What is the Non-Injectable Insulin Market Size?
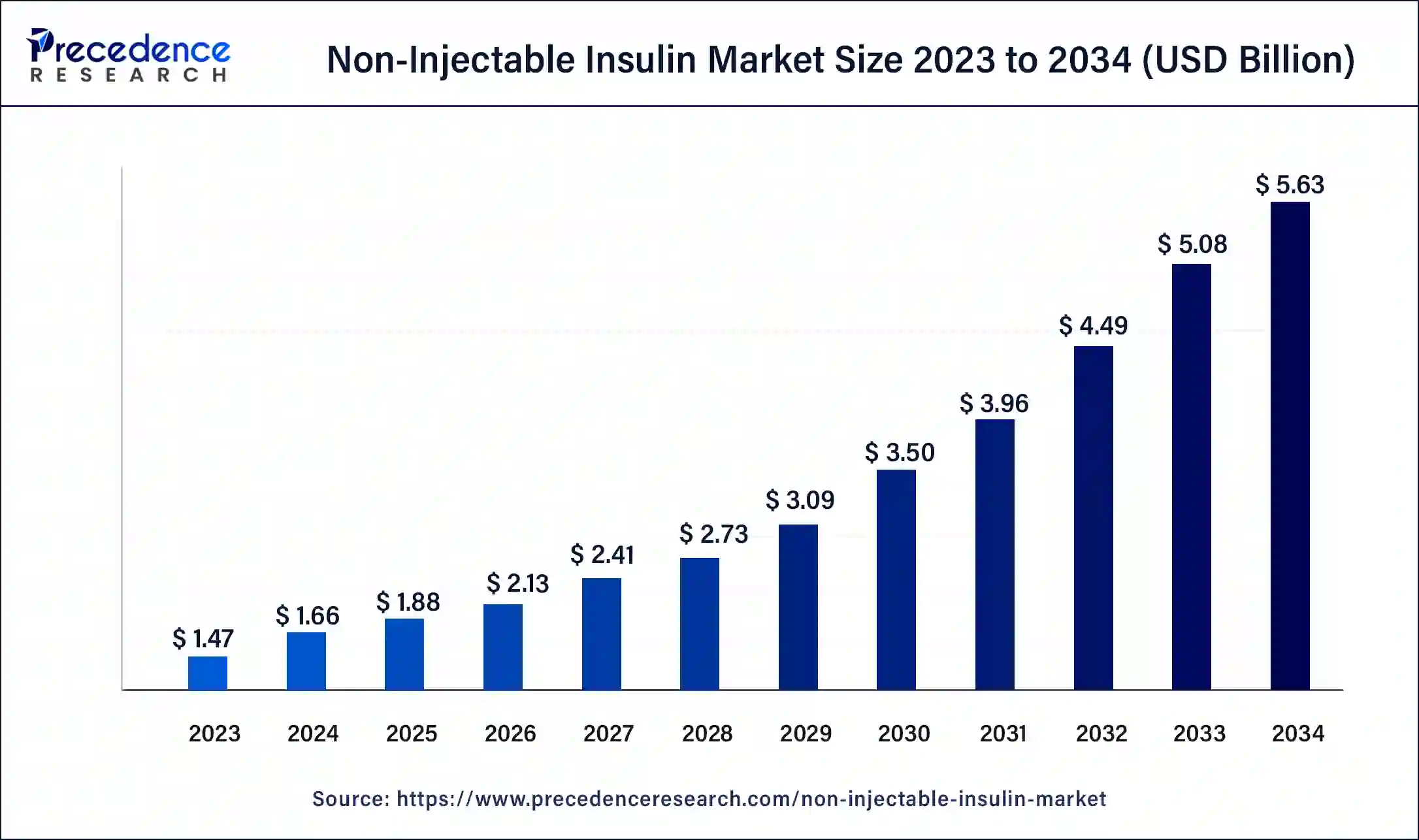
The global non-injectable insulin market size is calculated at USD 1.88 billion in 2025 and is predicted to increase from USD 2.13 billion in 2026 to approximately USD 5.63 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 12.99% from 2025 to 2034.
