What is the Bio-LNG Market Size?
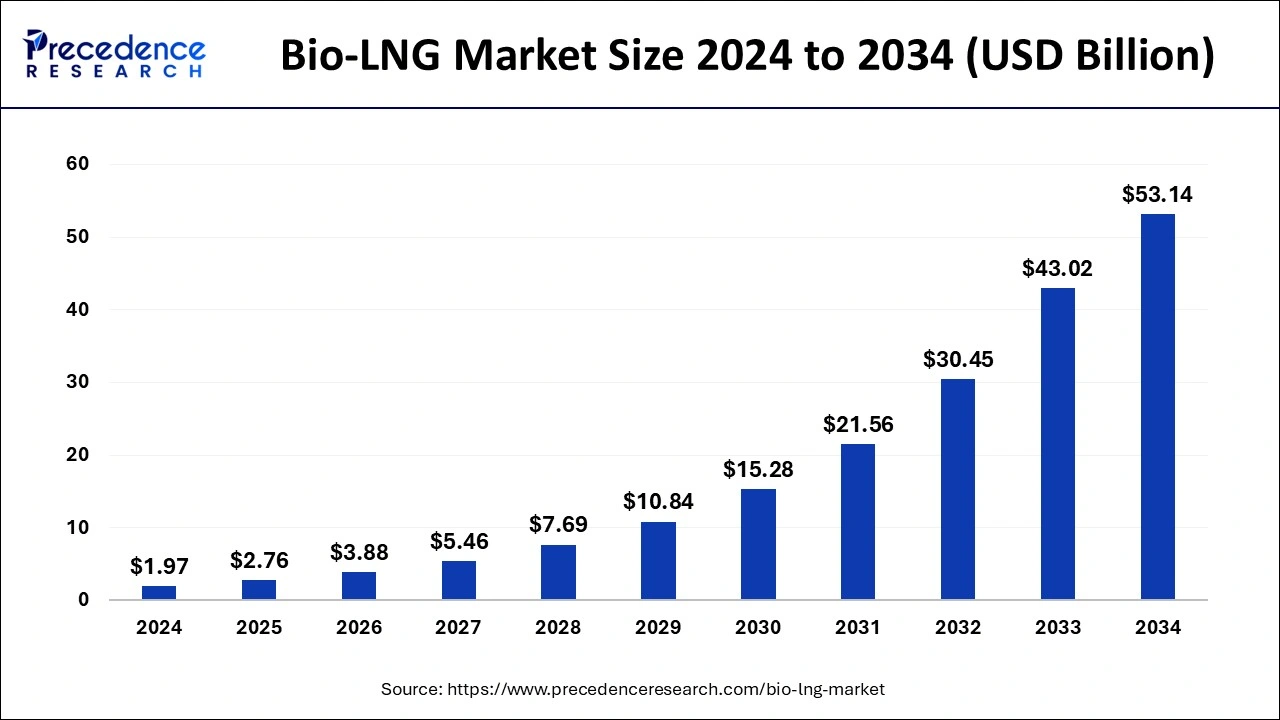
The global bio-LNG market size is calculated at USD 2.76 billion in 2025 and is predicted to increase from USD 3.88 billion in 2026 to approximately USD 64.89 billion by 2035, expanding at a CAGR of 37.13% from 2026 to 2035.
Bio-LNG MarketKey Takeaways
- The bio-LNG market is valued at USD 2.76billion in 2025.
- It is projected to reach USD 64.89billion by 2035.
- The bio-LNG market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 37.13% from 2026 to 2035.
