Modern consumers are shifting toward proactive, preventive, and value-driven wellness choices, shaped by trust, convenience, personalization, and digital influence. Health, ethics, and intelligent technology now guide purchasing decisions, redefining long-term consumer brand relationships.
Contemporary consumer behavior reflects a fundamental reorientation of health, wellness, and performance priorities. Individuals are increasingly adopting preventive, integrative, and evidence-informed approaches to well-being, moving away from episodic or symptom-driven consumption. This article examines key consumer signals that shape purchasing decisions, behavioral patterns, and value perception, highlighting how trust, cognition, convenience, and personalization are redefining modern wellness engagement.
Introduction
A defining consumer signal is the transition from reactive health management toward proactive and preventive wellbeing practices. Consumers are no longer motivated solely by the alleviation of illness but by the optimization of long-term physical and mental resilience. Daily routines increasingly incorporate wellness products positioned as supportive rather than therapeutic. This behavioral shift reflects a growing awareness of lifestyle-related health risks and a desire for sustained vitality across life stages.
What is the Health and Wellness Market Size?
The global health and wellness market size was estimated at USD 6.87 trillion in 2025 and is predicted to increase from USD 7.19 trillion in 2026 to approximately USD 11 trillion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 5.40% from 2025 to 2034.
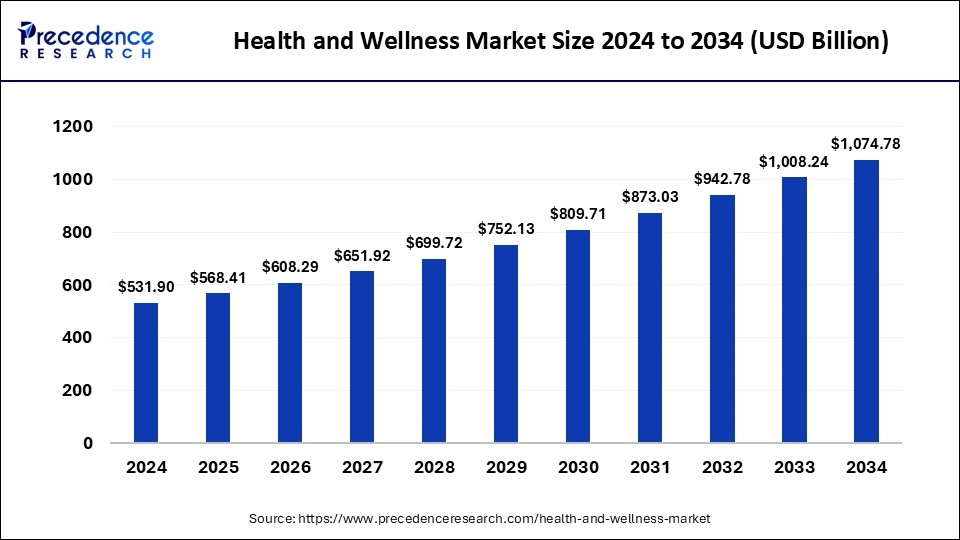
Market Highlights
- North America dominated the global market with the largest share of 38.04% in 2024.
- Asia Pacific is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR during the period.
- By sector, the integrated wellness and personal care services segment held the major market share of 21.72% in 2024.
Factors of Consumer Signals
Consumer signals are the result of a multidimensional interaction between social, economic, psychological, and technological forces. All these factors together define the perception of value, buying habits, and interactions of individuals with health and wellness solutions in the long run. The knowledge of these drivers offers a conceptual framework through which changing consumer behavior can be observed.
- Time Scarcity and Lifestyle Transformation: There is a high rate of urbanization, work environments mediated by digital means, as well as a rise in daily schedules, which have significantly changed the lifestyle pattern. Consumers are increasingly demanding solutions that align with their time-saving habits and reduce mental or behavioral capital. This time deficiency increases the desire for convenience and integrates habitually, promoting the use of products that have perceived benefits without causing inconvenience. Consequently, the use of practicality influences consumption decisions instead of efficacy.
- Increasing Health Consciousness and Preventionist Lying: Increased exposure to health data has increased the level of awareness of the risks to long-term well-being. Consumers are becoming increasingly proactive, with an emphasis on prevention rather than treatment. The changed direction promotes long-term adherence to daily wellness routines and affirms the need for supportive and maintenance-based solutions. Health is considered an asset that needs constant investment instead of periodic attention.
