Flight Simulator Market Size and Forecast 2025 to 2034
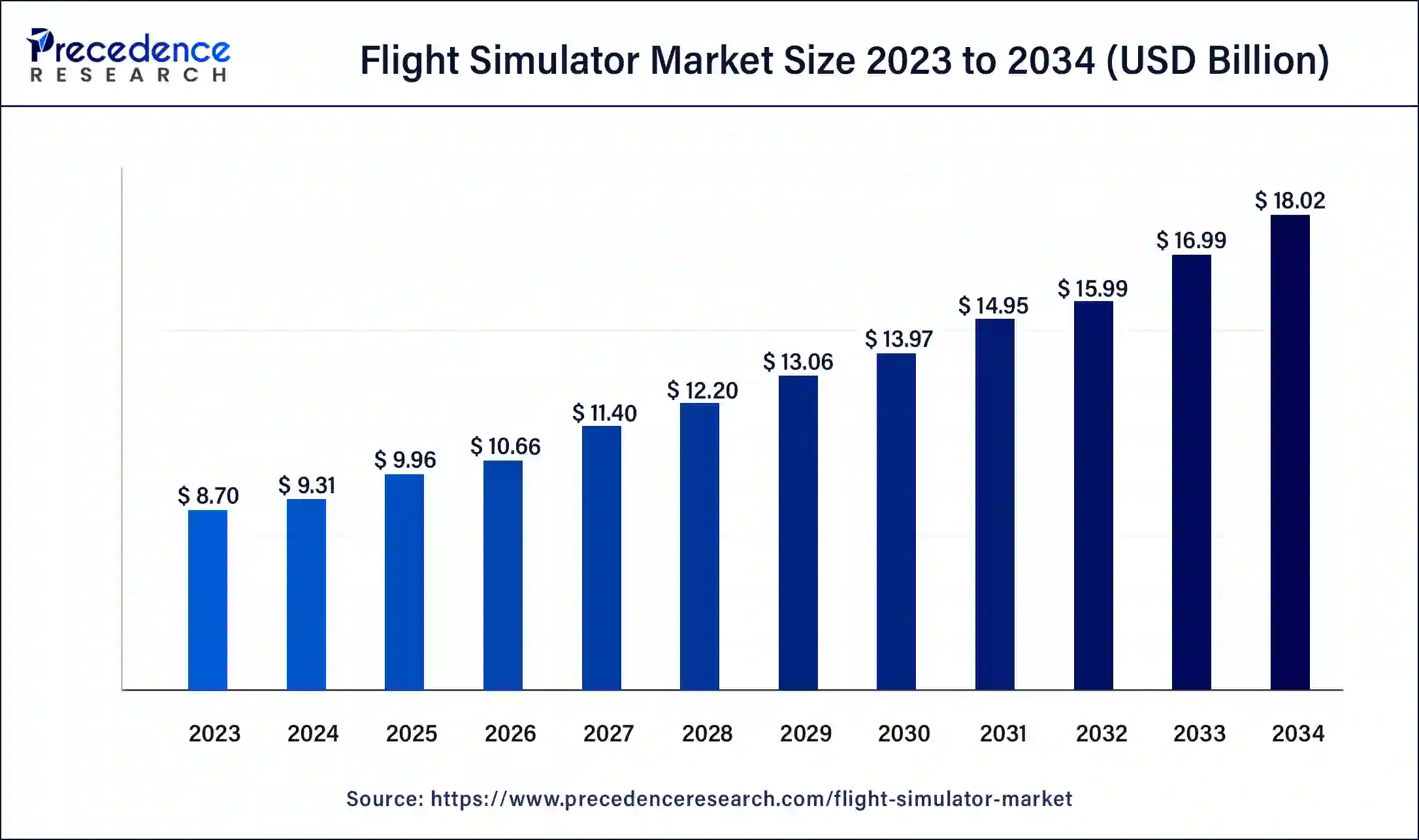
The global flight simulator market size accounted for USD 9.31 billion in 2024, and is expected to reach around USD 18.02 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 6.80% from 2025 to 2034. The North America flight simulator market size reached USD 3.13 billion in 2023.
