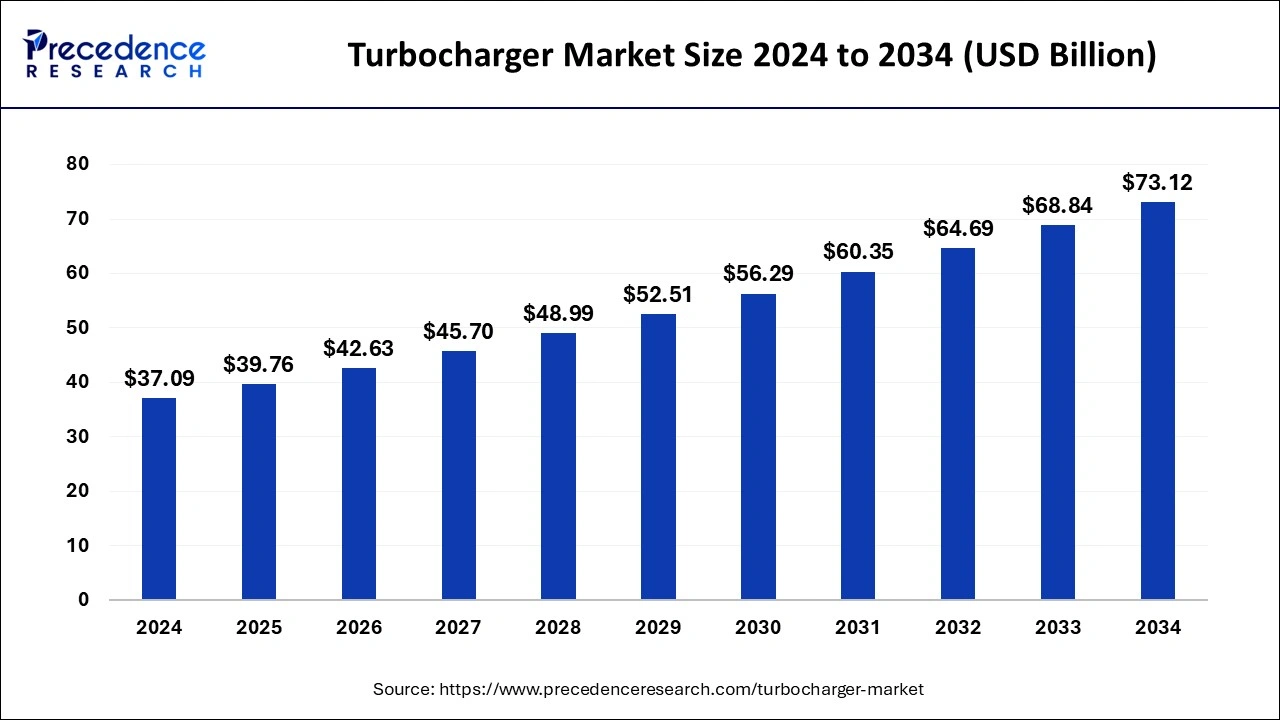
Turbocharger Market Size and Forecast 2025 to 2034
The global turbocharger market size was estimated at USD 37.09 billion in 2024 and is predicted to increase from USD 39.76 billion in 2025 to approximately USD 73.12 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 7.02% from 2025 to 2034.