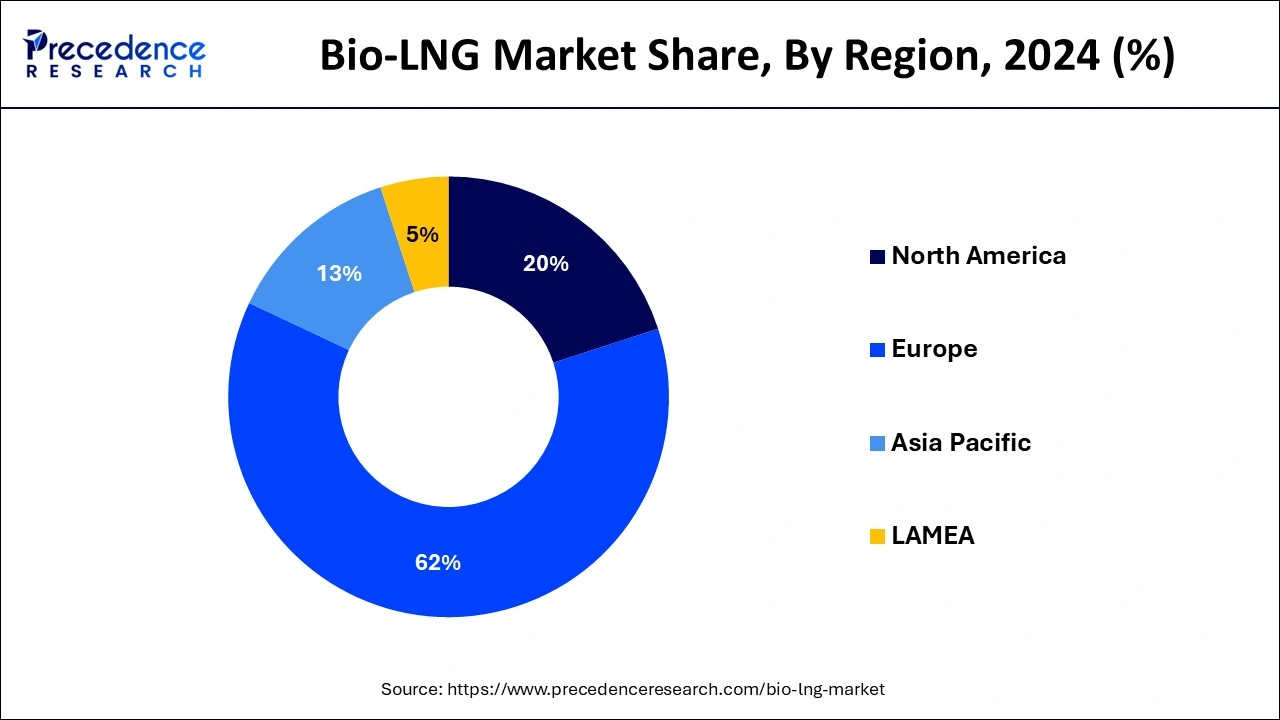
- Europe held the largest market share of 62% in 2025.
- By source, the organic household waste segment held the largest market share of 41% in 2025.
- By source, the municipal waste segment is expected to expand at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period of 2026-2035.
- By application, the transportation segment held the largest share of 56% in 2025.
Market Overview
The purchasing and selling of liquefied biomethane (LBM), referred to as bio-LNG, is called the bio-LNG market. The growing need for clean, sustainable energy sources drives this relatively new and quickly expanding business. Buses, heavy-duty trucks, and other vehicles can run on bio-LNG fuel. In comparison with traditional diesel, it provides a cleaner and lower-emission option. It can be used as a marine fuel, lessening the effect of shipping on the environment and assisting the maritime sector in adhering to tighter emission standards.
In industrial activities like manufacturing, food processing, and chemical manufacture that need high-temperature heat, it can replace conventional natural gas. Compared to traditional energy sources, bio-LNG is a dependable and greener energy source that may be used in power plants to create electricity.
- In July 2023, at the BioEnergie Park Gustrow, announced a successful conversion and assembly work that is observed to pave the way for opening Germany's greatest comprehensive bio-liquefied natural gas (Bio-LNG) facility. The task required attaching a 300,000-liter liquefied carbon dioxide (LCO2) tank to the plant by project operator EnviTec Biogas. The site's raw biogas will be refined to natural gas quality and then fed into the CO2-enriched exhaust gas plant, creating 15,000 metric tons of LCO2 annually.
Bio-LNG Market Growth Factors
- Many renewable energy regulations and targets have been implemented due to the increased focus on lowering greenhouse gas emissions worldwide. A favourable environment for bio-LNG is being created by governments worldwide that are offering incentives for biofuels and renewable energy sources.
