Satellite Market Size and Forecast 2025 to 2034
The global satellite market size was estimated at USD 334.83 billion in 2024 and is predicted to increase from USD 362.28 billion in 2025 to approximately USD 729.53 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 8.10% from 2025 to 2034.
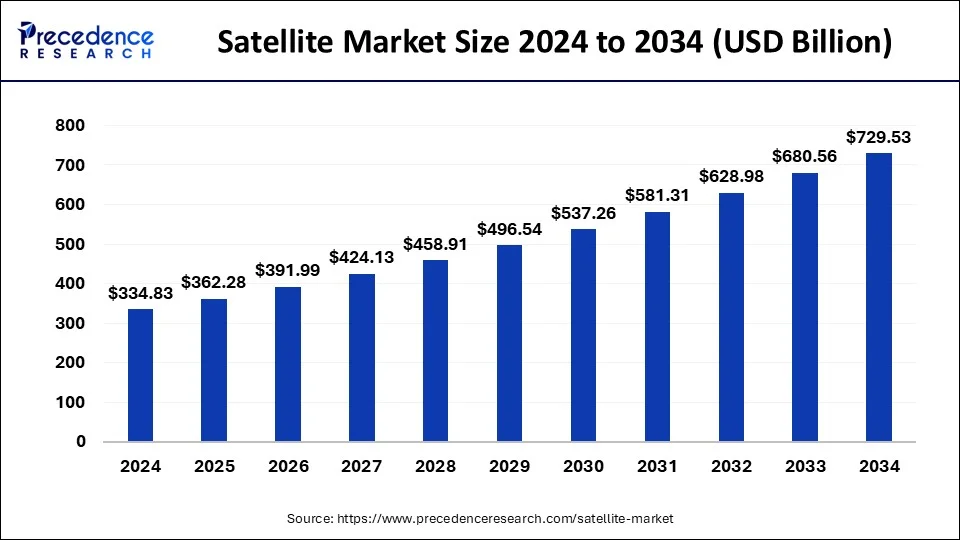
Satellite Market Key Takeaways
- North America dominated the global market with the largest market share of 37% in 2024.
- Asia-Pacific is expected to expand at the fastest CAGR from 2025 to 2034.
- By Type, the small satellite segment is projected to grow at the quickest CAGR between 2025 and 2034.
- By Application, the commercial communications segment held the highest market share in 2024.
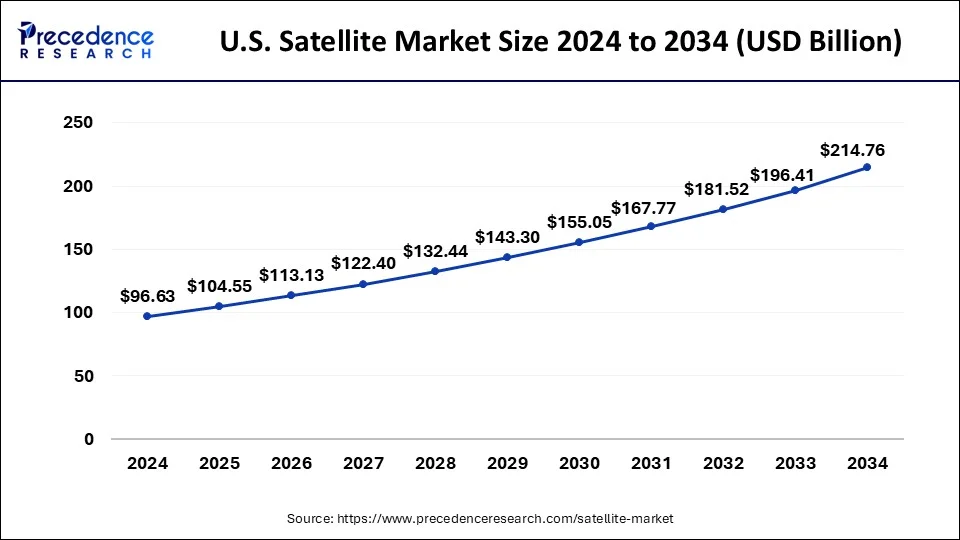
U.S. Satellite Market Size and Growth 2025 to 2034
The global satellite market size was valued at USD 96.63 billion in 2024 and is predicted to be worth around USD 214.76 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 8.31% from 2025 to 2034.
