Technetium-99m Market Size and Forecast 2025 to 2034
The global technetium-99m market size accounted for USD 7.15 billion in 2024 and is predicted to increase from USD 7.49 billion in 2025 to approximately USD 11.46 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 4.83% from 2025 to 2034.The market is growing due to the rising demand for diagnostic imaging procedures, especially in oncology and cardiology.
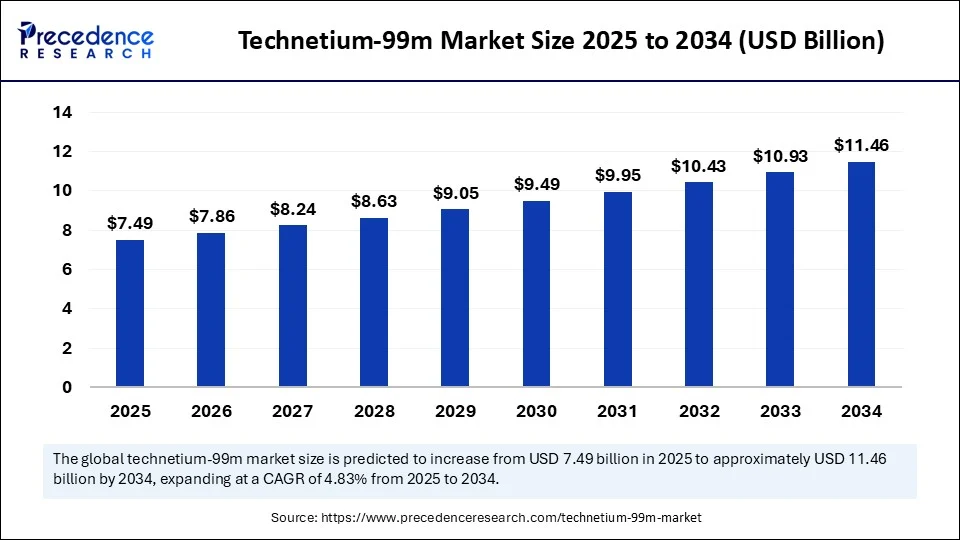
Technetium-99m MarketKey Takeaways
- In terms of revenue, the technetium-99m market was valued at USD 7.15 billion in 2024.
- It is projected to reach USD 11.46 billion by 2034.
- The market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 4.83% from 2025 to 2034.
- North America dominated the technetium-99m market with the largest share in 2024.
- Asia Pacific is expected to grow at the fastest rate between 2025 and 2034.
- By clinical service, the cardiac scan segment held the largest share of the market in 2024.
- By clinical service, the bone scan segment is expected to grow at the fastest rate during the forecast period.
- By isotopic application, the SPECT segment held the largest share of the market in 2024.
- By isotopic application, the gamma camera segment is expected to grow at the fastest rate in the upcoming period.
- By end-user, the hospitals segment dominated the market in 2024.
- By end-user, the diagnostic centers is the fastest-growing segment in the market.
How is Artificial Intelligence (AI) Transforming the Production and Application of Technetium-99m?
By improving productivity, precision, and clinical results throughout the supply chain, Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing the manufacturing and use of technetium-99m (Tc-99m). To guarantee a consistent and economical supply of Tc-99m, AI is used in production to enhance Mo-99 extraction procedures, forecast equipment failures, and optimize reactor and cyclotron operations. Through real-time anomaly detection and production parameter tuning, it also supports quality control, increasing yield and purity. AI enhances diagnostic imaging in clinical settings by reducing radiation doses, facilitating quicker image reconstruction, and improving SPECT scan resolution. Additionally, AI-powered technologies aid in automated scan interpretation, facilitating speedier and more precise diagnoses and, ultimately, better patient care.
Market Overview
The global technetium-99m market is witnessing steady growth, driven by an increase in the number of cases of chronic illnesses, including cancer, heart disease, and conditions relating to bones, that need sophisticated diagnostic imaging. Nuclear medicine utilizes technetium-99m extensively due to its excellent physical characteristics, short half-life, and high diagnostic precision. The increasing demand for non-invasive and early-stage diagnostic procedures, combined with the growing adoption of SPECT and hybrid imaging systems, is driving market expansion. Improvements are also aiding growth in isotope supply chains, technological developments in radiopharmaceutical formulations, and the spread of nuclear medicine infrastructure throughout developing nations. Nonetheless, supply constraints and regulatory obstacles associated with the production of radioisotopes remain major issues for interested parties.
Why is Tc-99m Gaining Traction in the Diagnostic Imaging Industry?
