What is the Ambulatory Infusion Centers Market Size?
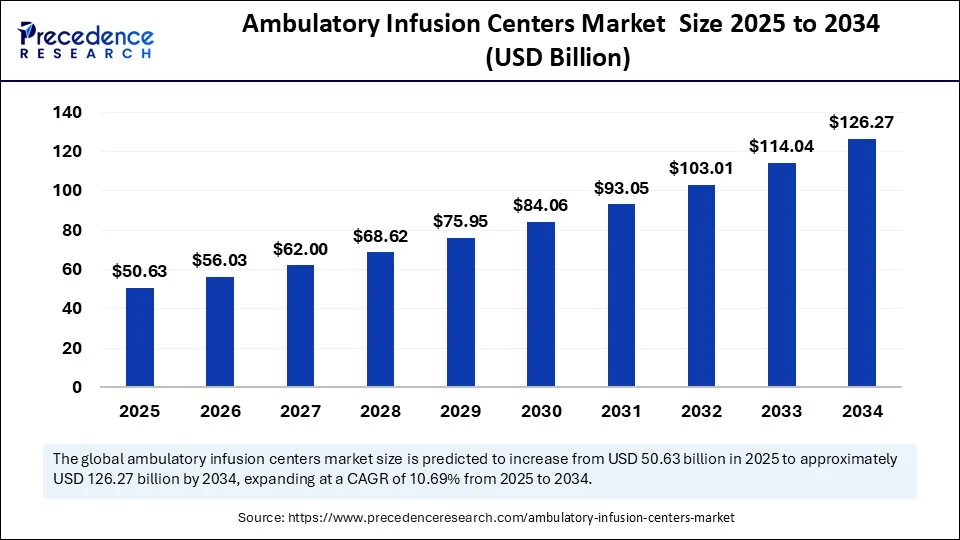
The global ambulatory infusion centers market size is accounted at USD 50.63 billion in 2025 and predicted to increase from USD 56.03 billion in 2026 to approximately USD 126.27 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 10.69% from 2025 to 2034. The ambulatory infusion centers market is experiencing robust growth due to the increasing number of cases of chronic diseases, such as diabetes, cancer, and autoimmune diseases. The rising demand for outpatient services due to the increased healthcare costs further contributes to market growth.
Ambulatory Infusion Centers Market Key Takeaways
- In terms of revenue, the global ambulatory infusion centers market was valued at USD 45.76 billion in 2024.
- It is projected to reach USD 126.27 billion by 2034.
- The market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 10.69% from 2025 to 2034.
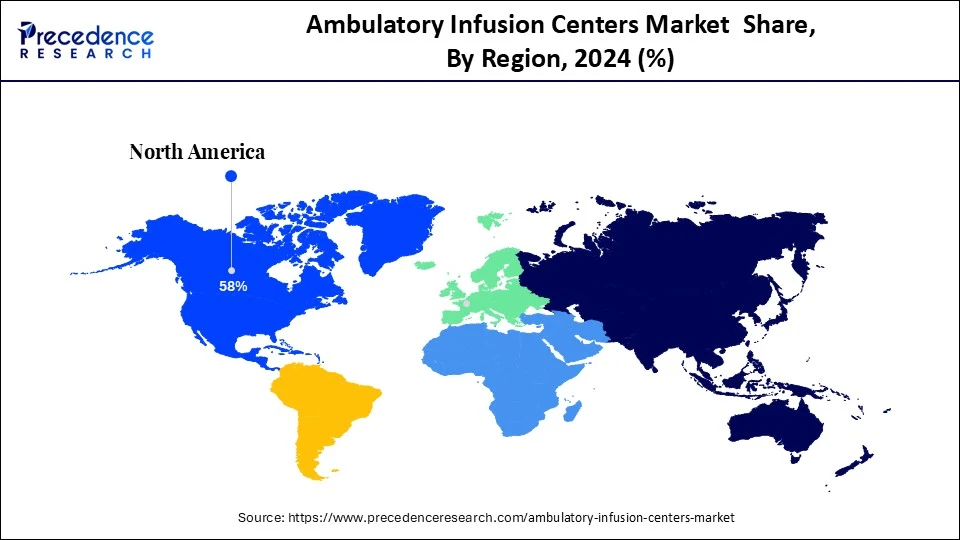
- North America dominated the ambulatory infusion centers market with the largest market share of 58% in 2024.