North America has held the largest revenue share in2024. This is owing to the increased spending from the United States government on the space sector. Furthermore, the presence of key players such as Northrop Grumman, Iridium Communications Inc., ViaSat Inc., Lockheed Martin Corporation, and Boeing, among others across the region is also likely to support the regional growth of the market. Additionally, NASA's growing research and development efforts and the military's rising investment on surveillance missions are also expected to contribute to the growth of the market across the region. The use of SKYWAN technology and a tri-band antenna by NASA allows for real-time communication, which is the ideal transmission for any application.
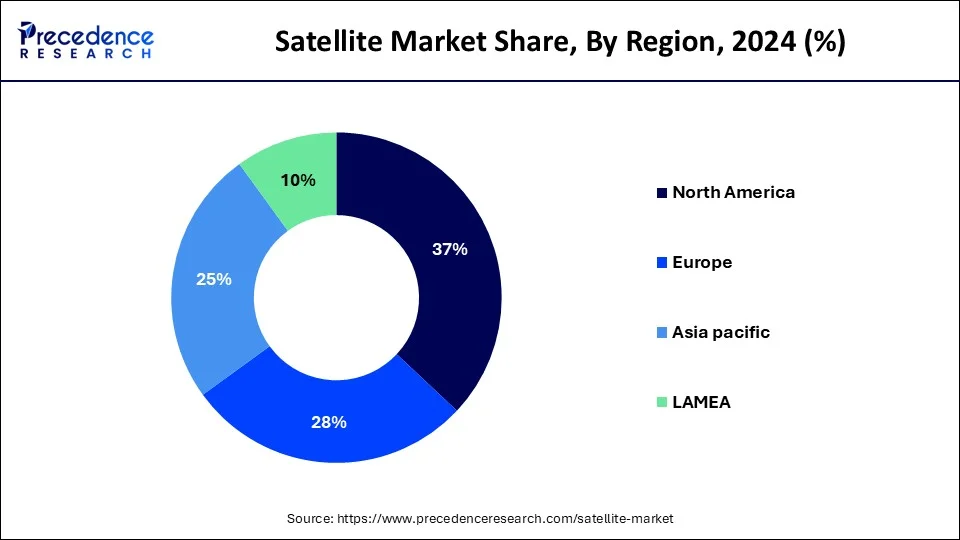
Asia-Pacific is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period. China held the largest share in the APAC region. This is attributable to the increasing demand for satellites from economies such as India, China, and Japan in the region. China launched a commercial communications satellite in January 2023 as part of its third space mission of the year.
The Xichang Satellite Launch Centre witnessed the launch of a Long March 2C rocket. Within an hour, the launch's success was declared by the China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC), which also developed the rocket and satellite. APT Satellite of Hong Kong placed the order for the APStar 6E satellite, which will increase the number of communications satellites in the company's fleet that are used to serve the Asia-Pacific area. Also, a medium-sized observation satellite of the next generation was launched by South Korea in March 2021 with the aim of producing precise observation footage of the Earth. These developments are likely to support the regional growth of the satellite market in the years to come.
Market Overview
This is a rapidly growing industry that offers a range of services, including communication, navigation, Earth observation, and space exploration. There are varieties of satellite types, including geostationary, low Earth orbit, medium Earth orbit, and high Earth orbit, with applications ranging from telecommunications to scientific research. The demand for satellite-based services is growing worldwide, driven by rising internet connectivity, digital transformation, and emerging technologies like IoT, autonomous vehicles, and AI.
Governments and military organizations worldwide also rely on satellite-based technologies for investigation, surveillance, communication, and other purposes. Commercial companies are investing heavily in LEO constellations to provide global internet connectivity, which is likely to support the growth of the satellite market. Further, the advancements in satellite technology, such as smaller and lighter satellite components, electric propulsion, and reusable rockets, are making satellites more efficient and cost-effective. Also, emerging markets such as Asia-Pacific, Africa, and Latin America offer significant potential for the growth of the satellite market in the years to come.
Satellite Market Growth Factors
- Increasing Demand for Connectivity- Increased reliance on high-speed internet globally -especially in remote locations. Demand for satellite broadband connectivity is increasing as more companies are considering investment in lower earth orbiting (LEO) satellite constellations to link connectivity more globally despite lower latency / more performance.
