Transient Voltage Suppressor Diode Market Size To Rise USD 1,911.46 Mn By 2032
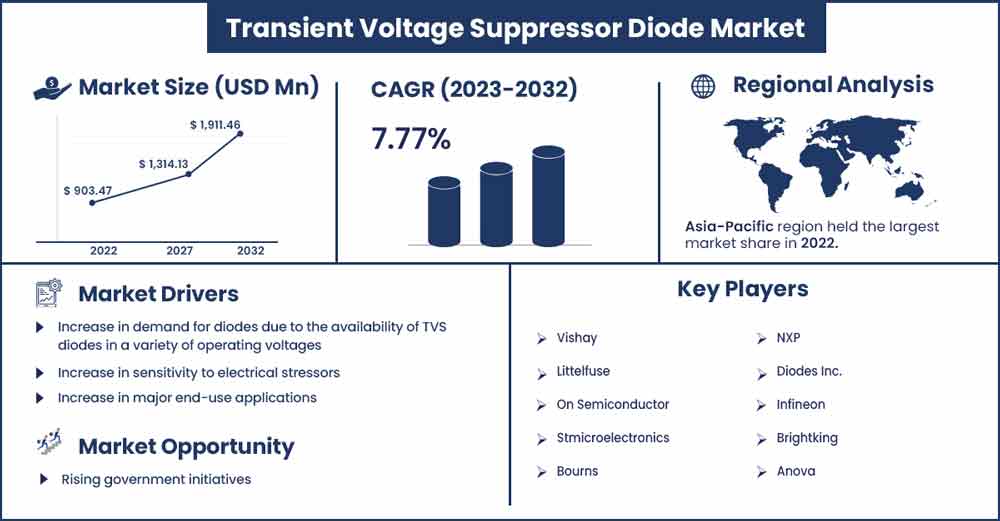
The global transient voltage suppressor diode market size surpassed USD 903.47 million in 2022 and is projected to rise to USD 1,911.46 million by 2032, anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 7.77 percent during the projection period from 2023 to 2032.
Weak circuits are protected against electrical stress using transient voltage suppressors (TVS), such as those caused by electrostatic discharge, inductive load switching, and triggered lightning. Damage-causing voltage spikes are prevented inside the TVS by the clipping or torrential sliding activity of a robust silicon p-n intersection, which reduces the transient's potency to a non-destructive level.
Transient voltage suppressors are defined as short-term electrical energy storage devices that are triggered by lightning or other powerful inductive loads. They are the result of the sudden release of electrical energy.
An overall configuration of many components called a transient voltage suppressor is designed to react to sudden or momentary overvoltage circumstances. Transient voltage suppressors (TVS) are expected to continue being one of the primary growth drivers for the transient voltage Suppressors (TVS) market as a result of the expanding trend of segment scaling down, which has increased electrical burdens' affectability and increased the popularity of transient voltage suppressors in significant end-use applications.
Transient voltage suppressor are defined as short-term surges of electrical energy that are caused by the unexpected release of energy that was previously stored or triggered by other methods, such as lightning or intense inductive loads. This energy can be released in an expected manner by regulated exchanging activities in electrical or, alternatively, electronic circuits, or it can be arbitrarily triggered into a circuit from outside sources.
The components known as transient voltage suppressors shield delicate electronics from being harmed by high-voltage transients. The solid-state pn junction devices are these diodes. Diodes' electrical properties are governed by factors including doping concentration, junction area, and substrate resistivity. To absorb strong transient currents, transient voltage suppressor (TVS) diodes are built with massive junction cross sections.
The properties of the diodes as a transient voltage suppressor are the same as those of zener diodes. While zener diodes are built for voltage control, TVS diodes are specifically designed, tested, and characterized as transient voltage suppressors. It is known that transient voltage suppressor diodes react nearly instantly. The transient voltage suppressor diode's response time is one of its key features.
The voltage overshoot is caused by PC board traces and lead inductance, according to the transient voltage suppressor diodes' quick reaction time. Transient voltage suppressor diodes are offered in a wide variety of working voltages; typical device voltage ranges for discrete devices vary from 5V to 440V. The size of the worldwide market for transient voltage suppressor diodes is expected to increase strongly over the short-term forecast period and nominally over the long-term forecast period.
Transient Voltage Suppressor Diode Market Report Scope:
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Revenue in 2023 | USD 973.78 Million |
| Projected Forecast Revenue by 2032 | USD 1,911.46 Million |
| Growth Rate from 2023 to 2032 | CAGR of 7.77% |
| Largest Market | Asia-Pacific |
| Base Year | 2022 |
| Forecast Period | 2023 to 2032 |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Regional Snapshots:
Geographically, North America dominated the transient voltage suppressors (TVS) market due to increased popularity and use of technology. Asia-Pacific and Europe were the second and third-largest markets for transient voltage suppressors (TVS), respectively, after North America. According to projections, the Asia-Pacific region will grow at the fastest rate due to the rapidly expanding demand for gadgets in this region's agricultural powerhouses, China and India.