The technetium-99m is gaining traction due to its critical role in nuclear medicine, particularly for accurate, safe, and cost-effective diagnostic imaging. Numerous clinical applications, including cardiac, bone, renal, and cancer scans, are made possible by its advantageous nuclear properties, which include a short half-life and optimal gamma emission. Long-term market demand has been fueled by rising rates of chronic illness, growing awareness of early disease detection, and growing use of SPECT and SPECT/CT technologies. The global adoption of technetium-99m-based procedures is also being aided by healthcare systems' growing investments in diagnostic infrastructure, particularly in emerging economies.
Technetium-99m MarketGrowth Factors
- Increasing prevalence of chronic diseases: Rising cases of cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and neurological disorders have increased the demand for nuclear imaging using Technetium-99m.
- Advancements in diagnostic imaging technologies: Ongoing innovation in SPECT and hybrid imaging systems boost the use of technetium-99m for enhanced accuracy and early disease detection.
- Rising geriatric population: The growing elderly population is more prone to chronic illnesses, increasing the need for medical imaging using isotopes like technetium-99m.
- Supportive government initiatives: Increased funding for nuclear medicine and collaborations with reliable radioisotope supply chains are fueling market growth.
- Short half-life and ideal imaging properties: Technetium-99m 6-hour half-life and excellent gamma-ray emission, making it highly suitable for real-time, safe diagnostic imaging.
- Growing awareness and adoption of nuclear medicine: Medical professionals and healthcare facilities are increasingly adopting nuclear diagnostic tools, expanding market demand.
Market Scope
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 11.46 Billion |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 7.49 Billion |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 7.15 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate from 2025 to 2034 | CAGR of 4.83% |
| Dominating Region | North America |
| Fastest Growing Region | Asia Pacific |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | Clinical Service, Isotopic Application,End-User, Application, and Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Market Dynamics
Drivers
High Utilization in SPECT Imaging
Technetium-99m is widely used in over 80% of all nuclear medicine procedures, particularly in SPECT scans, due to its gamma-ray emission at 140 keV and its ideal physical characteristics, including a 6-hour half-life. These characteristics enable patients to receive minimal radiation exposure while still receiving high-quality imaging. It can be used to diagnose a variety of conditions because of its exceptional image resolution. Tracers based on technetium-99m are preferred by medical professionals for evaluating organ function, bone metabolism, and blood flow. Market demand remains stable because SPECT is still the preferred imaging modality over others. Its use is also being further supported by the increasing modernization of SPECT systems to hybrid technologies.
Rising Diagnostic Imaging Procedures
The rising volume of diagnostic imaging procedures drives the growth of the technetium-99m market. Tc-99m use is being driven largely by the global increase in diagnostic imaging, especially for skeletal disorders, cardiovascular diseases, and cancer detection. Nuclear imaging is crucial to patient care, as healthcare systems place a strong emphasis on early and accurate diagnosis. Hospitals and clinics are doing more scans as a result of the rising prevalence of chronic illnesses. Additionally, the need for imaging is increased by routine health screenings in older populations. As minimally invasive diagnostic techniques become more popular, radiopharmaceuticals such as technetium-99m are gaining increasing popularity. In developed healthcare markets like the United States, this trend is especially evident in Western Europe and Canada.
Restraints
Short Life and Logistical Challenges
Technetium-99 m has a half-life of approximately 6 hours. Production, transportation, and clinical use must be carefully coordinated. Any delay in them can lead to canceled or postponed scans, whether it's because of transportation problems or generator availability. For rural or isolated hospitals without nearby radio pharmacies, this is particularly difficult. Workflows in imaging become much more complex and expensive due to the requirement for reliable just-in-time delivery. Additionally, imaging schedules can be disrupted by delays in customers' clearance for imported molybdenum or airport logistics. Hospitals frequently must rearrange patient schedules to accommodate generator arrival times, which leads to inefficiencies and unhappy patients. Even small chains can have a nationwide impact.
- In December 2024, the American Society of Nuclear Cardiology (ASNC) reported a 50% reduction in Tc-99m supply over three weeks due to an unplanned shutdown of the HFR reactor in Petten, Netherlands, resulting in rescheduled imaging and wasted tracer inventory.
(Source: https://www.asnc.org)
High Costs
High costs associated with Tc-99m production hampers the growth of the technetium-99m market. It takes a large financial commitment to set up nuclear medicine services, including shielded buildings, cyclotrons, generators, and procedures for handling radioactive materials. Facilities must abide by safety, transportation, and environmental regulations, which adds complexity. Due to these overheads, hospitals with limited resources or those that are small may decide not to use Tc-99m imaging. Operating costs are also raised by ongoing quality assurance and compliance monitoring. Mid-sized diagnostic centers frequently cannot afford these expenditures, particularly in emerging economies. Additional strain is added by stringent licensing procedures and staff training requirements. Additionally, to maintain compliance with radiation safety regulations, frequent audits and upgrades are required.