- The need for greener fuels is rising in the transportation sector. For heavy-duty vehicles like trucks and buses, bio-LNG is a practical alternative that offers a more environmentally friendly long-distance transportation choice. Reusing or repurposing resources while minimizing waste is the idea of the circular economy, which is gaining traction. This framework is met by bio-LNG, which creates a clean and renewable energy source from organic waste streams.
- The market for bio-LNG is benefited by the rise in demand for liquefied natural gas, or LNG. If LNG remains a significant part of the world's energy mix, there will probably be a greater need for greener, sustainable LNG substitutes like bio-LNG.
- The market is expanding due to increased expenditures in bioenergy infrastructure, such as facilities for producing and distributing bio-LNG. Building the infrastructure needed to support the bio-LNG supply chain requires public and commercial sector investments.
Major Key Trends in Bio-LNG Market
- Increasing Use in Transportation Sector: Bio-LNG is receiving attention as a cleaner fuel option for heavy-duty trucks and maritime vessels, bolstered by appropriate infrastructure and a growing demand for carbon-neutral logistics solutions.
- Innovations in Production Technology:Advancements in gas upgrading and liquefaction techniques are enhancing the efficiency and scalability of Bio-LNG production, allowing for the utilization of various waste feedstocks and lowering operational expenses.
- Collaborations and Infrastructure Development: Partnerships between energy firms, waste management companies, and governmental bodies are hastening the development of Bio-LNG facilities and refueling networks to improve market access and ensure long-term sustainability.
Market Scope
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Growth Rate from 2026 to 2035 | CAGR of 37.13% |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 2.76 Billion |
| Market Size in 2026 | USD 3.88 Billion |
| Market Size by 2035 | USD 64.89 Billion |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 to 2035 |
| Segments Covered | Source and Application |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Market Dynamics
Drivers
Growing demand for clean energy
Sustainable and ecologically friendly energy sources are becoming increasingly important as the world turns its attention to cutting greenhouse gas emissions and combating climate change. Bio-LNG is a feasible substitute for conventional fossil fuels since it is made from organic materials like organic waste, leftovers from agriculture, and other biomass sources.
By leveraging organic waste streams, bio-LNG contributes to the circular economy and has several advantages over conventional LNG. Often, organic materials are converted into biogas throughout its production process, which is then cleaned and liquefied to create bio-LNG. Developing a more sustainable energy environment and lowering dependency on fossil fuels align with this low-carbon, renewable fuel.
Increasing awareness of the environmental benefits of bio-LNG
Growing awareness has led to a greater emphasis on the environmental advantages of bio-LNG, which has helped to fuel its ascent in popularity as a substitute fuel. This tendency is consistent with a more significant worldwide movement toward ecologically friendly and sustainable energy sources.
Restraints
Lack of infrastructure and standardization
The need for more essential infrastructure, including distribution networks, storage facilities, and production units, hampers bio-LNG's widespread use. Furthermore, the business is unpredictable due to the need for established procedures and regulations, making it difficult for stakeholders to invest confidently in bio-LNG projects. The market for bio-LNG is growing slowly due to a need for more infrastructure and standards, which limits its potential to become a widely recognized and mainstream alternative in the energy industry.
Uncertain feedstock availability
Seasonality is a feature of several feedstocks utilized in manufacturing bio-LNG, including energy crops and agricultural leftovers. The availability of these resources is influenced by weather patterns and farming cycles, which causes variations in the feedstock supply all year. There may be competing uses for the same organic waste materials utilized in manufacturing bio-LNG, including composting, animal feed, or other agricultural uses. This resource rivalry may affect the steady supply of feedstocks needed to produce bio-LNG. The availability of waste streams is necessary for bio-LNG production, and modifications to waste management policies or procedures may impact the amount and caliber of feedstocks. Unclear waste management policies might impact the stability of the feedstock supply.
Opportunities
Growing demand for sustainable fuels
Growing public awareness of environmental degradation and climate change has increased demand for energy sources that lower greenhouse gas emissions. Conventional LNG derived from fossil fuels is less sustainable than bio-LNG derived from organic sources. Many companies are resolving to lessen their carbon impact and embracing sustainability objectives. Corporate sustainability initiatives might include bio-LNG as an alternative fuel that can help meet emission reduction goals. Various feedstocks, such as organic waste, agricultural residues, and specialty energy crops, can manufacture bio-LNG. This flexibility in raw materials lessens reliance on feedstocks by ensuring a steady and varied supply chain.
