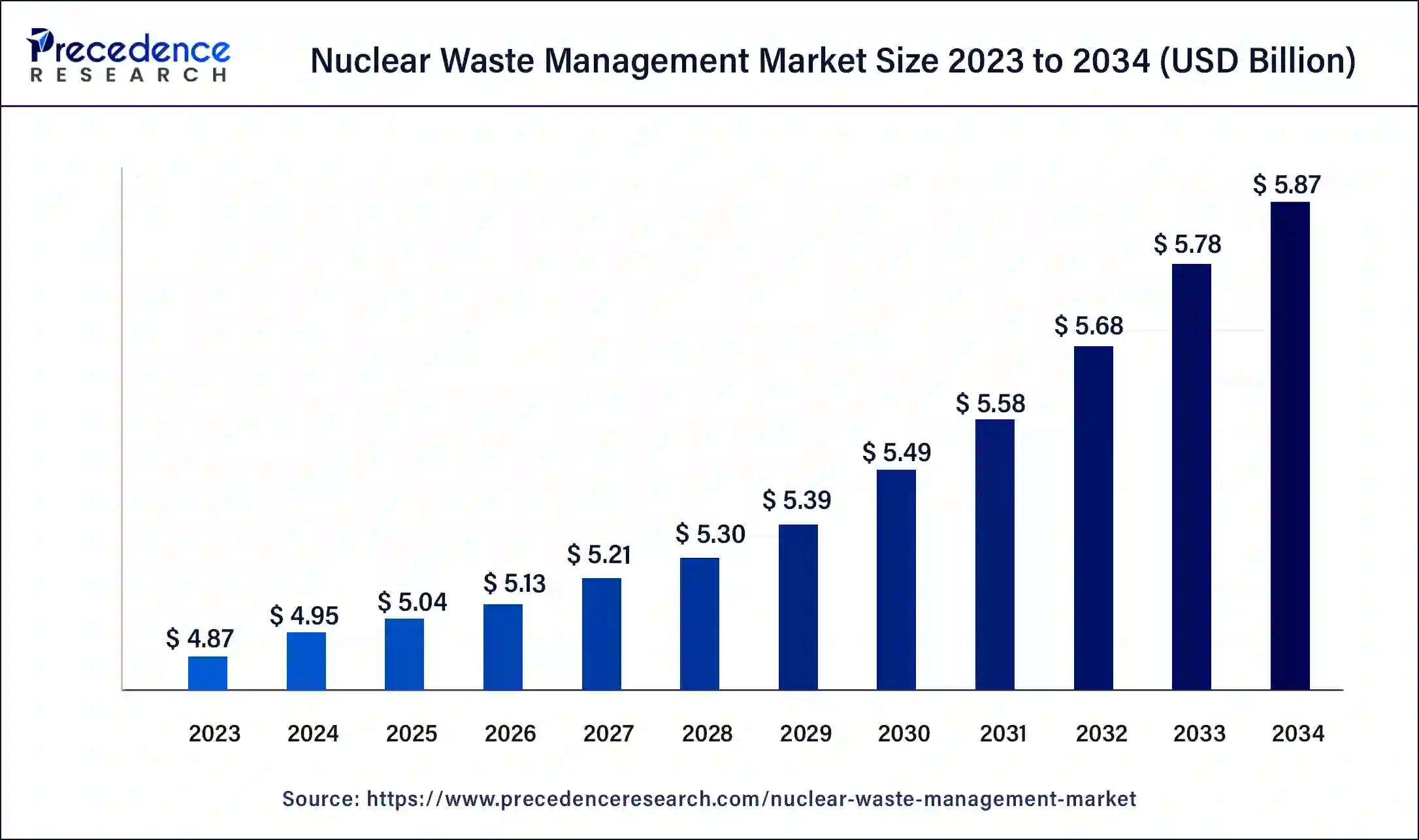
Nuclear Waste Management Market Size and Forecast 2025 to 2034
The global nuclear waste management market size is accounted at USD 5.04 billion in 2025 and predicted to increase from USD 5.13 billion in 2026 to approximately USD 5.87 billion by 2034. The nuclear waste management market growth is attributed to the increase in nuclear energy production.
Nuclear Waste Management Market Key Takeaways
- The global nuclear waste management market was valued at USD 4.87 billion in 2024.