- Technological Advancements - Technological advancements that have enabled small, lighter and more cost-efficient satellites have allowed for more frequent launches. More launches mean more satellites. The miniaturization allows for even miniaturized satellites, sometimes CubeSats, to support young missions, from earth observation, to IoT.
- Commercialization of Space- The increase in private satellite, launch services, and platforms will increase commercialization of satellites, which will continue to increase access to space, built in innovation, lower term of business, and increase commercial satellite applications.
- Increase in Remote Sensing Applications- The increased demand for more Earth observation data, remote sensing, for purposes such as agricultural monitoring, disaster recovery, environmental monitoring will all continue to grow and drive demand for satellites with specialized imaging and sensing capability to influence decisions in public and private use.
Market Scope
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 |
USD 334.83 Billion |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 362.28 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 729.53 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate from 2025 to 2034 | CAGR of 8.1% |
| Largest Market | North America |
| Fastest Growing Market | Asia Pacific |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 To 2034 |
| Segments Covered | By Type, By Orbit, By Application, andBy End-User |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Market Dynamics
Driver
Increasing demand for satellite-based IoT networks for emerging applications
The internet of things (IoT) has established itself as a common technology for both old and new applications. In the new services and applications, it can offer both accuracy and sustainability. IoT provides a number of benefits and can offer various levels of coverage in various environments and circumstances. Numerous applications place a high value on communication reliability, low power consumption, and wide coverage.
IoT and satellite network integration can make it very appealing for these applications. For instance, agriculture is a significant industry where farmers always strive to boost yields. IoTs can be utilized in precision agriculture. The IoT networks can be used to gather the data required for agriculture. The water level, temperature, and various other characteristics may then be monitored using this information by the SIoT sensors via the satellite backhaul.
Also, the emergency and vital services that depend on the networks' continuous availability are mission-critical applications. Disaster management during emergencies, military data collection and transmission, and real-time control of crucial systems are a few examples of mission-critical applications. Even a brief network outage is unaffordable for these systems. The wireless infrastructures are immediately impacted by natural catastrophes like landslides, storms, cyclones, and floods. The networks frequently go offline for days, and perhaps even for months. The satellites are resistant to these issues, though. Due to this, satellite-based Internet of Things is favored when the infrastructure is susceptible to natural disasters. Applications for SIoT are numerous, and new ones are constantly being developed. Numerous companies that offer services in a variety of ways using SIoT have been established in response to these demands for SIoT.
Restraints
High cost of satellite
Costs associated with satellites are high. Design, construction, launch, and maintenance of them are quite expensive. The tools and materials used to create satellites are some of the elements that affect their price. In contrast to bandwidth costs per MHz, which start at a minimum of $3,500 per month, transponders alone have annual maintenance costs of hundreds of thousands of dollars. Over $1.5 million a year will be spent to operate a satellite at a 36MHz bandwidth. In order for the satellite to fulfill its intended purpose, additional devices and pieces of technology must be integrated into it. Computers, software, and cameras are some examples of them.
The price of placing a satellite into orbit is another element that contributes to the cost of satellites. According to estimates, the price of launching a single satellite might range from $50 million to $400 million. Despite the fact that a single space shuttle mission is capable of transporting numerous satellites and putting them into orbit, the cost of launching a mission can easily reach around $500 million.
The cost of maintaining satellites must also be taken into account. One must be placed into orbit, and once there, it must be watched over from a base station, requiring labor. Additionally, satellites are not immune to harm or outages. Furthermore, if a launch doesn't go well, a multi-million dollar project could either fail or sustain losses that will cost more money to fix. Consequently, this is likely to restrain the growth of the market during the forecast period.
Opportunities
Rising funding and investments in the satellite market
The increasing funding and investments are likely to create lucrative opportunities for the growth of the satellite market in the years to come. For instance, in December 2022, Reflex Aerospace revealed that their initial fundraising round brought in US $7.47 million (€7 million). The business is a member of the joint venture UNIO, which aspires to create a European satellite constellation for broadband internet access, along with Isar Aerospace, Mynaric, and SES. By the end of the first quarter of 2023, the second stage is expected to raise investments to US $12.8 million (€12 million). Alpine Space Ventures, the VC High-Tech Gründerfonds (HTGF), and an additional undisclosed investor based in Bavaria were among the investors. Further, in November 2022, Apple revealed that it will spend $450 million on a satellite network and ground stations to enable Emergency SOS as part of its Advanced Manufacturing Fund. Globalstar, the satellite company with which Apple already has an agreement to offer Emergency SOS when it launches will receive the majority of the investment. Consequently, these investments are likely to support the growth of the market in the near future.