Additionally, the market presence of transient voltage suppressors in the major nations of North America, Asia-Pacific, Europe, Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa. Due to the region's developing creative work activities and rising speculative activity, the Asia-Pacific will need to demonstrate significant growth over the coming decades. North America and Europe contribute significantly to global revenue and are expected to continue doing so in the transient voltage suppressor market over the long future.
Report Highlights:
- In 2022, the segment of uni polar TVS accounted for the largest revenue share of the market. Bi-polar TVS are expected to grow at the fastest rate during the projected period due to the fact that they are growing in popularity among consumers.
- The AC supply protection sector had the largest revenue share in 2022 and is expected to keep leading over the projected period due to the increased use of alternative current in residential power supply stations.
- The industrial power supplies market is predicted to develop at the quickest pace in terms of revenue during the forecast period due to increased power demand in industries, continued technological improvements, and government backing for the installation of necessary transient voltage suppressors.
- Asia-Pacific accounted for the largest revenue share in 2022 and is anticipated to maintain its dominance in the transient voltage suppressor market throughout the forecast period due to the region's rapid urbanization, rising energy demand, and the implementation of successful solar and wind power projects.
Market Dynamics:
Drivers:
The requirement for continuous electrical supply, expanding emphasis on dynamic mobility, and rising awareness of its relevance among people in developed nations have all had a substantial influence on the market's revenue growth in recent years. Transient voltage suppressors, which were traditionally created to safeguard delicate electrical equipment from being harmed by high-voltage transients, are increasingly being employed in the automotive, computing, and telecommunications sectors. Compared to their traditional diode-based predecessors, they offer a very rapid reaction time. The trend toward component downsizing has enhanced electrical stress sensitivity and raised the need for TVS in significant end-use applications.
Restraints:
During the projected period, factors include high installation costs, the availability of many traditional instruments for managing the energy supply, unequal suppression in certain models, the absence of TVS in some locations, and low consumer awareness may limit market revenue growth. The market's potential for revenue growth may also be seriously hampered by factors such as fluctuating prices of advanced diode raw materials, low energy handling capacity, complex manufacturing processes, a lack of suitable Research & Development (R&D) facilities in developing nations, and strict governmental regulations.
Additionally, the failure of TVSS devices as a result of a power overload that exceeds the capabilities of microprocessors or integrated circuits may hamper the market's growth for the predicted period of time.
In order to serve as effective barriers against transients and power changes over time, TVSS devices are frequently installed at AC and DC inputs and outputs.
Opportunities:
During the projected period, rising government initiatives to improve electrical infrastructure and rising public and private sector investments are anticipated to fuel market revenue growth. For transient voltage suppression, TVS are specifically built, tested, and described with large cross sectional area junctions to absorb strong transient currents. Additionally, as more electronic devices are used, more people are becoming aware of the advantages of TVS, such as their low incremental surge resistance and ability to provide high current protection for 6KA to 10KA, which is driving up their use across a variety of sectors.
Challenge:
In contrast, the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on key industries could pose a threat to the growth of the transient voltage suppressor (TVS) diode market between 2021 and 2028. The low energy handling and high cost of the product are supposed to act as the major limitations for the expansion of transient voltage suppressor (TVS) diodes in the aforementioned forecasted period.
Recent Developments:
- The first broad voltage range hot-swap controller for data centers with programmable digital SOA control will be made available by Infineon in November 2022. The hot-swap and system monitoring controller IC's input voltage range is 5.5 V to 80 V, with transients up to 100 V for 500 ms.
- Vishay has introduced three series of 24V surface-mount transient voltage suppressors (TVS) that can dissipate peak pulse power at 10/1000s in SMC (DO-214AB) packaging and 10/10,000s in DO-218AB, providing peak pulse power dissipation similar to 7kW of conventional TVS.
Major Key Players:
- Vishay
- Littelfuse
- On Semiconductor
- Stmicroelectronics
- Bourns
- NXP
- Diodes Inc.
- Infineon
- Brightking
- Anova
- Semtech
- MDE
- Toshiba
- EIC
- Protek
- Wayon
- Inpaq
- Socay
- Un Semiconductor
- Microsemi
Market Segmentation:
By Type
- Uni-polar TVS
- Bi-polar TVS
By Application
- DC Supply Protection
- DC Load Protection
- AC Supply Protection
- Electro-Magnetic Interference Limiting
- Operational Amplifier Protection
- Others
By End User
- Automotive
- Industrial Power Supplies
- Military/Aerospace
- Telecommunication
- Computing
- Consumer Goods
- Others
Buy this Research Report@ https://www.precedenceresearch.com/checkout/2583
You can place an order or ask any questions, please feel free to contact at sales@precedenceresearch.com | +1 9197 992 333