- It is projected to reach USD 5.87 billion by 2034.
- The nuclear waste management market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 1.72% from 2025 to 2034.
- North America dominated the nuclear waste management market with the largest market share of 35% in 2024.
- Asia Pacific is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR in the market during the forecast period.
- By waste type, the low level waste segment dominated the market in 2024.
- By waste type, the high level waste segment is projected to grow rapidly in the market in the future years.
- By reactor type, the pressurized water reactor segment held the largest share of the market in 2024.
- By reactor type, the boiling water reactors segment is projected to expand significantly in the market in the coming years.
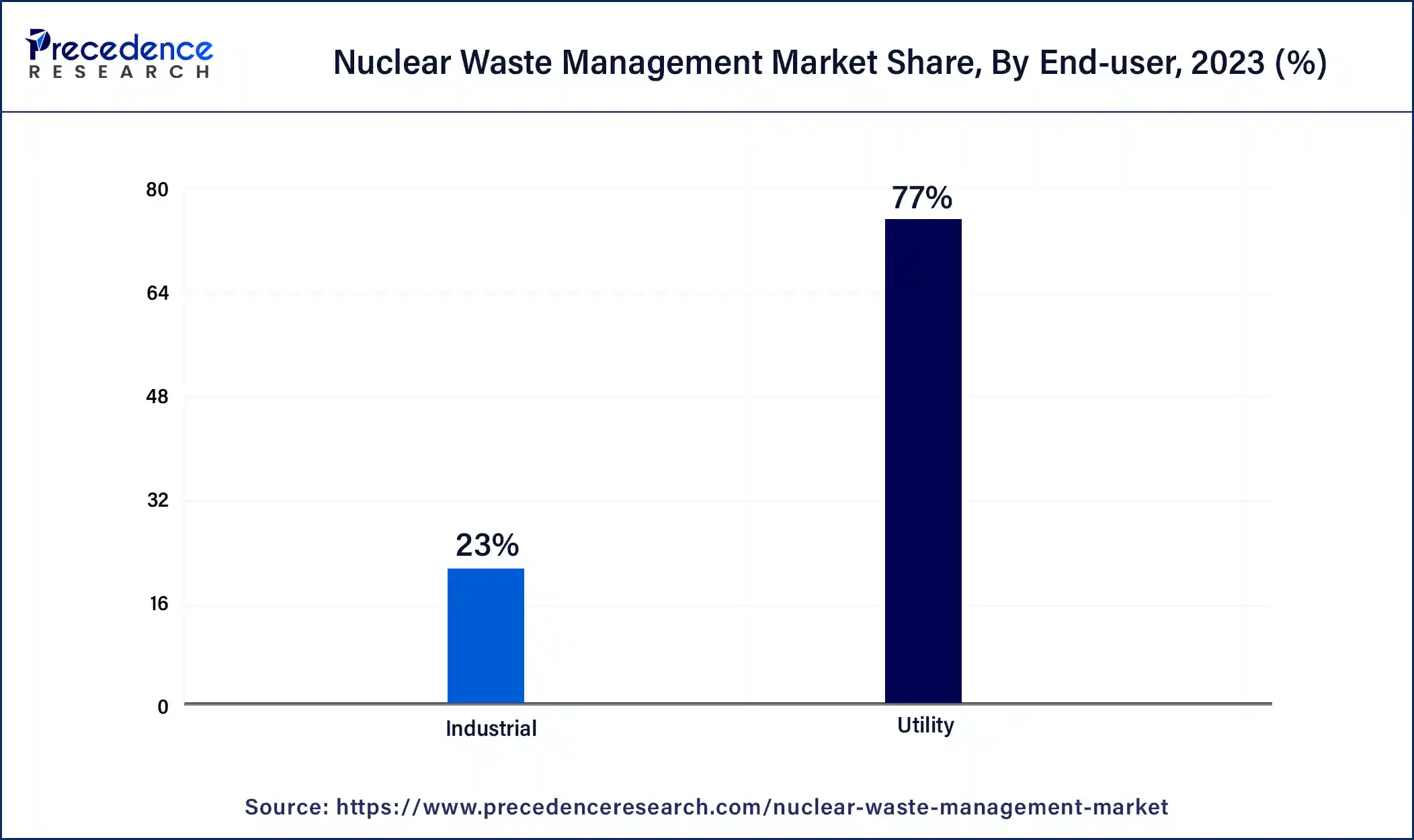
- By end-user, the utility segment accounted for the highest market share of 77% in 2024.