- Asia Pacific is expected to expand at the fastest CAGR between 2025 and 2034.
- By therapy type, the biological therapy segment held the biggest market share of 28% in 2024.
- By therapy type, the immunoglobulin therapy segment is anticipated to grow at a remarkable CAGR between 2025 and 2034.
- By application, the autoimmune disorders segment captured the highest market share of 33% in 2024.
- By application, the oncology segment is expected to expand to a notable CAGR over the projected period.
- By end user, the standalone/independent infusion centers segment contributed the major market share of 42% in 2024.
- By end user, the physician office infusion centers segment is expected to expand at a notable CAGR over the projected period.
- By payor type, the commercial insurance segment generated the largest market share of 48% in 2024.
- By payor type, the medicare segment is expected to expand at a notable CAGR over the projected period.
How is Artificial Intelligence Transforming the Ambulatory Infusion Centers Market?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is truly transforming the market for ambulatory infusion centers by enabling smarter, leaner, and more patient-centric care. AI-powered operations reduce patient wait times, optimize chair time scheduling, and improve nursing productivity through real-time analytics. AI-driven infusion pumps and remote patient monitoring tools now allow personalized delivery for complex gene and cell therapies, allowing ambulatory infusion centers to provide advanced therapy practices outside the walls of the hospital.Fully integrated AI systems also increase administrative efficiency by automating several tasks, such as scheduling appointments, managing patient records, and handling billing processes. This automation frees up staff to focus on patient care. AI systems also optimize resource allocation, ensuring that ambulatory infusion centers meet patient needs.
What are Ambulatory Infusion Centers?
The ambulatory infusion centers market refers to the healthcare services ecosystem comprising outpatient facilities where patients receive intravenous (IV) therapies, biologics, antibiotics, and specialty medications without hospitalization. These centers are typically staffed by nurses and clinical professionals and are used for chronic disease management (e.g., autoimmune diseases, cancer, neurological disorders) in cost-effective, non-acute care settings. Their growth is driven by rising biologic use, payer cost-containment policies, increasing outpatient preference, and specialty drug approvals.
The market is evolving with the move from inpatient to outpatient care and emerging infusion technologies and digital monitoring devices. The increased pertinence of specialty therapies and bundled payment models is supporting market growth. Moreover, the shift toward patient-centric care is encouraging providers to move from hospital systems to independent or integrated clinic-based models, contributing to market growth.
What are the Growth Factors of the Ambulatory Infusion Centers Market?
- Increased Adoption of Biologic Drugs: Biologics are increasingly prescribed for chronic health conditions and currently require intravenous administration. Ambulatory centers provide an ambulatory setting for these long-term biologic therapies as they are more convenient and cost-effective for the patients and their payers.
- Transition from Inpatient to Outpatient Care: There is a transition occurring among the health systems from inpatient to outpatient care in order to decrease costs and make the patient experience more streamlined. The ambulatory infusion center provides a way to provide care through efficient, non-acute infusion service delivery.
- Increased Approvals of Specialty Drugs: More FDA and global approvals of complex specialty infusion drugs are contributing to the demand for specialized infusion services, which can take place outside of traditional hospital settings, and those who specialize in infusion services, ambulatory, etc., are benefiting.
- Higher Incidence of Chronic Diseases: An increase in autoimmune disorders, oncological disorders, and neurological disorders are contributing to the need for long-term therapies or therapies, placing ambulatory infusion centers to be an integral element of where to delivered care, the populations, and behavior one can get when/where they want treatment.
Ambulatory Infusion Centers Market Outlook
- Industry Growth Overview: From 2025 to 2030, the infusion market is expected to grow strongly, driven by rising demand for cost-effective outpatient care options, the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, and patient preference for shorter hospital stays. Growth has been fueled largely by payers advancing infusion services into outpatient settings outside an inpatient, acute-care setting, as well as improved treatment protocols for oncology, immunology, and pain management.
- Global Expansion: Significant infusion operators have expanded into Asia-Pacific, Eastern Europe, and LATAM with hopes of serving a rapidly growing patient population looking for infusion treatment, while simultaneously benefiting from lower operating costs. Major infusion companies were established to provide outpatient infusion suites next to specialty clinics and facilities providing diagnostic services.