Opportunities
Expansion of Nuclear Imaging in Emerging Markets
Emerging economies, such as India, Brazil, and parts of Southeast Asia, are rapidly expanding their nuclear medicine infrastructure, creating immense opportunities in the technetium-99m market. As healthcare spending increases and awareness about early disease detection grows, the demand for affordable, reliable imaging tools such as Tc-99m rises. There's an opportunity for international suppliers and local radio pharmacies to collaborate on technology transfer and capacity building. Lower production costs and favorable regulations in these regions add further incentives.
Hybrid Imaging Modalities Supporting Tc-99m Use
The increasing number of hybrid systems being installed among hospitals permits the use of Tc-99m with enhanced anatomical correlation. This creates the possibility of re-establishing Tc-99m as a cutting-edge imaging agent despite PET competition. Businesses can obtain a competitive advantage by providing bundled packages of imaging devices and radiotracers. Additionally, SPECT-based diagnostics in cardiology, oncology, and bone scans are still supported by clinical guidelines.
Clinical Service Insights
What Made Cardiac Scans the Dominant Segment in the Technetium-99m Market in 2024?
The cardiac scans segment dominated the technetium-99 market with the largest revenue share in 2024. This is mainly due to the increased prevalence of heart conditions like coronary artery disease and congestive heart failure, in which nuclear cardiology is now a common diagnostic technique. A precise and non-invasive assessment of myocardial viability and perfusion can be obtained through cardiac SPECT imaging, which uses agents labeled with technetium-99m. SPECT systems are widely used in hospitals for cardiac imaging, particularly in North America and Europe. In addition, ongoing developments in radiopharmaceutical formulations are improving the effectiveness and safety of cardiac scans. Established procedures and reimbursement support further cement the segment's dominance.
Meanwhile, the bone scans segment is expected to grow at the fastest rate in the upcoming period because they play a vital role in the early detection of skeletal abnormalities like infections, tumors, microfractures, and metastases. Nuclear imaging in orthopedics is now much more necessary due to the growing elderly population, which is more vulnerable to diseases like osteoporosis and arthritis. Bone metastases are frequently monitored in oncology using technetium-99m bone scans, particularly in patients with breast and prostate cancer. The use of bone scans is expanding in both developed and emerging economies as healthcare systems around the world place an increasing emphasis on early diagnosis and preventive care. Their growing use is further augmented by their role in the diagnosis and rehabilitation of sports injuries.
Isotopic Application Insights
Why Did the Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography Segment Dominate the Technetium-99m Market in 2024?
The single photon emission computed (SPECT) segment dominated the market with a major revenue share in 2024. Due to its ideal properties as a radiotracer, Tc-99m finds applications in SPECT. It offers precise 3D imaging, which is essential for identifying anomalies in tissues and organs, particularly the heart, brain, and bones. By providing both functional and anatomical information, the SPECT/CT combination further improves diagnostic accuracy. Large corporations in the medical imaging sector are constantly improving SPECT systems with faster acquisition times and higher resolution. Using sophisticated detectors such as cadmium zinc telluride (CZT) also reduces radiation exposure and enhances image clarity. Because of these technological advantages, SPECT is the method that clinicians around the world prefer.
The gamma camera segment is expected to grow at the fastest rate in the coming years, driven by its low cost, simplicity of use, and growing popularity in independent diagnostic facilities. Gamma cameras have historically been used in conjunction with SPECT, but they can also be used separately for planar imaging in the diagnostics of the thyroid, skeleton, and kidneys. Opportunities in mobile imaging services and point-of-care diagnostics have been made possible by the portability and miniaturization of more recent gamma camera models. These systems are being used more and more in emerging economies as an affordable way to expand nuclear imaging infrastructure. Additionally, advances in technology have enhanced the sensitivity and resolution of gamma cameras, making them competitive substitutes for fundamental nuclear diagnostic requirements. Their increasing usefulness in research and clinical settings fuels ongoing demand.
End-User Insights
How Does the Hospitals Segment Dominate the Market?
Hospitals are the dominant end-users of technetium-99m-based diagnostics due to their comprehensive imaging capabilities and integration of nuclear medicine departments. They cater to a large patient base and are typically the first point of contact for diagnostic procedures. Hospitals are also more likely to afford and maintain complex imaging equipment such as SPECT and PET/CT systems. Additionally, they benefit from established supply chains for radiopharmaceuticals, enabling consistent access to Technetium-99m isotopes. The ability to handle emergency cases and inpatient diagnostic needs reinforces their dominant position. With multi-specialty capabilities and specialized nuclear medicine teams, hospitals continue to account for the majority of Tc-99m usage globally.