- By end-user, the industrial segment is projected to grow rapidly in the market in the coming years.
Market Overview
Nuclear energy is being produced and developed further, adding to the energy diversity and minimizing the emission of GHG. Safe control and disposal of nuclear wastes refer to containment storage and processing, which reduce the probability of radiation hazards to personnel, the populace, and the ecosystem. In this way, it preserves the environment and does not allow the penetration of soil, water, and air, which prevents contamination.
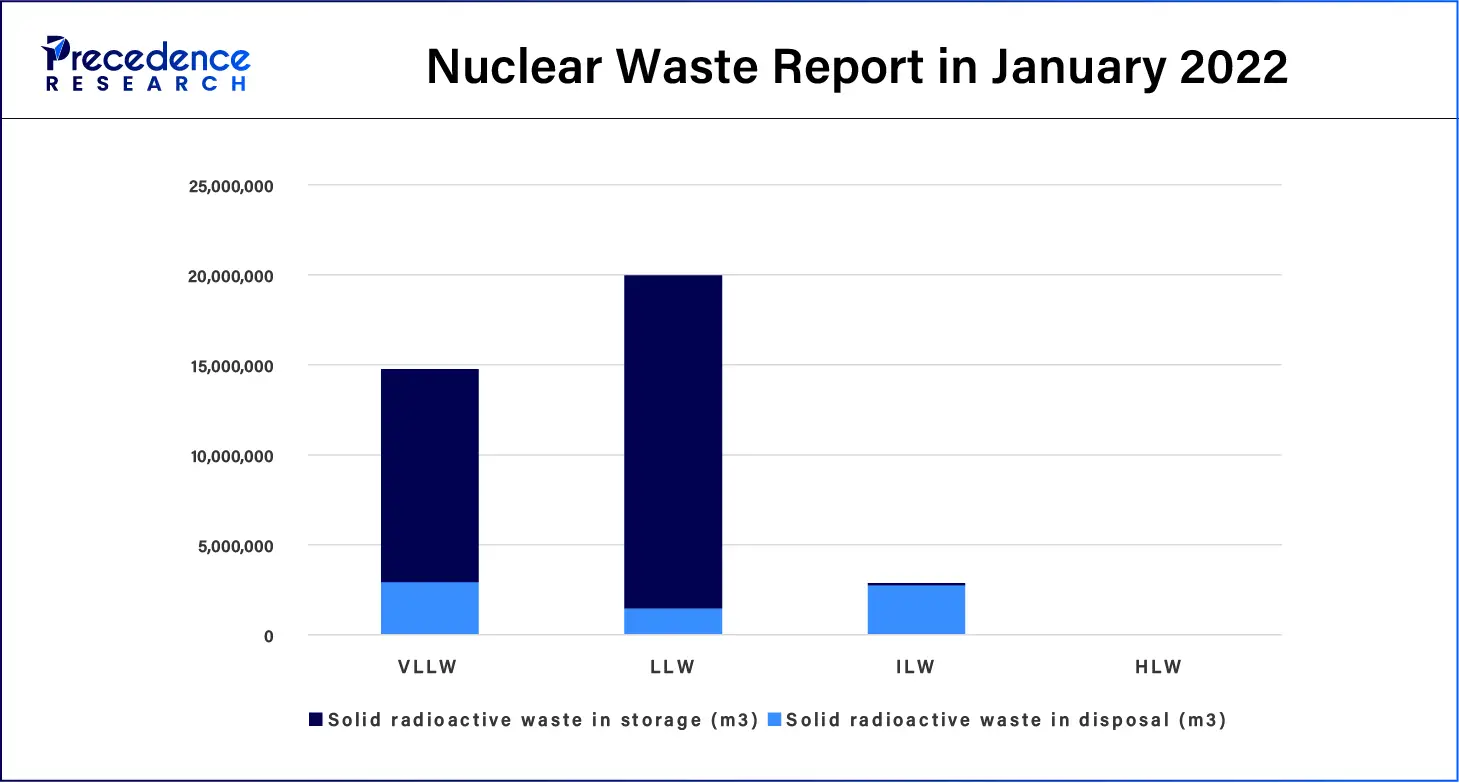
- According to Business Waste Management and Collection, since the genesis of nuclear energy production in 1954, around 400,000 tonnes of nuclear waste has been discharged globally. The contributing radioactivity of the total volume of nuclear waste is 3% for high-level waste, 7% for intermediate-level waste, and 90% low-level waste.