- Major Investors: Private equity firms and healthcare investors quickly became involved in this market because of the high margins when compared to other health sectors, the repeat-visit models within infusion therapy, and the strong reimbursement outlook. Venture investors such as Bain Capital, TPG, and KKR backed infusion-chain models focused on both oncology and biologics and specialty drugs. Investors seemed particularly interested in infusion centers with scalable technologies, strong regulatory compliance, and relationships with large hospital systems.
- Startup Ecosystem: The startup ecosystem has continued to strengthen with solutions to support better patient experiences, such as AI-based scheduling, remote monitoring for reactions to infusion, and safer dilution or mixing solutions. Newer companies are integrating home-to-center, automated pharmacy compounding, and better patient tracking platforms.
Market Scope
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 126.27 Billion |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 50.63 Billion |
| Market Size in 2026 | USD 56.03 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate from 2025 to 2034 | CAGR of 10.69% |
| Dominating Region | North America |
| Fastest Growing Region | Asia Pacific |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | Therapy Type, Application, End-User, Payor Type, and Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Market Dynamics
Drivers
How the Growth of Ambulatory Infusion Centers is Driven by a Rise in Chronic Disease Prevalence
The increasing prevalence of chronic and autoimmune diseases, specifically cancer, rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn's disease, and multiple sclerosis, is certainly a major driver of the ambulatory infusion centers market. According to the World Health Organization, chronic diseases account for 74% of all global deaths, and there is an increasing number of patients who require consistent intravenous treatments. Ambulatory infusion centers provide a non-hospital, cost-effective alternative to administering biologics, antibiotics, hydration, and nutritional therapy.
(Source: https://www.who.int)
This ultimately reduces hospital admissions and allows patients to continue outpatient therapy instead of an inpatient setting. The demands for personalized and continuous care for chronic conditions will be further realized as the role of infusion centers becomes more formalized in our modern healthcare delivery model.
Restraint
Limited Reimbursement
One of the most prevalent restraints for the ambulatory infusion centers market is the inconsistency and limitations of insurance reimbursement. There are many outpatient infusion therapies, especially the more expensive biologics used to treat autoimmune and chronic diseases, that are not uniformly covered by either private payers or government programs. The variability in reimbursement rates, pre-authorization, and fluidity of insurance policies create financial uncertainty for providers. Some infusion centers limit the types of therapies they can provide, directly impacting patient access to appropriate services, as too great a financial investment could put them at a loss.
Additionally, even patients with insurance coverage may find high out-of-pocket expenses dissuading them from continuing long-term therapies, and from their perspective, these expenses are simply unacceptable. The U.S. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) suggests that outpatient services often carry a greater expectation of scrutiny and narrower approval than inpatient Medicare claims related to inpatient hospital care. Insurance reimbursement and coverage-related obstacles inhibit the scale advantages of infusion centers in serving larger.
Opportunity
Expansion of Services
One emerging opportunity in the ambulatory infusion center space stems from the expansion of service offerings to include a broader range of infusion therapies and a shift in public and private payer policies that promote site-of-care optimization. Payers, including the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), continue to promote alternative sites of care, moving infusion services out of hospital outpatient departments to lower-cost, higher-quality options, such as physicians' offices and free-standing infusion centers. CMS notes that the agency expanded the scope of the Home Infusion Therapy Services benefit as part of the agency's 2025 update, allowing providers higher reimbursement for professional services rendered outside the hospital in conjunction with therapy.
(Source: https://www.cms.gov)
The site-of-care policy in support of shifting infusion services from hospitals to alternatives has been adopted by leading payers such as UnitedHealthcare and Aetna and restricts hospital-based infusions for non-urgent patients while fostering the use of ambulatory or home-based infusion therapy services. The reimbursement environment creates favorable opportunities and contributes to the financial sustainability of independent or physician-mixed infusion centers, resulting in an influx of new openings in unserved suburban and rural markets.
Therapy Type Insights
Why Did the Biological Therapy Segment Dominate the Market in 2024?