- Psychological Stress and Cognitive Load: Constant stress, screen burnout, and work-related pressure are increasing the pressure on the solutions that are capable of assisting mental health. Consumers are increasingly indicating sensitivity to emotional equilibrium, lucidity, and concentration. This mental background is one of the factors affecting the inclination towards products that appear to be soothing, customizing, and non-invasive. Mental well-being has therefore been made one of the key determinants of consumption behavior.
- Lack of Trust and Credibility Demand: The sceptical attitude of consumers has been promoted by the wide exposure to exaggerated claims and misinformation. Consequently, trust has emerged as a very serious screening process in decision-making. Transparency, scientific validation, and authenticity are gaining popularity among consumers as proxies for credibility. Brands that are unable to develop trust are quickly eliminated.
- Influence and Availability of Information: Digital platforms are a decisive factor in the consumer perception and awareness. Peer reviews, expert commentary, and educational materials have enabled consumers to make their own judgments. Such an information-saturated environment increases positive as well as negative signals, and these improve the adoption or rejection process. Consumer discernment and expectation are hence directly affected by digital literacy.
- Cultural Transformation to the Natural and Holistic Ways of Life: Consumption priorities are being shaped by a wider cultural shift in favor of natural, holistic, and sustainable ways of living. Consumers are becoming increasingly associated with natural solutions as safe, balanced, and compatible in the long run with the body. This cultural orientation favors minimally processed, tradition-based, but modernized products. Values are therefore as much a determinant of consumption as functionalism.
- Economic Factors and Value Perception: Although there is premiumization, value-conscious customers exist. The buying decisions weigh prices against perceived long-run value, quality, and credibility. Goods that are positioned as long-term investments in well-being will be more successful in supporting elevated prices. This is an indication of the change in cost-based assessment to outcome-based value assessment.
- Personal Control and Agency Desire: Consumers are also demanding more control in their health and lifestyle choices. Perceived control is increased by the fact that it is self-selected, customized, and adjusted by changes in consumption patterns. Such an agency enhances interest and dedication, which solidifies adoption on a routine basis. Consumer signals, hence, are not only need-based, but also empowerment-driven.
Continuous Consumer Buying Cycle
Generative Artificial Intelligence: The Changing Curve
Generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) is now a capability shifting to a foundational layer of digital ecosystems in the 21st century. Its history indicates not just a rapid change in the technical field but also a more fundamental one in the integration of intelligence, creativity, and decision-making into the economic and social systems. What started as a creation of content is increasingly becoming a dynamic, context-sensitive engine changing workflows, value creation, and human-machine interaction.
- Automation to Augmentation: Initial uses of AI were mostly aimed at automation, copying repetitive and rule-based activities with efficiency and scale. GenAI will be the turning point for augmentation systems that operate in collaboration with people and not to take over them. GenAI expands cognitive abilities and accelerates issue resolution by creating language, code, designs, and strategic conceptualization. This development makes AI not a replacement for human judgment, but a multiplier of human creativity and the depth of their analysis.
- Sharpening Contextual Intelligence: One of the major characteristics of the development of GenAI is its tendency to comprehend shared concepts more accurately and discern the tone, meaning, and intent. Models are going beyond shallow pattern recognition to a more profound semantic reasoning on multimodal inputs of text, images, audio, and structured data. Contextual intelligence enables more relevant outputs, adaptations, and domain-specific applications. Consequently, GenAI is becoming increasingly integrated with decision-support systems rather than being a standalone tool.
- Entry into Core Business and Knowledge Systems: GenAI is quickly moving out of peripheral research and development to core business operations. The processes of knowledge management, research synthesis, customer engagement, product design, and strategic planning are reorganized with the help of AI-assisted processes. GenAI integration transforms the way organizations view institutional knowledge, enabling them to put it into action. In the long run, GenAI will become a continuous level of intelligence, capable of learning through the organizational data and with business priorities.
- Creation and Expertise have been Democratized: The other important pathway that is of critical concern is the democratization of complex capabilities. GenAI reduces the entry barriers of tasks that were previously specialized technical or creative skills. High-quality content and software prototypes, as well as analytical insights, can now be created by individuals and small teams more rapidly than ever before. The productivity, entrepreneurship, and competitive forces are the consequences of this redistribution of capability, especially in the knowledge-driven fields.