Methods for volume reduction of waste facilitate compact storage and also minimize the demand for more storage facilities, including compaction and vitrification. Moreover, other atomic facility wastes that are reprocessed to recover useful content, including spent fuel, help minimize the amount of waste generated. These factors will increase the growth of the nuclear waste management market in the coming years.
Impact of Artificial Intelligence on the Nuclear Waste Management Market
The implementation of sophisticated artificial intelligence algorithms makes it possible to monitor nuclear waste storage facilities and estimate possible failures in order to avoid them and reduce the level of unfavorable impact on the environment. In the nuclear waste management market, artificial intelligence makes it easier to arrive at appropriate decisions concerning the treatment and disposal of waste since it employs algorithms that examine data volumes to define precise approaches.
Additionally, artificial intelligence enhances the use of robotics and serves as an essential means of transporting radioactive substances to reduce human contact with radiation. These AI innovations enhance the management of waste, leading to increased efficiency and compliance with regulatory requirements and public safety standards.
Nuclear Waste Management Market Growth Factors
- The growing reliance on nuclear power as a clean and efficient energy source is expected to drive the demand for the nuclear waste management market.
- Governments worldwide are imposing stricter regulations on the handling, storage, and disposal of nuclear waste to protect public health and the environment.
- Ongoing research and development in nuclear waste management technologies, such as improved containment methods, recycling processes, and long-term storage solutions, are expected to drive the nuclear waste management market growth.
Market Scope
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 5.87 Billion |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 5.04 Billion |
| Market Size in 2026 | USD 5.13 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate from 2025 to 2034 | CAGR of 1.72% |
| Largest Market | North America |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | Waste Type, Reactor Type, End-user, and Regions |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Market Dynamics
Driver
Increasing global energy demand
Increasing global energy demand is expected to drive the nuclear waste management market as countries continue to rely on nuclear power to meet their energy needs. Nuclear is viewed as a base load energy that is clean, and necessary for GHG emissions reduction. The increased generation of nuclear energy comes with challenges of radioactive wastes, thus the need for effervescent waste management systems. Addressing the handling, treatment, and disposal of this waste, various governments and energy providers are investing in high-end technologies.
The trend of nuclear also opens a potential for cooperation in the frame of joint projects and knowledge exchange in countries that have not developed their nuclear sector yet, with increasing frequency of international partnerships. Furthermore, emergent countries are utilizing large amounts of radioactive fuels for nuclear energy creating demand for sustainable waste disposal, thus propelling the nuclear waste management market.
- According to a report from the United States Nuclear Regulatory Commission, approximately 2.32 million cubic feet and 154 thousand curies of low-level radioactive waste were disposed of in 2022.
Restraint
High costs of nuclear waste management
The high cost of nuclear waste management is expected to hinder the market. The process is rather complicated and costly, involving techniques for the safe handling, transportation, and disposal of radioactive substances. Sophisticated techniques, rules, and requirements that focus on safety and the challenge of repository push up expenses and financial load of governments and nuclear stations. Such high costs prevent investment in nuclear energy projects and the development of handling nuclear waste. Furthermore, the low profitability of nuclear waste management, especially where the economy of the concerned country is at a lower level, poses another hindrance to the nuclear waste management market growth in the coming years.
Opportunity
Growing investment in advanced technologies
A rise in spending on innovative technologies, such as vitrification and deep geological repositories, is expected to create immense opportunities for the players competing in the nuclear waste management market. These technologies are intended to work under close environmental containment to safely store high-level radioactive waste for longer periods. Many IT firms are in the process of designing solutions for making these processes more effective, and the companies that find themselves in the focus of such technologies can record high interest from the governments and private investors searching for effective solutions for managing waste in a proper manner.
The trend of durability in safety and the reduction of environmental impact is pushing researchers further in the search for new substances for storage and improved containment. Furthermore, modern technologies, such as robotics and automation, are also being applied to these technologies, making it easier to handle radioactive wastes more safely and accurately. Such involvements with research institutes are witnessing the advancement of these innovations, with the needed compliances and cost considerations addressed by key industry players. All these factors contribute to boosting the nuclear waste management market in the coming years.