Government subsidies and incentives
In pursuing cleaner energy sources and reduced greenhouse gas emissions, many countries have set ambitious targets for renewable energy. Bio-LNG, as a renewable fuel, aligns perfectly with these objectives. As critical decision-makers, government officials have the power to shape more extensive clean energy plans, including promoting and expanding the bio-LNG sector. Governments can reward bio-LNG producers for reducing greenhouse gas emissions by implementing carbon credit systems or offset programs. The opportunity to trade these credits on carbon markets introduces an additional revenue stream, enhancing the financial attractiveness of bio-LNG plants.
Governments can stimulate the bio-LNG market by offering incentives for the construction of vital infrastructure, such as production facilities, storage facilities, and distribution networks. This support paves the way for a robust bio-LNG supply chain, promising a future where clean energy is readily accessible for enterprises and consumers.
Segment Insights
Source Insights
The organic household waste segment dominated the market in 2025 with a 41% market share. Much of the world's municipal solid trash comprises organic home garbage, such as food scraps and yard debris. The conversion of the organic portion into renewable energy sources like bio-LNG is becoming increasingly important as governments and communities emphasize sustainable waste management methods.
Anaerobic digestion of biodegradable materials yields biogas in the organic waste-to-bio-LNG process. By liquefying this biogas, which is mostly made of methane, bio-LNG can be produced. Unlike conventional LNG from fossil fuels, this bio-LNG is an environmentally friendly and renewable substitute that reduces greenhouse gas emissions and reliance on non-renewable resources.
The municipal waste segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period of 2025-2034. For bio-LNG manufacture, municipal waste including organic and biodegradable materials, is a plentiful and easily accessible feedstock. Since this waste is often produced in cities, bio-LNG-producing facilities have a steady source. The idea of a circular economy, which recycles and repurposes resources, is gaining popularity worldwide. This architecture is particularly suited to generating bio-LNG from municipal trash, which turns waste materials into a lucrative energy source and encourages a more circular and sustainable approach to waste management. Technological developments in waste-to-energy and bio-LNG production have increased the economic viability and efficiency of turning municipal trash into bio-LNG. This area is attractive and scalable in part because of improved technologies.
Application Insights
The transportation fuel segment held the largest share of 56% in 2025. Reducing greenhouse gas emissions by switching to greener, more sustainable energy sources is becoming increasingly important worldwide. Because it is made from organic and renewable resources, bio-LNG is a better option for the transportation industry that wants to reduce its carbon footprint.
Bio-LNG can be used as a substitute for conventional fossil fuels, especially in heavy-duty vehicles like buses, trucks, and ships. It can be blended with or used instead of traditional LNG without requiring significant changes to the engines and infrastructure already in place. This is known as "drop-in" fuel. Because of its simplicity of integration, fleet operators looking for better energy options without major overhauls find bio-LNG a compelling alternative.
Regional Insights
What is the Europe Bio-LNG Market Size?
The Europe bio-LNG market size was exhibited at USD 1.71 billion in 2025 and is projected to be worth around USD 40.58 billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of 37.26% from 2026 to 2035.