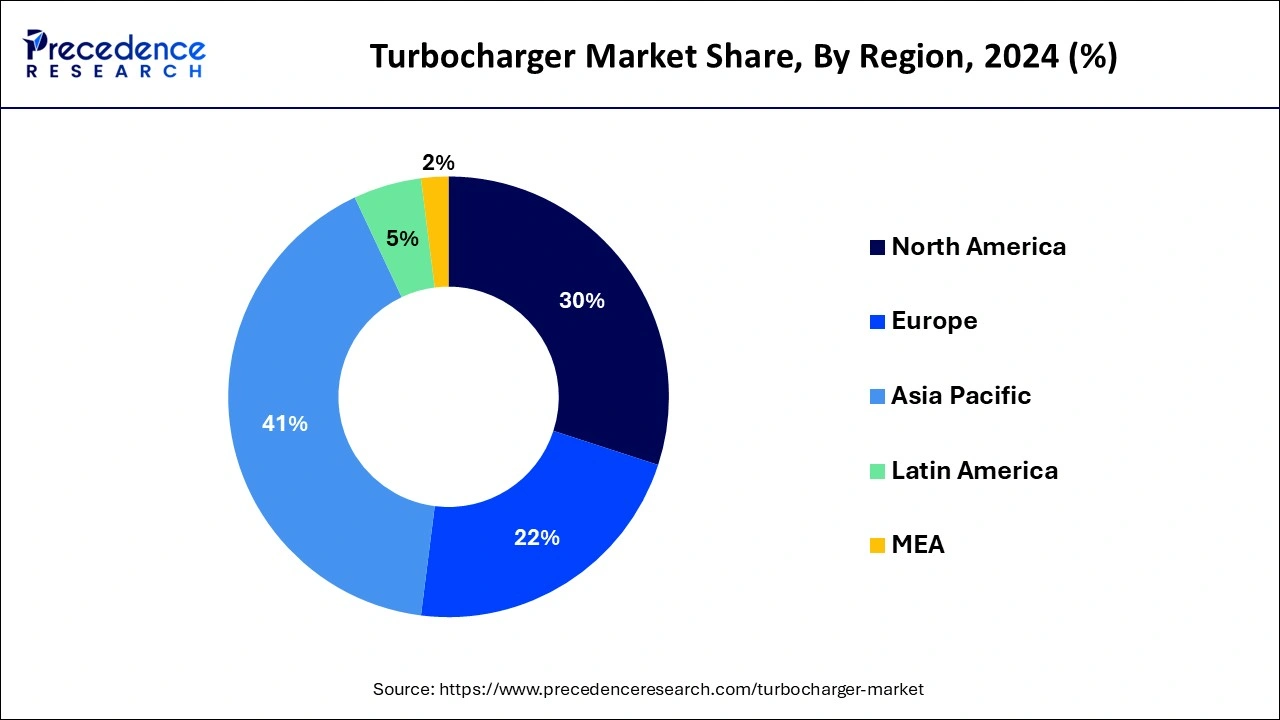
Turbocharger Market Key Takeaways
- Asia Pacific region led the global market with a market share of 41% in 2024.
- By Technology, the twin-turbo segment has accounted revenue share of 46% in 2024.
- By Material, the cast Iron segment has generated a revenue share of 69% in 2024.
- By Fuel Type, the diesel segment has captured a revenue share of around 59% in 2024.
- By End User, the OEM type has held 69% of the total revenue share in 2024.
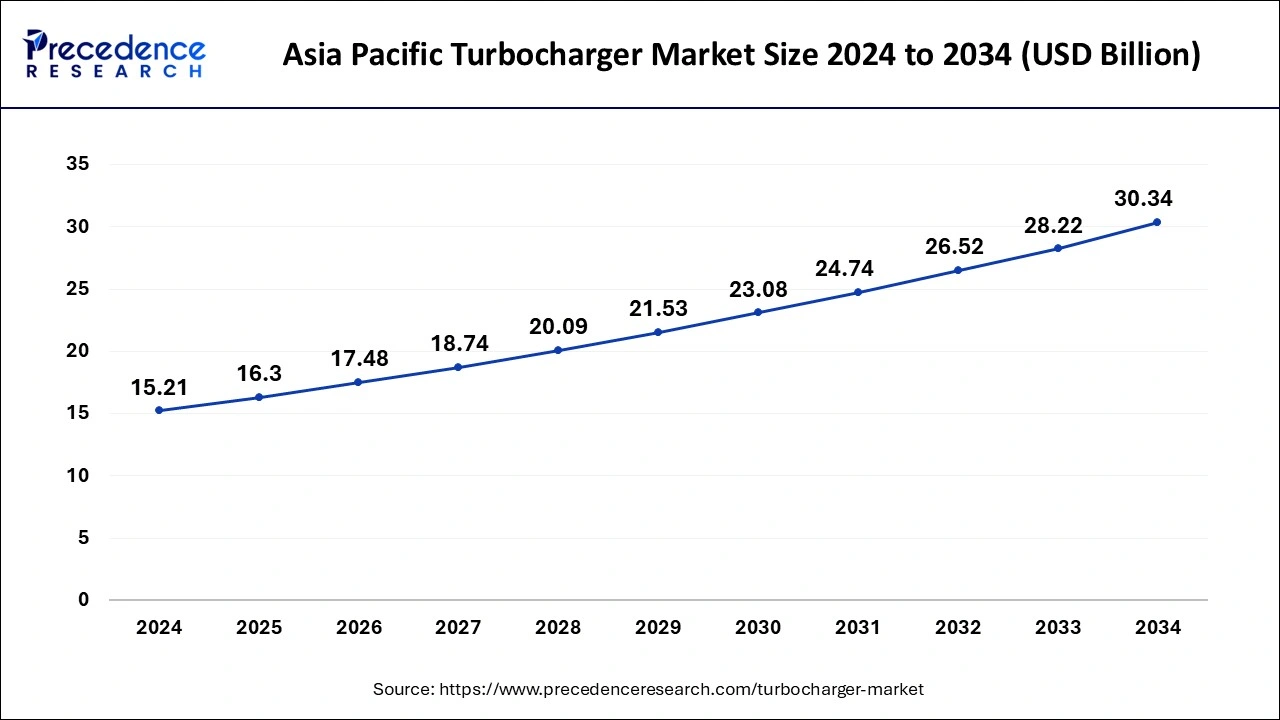
Asia PacificTurbocharger Market Size and Forecast 2025 to 2034
The Asia Pacific turbocharger market size reached USD 15.21 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to be worth around USD 30.34 billion by 2034, poised to grow at a CAGR of 7.15% from 2025 to 2034.