Flight Simulator Market Key Takeaways
- In terms of revenue, the market is valued at $9.96 billion in 2025.
- It is projected to reach $18.02 billion by 2034.
- The market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 6.80% from 2025 to 2034.
- North America led the global market with the highest market share of 36% in 2024.
- Asia-Pacific region is estimated to expand at the fastest CAGR between 2025 and 2034.
- By Type, the full flight simulator (FFS) segment accounted for the largest market share in 2024.
- By Platform, the fixed wing simulator segment contributed more than 61% of revenue share in 2024.
- By Platform, the UAV simulators segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR from 2025 to 2034.
- By Application, the commercial segment had the biggest market share in 2024.
- By Application, the military segment is expected to expand at the fastest CAGR from 2025 to 2034.
U.S. Flight Simulator Market Size and Growth 2025 to 2034
The U.S. flight simulator market size was estimated at USD 2.36 billion in 2024 and is predicted to be worth around USD 4.64 billion by 2034, at a CAGR of 7% from 2025 to 2034.
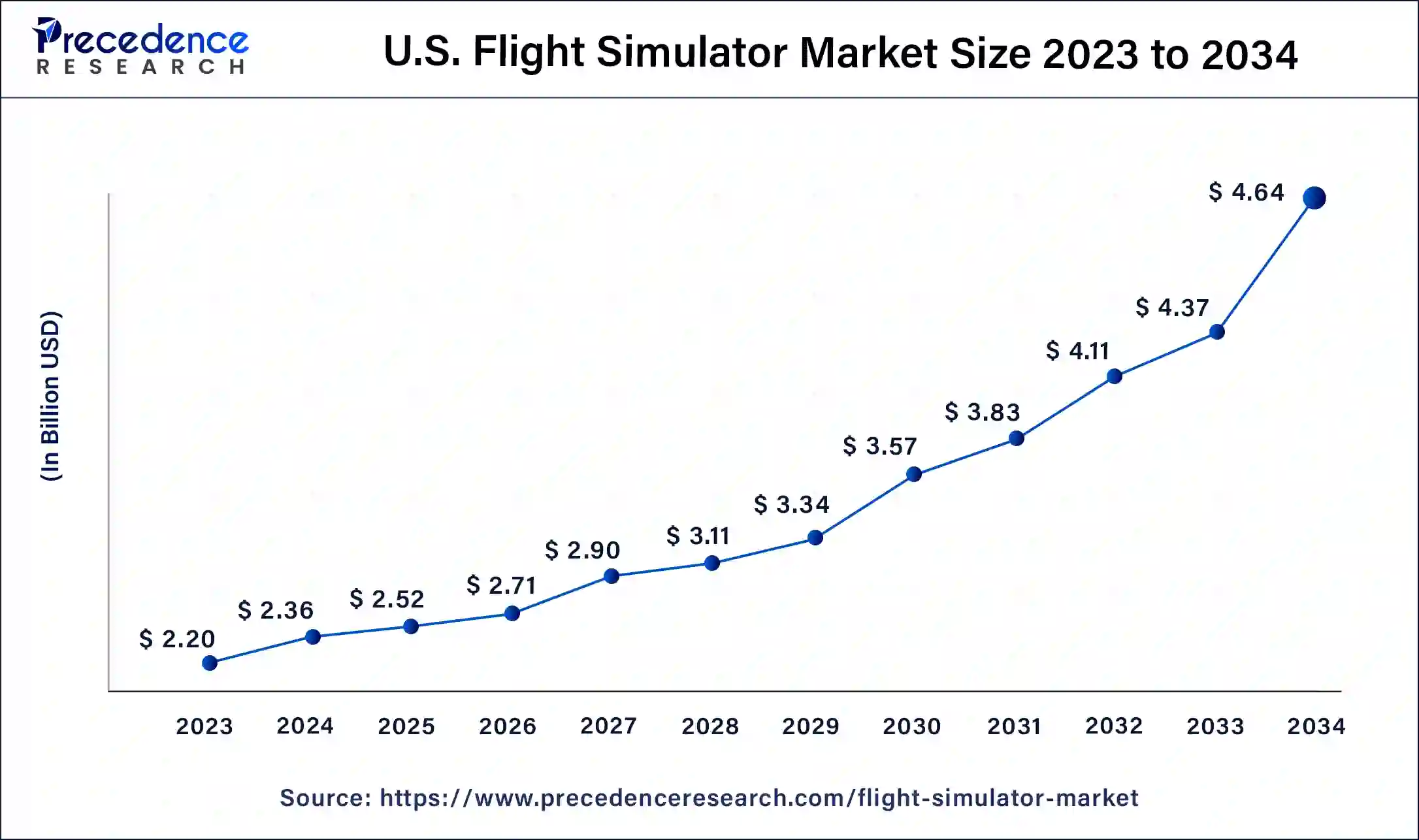
This is due to various factors such as the increasing demand for skilled pilots, continuous advancements in simulator technology, and the imperative for safe and cost-effective training solutions.