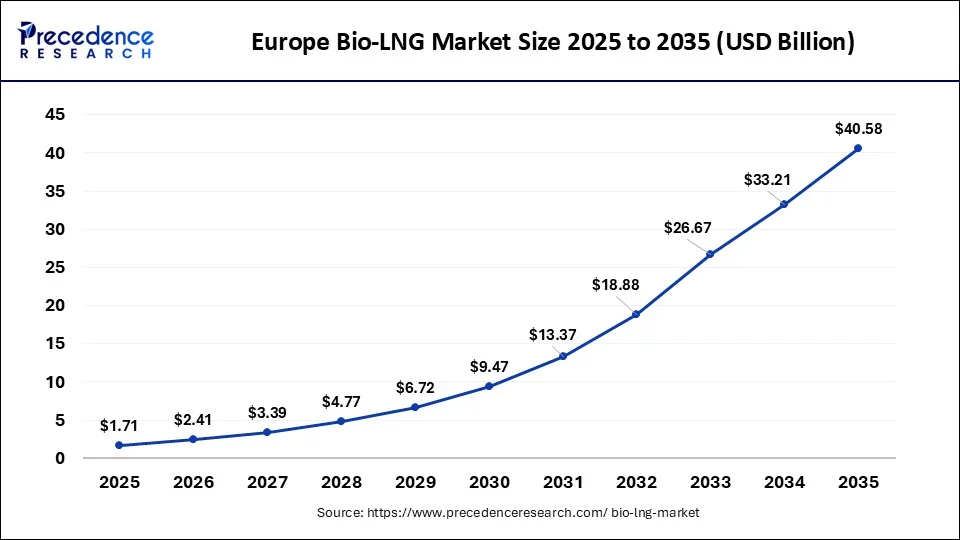
Europe has its largest market share of 62% in 2025. European nations have led the way by enacting laws and policies that support renewable energy sources and lower greenhouse gas emissions. A supportive legislative and regulatory environment can propel the bio-LNG industry's expansion. Its goals for cutting carbon emissions and raising the proportion of renewable energy in its energy mix are high. Because of this dedication to sustainability, bio-LNG, a cleaner substitute for conventional LNG, may become more widely used. It frequently devotes a lot of funds to research and development in renewable energy. The competitiveness and appeal of bio-LNG technologies can be increased with ongoing investment in their development and improvement.
UK Bio-LNG Market Analysis
The market in the UK is growing due to strong decarbonization targets, rising demand for low-carbon fuels in transport and maritime sectors, and government support for renewable gas initiatives. Increased investment in anaerobic digestion, waste-to-energy projects, and expanding LNG refueling infrastructure is further enabling bio-LNG adoption across industrial and transportation applications.
How is the Opportunistic Rise of North America in the Bio-LNG Market?
North America shows a significant growth in the bio-LNG market during the forecast period. Growing emphasis on cutting carbon emissions and achieving renewable energy goals may spur the use of bio-LNG, a greener fuel than conventional LNG. Technological developments in the bio-LNG production sector, such as enhanced feedstock conversion procedures and more productive production techniques, can raise bio-LNG's cost-competitiveness and investor interest. Energy sources with smaller carbon footprints are in greater demand as environmental sustainability and climate change become more widely recognized. Bio-LNG meets this need since it is made from renewable resources or organic waste.
U.S. Bio-LNG Market Analysis
The U.S. market is expanding due to stricter emission regulations, growing demand for renewable fuels in heavy-duty transport, and strong incentives under federal and state clean energy programs. Abundant organic waste feedstock, advancements in biogas upgrading technologies, and rising investments in LNG infrastructure are further supporting large-scale bio-LNG production and adoption.
What Potentiates the Market in Asia Pacific?
Asia Pacific is observed to grow at a considerable growth rate in the upcoming?period, fueled by rising demand for clean and sustainable energy solutions. Governments in this area are actively endorsing renewable energy projects to promote the use of Bio-LNG in transportation, industrial applications, and power generation. The plentiful availability of organic waste and agricultural byproducts provides sufficient feedstock for Bio-LNG production. Moreover, the development of infrastructure and international collaborations are facilitating the establishment of new Bio-LNG facilities and refueling stations. Nations such as China, Japan, and India are pivotal in advancing innovation and regulatory frameworks for Bio-LNG technologies and their applications.
China
China is becoming a key player in the expansion of the Bio-LNG market within the Asia-Pacific region. With a strong government emphasis on lowering greenhouse gas emissions and fostering circular economy practices, Bio-LNG is increasingly being examined as a viable sustainable fuel alternative. Numerous pilot initiatives and commercial-scale facilities are being developed, utilizing organic waste generated from households, agriculture, and industrial sectors. Additionally, the country is enhancing its infrastructure to facilitate Bio-LNG distribution and transport.
Value Chain Analysis
- Feedstock Procurement: Bio-LNG feedstock sourcing focuses on securing organic waste streams, converting biogas into liquefied biomethane through reliable, certified supply chains.
Key players: Shell, TotalEnergies, Air Liquide, BP, and ENGIE - Distribution to Industrial Users: Bio-LNG is supplied to industries using established gas networks, LNG terminals, and cryogenic transport systems for efficient distribution.