The necessity to fulfill the Environmental Protection Agency's (EPA) fuel efficiency and emissions rules, as well as the rising demand for high-performance automobiles, are the key drivers of turbocharger expansion in the North American aftermarket. Increased average vehicle life, shifting customer preferences for high-power cars, and increased knowledge of replacement and maintenance needs in Europe and North America are further factors influencing the aftermarket turbocharger market growth. Because pick-up truck sales are so strong in the US, North America also has the largest LCV market in the world. However, the main factor in the poor penetration of turbochargers in North American LCVs is that they are often driven by petrol.
Market Overview
A fundamental component of internal combustion (IC) engines, turbochargers boost output by boosting air intake in the process of a combustion chamber with the aid of expelled burned air. Because IC engines need more air to burn more fuel for big power output, which reduces their efficiency, turbochargers are essential for improving efficiency by delivering compressed air.
As these chargers guarantee maximum engine performance and increased fuel efficiency, the global turbocharger industry is anticipated to have a noticeable expansion in the years to come. Particularly, a turbocharger operates without a power supply and performs best at high engine speeds. It is propelled by the engine's exhaust gases that have been burned. Currently, the automobile and aerospace sectors make heavy use of this technology. For instance, to produce enormous amounts of power even under difficult and hot circumstances, manufacturers use turbochargers in the engines of fast racing vehicles.
Turbocharger Market Growth Factors
Due to the limited supply of gasoline, fuel prices are currently soaring daily, and customers' top worry is fuel economy. Vehicle performance is also influenced by the engine. As a result, automakers are under pressure to create effective engines that can meet both demands and provide enhanced performance and fuel efficiency simultaneously. In order to maximize fuel efficiency following the Corporate Average Fuel Economy criteria, which are applicable worldwide, turbochargers are typically turbo-boosted engines that are small in size.
Additionally, these chargers provide several benefits, including improved combustion chamber air intake, high engine efficiency, and reuse of expelled air. In particular, turbochargers run without a power supply and perform best in fast engines. Improved engine economy and performance are therefore seen as two of the main factors propelling the growth of the global turbocharger industry.
The increased desire for automakers to comply with environmental pollution rules is the main factor behind the continued expansion of turbochargers. Increased manufacture of automobiles, vessels, and planes on a worldwide scale also supports it. Additionally, the trend of shrinking engines is rising as concern about vehicle weight rises. The market is now growing due to fuel efficiency rules and improved performance since low-weight alloys used in the production of turbochargers reduce the consumption of fuel. Additionally, because they are so small, turbochargers contribute to smaller engines and smaller overall vehicles.
Market Scope
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 39.76 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 73.12 Billion |
| Growth Rate from 2025 to 2034 | CAGR of 7.02% |
| Largest Market | Asia Pacific |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | By Technology, By Fuel Type, By Application, By Material, By End-User, and By Actuators |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Market Dynamics
Driver
Stringent emission norms & increase in sales of gasoline passenger cars
The fall in diesel engines' growth can be attributed to several factors. Some of these are increased fuel costs, global warming, and higher diesel car pricing than gasoline-powered automobiles. Diesel car sales have slowed down as demand for petrol engines has surged in nations like India, South Korea, and Indonesia. Multiple emission standards, including Euro-6, China-VI, and PROCONVE P-8, have fueled the growth of the petrol engine sector. As a result, the manufacturing of passenger car turbochargers has increased more quickly and the environment has become less polluted.
The market share of gasoline-powered cars in the passenger car class has increased as a result of the new emission laws' lower emission thresholds. The current standard, known as Euro 6d, which entered into effect in January 2020 and applies to all new cars sold in Europe, sets NOx limits of 80 mg/km for gasoline-powered cars and 114.4 mg/km for diesel cars, as well as particle matter limits of 0.0045 g/km for gasoline-powered cars and 0.005 g/km for diesel cars. In July 2025, the Euro 7 standards will take their place. The majority of automobiles are outfitted to meet the emission restrictions.