North America flight simulators market encompasses both the commercial and military sectors, with commercial airlines, flight training institutions, and aviation academies relying heavily on simulators for pilot instruction and certification. Concurrently, the U.S. Department of Defense and defense contractors employ sophisticated simulators for military pilot training and mission rehearsal.
Notably, North America often leads in technological innovations, including the development of high-fidelity Full Flight Simulators (FFS) and advanced training devices for a variety of aircraft types. Regulatory oversight by the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) further ensures that simulators meet rigorous standards for pilot training and certification.
Key market players like CAE Inc., L3Harris Technologies, FlightSafety International, and TRU Simulation + Training maintain a strong presence, and the region is home to numerous pilot training centers and flight schools.
North America holds the largest market share due to its well-established aviation industry and significant investments in defense training programs. The presence of major simulator manufacturers like CAE Inc., L3Harris Technologies, and Boeing further strengthens the region's technological edge. Government contracts from the U.S. Air Force and Navy, along with strong demand from commercial aviation training schools, drive continued simulator adoption. In addition, ongoing upgrades to NextGen flight systems and automated training platforms ensure that North American pilots remain trained on the most advanced flight protocols available.
Key Growth Drivers
- Massive domestic air travel demand in the U.S. and Canada
- Government-backed modernisation and expansion projects (e.g., FAA's NextGen initiative)
- Strong ecosystem of tech providers driving digital transformation
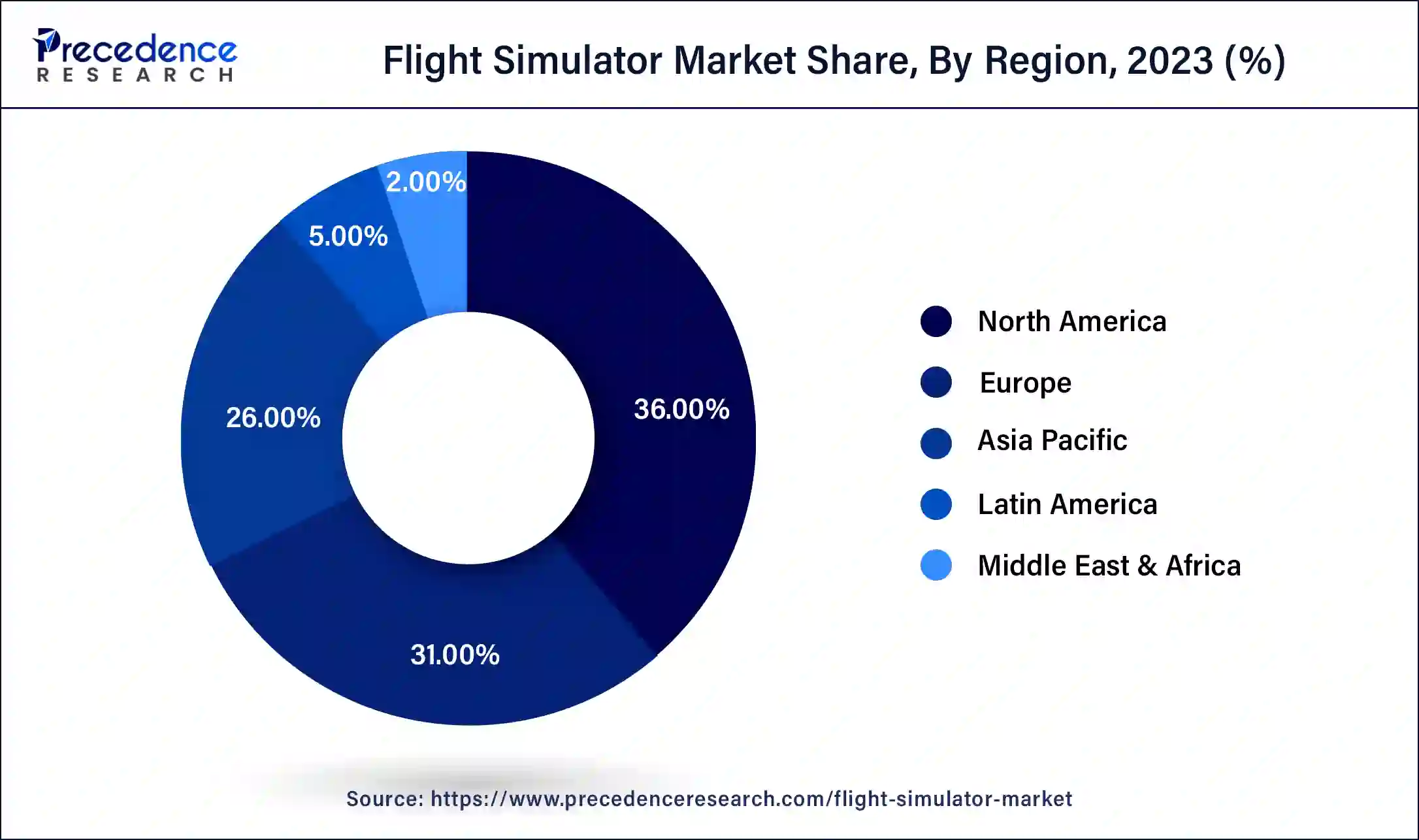
Asia-Pacific is estimated to observe the fastest expansion in the flight simulators market.This is due to commercial aviation growth, including the emergence of low-cost carriers, has fueled the need for pilot training facilities and simulators. In addition, the Asia-Pacific region is home to a diverse range of aircraft operators, including airlines, general aviation companies, and military forces, all of which require effective training solutions. Governments in the region have also recognized the importance of aviation safety and pilot competence, leading to increased investments in pilot training infrastructure.