Waste Type Insights
The low level waste segment dominated the nuclear waste management market in 2024 due to the large amount of waste produced by nuclear power plants, facilities involved in the use of radioisotopes in the medical field, and several industrial applications. In comparison with high-level and intermediate-level waste, LLW is comparatively easier to deal with and does not call for equally high levels of containment.
Due to the high generation of LLW from various sources, bulk facilities for handling and disposal have been established for volume reduction techniques. There has been a continuous increase in the number of nuclear power plants and medical centers, especially in the developed nations, which are creating constant production of LLW, hence making it the largest segment in the nuclear waste management industry. Moreover, the growing number of contaminated protective wear, tools, filters, and any other articles that may have been used in the nuclear process are expected to boost the market.
- The International Atomic Energy Agency reports that as of January 2022, more than 80% of solid radioactive waste is in disposal. In the same year, the U.S. disposed of approximately 2.32 million cubic feet and 154 thousand curies of low-level radioactive waste.
The high level waste segment is projected to grow rapidly in the nuclear waste management market in the future years. HLW is made up of highly radioactive by-products resulting from the reprocessing of used nuclear fuel and from the use of nuclear reactors. The inherent complexities in dealing with and storing HLW by the development of higher containment systems and safe geological facilities are anticipated to fuel a major residence in this sub-segment. The number of facilities with decommissioned nuclear reactors, especially in such regions as Europe and North America, is expected to fuel the demand for nuclear waste management solutions.
The low-level waste (LLW) segment held the largest share of 43.70% in the 2024 global nuclear waste management market. The LLW holds a fundamental position in the market by ending up with the vast volume of generated waste. This waste type contains a lower radiological risk than any other waste type. The key trend in the LLW management aims to alleviate the volume and safely embed it in the nuclear waste management spectrum. Alongside the establishment of advanced treatment technologies, the segment, with its dedication to evolving, doubles the expectation in this market.
The high-level waste (HLW) segment is expected to grow at a CAGR of 7.80% during the forecast period. The HLW segment is a vibrant and harmful form of nuclear waste, holding a vast management challenge because of its extreme radiation and heat that needs isolation for a longer duration. The main global role of HLW management is to collect the waste via a multi-stage process. Whereas the development aims for long-standing solutions with strong, deep geological disposal.
Reactor Type Insights
The pressurized water reactor segment held the largest share of the nuclear waste management market in 2024. PWRs remain the most popular reactors across the world, as they contribute to more than half of the global nuclear power production. This is due to their durability, reliability, safety measures, high temperatures, pressure performance, and efficiency. There is currently a near-disposal issue of nuclear waste requiring new management and efficient disposal methods. Furthermore, with high levels of spent fuel generated by these reactors, there is a need for special waste containment facilities. Global development of nuclear power infrastructure, especially in the developed world, boosts the demand for PWR reactor nuclear waste management solutions.
The boiling water reactors segment is projected to expand significantly in the nuclear waste management market in the coming years due to their lower complexities of design and operating costs, which make them ideal for new nuclear power generation. The use and expansion of BWRs, especially in areas that are aimed at developing the security of the supply of energy and at the minimum emission of carbon, leads to the creation of a voluminous quantum of radioactive waste, which needs very careful handling. The existing BWRs, which include old models of reactors, are also expected to feature in waste management since, as they undergo decommissioning, they create other waste products.
End-user Insights
The utility segment dominated the nuclear waste management market in 2024 due to the high proliferation of nuclear power plants for generating electricity. Utilities are the largest generators of nuclear waste, with high-level waste arising from spent nuclear fuel because utilities supply energy on a constant basis. The world's continuing need for electricity and the rising leaning toward nuclear energy as a clean and sure source of power.
A large number of countries are using nuclear energy in the consumption mix in order to supply environmental objectives, therefore bringing relevant investments in the management of waste utilities. Furthermore, the utility has been the largest segment of the market, most likely due to the stringent laws regarding the management and treatment of waste in its operation; hence, utilities are forced to adhere to more sophisticated waste management standards to avoid the risk of being policy or lawfully sued on issues relating to waste handling and disposal.