Non-Injectable Insulin Market Key Takeaways
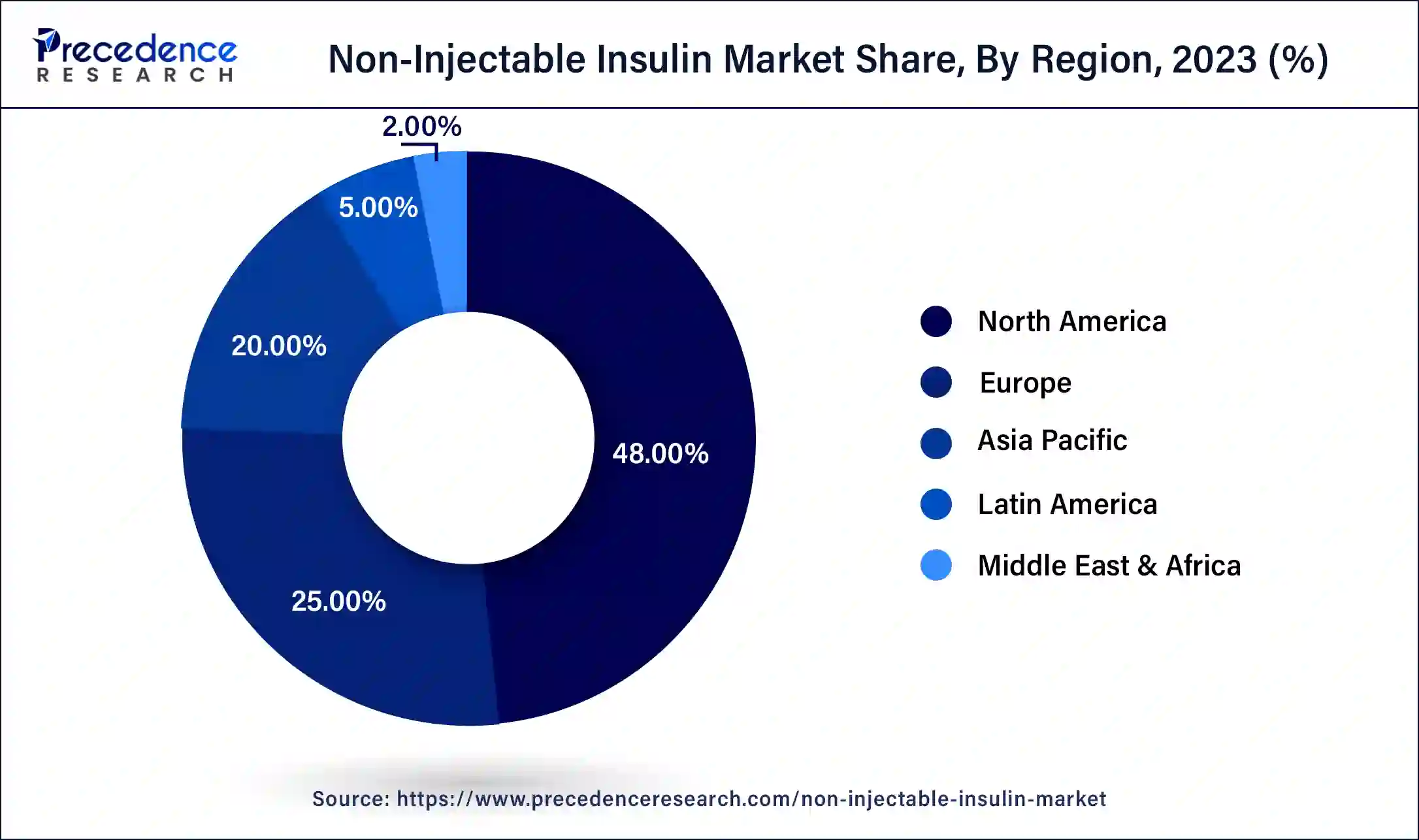
- North America led the global market with the highest market share of 48% in 2024.
- Asia-Pacific is estimated to expand at a remarkable CAGR of 15.3% during the forecast period.
- By Product, the pills segment has held a major revenue share of 45% in 2024.