The Asia Pacific region is experiencing rapid growth in the flight simulator market, driven by increasing air traffic, expanding low-cost airlines, and growing investments in pilot training infrastructure. Countries such as India, China, and Singapore are heavily investing in aviation academies and defense modernization, requiring advanced simulator systems to meet pilot demand. Government support, rising defense budgets, and a booming civil aviation sector areall key contributors to the market's momentum. Additionally, regional partnerships with global simulator providers are accelerating access to cutting-edge technologies.
The Middle East and Africa are expected to grow significantly in the flight simulator market during the forecast period. The demand for flight simulators is increasing in the Middle East and Africa due to a growing fleet expansion. At the same time, various investments are being provided by the government to enhance the pilot training, which is increasing the use of flight simulators. Additionally, the growing innovations for the development of virtual reality (VR) and cloud-based simulators are driving these investments, providing affordable training solutions, as well as enhancing their training. Thus, all these factors are promoting the market growth.
Key Growth Drivers
- Explosive growth in middle-class air travellers
- Government investment in mega airport infrastructure (e.g., Beijing Daxing, Noida International Airport)
- Rise of budget carriers creating demand for efficient, low-cost airport services
The Europe flight simulator market represents a vital and established sector within the global aviation training industry. Comprising countries like the United Kingdom, France, Germany, and Spain, among others, Europe boasts a rich aviation heritage and is home to a diverse range of aviation operators, from commercial airlines to military forces. This diversity has driven a robust demand for high-quality flight simulation training solutions. In the commercial sector, European airlines and flight training organizations rely on advanced simulators, including Full Flight Simulators (FFS) and Flight Training Devices (FTD), for pilot training, type rating, and recurrent training. Furthermore, Europe has a significant military aviation presence, necessitating the use of simulators for military pilot training and mission rehearsal.