The industrial segment is projected to grow rapidly in the nuclear waste management market in the coming years, owing to the increased demand for nuclear technology in various industries. Specific sectors, including healthcare, research sectors, and manufacturing sectors, use nuclear technology for different purposes, such as diagnostic, food irradiation, testing of material, etc., which produces different types of wastes that are radioactive in nature. This has instigated the need for the management of industrial wastes, including nuclear waste. As the services expand, there will be more service opportunities for waste management services.
The utility companies (power generators) segment held the largest share of 49.60% in the 2024 global nuclear waste management market. The utility companies that run nuclear power plants stand in a crucial and transforming position in the market. The utility's duty of segregating and managing all radioactive waste is the key existence of the segment. The research, innovation, financial responsibility, and development led this segment to exponential growth to further flourish in the market.
The government and regulatory bodies segment is expected to grow at a CAGR of 7.90% during the forecast period. The segment is fundamental to the responsible and secure management of nuclear waste. Their responsibility and designation transitioned via international cooperation and national frameworks. These objective develops the technical, financial and legal structures which are essential to safeguard the environment and public health from adverse effects featuring radioactive waste.
Waste disposal method Insights
The storage (dry and wet) segment held the largest share of 38.90% in the 2024 global nuclear waste management market. The segregated term for the storage has improved waste management globally. It's a crucial and revolutionary change with an effective role in the global management of nuclear waste. The storage methods have evolved prominently, and the future innovations are aimed at mitigating the long-standing stress of HLW and advancing containment.
The deep geological disposal segment is expected to grow at a CAGR of 9.20% during the forecast period. The segment has been approved at the international level with the tag of an excellent solution beneficial for long-term management of high-level nuclear waste. The main role of the segment is to promote long-term containment with the help of a multi-barrier system of natural and designed barriers. The development is its latest ongoing research into barrier materials, site selection and more.
Waste phase/form Insights
The solid waste segment held the largest share of 69.50% in the 2024 global nuclear waste management market. The solid waste is crucial to nuclear waste management due to its immobilising and processing management of the radioactive materials to turn them into a balanced form for long-term secure disposal and storage. The major development involves solidification processes such as cementation and vitrification to alleviate mobility and volume.
The liquid waste segment is expected to grow at a CAGR of 7.10% during the forecast period. The segment is gaining traction with the rising liquid-based products, mainly affecting the environment seasonally. The liquid nuclear waste management includes pre-treatment to mitigate volume and focus on radioactivity. The major developments contain advanced techniques such as vitrification and reverse osmosis for recovering valuable isotopes and a high level of waste for the population and localities.
Service type Insights
The disposal services segment held the largest share of 33.40% in the 2024 global nuclear waste management market. The disposal service has come into action with the increased waste in different forms, affecting the environment largely and disturbing the sustainable life cycle of the ecosystem to the core. The disposal service is crucial for maintaining stability and promoting waste management at the industrial as well as the local level. The basic normal waste is rapidly increasing with the growing population and industrial waste due to growing business. The segment holds an important position in both circumstances.
The monitoring and surveillance segment is expected to grow at a CAGR of 8.90% during the forecast period. The segment is the latest trend in global nuclear waste management. The segment raises regular awareness and a sense of responsiveness in waste management. The segment is crucial to the visible and safe management of nuclear waste in its whole spectrum. Its role and responsibilities have been upgraded with a positive impact on a unified socio-technical process, fuelled by technological advancement and international regulations.
Regional Insights
U.S. Nuclear Waste Management Market Size and Growth 2025 to 2034
The U.S. nuclear waste management market size is exhibited at USD 1.23 billion in 2025 and is projected to be worth around USD 1.47 billion by 2034, poised to grow at a CAGR of 1.97% from 2025 to 2034.