Restraints
High maintenance charge
While adding a turbocharger to an engine provides advantages, the system tends to work harder, which leads to system wear and tear. The turbocharger must endure scorching exhaust fumes that can reach 1200°F in temperature. As a result, it becomes crucial to circulate cooling oil often to maintain the turbocharger's cooling. Due to the need for cooling oil, turbocharged engines have substantial maintenance costs. The cost of replacing a turbo is likewise high. Premature breakdowns of the turbochargers due to poor maintenance put more strain on the engine cooling oil. But water-cooled turbochargers will become more user-friendly due to technological developments.
Opportunities
An increase in the demand for gasoline engines and fuel-efficient engines
Due to the growing use of turbochargers in petrol engines, there is a significant amount of development potential for the market. Contrary to their petrol counterparts, practically all current diesel engine cars come with turbochargers. But in recent years, turbocharged engines have also been used in petrol engines. Turbocharging makes Downsizing possible in petrol engines, which increases fuel efficiency by 5 to 20%. This invention has accelerated the growth of the turbocharger market in nations that rely heavily on petrol engines, such as China and the United States. Additionally, because they contribute very little to environmental pollutants, electric turbochargers are expected to dominate turbocharger technology in the future. One of the first automakers to provide an automobile with an electric turbocharger is predicted to be Audi. Worldwide growth in automobile demand and manufacturing is anticipated. The industry for turbochargers is also primarily driven by this.
Technology Insights
The compression ratio may be precisely controlled throughout the turbine thanks to the variable geometry turbine (VGT). This flexibility may be utilized to enhance diesel engine EGR flow, reduce turbocharger delay, and enhance low-speed torque characteristics. The two most common types of variable geometry turbochargers are the moving wall and pivoting vane versions. These turbochargers are also far less costly than other turbochargers and produce the most torque and engine power. As a result, in the next years, this category will dominate the global market for vehicle turbochargers.
Fuel Insights
The growth in popularity of gasoline vehicle turbochargers is being driven by the increasing demand for small, gasoline-powered passenger cars on a global scale. The engines in these cars are now more powerful and fuel-efficient. Exhaust system turbocharging technology is used by built-in gasoline vehicle turbochargers to boost inefficient engine fuel combustion and increase engine performance. On the other hand, because diesel engines are growing more costly and the implementation of new environmental rules boosts the cost of diesel-powered vehicles, particularly in light-duty cars, the pandemic effect is anticipated to favor gasoline turbochargers over diesel-powered engines.
Application Insights
Due to their excellent engine performance and sufficient vehicle torque, diesel engines are typically used by LCVs used by small enterprises or in metropolitan areas. LCVs are using turbochargers more frequently as a result of the benefits they provide, which include better fuel efficiency, higher power, and lower emissions. According to the AECC, China, and India are the top two markets for diesel-based light commercial vehicles, each with 1.5 million and 500,000 units sold, respectively. Due to the region's expanding urbanization, LCV demand is increasing.
Material Insights
Cast iron is a common material used for the housing of the turbine and intake and exhaust manifolds in many turbochargers due to its popularity and ability to tolerate high temperatures up to 900°C. The turbine housing is where this cast iron is mostly used. Turbine housings are constructed by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) from cast iron, which can survive temperatures up to 700°C, and austenitic stainless cast steel, which can handle temperatures up to 1,000°C.
The heavy-duty pick-up truck models provided by Ford, such as the F-Series Super Duty, feature turbocharged diesel-powered engines with cast iron turbine housings. Cast iron is predicted to lead the material type sector in the turbocharger market taking into account all the relevant criteria and their significance.
End-user Insights
OEM passenger vehicle turbochargers are made to optimize engine power output and cut down on fuel usage. The most crucial component among all passenger car parts is the turbocharger, which is typically installed to improve high-end performance. When the driver depresses the gas pedal, the OEM passenger vehicle turbocharger also produces a power boost.