Market Overview
- The flight simulator market involved flight simulation equipment and software used for training, entertainment, research, and various aviation-related purposes. Flight simulators are devices or systems that replicate the experience of flying an aircraft in a simulated environment.
- Furthermore, they are a critical tool in pilot training programs, allowing aspiring pilots to develop and refine their skills in a safe and controlled environment. They can simulate various types of aircraft, weather conditions, and emergency scenarios.
- Aerospace companies use flight simulators to test and refine aircraft designs, systems, and performance characteristics before physical prototypes are built. This helps reduce development costs and improve safety.
Technological advancement
The global flight simulator market is witnessing robust growth, propelled by advancements in virtual training technologies and a rising demand for pilot safety and precision. As aviation expands across both commercial and defense sectors, flight simulators are becoming essential tools for cost-effective and risk-free training. Recent innovations have transformed traditional simulation systems into immersive, high-fidelity training environments. Integration of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) has enhanced the realism of cockpit environments, improving trainee engagement and decision-making skills. Advanced AI-driven behavioural modelling enables real-time scenario responses based on pilot actions, while cloud-based simulators allow for remote access and scalability. Moreover, motion tracking systems and multi-screen 3D visualization technologies are increasingly adopted to simulate actual flight dynamics with near-perfect accuracy. These technological upgrades are also reducing operating costs and improving training cycle times.
Flight Simulator Market Growth Factors
- The growth of the flight simulator market is driven by a various factors such as technological innovation, economic factors, safety considerations, regulatory requirements, and the ongoing growth of the aviation industry. These factors may continue to propel the flight simulator market during the forecast period.
- In addition, the aviation industry has been growing globally, leading to a rising demand for well-trained pilots. Flight simulators provide a profitable, efficient and safe way to train new pilots and provide recurrent training for experienced ones. As airlines continue to grow and replace retiring pilots, the demand for flight simulators remains strong, which further boosts the demand for the flight simulator market. For instance, in July 2023, Boeing announced that it is planning to invest $100 million in programs and infrastructure for catering to the need of training facilities in India. According to the company, India requires 31,000 new pilots over the next 20 years; thus, the initiative will support in fulfilling the requirement of pilots.
- Furthermore, continuous advancements in simulation technology, from hardware to software, have significantly enhanced the realism of these systems, attracting both aviation training centers and military organizations. The cost savings associated with simulator-based training, including reduced fuel and maintenance expenses, are compelling for organizations. Also, the growing importance on risk mitigation and safety, as simulators enable trainees to practice various emergency scenarios in a controlled environment, is a key factor driving the demand for the market.
Market Scope
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 9.96 Billion |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 9.31 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 18.02 Billion |
| Growth Rate from 2025 to 2034 | CAGR of 7% |
| Largest Market | North America |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | Type, Platform, Application, and Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Market Dynamics
Drivers
Rise in demand for pilot training
With the global aviation industry undergoing unprecedented growth and a constant need for proficient pilots, flight simulators have developed as a vital solution to meet this demand. As the number of air travelers rises, airlines are growing their fleets and routes, forming a pressing need for well-trained flight crews. Flight simulators provide a flexible training environment and cost-effective solution, enabling aspiring pilots to hone their skills while decreasing the reliance on actual flight hours, which can be prohibitively costly. Moreover, recurrent training for experienced pilots is essential for maintaining proficiency and staying up-to-date with the latest aviation technologies and safety procedures. Flight simulators facilitate this ongoing training by providing a controlled environment for practicing emergency scenarios and complex maneuvers, ultimately enhancing aviation safety.
- For instance, in September 2023, Embraer S.A and CAE Inc. announced the launch of a novel piloting program utilizing the E-Jet E2 full-flight simulator (FFS). The Training Services anticipates extending the training programs for pilots and cabin crews to other strategic locations within CAE's global network.