- By Product, the sprays segment is anticipated to grow at a notable CAGR of 14.3% during the projected period.
- By Distribution Channel, the hospital pharmacies segment had the largest market share of 49% in 2024.
- By Distribution Channel, the online pharmacies segment is projected to expand at the fastest CAGR over the projected period.
Strategic Overview of the Global Non-Injectable Insulin Industry
The non-injectableinsulin marketpertains to a sector within the pharmaceutical industry dedicated to insulin delivery methods that diverge from conventional needle injections. This market chiefly encompasses alternative approaches to administering insulin, such as inhalable insulin, oral insulin, and transdermal patches. Non-injectable insulin alternatives are designed to offer more convenient and less discomforting options for individuals with diabetes, potentially enhancing patient compliance and overall quality of life. These innovations are continually advancing, propelled by breakthroughs in drug delivery technology and the growing desire for more patient-friendly solutions in the management of diabetes. The non-injectable insulin market embodies a promising frontier in diabetes care and treatment.
Non-Injectable Insulin Market Growth Factors
The non-injectable insulin market stands as a dynamic niche within the pharmaceutical sector, providing inventive substitutes to the conventional insulin injection method for managing diabetes. It encompasses diverse strategies, including inhalable insulin, oral insulin, and transdermal patches, with the goal of offering patients more convenient and less discomforting choices.
Promising industry trends and growth catalysts underscore a bright future for this market. An escalating preference among patients for non-injectable insulin is driven by the convenience it affords, potentially enhancing adherence and overall patient satisfaction. Pioneering advancements in drug delivery technology have led to the development of more dependable and efficient non-injectable insulin alternatives, propelling market expansion. Moreover, the global surge in diabetes cases adds to the market's growth trajectory as more individuals seek user-friendly approaches to managing their condition.
Nevertheless, the non-injectable insulin market confronts its fair share of challenges. Stringent regulatory approval processes for these innovative delivery methods demand extensive clinical trials to ensure safety and efficacy. The competition within the diabetes treatment landscape remains fierce, necessitating substantial research and development investments to distinguish one's offerings. The affordability and insurance coverage aspects can pose impediments for patients seeking access to non-injectable insulin alternatives.
Despite these hurdles, the market presents enticing business prospects. Enterprises capable of navigating the regulatory landscape and crafting patient-centric, inventive products have the potential to capture a substantial portion of the burgeoning diabetes management market. Strategic partnerships with healthcare providers and insurers and investments in marketing and educational efforts to heighten awareness about non-injectable insulin choices can bolster consumer adoption and spur market growth.
In summation, the non-injectable insulin market represents a rapidly evolving and innovative segment within the pharmaceutical industry, providing patient-friendly alternatives for diabetes management. It is underpinned by favorable industry trends and growth drivers, though it does face regulatory complexities. For businesses willing to invest in innovation, collaboration, and awareness-building, this market offers significant opportunities within the ever-expanding realm of diabetes care.
Market Outlook
- Market Growth Overview: The Non-Injectable Insulin market is expected to grow significantly between 2025 and 2034, driven by the growing demand for alternative delivery methods, advances in drug formulation and delivery systems, and increasing prevalence of diabetes. The shift towards at-home diabetes management is fueling demand for non-injectable options and digital health integration.
- Sustainability Trends: Sustainability trends involve improving patient access and health equity through flexible pricing and awareness initiatives. Environmentally, the industry is addressing concerns by focusing on energy-efficient manufacturing, optimizing supply chains, and adopting eco-friendly packaging and waste management programs for associated devices.
- Major Investors: Major investors in the Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, and Sanofi.
- Startup Economy: The startup economy in the market is focused on bioavailability and novel formulations, specialized device innovation, and significant venture capital funding.