The biological therapy segment dominated the ambulatory infusion centers market with the largest share in 2024. This is due to the increased number of cases of autoimmune and chronic inflammatory diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis and Crohn's disease. Biologics (most commonly monoclonal antibodies or cytokine inhibitors) require dosing and monitoring, making infusion centers an attractive option for their administration. Combined with the high treatment frequency and long duration of treatment, this will continue to be an area of growth for infusion centers and outpatient specialty pharmacies.
The immunoglobulin therapy (IVIG) segment is expected to grow at the fastest rate in the coming years because of the increased number of diagnoses of immunodeficiency disorders and also the increasing prevalence of neurological disorders, including chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP). The increased demand for more targeted and specialty infusion treatments in ambulatory centers is contributing to this growth. Similarly, the increase in the elderly population and increased off-label use of IVIG for autoimmune disorders are helping increase the use of IVIG in outpatient settings.
Application Insights
Which Application Segment Dominate the Market in 2024?
The autoimmune disorders segment dominated the ambulatory infusion centers market in 2024. This is mainly due to the increased number of cases of rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and Crohn's disease. These diseases require long-term infusion-based biologic therapy. Ambulatory infusion centers provide a far more comfortable and cost-efficient alternative to inpatient care. The additional increase in the number of autoimmune conditions and new diagnoses, in addition to the increasing number of patients receiving access to more complex biologics, continues to support this dominant application segment.
The oncology segment is expected to expand at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period. The growth of the segment is attributed to the increasing transition of cancer care from the inpatient to the outpatient environment. Ambulatory infusion centers offer the ability to administer safe and effective oncology therapies in a far more cost-effective and convenient manner than a hospital or inpatient care setting. The increasing incidence of cancer and new infusion-based immunotherapies will further bolster this trend.
End User Insights
How Does the Standalone/Independent Infusion Centers Segment Dominate the Ambulatory Infusion Centers Market in 2024?
The standalone/independent infusion centers segment dominated the market while holding the largest share in 2024 due to their flexibility, longer hours of operation, and patient-centric nature. Patient-centered infusion services attract a broad mix of patient types with chronic conditions who may need regular infusions. Compared to hospital centers, patients experience shorter wait times and enjoy low-cost, high-quality infusion services, which improve their overall satisfaction levels.
Physician office infusion centers (POICs) are the fastest-growing segment of infusion users. POICs are gaining traction as they provide seceded infusion services into their practice to ensure continuity of care for patients. POICs particularly benefit chronic disease patients by providing them with convenience, personalized treatment plans, and immediate access to a physician for medical supervision. Improvements in reimbursement and the demand for in-office services have prompted additional physicians to expand their infusion capabilities.
Payor Type Insights
Why Did the Commercial Insurance Segment Dominate the Ambulatory Infusion Centers Market in 2024?
Commercial insurance is the most dominant payor because employer coverage often includes extensive benefits that facilitate chronic condition management, as well as the fact that the majority of these plans will result in more expedited approvals and wider access to high-cost biologics and infusion therapies for patients. Commercial insurance tends to provide infusion centers with better reimbursement, thus creating more incentive for the infusion center to prefer these prospects.
The medicare segment is expected to expand at the fastest rate in the upcoming period, driven by an aging and chronically ill population of seniors. Older adults often require infusion services for their arthritis, cancer, and immune disorders at an increasing pace. Medicare infusion services are on the rise. Policy revisions to boost reimbursement rates for outpatient services have enhanced the ability of medicare patients to receive treatment at community-based ambulatory infusion centers.