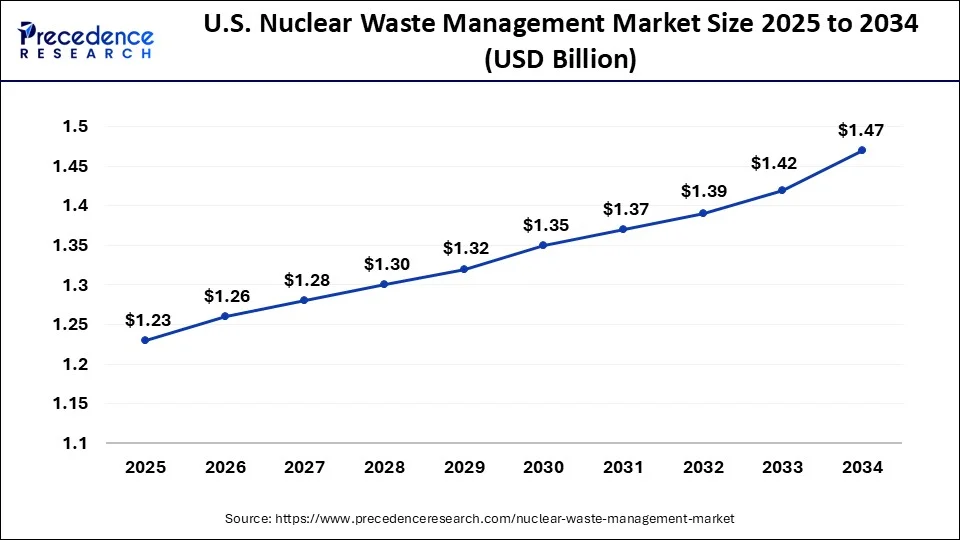
North America dominated the nuclear waste management market in 2024 due to the developed nuclear energy system and the adoption of rigid regulatory policies. The United States boasts of having a large number of active nuclear reactors, creating large amounts of radioactive waste. The relatively mature infrastructure for waste storage and disposal has most probably continued to drive the region's market.
Moreover, the growing deployment of decommissioning for obsolete nuclear power stations in the respective region might have contributed to the need for proper waste management solutions. The increasing trend of utilizing environmentally friendly technologies and methods of waste disposal might have also strengthened the region in the market, along with the presence of the nuclear waste management market players in North America.
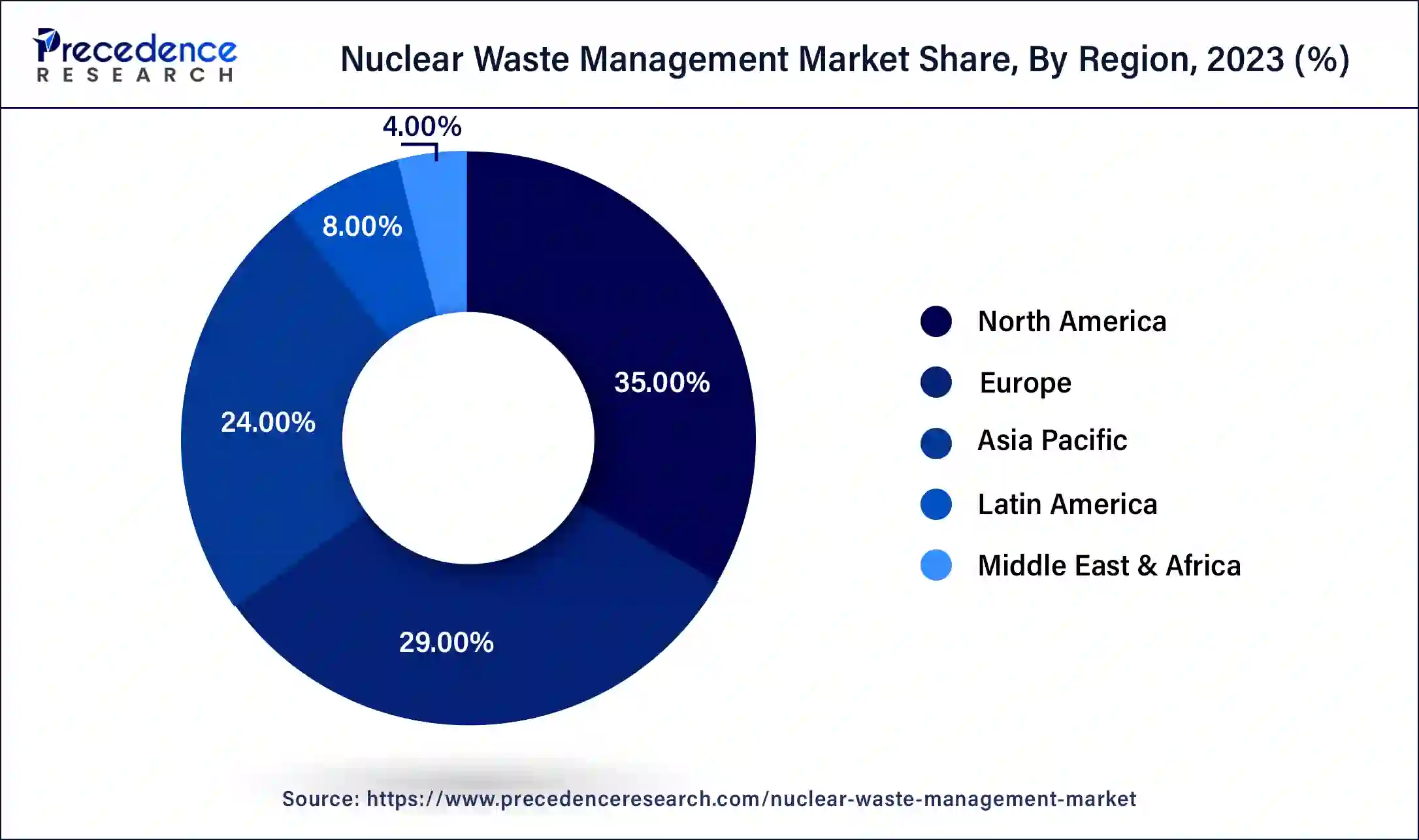
Asia Pacific is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR in the nuclear waste management market during the forecast period, owing to the fast expansion of nuclear energy in nations such as China or India. These countries have, in the very recent past, embraced nuclear power as a way of meeting their energy market needs while at the same time minimizing emissions. This has led to the expansion of the facilities generating nuclear energy, thus increasing the generation of radioactive waste for which effective management systems are largely required.
The growing interest in developing nuclear power, the capability of the region's states, and the governmental efforts to address the waste generating and disposal issues are expected to inhibit the development of these management technologies. Additionally, cooperation with other countries and recent innovations in nuclear waste treatment and storage predict Asia Pacific is a leader in nuclear waste management, further boosting the nuclear waste management market in this region.
Nuclear Waste Management Market Companies
- Augean Plc
- Perma-Fix Environmental Services, Inc.
- Svensk Kärnbränslehantering AB
- Ansaldo Energia
- Republic Services, Inc.
- Veolia Environmental Services