Market Scope
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Growth Rate from 2025 to 2034 | CAGR of 13.2% |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 1.88 Billion |
| Market Size in 2026 | USD 2.13 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 5.63 Billion |
| Largest Market | North America |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | By Product and By Distribution Channel |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East & Africa |
Market Dynamics
Driver
Advancements in drug delivery technology
The non-injectable insulin market's growth is significantly propelled by the ongoing advancements in drug delivery technology. These cutting-edge technological progressions are reshaping the landscape of diabetes management, rendering non-injectable insulin alternatives more effective, dependable, and attractive to both patients and healthcare professionals. To commence, drug delivery technology breakthroughs have paved the way for innovative insulin administration methods, including inhalable insulin, oral insulin, and transdermal patches. These groundbreaking developments have the potential to supplant or complement traditional injections, presenting patients with convenient choices that alleviate the physical and emotional burdens associated with diabetes care.
Moreover, these advancements have elevated the precision and consistency of insulin dosing, amplifying the overall efficiency of non-injectable insulin products. Patients now benefit from more precise and tailored insulin therapy, leading to superior glycemic control and an elevated quality of life. Furthermore, drug delivery technology has facilitated the creation of inventive devices and formulations that are user-friendly and straightforward to employ. This fosters patient adherence to treatment regimens, consequently fueling the acceptance and demand for non-injectable insulin solutions. In summary, the ongoing evolution of drug delivery technology plays a pivotal role in making non-injectable insulin alternatives more accessible, potent, and patient-centered, thus driving the growth of this market and revolutionizing the domain of diabetes management.
Restraints
Patient acceptance
The resistance of patients to adopt non-injectable insulin methods acts as a notable hindrance to the expansion of the non-injectable insulin market. Despite the evident advantages and convenience of non-injectable insulin options, certain individuals exhibit reluctance to shift away from the familiar and well-established practice of insulin injections. Several factors contribute to this reluctance. Firstly, patients may harbor concerns regarding the efficacy and dependability of non-injectable insulin approaches, fearing that they might not offer the same degree of blood sugar control as conventional injections. These doubts can lead to hesitance in transitioning to alternative insulin delivery methods.
Secondly, there exists a psychological attachment to insulin injections that patients have grown accustomed to over time. Some individuals may have developed a sentimental connection to this method and might encounter difficulties breaking away from the established routine. Overcoming these challenges necessitates effective educational campaigns and enhanced awareness, along with continuous technological advancements in non-injectable insulin options to ensure they instill the same level of confidence and contentment as injections. Moreover, healthcare professionals play a vital role in guiding patients toward embracing and integrating these alternative insulin delivery methods into their diabetes management routines.
Opportunities
Expanding patient base
The expansion of the patient base presents a compelling opportunity within the non-injectable insulin market. As the global incidence of diabetes continues to surge, there is a growing and diverse population in need of effective solutions for managing their condition. This demographic transformation offers a substantial opening for non-injectable insulin products to cater to an ever-widening audience. A larger patient base allows pharmaceutical companies to scale up production and extend their market reach, potentially reducing the unit cost of non-injectable insulin offerings and enhancing affordability. It also encourages increased investment in research and development, fostering the creation of a wider array of innovative insulin delivery options.
Furthermore, the diverse requirements of this expanding patient base fuel the development of a range of non-injectable insulin products, facilitating customization and adaptation to individual patient needs. This tailoring can result in improved glycemic control, heightened patient compliance, and the cultivation of enduring patient loyalty, all of which contribute significantly to the market's expansion.
Product Insights
According to the product, the pills segment held a 45% revenue share in 2024. The pills segment holds a significant share in the non-injectable insulin market due to several factors. First, oral insulin pills are often more convenient and less invasive than injections, making them more appealing to patients. Secondly, they offer a potential alternative for patients who have a fear of needles or discomfort associated with injections. Additionally, pills are easier to administer, promoting better patient adherence to treatment regimens. As technology and research advance, the development of effective and reliable oral insulin options has gained traction, further solidifying the pills segment's dominant position in the non-injectable insulin market.
The sprays segment is anticipated to expand at a significant CAGR of 14.3% during the projected period. The sprays segment commands a substantial growth in the non-injectable insulin market primarily due to its convenience and patient-friendly attributes. Inhalable insulin sprays offer a less invasive alternative to injections, making them attractive to patients seeking easier and less painful methods for managing diabetes. Moreover, these sprays have witnessed significant advancements in drug delivery technology, ensuring precise and effective dosing. As a result, patients and healthcare providers increasingly favor this segment, contributing to its dominant growth within the non-injectable insulin market.