Regional Insights
U.S. Ambulatory Infusion Centers Market Size and Growth 2025 to 2034
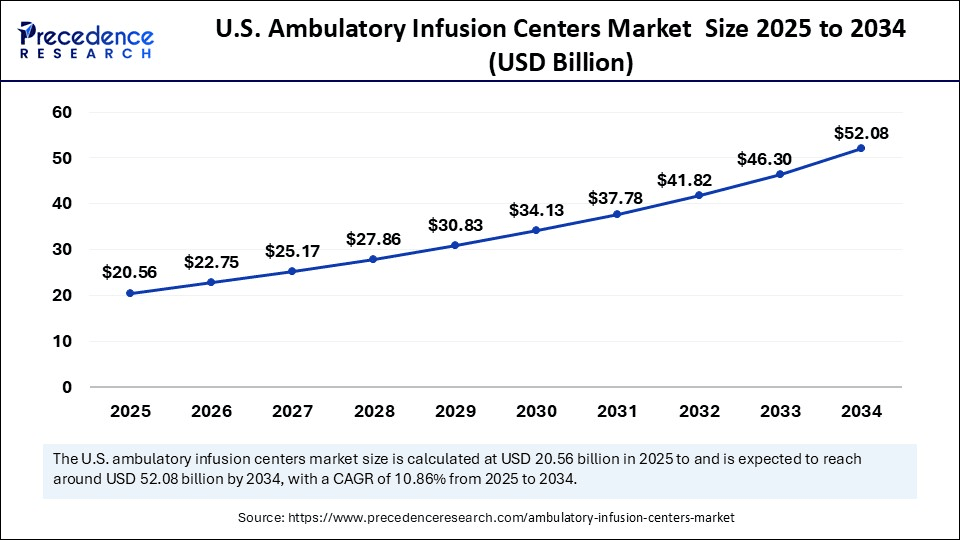
The U.S. ambulatory infusion centers market size is evaluated at USD 20.56 billion in 2025 and is projected to be worth around USD 52.08 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 10.86% from 2025 to 2034.
What Made North America the Dominant Region in the Ambulatory Infusion Centers Market in 2024?
North America dominated the market by capturing a 58% share in 2024. This is mainly due to solid Medicare reimbursement support and an established outpatient system in place. The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) allows "incident to" billing under Place of Service 11, which allows AICs to bill Medicare an infusion fee for the administration of infusion drugs. Meanwhile, the CMS Home Infusion Therapy payment data files provided revisions in March 2025, with rates and geographical adjustments remaining unchanged for home infusion and clinical infusion locations. There is a high demand for outpatient services, supporting regional market growth.
North America: U.S. Ambulatory Infusion Centers Market Trends
The U.S. is a major player in the market in North America. Healthcare providers in the country are increasingly moving infusion services from hospitals to ambulatory settings to reduce hospital congestion. Meanwhile, the CMS Physician fee schedule created enhancements for outpatient infusion services in 2025, ensuring stable support for outpatient infusion services. This outpatient infusion reimbursement parity between outpatient departments and private infusion centers represents significant opportunities for AIC growth across the U.S.
Europe: The Second-Largest Region in the Ambulatory Infusion Centers Market
Europe is the second largest market due to its strong healthcare delivery network, an elderly population with the accompanying burden of chronic disease, and a growing demand for outpatient rather than inpatient treatment. Like other countries, Germany, France, and the UK are moving many treatments and therapies from inpatient to outpatient to contain costs and increase access and patient comfort in receiving care wherever possible. The infusion center market is growing due to supportive reimbursement and government-funded home-based infusion therapy service initiatives, expanding infusion "ownership" and therapy treatment options in the region.
Europe: Germany Ambulatory Infusion Centers Market Trends
Germany is the leading country in the European ambulatory infusion centers market, partly due to a strong healthcare delivery system, comprehensive insurance coverage, and highly accessible care from and among physicians, which has led to the rapid adoption of outpatient infusion therapy. Additionally, Germany has seen an increase in daycare treatment models, a diminished burden on hospitals, and reduced wait times for chronic care patients.
Asia Pacific: The Fastest-Growing Region
Asia Pacific is expected to experience the fastest growth in the coming years due to rising healthcare policies and outpatient coverage. In September 2023, the National Healthcare Security Administration (NHSA) of China stated that 99% of outpatient institutions were included in the integrated medical reimbursement system, which processed ¥124?billion in outpatient reimbursements through employer-employee insurance coverage. The changes will ultimately allow outpatient clinics, inclusive of AICs, to provide affordable chronic and specialty care outside hospital settings.
(Source: https://govt.chinadaily.com.cn)
Asia Pacific: China Ambulatory Infusion Centers Market Trends
In China, infusion services are shifting away from tertiary hospitals and are being located in community and district-level clinics. Recently, the government has also supported "three models" of outpatient infusion service systems, including standalone centers, hospital-third-party partnerships, and pharmacy-based centers, all of which require emergency readiness and adequately trained staff. As chronic diseases and patients' access to insurance coverage increase, China's infusion service system can evolve into a safer and more accessible system for outpatient service implementation.