- Human-AI Co-Creation Model Emergence: The interaction between humans and GenAI is moving towards co-creation, rather than command-based interaction. Iterative refining, feedback-based, and instant refinements are taking center stage in successful usage. Such transformation demands new abilities, including critical analysis, the ability to put things into perspective, and ethical judgment, instead of technical expertise alone. The trend suggests that prosperity will not be in access to AI but in the possibility to act wisely with it.
- Structural Constraints of Governance, Ethics, and Trust: Governance and trust are emerging as some of the defining limitations to the development of GenAI as it grows. The regulatory and organizational responses are being defined by concerns related to bias, data provenance, intellectual property, and accountability. Societal norms and institutional safeguards will also significantly contribute to the future path of GenAI, along with the performance of the models. Sustainable adoption is emerging as a requirement for responsible deployment.
- Towards Adaptive and Autonomous Intelligence: In the future, GenAI is moving towards more dynamic, self-informed systems that can more autonomously act within certain limits. These systems will be more predictive, personalized, and real-time in aiding decision-making in complex situations. Nevertheless, complete autonomy is still limited by the necessity of having human control, especially in high-stakes areas. The movement is directed towards symbiotic intelligence, whereby human values drive the power of machines.
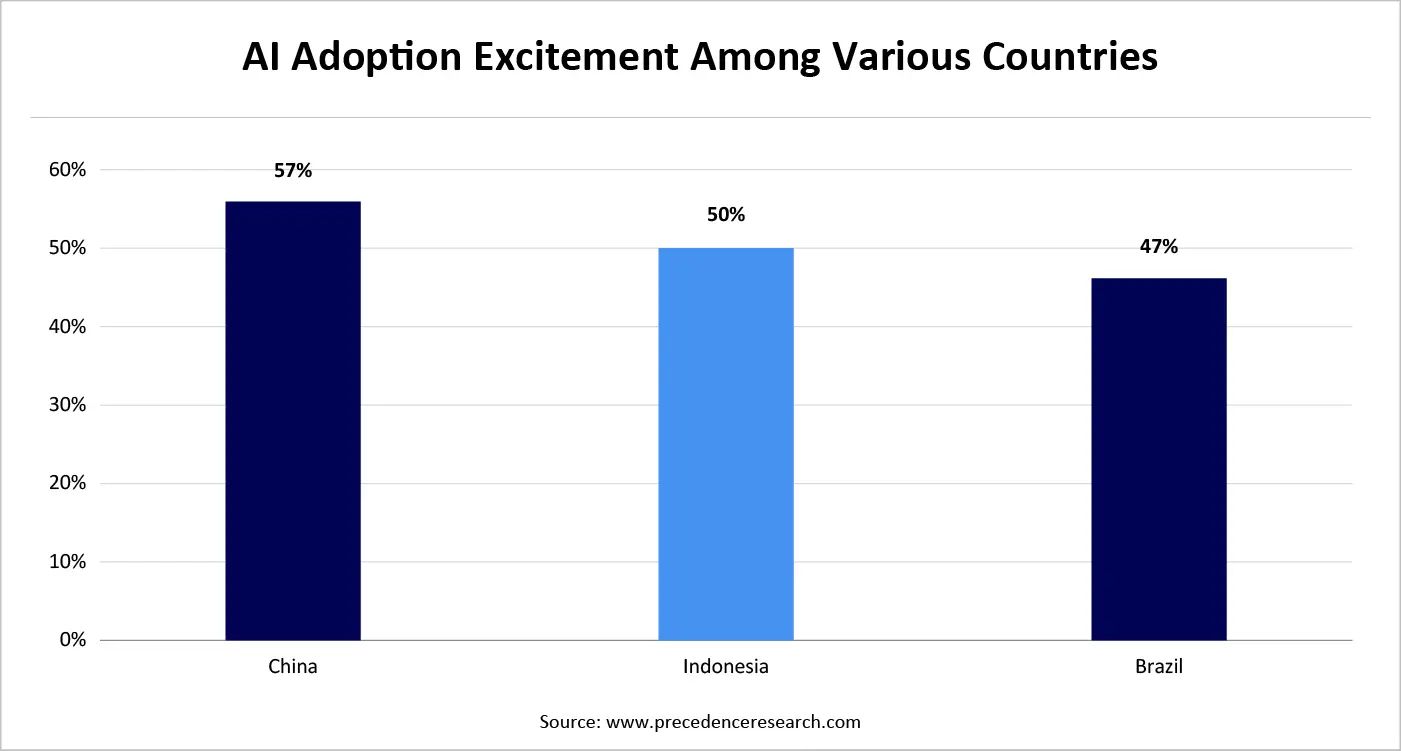
The above graph demonstrates the rate of respondents that were excited by the adoption of Al in diverse sectors across numerous countries. China, Indonesia, and Brazil are countries with the highest awareness and excitement for Al adoption globally.