Distribution Channel Insights
In2024, the hospital pharmacies segment had the highest market share of 49% on the basis of the distribution channel. The hospital pharmacies segment holds a significant share in the non-injectable insulin market due to several reasons. First, hospitals are key centers for diabetes treatment and care, making them prominent distribution points for non-injectable insulin products. Second, healthcare professionals in hospital settings often prescribe and administer these products, influencing patient choices. Third, hospital pharmacies provide a reliable supply chain, ensuring consistent availability. Lastly, the clinical setting of hospitals inspires patient trust in non-injectable insulin options. This combination of factors positions hospital pharmacies as major players in promoting and providing non-injectable insulin solutions to a wide patient base.
The online pharmacies segment is anticipated to expand at the fastest rate over the projected period. Online pharmacies have garnered significant growth in the non-injectable insulin market due to their convenience, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness. Patients can easily browse and purchase non-injectable insulin products from the comfort of their homes, reducing the need for physical visits to traditional pharmacies. This is particularly advantageous during the COVID-19 pandemic and for patients with mobility issues. Additionally, online platforms often offer a broader range of products and competitive pricing, making them an attractive option for patients seeking non-injectable insulin solutions. The convenience and variety offered by online pharmacies have contributed to their substantial market growth.
Regional Insights
U.S. Non-Injectable Insulin Market Size and Growth 2025 to 2034
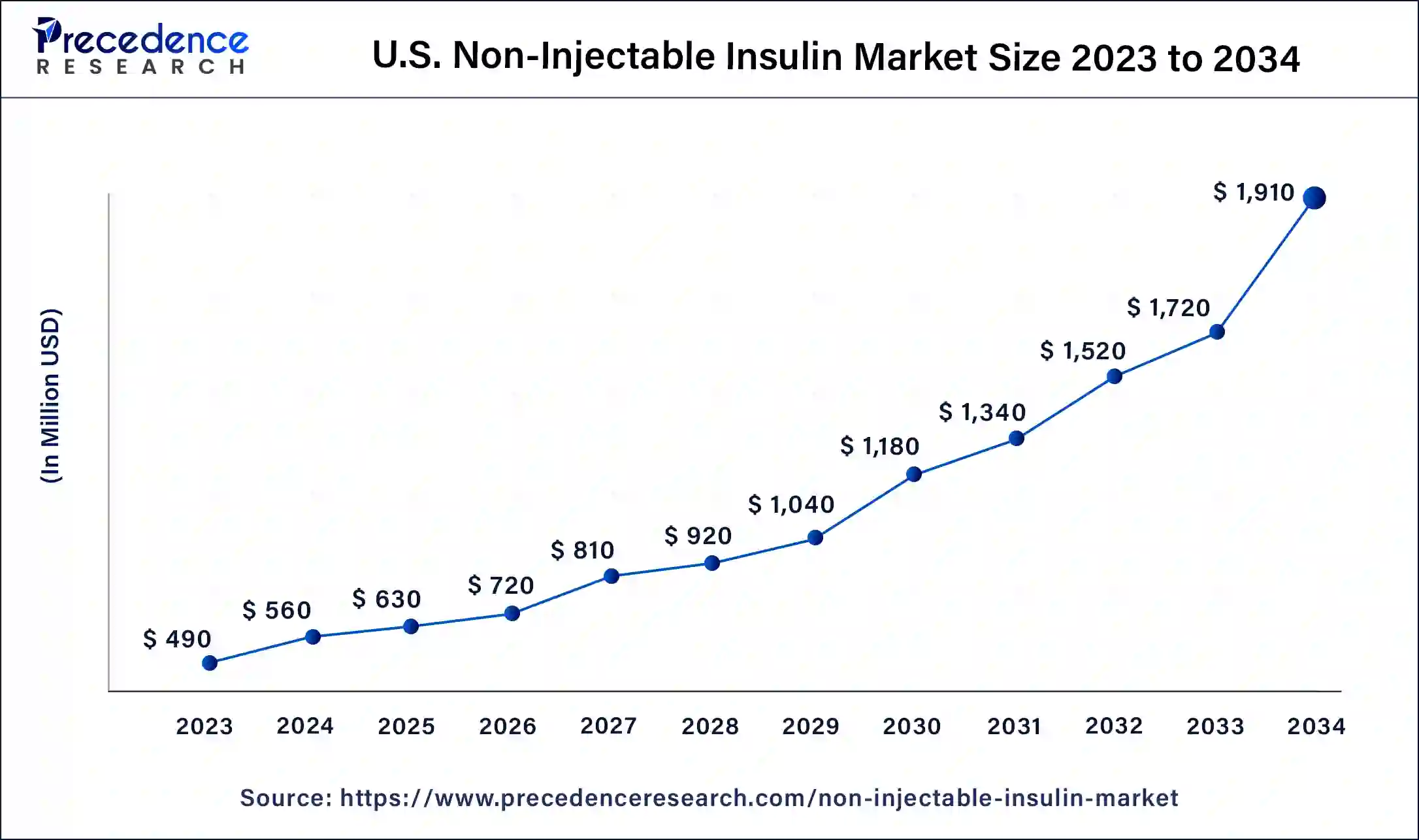
The U.S. non-injectable insulin market size was estimated at USD 630 million in 2025 and is predicted to be worth around USD 1,910 million by 2034, at a CAGR of 13.05% from 2024 to 2034.
North America has held the largest revenue share 48% in 2024. North America commands a significant portion of the non-injectable insulin market due to a confluence of factors. High diabetes prevalence, a robust healthcare infrastructure, and a strong emphasis on research and innovation in the region contribute to its prominence. Furthermore, patient awareness and willingness to adopt non-injectable insulin alternatives are notable. The regulatory landscape is generally favorable, with efficient approval processes for cutting-edge healthcare solutions. The region's strong demand for convenient and patient-centric diabetes management options solidifies North America's substantial presence in the non-injectable insulin market.