The pandemic-induced disruptions to traditional training methods underscored the resilience and adaptability of flight simulators. As social distancing and health safety measures became paramount, simulator-based training became the go-to solution to ensure the continuity of pilot education. Regulatory bodies also play a crucial role in driving simulator adoption by mandating simulator hours for pilot certification and recurrent training. This ensures that a certain percentage of a pilot's training must occur within a simulator, creating a consistent demand for simulator products and services. Thus, the rising demand for pilot training, fueled by the growth of the aviation industry and regulatory requirements, positions flight simulators as an indispensable tool in meeting these needs, fostering safety, and promoting cost-effectiveness in the aviation sector.
Restraint
High initial investment costs
Acquiring or developing high-quality flight simulators demands a substantial upfront financial commitment, which can pose a significant barrier to entry for smaller aviation training centers, educational institutions, or organizations seeking to implement simulator-based training solutions. Investing in flight simulators involves not only the purchase of the simulator hardware but also the integration of sophisticated software, maintenance infrastructure, and the creation of a suitable training environment. For particularly smaller players in the aviation industry, these costs can be prohibitively expensive.
Moreover, the expenses do not end with the initial purchase. Ongoing operating and maintenance costs add to the financial burden. Regular updates to software and hardware, compliance with evolving regulatory standards, and the employment of skilled personnel for simulator operation and maintenance contribute to the long-term costs of ownership. This high cost of entry limits the accessibility of advanced flight simulator technology to a broader audience, potentially hindering the overall growth of the market. It can result in a divide where larger, well-funded organizations can fully harness the benefits of simulators, while others are left with limited or suboptimal training resources.
Opportunities
Rise in demand for simulators from the defense sector
Defense organizations of various countries are surging the use of advanced simulators for various applications, and this may drive growth and innovation within the flight simulator industry. Need for realistic and cost-effective pilot training is one of the primary opportunities provided by flight simulators in defense sector. Moreover, the growth in complexity of modern military aircraft and the significance of maintaining combat readiness, advanced simulators are essential tools for ensuring that pilots are well-trained and proficient.
It also plays an important role in organizing military aviators for combat scenarios, complex missions, and tactical maneuvers. Furthermore, simulators are also used for mission rehearsal and planning, supporting military personnel fine-tune strategies, practice operational scenarios, and simulate real-world combat situations. This not only enhances preparedness but also contributes to the safety and success of military missions.
Simulators also enable defense organizations to save significantly on training costs. They reduce the need for expensive live-flight training hours and mitigate the risks associated with actual flight exercises. As military technologies continues to advance, simulators are becoming more and more sophisticated, incorporating state-of-the-art graphics, virtual reality, and high-fidelity controls. This provides an opportunity for flight simulator manufacturers to collaborate with defense agencies or key players in developing tailored solutions that meet the specific training and mission planning needs of modern armed forces.
For instance, in April 2023, Advanced Real-Time Tracking (ART) partnered with Vrgineers, to launch an innovative Mixed Reality (MR) pilot simulation technology. The partnership helps in integrating the SMARTTRACK3/M and XTAL 3 Virtual Reality (VR) headset into a mixed-reality pilot training system for pilot training. Thus, the rising demand for simulators from the defense sector not only offers a lucrative market but also fosters innovation in simulation technology. By delivering high-quality, realistic training experiences and mission planning capabilities, flight simulator providers can position themselves to meet the evolving needs of defense organizations worldwide.
Type Insights
According to the type, the Full Flight Simulator (FFS) segment has held the highest revenue share and is anticipated to expand significantly during the projected period in 2024. FFS provides a highly realistic and immersive training experience, replicating the cockpit of a specific aircraft model in full detail. It can simulate a wide range of flight conditions, including normal and emergency procedures, various weather conditions, and more. These simulators are primarily used for type rating and recurrent training for airline pilots and are certified by aviation authorities such as the FAA and EASA.
FTD offers a less immersive but still effective training experience. FTDs may not replicate the exact cockpit of a specific aircraft model but provide a representative training environment. It is used for various training purposes, including instrument training, procedural training, and initial pilot training. It is generally more cost-effective than FFSs and are used by flight schools, aviation academies, and training centers.