Type Insights
The small satellite segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period. Numerous small satellites are being developed for use in a variety of fields, including military, commercial, and civil applications. The space industry's operating dynamics make it resilient to economic shocks while also spurring demand from a variety of sectors, which is anticipated to drive the market throughout the forecast period. The expansion of military satellite-based communications and ISR, along with an increase in global defense spending, is anticipated to have a beneficial effect on the segment throughout the projected period.
Application Insights
Based on the application, the commercial communications segment held the largest market share in 2024.This is a result of rising interest in satellite television, commercial satellite imagery, and satellite navigation. Further, the increase in various launches is also likely to support the segmental growth of the market. For instance, India's Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle PSLV-C51 launched Amazonia-1 and 18 co-passenger satellites in February 2021. The National Institute for Space Research's (INPE) Amazonia-1 is an earth observation satellite. Users will be able to analyze various agricultural practices throughout Brazil's territory using remote sensing data, and the Amazon region's deforestation will be tracked.
Key Market Companies
- Airbus Defence and Space
- Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp.
- Boeing Satellite Systems International
- Eutelsat Communications SA
- General Dynamics Mission Systems
- Harris Corporation
- Intelsat SA
- Iridium Communications Inc.
- Maxar Technologies Inc.
- Raytheon Technologies Corporation
- SES S.A.
- Space Exploration Technologies Corp. (SpaceX)
- Telesat Canada
- Thales Alenia Space
- ViaSat Inc.
Recent Developments
- In May 2025, Space42 , the UAE-based AI-powered SpaceTech company, advances direct-to-device satellite messaging through collaboration with Gatehouse Satcom a Danish-based software company specializing in mission-critical satellite communications, to advance direct-to-device (D2D) connectivity.
- In May 2025, Airtel Africa and spacex sign agreement to expand Starlink's satellite-based internet services to millions of users across Africa. This agreement marks one of the most significant telco-satellite collaborations in Africa to date and comes as demand for last-mile connectivity solutions continues to grow.
- In November 2024, Billionaire ELon Musk's SpaceX on successfully launched the Indian Space Research Organisation's (Isro) communication satellite, GSAT-N2, from the Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida.
- In November 2024, Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited (BSNL), the state-owned telecom service provider, has officially launched India's first Direct-to-Device satellite connectivity service, marking a significant milestone in the country's communications landscape.
- In November 2024, Impulso.Space USA Corp. is excited to announce the signing of a multi-mission launch services contract with D-Orbit, reinforcing a longstanding collaboration that continues to elevate the scope of end-to-end space solutions.
- In October 2022,36 satellites of the UK-based OneWeb satellite Communications Company were successfully launched by the Indian Space Research Organization's biggest rocket, Launch Vehicle Mark-3 (LVM-3), from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota.
- In February 2023,Inmarsat confirmed the achievement of the launch of its latest I-6 F2 spacecraft onboard a reusable SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from the Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. The satellite will be spending several months utilizing its onboard electric propulsion engine to journey to its geostationary orbit, 36,000 kilometers above the Equator. Following rigorous in-orbit technical testing, it is expected to connect its first customers in 2024.
- In September 2022,Hughes Communications India, a provider of satellite internet, announced the official launch of India's 1st high-throughput satellite (HTS) broadband service which is powered by the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO), at the same time that Elon Musk's SpaceX decided not to proceed with its low-cost Starlink project in the nation. In order to connect business and government networks, the service seeks to provide high-speed broadband over the entire nation, particularly in the unsociable regions which are not in the range of terrestrial networks.
Segments Covered in the Report
By Type
- Large Satellite
- Medium Satellite
- Small Satellite
By Orbit
- Low Earth orbit (LEO)
- Medium Earth Orbit (MEO)
- Geosynchronous orbit (GEO)
- Others
By Application
- Commercial Communications
- Space Observation
- Navigation
- Scientific Research
- Military Surveillance
- Others
By End-User
- Government & Civil
- Military
- Commercial
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa
 Get a Sample
Get a Sample
 Table Of Content
Table Of Content