On the other hand, the diagnostic centers segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR during the projection period due to the growing patient volumes undergoing diagnostic procedures. These facilities offer faster access to diagnostics than hospitals, frequently with shorter wait times and cheaper prices. Nuclear imaging modalities are one of the new services that diagnostic centers are offering as the demand for healthcare in urban and semi-urban areas grows. To set up internal isotope handling and imaging infrastructure, many are collaborating with equipment suppliers and pharmaceutical companies. High-throughput imaging scalability and flexibility make them an essential growth engine in the Tc-99m value chain. In addition, the rising demand for decentralized care and outpatient services contributes to segmental growth.
Regional Insights
Which Region Holds the Largest Share of the Global Technetium-99m Market?
North America dominated the technetium-99m market by holding the largest share in 2024. This is mainly due to its sophisticated healthcare system, extensive nuclear medicine departments, and established radiopharmaceutical supply chains. The region performs a high volume of nuclear diagnostic procedures, particularly in the fields of cardiology and oncology, where technetium-99m is routinely used. Government support for isotope production, regular equipment upgrades, and extensive insurance coverage all play a big role in market leadership. The region's leading market position is also maintained by public-private partnerships in the development of diagnostic technologies and radiopharmaceuticals, which guarantee ongoing innovation and supply chain effectiveness.
Asia Pacific is the fastest-growing region, driven by rapidly expanding healthcare infrastructure, rising investment in diagnostic imaging, and increasing awareness of early disease detection. Healthcare providers across the region are increasingly adopting advanced nuclear medicine technologies to meet the rising demand for non-invasive diagnostics. Government initiatives aimed at improving access to modern healthcare services and the emergence of private diagnostic chains are further accelerating growth. The region also benefits from increasing demand for outpatient diagnostic services and a shift in focus toward preventive healthcare. These factors together are fostering a favorable environment for the accelerated adoption of Technetium-99m in nuclear imaging.
Europe remains a notable region in the technetium-99m market, characterized by a mature healthcare system, strong presence of nuclear medicine professionals, and structured diagnostic protocols. Regulatory support for the use of radiopharmaceuticals and the integration of nuclear imaging into routine clinical workflows sustains the region's relevance. Ongoing investments in hybrid imaging technologies and radiopharmaceutical innovation continue to make Europe a significant contributor to the global technetium-99m landscape. Public health programs emphasizing cancer and cardiac disease screening also contribute to regional market growth.
Technetium-99m Market Companies

- Advanced Accelerator Applications S.A.
- Advanced Cyclotron Systems, Inc
- Bayer AG
- GE Healthcare
- Philips Healthcare
- Siemens Healthineers
- Eckert & Ziegler
- IBA Radio Pharma Kft
- Medi Radio Pharma
- Lantheus Holdings Inc
- Nordion Inc
- Sumitomo Heavy Industries
- Jubilant Life Science
- China Isotope & Radiation Corporation
- SDS Lifesciences Pvt Ltd
- BWX Technologies, Inc.
Recent Developments
- In May 2025, Lantheus Holdings, Inc. announced a definitive agreement to sell its single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) business to Illuminated Holdings, Inc. Under the terms of the agreement, SHINE will acquire Lantheus' SPECT business, including its diagnostic agents (TechneLite (Technetium Tc 99m generator), NEUROLITE (Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc 99m Bicisate for Injection), Xenon Xe-133 Gas (Xenon Xe-133 Gas), and Cardiolite (Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc99m Sestamibi for Injection)), the portion of the North Billerica, Massachusetts campus that manufactures Lantheus' SPECT products, and the SPECT-related Canadian operations.
(Source: https://www.globenewswire.com) - In April 2025, Curium received FDA approval for its generic version of the Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc 99m Pentetate Injection, often referred to as DTPA (diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid). Curium is now able to offer hospitals and nuclear pharmacies a suite of products used in ventilation/perfusion (V/Q) scans, streamlining product fulfillment and bolstering the supply chain to include a second supplier of this medication.
(Source: https://www.biospace.com)
Segments Covered in the Report
By Clinical Service
- Bone Scans
- Renal Scans
- Cardiac Scans
- Neurology Scans
By Isotopic Application
- Gamma Camera
- Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography
By End-User
- Hospitals
- Diagnostic Centers
- Others
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Ask For Sample
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
 Get a Sample
Get a Sample
 Table Of Content
Table Of Content
 sales@precedenceresearch.com
sales@precedenceresearch.com
 +1 804-441-9344
+1 804-441-9344
 Schedule a Meeting
Schedule a Meeting