Nano Healthcare Technology for Medical Equipment Market Size and Forecast 2025 to 2034
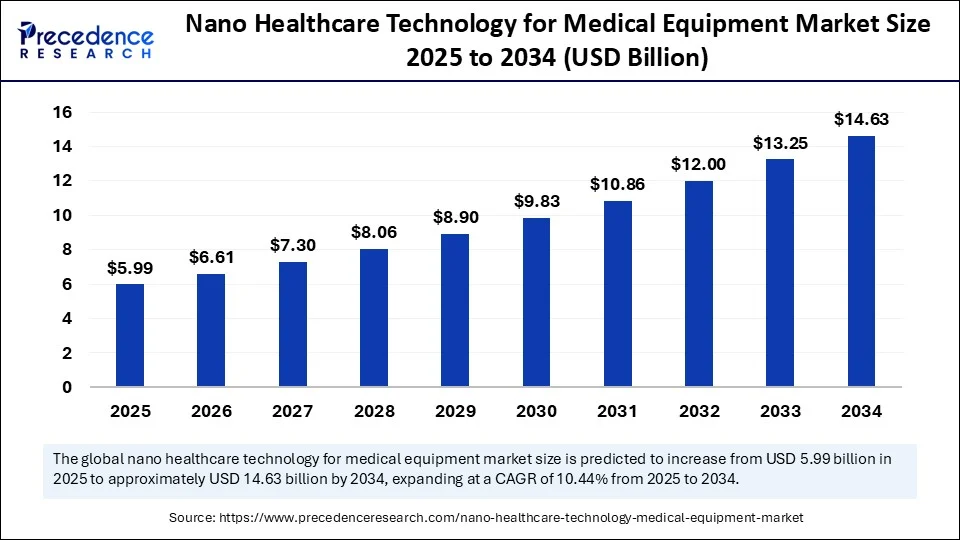
The global nano healthcare technology for medical equipment market size accounted for USD 5.42 billion in 2024 and is predicted to increase from USD 5.99 billion in 2025 to approximately USD 14.63 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 10.44% from 2025 to 2034.
Nano Healthcare Technology for Medical Equipment Market Key Takeaways
- In terms of revenue, the nano healthcare technology for medical equipment market was valued at USD 5.42 billion in 2024.
- It is projected to reach USD 14.63 billion by 2034.
- The market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 10.44% from 2025 to 2034.
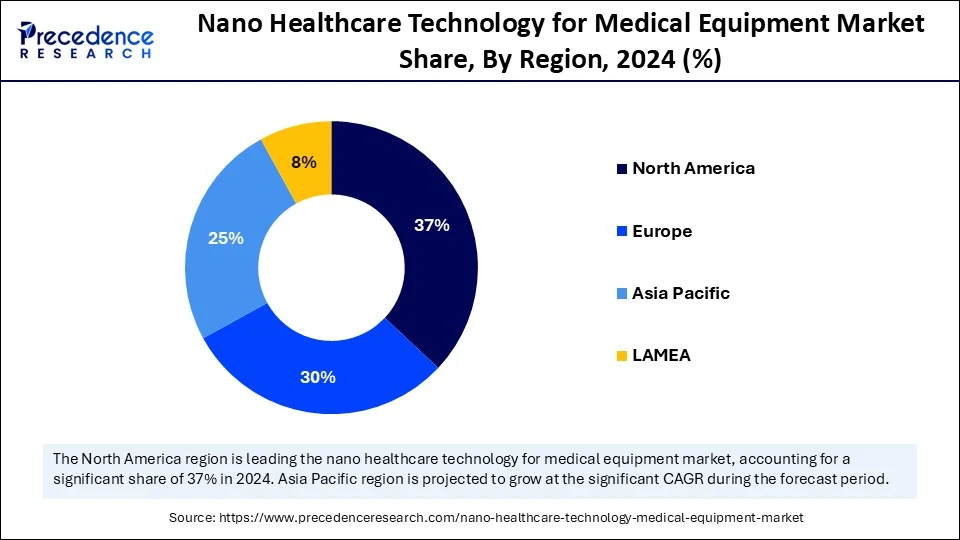
- North America generated the highest market share of 37% in 2024.
- Asia Pacific is estimated to expand the fastest CAGR in the market between 2025 and 2034.
- By application, the therapeutics segment held the largest market share in 2024.
- By application, the drug delivery segment is anticipated to grow at a remarkable CAGR between 2025 and 2034.
- By medical equipment, the nano sensors segment captured the biggest market share in 2024.
- By medical equipment, the nano carriers segment is expected to expand at a notable CAGR over the projected period.
- By end user, the hospital segment captured the biggest market share in 2024.
- By end user, the home care segment is expected to expand at a notable CAGR over the projected period.
- By material type, the nanoparticles segment captured the biggest market share in 2024.
- By material type, the nanocomposites segment is expected to expand at a notable CAGR over the projected period.