Key players: Gasum, Chart Industries, Linde, Wärtsilä, and Pavilion Energy - Waste Management and Recycling: Bio-LNG waste management converts organic waste into renewable fuel and fertilizer through anaerobic digestion, supporting circular economy goals.
Key players: Veolia, SUEZ, Gasum, ENGIE, and Future Biogas
Bio-LNG Market Companies
- TotalEnergies – Provides bio-LNG production, supply, and distribution solutions, focusing on renewable liquefied biomethane for heavy transport, maritime fuel, and industrial applications with strong European infrastructure and sustainability commitments.
- Titan LNG – Specializes in delivering bio-LNG fuel for heavy-duty vehicles and maritime clients, leveraging flexible supply logistics and partnerships to support low-carbon transportation across Europe.
- DBG Group B.V. – Offers bio-LNG production and distribution services, converting organic waste into renewable LNG for transport and industrial energy, emphasizing sustainability and circular economy solutions.
- BoxLNG Pvt. Ltd. – Provides modular bio-LNG production units and logistics solutions, enabling decentralized renewable gas conversion and fueling infrastructure in emerging and established markets.
- Shell Plc – Supplies bio-LNG as part of its LNG fuel portfolio, supporting decarbonization in heavy-duty transport and marine sectors while expanding renewable gas procurement and refueling networks.
- Flogas Britain Ltd. – Offers bio-LNG supply and energy services in the UK, focusing on low-carbon fuel solutions for industrial use, transport fleets, and energy-intensive applications.
Other Major key Player
Recent Developments
- In July 2025, NYK Line began using bio-LNG continuously for its LNG-powered car carriers, Daisy Leader and Sumire Leader, supplied by Titan at Zeebrugge. The mass-balanced bio-LNG enables tracking of emissions reductions, supporting the company's decarbonization goals and demonstrating a practical way to lower greenhouse gas emissions using existing infrastructure.
(Source: https://www.nyk.com ) - In March 2025, Titan and Mitsui O.S.K. Lines completed their first bio-LNG bunkering at Belgium's Port of Zeebrugge, delivering a certified waste-based bio-LNG blend to the Celeste Ace. This operation, part of a multi-delivery agreement, supports emission reductions and establishes a long-term partnership to supply low-carbon fuel for the shipping company's LNG-powered fleet.
(Source: https://titan-cleanfuels.com ) - In April 2024, Shell inaugurated its first Bio-LNG facility in Germany to assist in the decarbonization of freight transport. The facility converts organic waste into renewable liquefied gas and supplies it to LNG vehicles through Shell's fueling network across Europe.
- In May 2024, Nordsol and Prodeval have collaborated to create a new Bio-LNG production facility in Portugal. This initiative will process organic waste sourced from local agriculture and aims to enhance renewable energy initiatives in Southern Europe.
- In July 2024, Woodside has broadened its involvement in the LNG and Bio-LNG sectors by acquiring LNG assets from Tellurian. This acquisition strengthens Woodside's strategic standing in the renewable gas markets, allowing for the future incorporation of bio-based LNG production technologies.
- In January 2024, the four Westfalen LNG filling stations located in Münster, Herne, Herford, and Cologne will switch from fossil fuel to bio-liquefied natural gas (LNG), according to Westfalen Group (Westfalen), a technological firm operating in the energy industry and based in Germany.
- In November 2023, in response to the growing demand for fuel in road transportation, Uniper's subsidiary Liqvis opened another LNG fueling station in Germany.
- In August 2023, Mediterranean Shipping Company (MSC) became a member of SEA-LNG, an industry partnership spanning many sectors that was established to demonstrate the advantages of LNG to achieve maritime decarbonization. MSC has invested in LNG-fueled boats across the sectors it serves in the last few years. In 2022, MSC's first five newly constructed cargo ships with dual-fuel LNG capability went into service.
Segments Covered in the Report
By Source
- Organic household waste
- Organic industrial waste
- Municipal waste
By Application
- Transportation Fuel
- Power Generation
- Others
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Tags
Ask For Sample
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
 Get a Sample
Get a Sample
 Table Of Content
Table Of Content




 sales@precedenceresearch.com
sales@precedenceresearch.com
 +1 804-441-9344
+1 804-441-9344
 Schedule a Meeting
Schedule a Meeting