Platform Insights
Based on the platform, the fixed wing simulator is anticipated to hold the largest market share 61% in 2024. Fixed-wing simulators are designed to replicate the flight characteristics and cockpit environments of fixed-wing aircraft, such as commercial airliners, general aviation aircraft, and military fighter jets. It is used for training pilots who will operate fixed-wing aircraft and can range from basic training devices to high-fidelity full flight simulators.
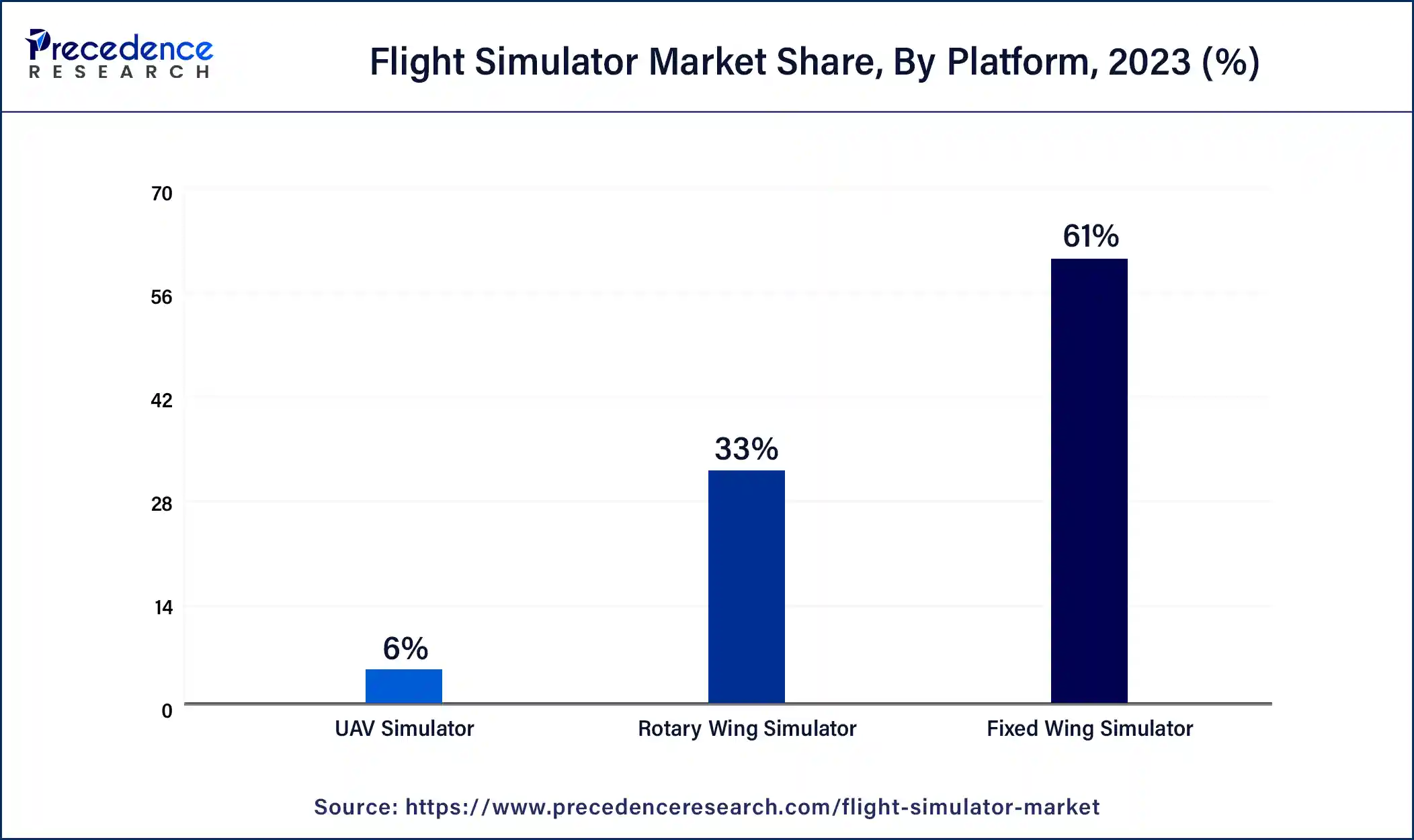
On the other hand, the UAV simulators segment is projected to grow at the fastest rate over the projected period. UAV simulators are used for training operators and pilots of unmanned aerial vehicles, commonly known as drones. They provide a virtual environment for practicing UAV operations, including flight planning, navigation, and mission-specific tasks. It is valuable for both civilian and military applications, such as drone pilot training and mission rehearsal.