Structured Behavioral Classification of Consumers
It is possible to categorize consumers systematically according to their motivation, decision-making styles, and patterns of engagement. These types of understanding help in the knowledge of how value is perceived, adopted, and maintained in various contexts.
- Value-Driven Consumers: Value-driven consumers do not give much attention to novelty, but to utility, reliability, and long-term benefit. Their buying preferences are based on a rational analysis of price and the result. They want products that demonstrate stability in performance and a reasonable justification of price. Trust, transparency, and quality that can be depended upon for brand loyalty. This segment is usually knowledgeable and sceptical toward exaggerated assertions.
- Convenience-Oriented Consumers: Consumers who are convenience-oriented are driven by convenience, accessibility, and time efficiency. Their solutions need to fit into current routines and reduce efforts. Ease of use, accessibility, and painless purchasing have a significant impact on their choices. Although this does not always make them price-insensitive, they are willing to pay a high price to have the least complexity. Addiction is a major factor that contributes to maintaining activity in this segment.
- Experience-Seeking Consumers: Experience-seeking consumers prefer engaging with emotions, newness, and sensuality. They are attracted to products that offer differentiation, storytelling, or discovery. This segment is better inclined to innovativeness and early adoption. Perceived experience usually prevails over functional benefits. Their loyalty revolves around brand identity, aesthetic, and narrative authenticity.
- Health- and Performance-Centered Consumers: The motivation of these consumers is the optimization of physical, mental, or emotional performance. They are keen on finding solutions that help them be enduring, focused, resilient, or have a generally good mood. Perceived efficacy, formulation integrity, and alignment with personal goals impact decision-making. They are well-versed and ready to spend on quality products. Retention is pegged on consistency and quantifiable gain.
- Trust-Centric Consumers: Consumers who tend to trust are trust-centric and believe in credibility as the main concern in their purchasing behavior. They are based on evidence, expert endorsement, and open communication. This group is risk-averse and is, therefore, conservative when it comes to new or unproven offerings. Consistency, moral behavior, and responsibility create loyalty in brands. When the trust is built, the behavior change is minimal.
- Digital-Native Consumers: Online ecosystems, peer reviews, and social validation are very influential to digital-native consumers. They can easily operate online and make decisions promptly. Interaction is informed by content quality, responsiveness, and community. Personalization and quick access to information are the expectations of this group. Digital fluency and quality of interaction are closely related to brand relevance.
- Purpose-Driven Consumers: Purpose-oriented consumers are those who align their buying behaviors to personal values like sustainability, ethics, and social responsibility. They do not just assess the product; they also evaluate practices. The trust is heavily impacted by transparency in sourcing, production, and corporate behavior. Strong brand loyalty is built on emotional compatibility and similar values. For this group, consumption is a continuation of identity.
- Experimental and Early Adoption Consumers: Interest and innovation drive these types of consumers. They are also proactive in finding new solutions and can accept imperfect things. The feedback and advocacy of early adopters affect the overall consumer perception. They have frequent but impactful engagement and are vital in indicating forthcoming market direction.