Asia-Pacific is estimated to observe the fastest expansion with the highest CAGR of 15.3% during the forecast period. The Asia-Pacific region dominates a significant share of the non-injectable insulin market due to several factors. The region's high diabetes prevalence, rapid urbanization, and expanding healthcare infrastructure have contributed to increased demand for innovative diabetes management solutions. Additionally, growing awareness of non-injectable insulin's advantages, such as convenience and reduced pain, has fueled adoption. Government initiatives and collaborations with pharmaceutical companies have further promoted market growth. As a result, Asia-Pacific's diverse and vast patient population, along with supportive healthcare policies, positions it as a major player in the non-injectable insulin market.
U.S. Non-Injectable Insulin Market Trends
The U.S. has a high prevalence of diabetes and a strong patient preference for convenient, pain-free delivery methods like oral and inhalable options. Recent technological advancements, including improved formulations and integrated digital health tools, are enhancing product efficacy and ease of use. The market is competitive, with major pharmaceutical companies investing heavily in R&D and strategic initiatives to capture market share
China Non-Injectable Insulin Trends
China has, for cost-effective insulin pens, facilitated the government's volume-based procurement (NVBP) policy. While no commercial oral or inhalable insulin products are yet available due to technical challenges, there is significant R&D in alternative non-insulin injectables like GLP-1 agonists. The market is increasingly utilizing faster-growing online distribution channels and is set for potential future disruption through R&D in transformative therapies like stem cell treatment.
United Kingdom Non-Injectable Insulin Trends
The U.K.'s non-injectable insulin market is limited by product availability and stringent NHS cost-effectiveness requirements. The only currently available option, inhaled insulin Afrezza, sees limited adoption due to a lack of NHS funding and historical market skepticism. Despite a strong latent patient demand for needle-free alternatives, market growth hinges on future product innovations that can successfully navigate the NHS reimbursement hurdles.
Value Chain Analysis
- Non-Injectable Insulin Market Value Chain Analysis
Research & Development (R&D) and Clinical Trials
This foundational stage involves scientific research into novel drug delivery mechanisms, such as oral, inhalable, and nasal pathways, and the formulation of insulin to maximize bioavailability and stability.