Application Insights:
In 2024, the commercial sector had the highest market share on the basis of the application. Commercial flight simulators are used primarily for training civilian pilots and aviation professionals in the commercial aviation sector. They are commonly employed for various purposes, including initial pilot training, recurrent training, type rating training, and proficiency checks. They play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and competence of airline pilots, as well as other personnel in the commercial aviation industry.
The military sector is anticipated to expand at the fastest rate over the projected period. Military flight simulators are designed for training military pilots and personnel involved in military aviation operations. It is used to simulate a wide range of military aircraft, including fighter jets, transport aircraft, helicopters, and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs).
Military flight simulators are instrumental in preparing military personnel for combat scenarios, mission-specific training, and tactical exercises. These simulators help train military pilots to operate complex and advanced aircraft, hone their combat skills, and practice mission planning and execution in a safe and controlled environment.
Flight Simulator Market Companies
- CAE Inc.
- FlightSafety International Inc.
- L3Harris Technologies Inc.
- The Boeing Company
- Thales Group
- TRU Simulation + Training Inc.
- Raytheon Technologies Corporation
- Indra Sistemas S.A.
- Aero Simulation Inc.
- HALVESAN
Recent Developments
- In June 2025, a significant shift in the training of pilots was marked by the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA), making it the first approach for providing a mixed reality (MR) headset that was certified for civil aviation training. The screens, which are cheaper and smaller versions of the full-flight simulators that are used in pilot training final phases, in a flight training cockpit, are successfully replaced by this headset, which is titled as XR-4 and is developed by Varjo, which is startup of Finnish.
- In February 2025, to accelerate the development of Corra's unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) and Hybrid Electric Range-Extending Microturbine Energy System (HERMES), a collaboration between Altair Aerospace Startup Acceleration Program (ASAP) and Meridian Flight Systems was announced. The UAV and hybrid power technologies of Meridian will be enhanced with the use of high-performance computing (HPC) software, simulation, and data analytics of Altair. Moreover, it was stated that the innovation in heavy-lift UAVs will be supported by this collaboration, as per the senior vice president of aerospace and defence at Altair, Pietro Cervellera.
- August 2023: CAE announced an agreement with Batik Air for the 10-year pilot training, at the Asia-Pacific Airline Training Symposium (APATS). The agreement will see CAE operate and deploy an advanced B737 MAX full-flight simulator at Batik Air's facility in Kuala Lumpur.
- May 2023: Lilium N.V. announced its partnership with FlightSafety International (FSI). The partnership helps in FlightSafety as the developer and provider for flight training devices for the Lilium Jet. This consists, mixed-reality and immersive simulators for training, as well as an early flight simulator representative of the Lilium Jet cockpit.
- April 2023:GE Digital announced its partnership with FlightSafety International (FSI) to further optimize flight Simulator Datasimulator data. The partnership helps FSI to use GE Digital's Flight Analytics platform to analyze data produced by its flight simulators, which supports as a pilot training tool by military, commercial, and government, organizations.
Segments Covered in the Report
By Type
- Full Flight Simulator
- Flight Training Devices
By Platform
- Fixed Wing Simulator
- Rotary Wing Simulator
- UAV Simulator
By Application
- Commercial
- Military
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Ask For Sample
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
 Get a Sample
Get a Sample
 Table Of Content
Table Of Content
 sales@precedenceresearch.com
sales@precedenceresearch.com
 +1 804-441-9344
+1 804-441-9344
 Schedule a Meeting
Schedule a Meeting