- Bechtel Corporation
- EnergySolutions
- BHI Energy
- Waste Control Specialists, LLC
Recent Developments
- In February 2024, Orano SA, a multinational nuclear fuel cycle company, announced a partnership with SHINE Technologies to develop a U.S. pilot plant with commercial-scale technology for recycling used nuclear fuel from light water reactors. The recovered nuclear material can be made into new fuel for advanced and existing reactor designs, and certain critical isotopes can be used for medical and industrial purposes.
- In July 2024, Oklo Inc, a fast fission clean power technology and nuclear fuel recycling company, announced the successful completion of the first end-to-end demonstration of the key stages of its advanced fuel recycling process, in collaboration with Argonne National Laboratory and Idaho National Laboratory.
- In November 2022, Argonne was awarded $6 million to develop technologies for recycling nuclear fuel. The funding was awarded through the Converting UNF Radioisotopes Into Energy (CURIE) program, which focuses on recycling used nuclear fuel (UNF).
Segments Covered in the Report
By Waste Type
- Low-Level Waste (LLW)
- Intermediate-Level Waste (ILW)
- High-Level Waste (HLW)
- Transuranic Waste (TRU)
By Waste Disposal Method
- Near-Surface Disposal
- Deep Geological Disposal
- Storage (Dry and Wet)
- Vitrification
- Transmutation
- Reprocessing & Recycling
By Waste Phase/Form
- Solid Waste
- Liquid Waste
- Gaseous Waste
By Service Type
- Transportation & Logistics
- Treatment & Conditioning
- Disposal Services
- Consulting & Compliance
- Monitoring & Surveillance
By End User
- Utility Companies (Power Generators)
- Government & Regulatory Bodies
- Research Institutes
- Military & Defence Organisations
- Healthcare Institutions
By Geography
- North America
- Asia Pacific
- Europe
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Ask For Sample
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
 Get a Sample
Get a Sample
 Table Of Content
Table Of Content
 sales@precedenceresearch.com
sales@precedenceresearch.com
 +1 804-441-9344
+1 804-441-9344
 Schedule a Meeting
Schedule a Meeting