Key Players: MannKind Corporation, Novo Nordisk A/S, Eli Lilly and Company, Oramed Pharmaceuticals Inc., and research institutions like the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF). - Manufacturing
This stage involves the large-scale production of insulin and its formulation into specific non-injectable formats, such as a powder for inhalation or tablets for oral consumption.
Key Players: MannKind Corporation, Novo Nordisk A/S, Eli Lilly and Company, and third-party contract manufacturing organizations (CMOs) specializing in complex drug delivery systems. - Distribution and Logistics
Finished products are distributed through a complex supply chain network from manufacturing facilities to wholesale distributors, hospital pharmacies, retail pharmacies, and directly to consumers via e-commerce channels.
Key Players: Cardinal Health, Inc., McKesson Corporation, Walgreens Boots Alliance, and global logistics providers. - Marketing and Sales
Companies promote their non-injectable insulin products to healthcare professionals, hospitals, and directly to patients using digital marketing, educational campaigns, and sales force efforts.
Key Players: MannKind Corporation, Novo Nordisk A/S, and the in-house sales and marketing teams of all major pharmaceutical companies.
Non-Injectable Insulin Market Companies
- Novo Nordisk
Novo Nordisk is a major global player investing heavily in diabetes care R&D, including novel drug delivery systems that might one day lead to non-injectable options. - Sanofi
Sanofi holds a significant share of the global insulin market and invests in R&D for next-generation diabetes treatments, including potential non-injectable formulations. - Eli Lilly
Eli Lilly is a global leader in diabetes treatment innovation, actively researching and developing new insulin formulations and alternative delivery methods. - MannKind Corporation
MannKind is a key player and the only company with an FDA-approved inhaled insulin product, Afrezza, which directly competes in the non-injectable market. - Biocon
Biocon is an India-based biopharmaceutical company that focuses on affordable biosimilars and novel insulins, including research into oral insulin formulations. - Janssen Pharmaceuticals
Janssen, a subsidiary of Johnson & Johnson, has been involved in diabetes research and drug development, though their direct contributions to a commercial non-injectable insulin product are limited. - Adocia
Adocia is a biotechnology company specializing in innovative formulations of proteins and peptides, including ultra-rapid-acting insulin options that can be used in pumps or potentially other novel delivery systems. - Oramed Pharmaceuticals
Oramed is a key player focusing specifically on the development of an oral insulin capsule (ORMD-0801) designed for the treatment of diabetes, representing a potential paradigm shift in delivery. - Dance Biopharm
Dance Biopharm is a private company focused on developing an inhalable insulin product using a proprietary soft-mist inhaler technology. - Medtronic
Medtronic is a leader in diabetes management devices, specifically insulin pumps and continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems, which are alternative delivery methods to traditional syringes.
Verily Life Sciences (formerly known as Google Life Sciences)
Verily, a subsidiary of Alphabet, focuses on data-driven health tech solutions, including research into a smart contact lens for glucose monitoring and other innovative technologies. - Zafgen
Zafgen was a biopharmaceutical company focused on developing novel therapies for obesity and metabolic diseases, including diabetes. - Senseonics
Senseonics contributes a long-term implantable continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) system, which, while a diagnostic tool, facilitates better diabetes management and helps optimize insulin delivery. - Bigfoot Biomedical
Bigfoot Biomedical is focused on developing an integrated insulin delivery system that includes an insulin pump, a continuous glucose monitor (CGM), and a smartphone app.
Recent Developments
- In February 2022, Biocon made a significant move by acquiring Viatris' biosimilar portfolio for a substantial sum of USD 3.335 billion. This strategic acquisition bolstered Biocon's biosimilar product offerings and had a positive impact on the company's revenue generation.
Segments Covered in the Report
By Product
- Pills
- Sprays
- Others
By Distribution Channel
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Online Pharmacies
- Drug Stores
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Ask For Sample
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
 Get a Sample
Get a Sample
 Table Of Content
Table Of Content
 sales@precedenceresearch.com
sales@precedenceresearch.com
 +1 804-441-9344
+1 804-441-9344
 Schedule a Meeting
Schedule a Meeting