What made Latin America grow at a steady pace in the ambulatory infusion centers market?
Latin America had steadily advanced as patients sought affordable and accessible outpatient care for chronic illnesses. Countries in the region expanded their infusion offerings to relieve hospital crowds. The market enjoyed benefits from growing cancers and more access to specialty drugs. Moreover, private hospitals and clinics opened new infusion suites in urban areas. Mobile infusion services, telehealth referrals, and partnering with global pharma to support entering the region represented opportunities.
Brazil Ambulatory Infusion Centers Market Trends
Brazil had led the region due to its population and growing private health sector. Many hospitals had renovated their outpatient units to accommodate the growing demand for oncological and immune-related infusions. Insurance coverage in Brazil had improved, which increased access to these services. New centers had opened in urban areas among private operators. Digital health tools improved coordination of care, too.
What made the Middle East & Africa region grow at a significant rate in the ambulatory infusion centers market?
The Middle East & Africa region experienced significant growth due to investment in developing healthcare infrastructure and the expansion of specialty care. The increase in cases of cancer and autoimmune conditions has created a strong demand for infusion services. In addition, governments had endorsed outpatient care as a way to limit hospital expenditures. Similar to the outpatient care trends, private hospitals have invested in outpatient infusion suites, particularly in the Gulf region. There is still a strong opportunity to develop telehealth support, international care partnerships, and increase the care footprint in underdeveloped regions.
The UAE Ambulatory Infusion Centers Market Trends
The UAE had been a leader in the region, given its world-class facilities, robust insurance coverage, and a higher-than-average uptake of specialty biologics. Private hospitals had invested in modern outpatient infusion centers focused on patients with cancer, immune disorders, and pain management. Additionally, medical tourism has led to greater demand for infusion services. Furthermore, the region had invested in digital systems and developed automated drug preparation systems to improve safety and care.
Ambulatory Infusion Centers Market Companies

- Option Care Health
- InfuCare Rx
- Coram CVS (now part of Option Care)
- KabaFusion
- BioScrip (now part of Option Care)
- Amerita (a PharMerica company)
- United Infusion
- Soleo Health
- Paragon Healthcare
- PromptCare
- ContinuumRx
- CareCentrix
- Chartwell Pennsylvania
- Intramed Plus
- AlayaCare
- ClearSky Health
- Healix Infusion Therapy
- Nufactor (a FFF Enterprises company)
- PharMerica Infusion Services
- Infusion Associates
Recent Developments
- In January2025, Optum, a UnitedHealth subsidiary, agreed to acquire FlexCare Infusion, a 30 location ambulatory infusion network across Alabama, Arizona, and Oklahoma, expanding outpatient infusion services amid growing antitrust scrutiny.
(Source:https://ramaonhealthcare.com)
- In July2024, New Harbor Capital's portfolio company AccessInfusionCare finalized the acquisition of BigSkyI.V.Care in Kalispell, Montana, enhancing home and specialty infusion services in a rural market.
(Source:https://healthcaredealflow.com)
Segments Covered in the Report
By Therapy Type
- Anti-infective Therapy
- Hydration Therapy
- Chemotherapy
- Immunoglobulin Therapy
- Biological Therapy
- Enteral and Parenteral Nutrition
- Others (e.g., corticosteroids, pain management infusions)
By Application
- Oncology
- Autoimmune Disorders
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Crohn's Disease
- Psoriasis
- Neurological Disorders
- Infectious Diseases
- Gastrointestinal Disorders
- Immune Deficiencies
- Others
By End-User
- Hospital-Affiliated Infusion Centers
- Physician Office Infusion Centers (POICs)
- Standalone/Independent Infusion Centers
- Home Infusion Service Providers (with ambulatory setups)
By Payor Type
- Commercial Insurance
- Medicare
- Medicaid
- Out-of-Pocket / Self-Pay
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Ask For Sample
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
 Get a Sample
Get a Sample
 Table Of Content
Table Of Content
 sales@precedenceresearch.com
sales@precedenceresearch.com
 +1 804-441-9344
+1 804-441-9344
 Schedule a Meeting
Schedule a Meeting