| Democratization | Average trap | Model collapse |
| Definition | When GenAI enables more and broader consumers to participate in consumption that was previously inaccessible to them | When models predict the next most likely token, outputs tend to converge toward average consumer behavior |
| Consumer | Human consumer
|
Hybrid consumer
|
| Data and model challenges |
Data reflect human biases
|
Models produce average biases
|
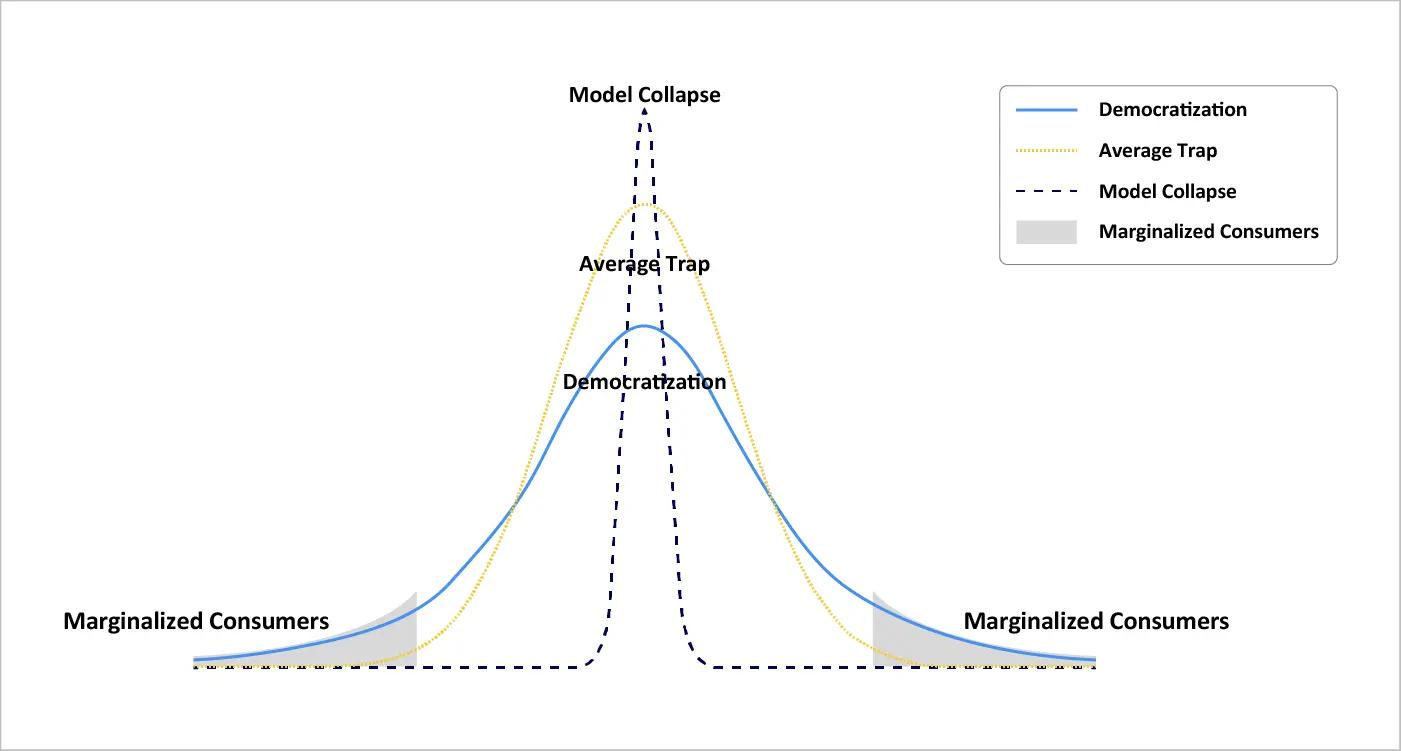
The above graph illustrates the distribution of democratization, average trap, and model collapse. The horizontal axis represents the range of consumer preferences or data distribution, while the vertical axis represents density probability. It indicates that the average trap affects marginalized consumers more, whereas every consumer suffers during model collapse.
From Global to Local: Consumers Turning Towards Indigenous Brands
Consumers are increasingly aware of purchasing products from local brands rather than international brands to promote domestic growth. This trend has been observed in both developed and developing countries. It is estimated that approximately 47% of global consumers consider locally owned companies important for their purchase decisions. The growing need for domestic products is associated with exorbitant import duties, global supply chain complexity, and the increasing population. Global trade agreements signal the importance of buying local products from the market. The average tariff rate in the second Trump Administration rose from 2.5% to 27% from January 2025 to April 2025.
Consumers prefer local products as they wish to promote domestic businesses and benefit from their high affordability. Countries such as the U.S., Canada, Japan, China, and India account for the highest consumer population with a preference for local products. Enterprises make constant efforts to tailor their products and services to local markets, localize sourcing, and make efficient strategic portfolio and brand decisions. This is usually applicable for enterprises active in categories such as apparel, cosmetics, and household supplies.