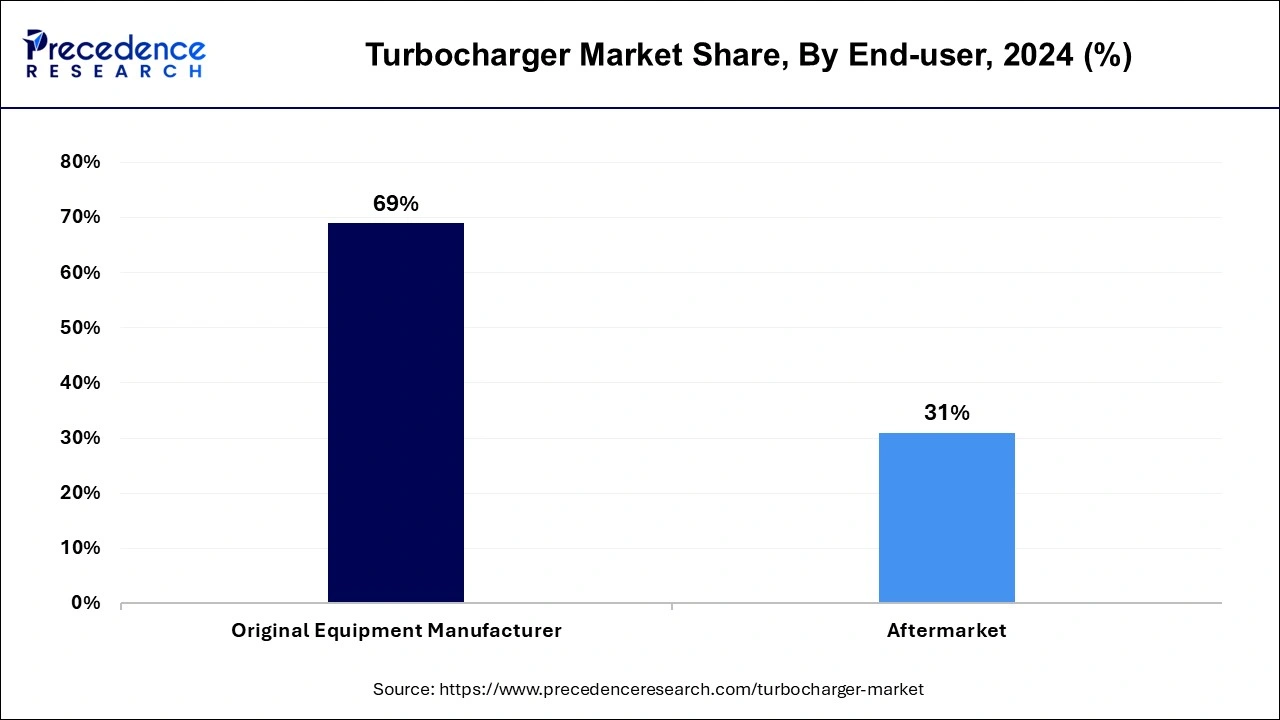
It can add more air to the engine, which allows for the injection and burning of more fuel, increasing the amount of horsepower produced by the engine. This procedure is referred to as "boosting." A turbocharged engine's boost capacity can rise by about 30%.
Turbocharger Market Companies
- Rotomaster International
- MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORPORATION
- BorgWarner Inc.
- CONTINENTAL AG.
- Turbo Dynamics Ltd.
- IHI Corporation
- Cummins Inc.
- Honeywell International Inc.
- Eaton
- Precision Turbo & Engine
- Garrett Motion Inc.
Recent Developments
- Garrett Motion Inc. (Honeywell) introduced the TR25R, TR30R, AND TR35R in May 2022. These new titanium housings have a water-cooled function for effective operation and optimal safety.
- In an auto show held in Shanghai in April 2022, Garrett Motion Inc. (Honeywell) introduced Next-Generation E-Boosting Technologies, which would be utilized in hybrid fuel cell cars to improve fuel efficiency and lower exhaust emissions.
- The HOLSET M turbocharger, created especially for heavy-duty and off-highway applications, was introduced by Cummins Inc. in May 2021. To accommodate the requirements of various applications, it comes in a variety of sizes and configurations.
Segments Covered in the Report:
By Technology
- Twin-Turbo
- Wastegate Technology
- Variable Geometry Technology
By Fuel Type
- Diesel
- Gasoline
By Application
- Light Commercial Vehicle
- Heavy Commercial Vehicle
- Ships & Aircrafts
- Agriculture & Construction
- Locomotives
By Material
- Cast Iron
- Aluminum
By End-User
- Original Equipment Manufacturer
- Aftermarket
By Actuators
- Hydraulic
- Pneumatic
- Electric
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Ask For Sample
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
 Get a Sample
Get a Sample
 Table Of Content
Table Of Content
 sales@precedenceresearch.com
sales@precedenceresearch.com
 +1 804-441-9344
+1 804-441-9344
 Schedule a Meeting
Schedule a Meeting