Future of Consumer Signals
Consumer signals are entering into a more complex, granular, and strategic stage. The nature of signals that consumers broadcast, in terms of behavior, preferences, and engagement, will change in response to increasing levels of their own and other consumers' insights, and by becoming increasingly digitally embedded and value sensitive. Customer signals will no longer be determined by what consumers say but rather by how they behave, change, and engage with each other in interdependent touchpoints in the future.
In the future, consumer indicators will be highly contextual by time, surroundings, emotional condition, and purpose. The dynamic interpretation of behavior will replace the traditional demographic segmentation. Micro actions to be inferred to give signals will include navigation patterns, dwell time, and the sequence of choices. This change is an indication of a transition from conceptualizing consumers to fluid situationally decision-makers rather than fixed personas.
With digital interfaces as the primary interface, consumer signals will begin to surface out of hybrid digital-human ecosystems. Transactional data will be collected with voice, sentiment, and conversational nuance. Human cues, including hesitation, confidence, and emotional tone, will become an object of analysis. Such convergence will enable a more profound interpretation of intent and trust, not just using classical quantitative measures. Reliability will become a key indicator, as such, deduced by the regularity of interaction, readiness to exchange information, and the richness of the relationship. Trust will be indicated by consumers through the acceptance of subscriptions, loyalty to long-term relationships, and being open to personalization. In turn, the loss of trust will become apparent at a young age contributing to disengagement and selectivity. Trust monitoring will be essential for maintaining long-term relationships with consumers. Personalization will become a two-directional signal exchange instead of a value proposition. Consumers will prefer systems that learn, adapt, and respond in real-time, and their reactions to personalization will also be their indicators of relevance and alignment. This will be informed by future engagement strategies based on acceptance, modification, or rejection of personalized offerings.
The consumer experience will be optimized, and so will signal accuracy under this feedback loop. Ethical considerations and data sovereignty will limit and define the nature of the future of consumer signals. Consumer comfort or resistance will be indicated through consent behavior, platform choice, and level of engagement. Even respect for privacy as such will be a competitive differentiator. Those organisations that are responsible for the way they interpret signals will still have access to more quality and richer insights.
Lastly, the future of consumer signals lies within their interpretation, rather than gathering. The amount of data available will only increase, and tactical benefits will be gained through the capacity to elicit meaning, trends, and insightfulness. Consumer signals will not be appreciated based on their number, but based on their ability to make human-focused decisions on time.
Conclusion
Consumer signals are primarily driven by a shifting trend towards preventive, integrative, and evidence-based approaches. The growing disposable income has a positive impact on consumer signals, allowing them to spend more on travel, entertainment, and wellness. The future of customer signals suggests a wider move of intelligent, anticipatory, and ethical consumer interactions. Signals will be made continuous, predictive, and highly contextual to allow organisations to be more aligned with the intent and values of consumers. Individuals who prepare to understand such signs accurately, empathically, and responsibly will determine the future of consumer relationships.
About the Authors

Aditi Shivarkar
Aditi, Vice President at Precedence Research, brings over 15 years of expertise at the intersection of technology, innovation, and strategic market intelligence. A visionary leader, she excels in transforming complex data into actionable insights that empower businesses to thrive in dynamic markets. Her leadership combines analytical precision with forward-thinking strategy, driving measurable growth, competitive advantage, and lasting impact across industries.

Aman Singh
Aman Singh with over 13 years of progressive expertise at the intersection of technology, innovation, and strategic market intelligence, Aman Singh stands as a leading authority in global research and consulting. Renowned for his ability to decode complex technological transformations, he provides forward-looking insights that drive strategic decision-making. At Precedence Research, Aman leads a global team of analysts, fostering a culture of research excellence, analytical precision, and visionary thinking.

Piyush Pawar
Piyush Pawar brings over a decade of experience as Senior Manager, Sales & Business Growth, acting as the essential liaison between clients and our research authors. He translates sophisticated insights into practical strategies, ensuring client objectives are met with precision. Piyush’s expertise in market dynamics, relationship management, and strategic execution enables organizations to leverage intelligence effectively, achieving operational excellence, innovation, and sustained growth.





 Request Consultation
Request Consultation