Role of AI in Nano Healthcare Technology for Medical Equipment Market
Artificial Intelligence is already disrupting nano healthcare technology through advances in the speed and precision of medical devices. AI-enabled nanosensors provide data on early stage cancer biomarkers in blood samples to promote early diagnosis. AI is also utilized to model and improve upon nanocarriers, with programmable emergence with age on nanocarriers to help personalize drug delivery while minimizing side effects of chemotherapy and other cancer treatments.
In 2025, clinical trials in Japan of smart nano-robots, equipped with AI programmed to decide optimal timing to release drugs in the case of brain tumors while responding to unique cellular conditions. Wearables with AI alongside nanosensors also process real-time data to be able to predict cardiovascular events in patients before they actually have clinical symptoms. The synergy of these nano and AI platforms is enabling predictive, preventive and precise health, where autonomous, self-regulating medical devices will have the capacity to transform patient care.
U.S. Nano Healthcare Technology for Medical Equipment Market Size and Growth 2025 to 2034
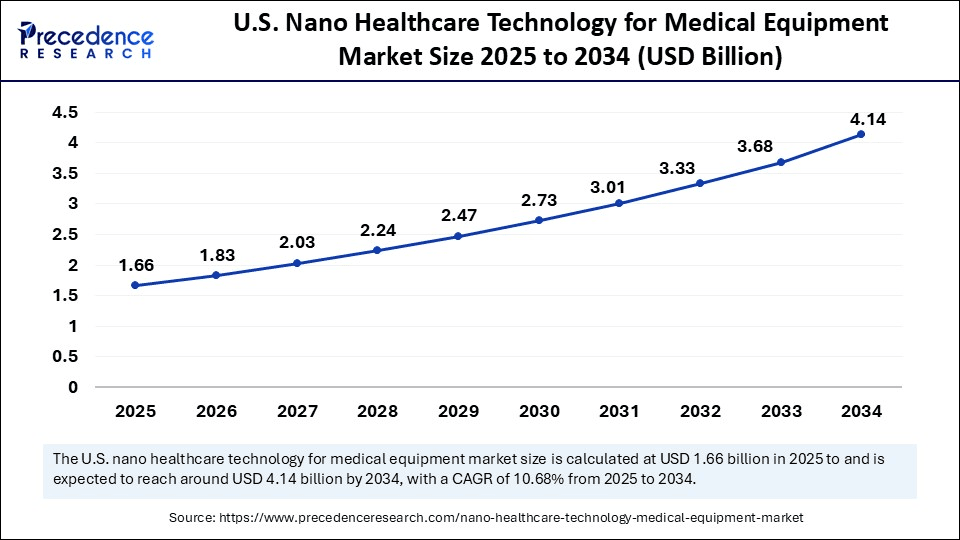
The U.S. nano healthcare technology for medical equipment market size was exhibited at USD 1.50 billion in 2024 and is projected to be worth around USD 4.14 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 10.68% from 2025 to 2034. Nano healthcare technology in the medical equipment market is advancing rapidly, driven by increasing demand for early diagnostics, minimally invasive procedures, and personalized treatments, with strong support from innovations in nanorobotics, biosensors, and targeted drug delivery.
Which Region Dominated the Nano Healthcare Technology for Medical Equipment Market in 2024?
With strong research institutions and resources, well-crafted medical infrastructure, and government subsidies for R&D, the North America held the largest market share of 37% in 2024 for the nano healthcare technology adoption in medical equipment (i.e. needleless injectors or drug delivery systems). The U.S. National Nanotechnology Initiative (NNI) has emerged as a powerful vehicle for funding programs, collaboration across agencies, and joining together similar organizations, so decisions can be made quickly as technologies are developed. More public entities such as the regulatory body services (e.g. U.S. FDA) are establishing routes for accelerated approvals for nano-tech based medical devices spurring commercialization for the technology. Many of the prime companies such as Medtronic and Boston Scientific are actively investing in adoption of nanoscale technologies for improved precision and outcomes for patients.
The U.S. market is the primary impetus in this region. Some of the prestigious universities (MIT, Stanford University) are developing nanobots for drug delivery to target drugs and develop nanosensors for early disease detection. Recent new innovations such as the development of “nanoswimmers,” have developed systems to work with the blood for non-invasive diagnostics. Nano-coating of implants and enabling products such as blankets, cushions, and even dog boots is showing the reduction of infection citation rates. Institutions such as NIH are providing funding and collaborating with organizations (company 3M) resulting in a rapidly growing environment for scaling nano-enabled medical solutions.
Europe Progressing with Regulations and Cross-Border Collaboration
Europe is the second most active region for smaller-scale nano healthcare technologies as a function of the regulatory framework and societal expectation of safe innovation. The European Union promotes nanotech research through funding opportunities like Horizon Europe, while agencies such as the Scientific Committee on Emerging and Newly Identified Health Risks (SCENIHR) ensure standards for safety and efficacy are translated for nano-integrated medical devices. In addition, regional bodies have strong collaboration models with academic institutions to facilitate the adoption of their research on a commercial stage.
Germany has received attention in Europe for its commitment to medical innovation and high standard of manufacturing. Organizations such as the Max Planck Society and Fraunhofer Institutes are leading research groups for nanomaterials development for implants and diagnostic tools. On the commercial side, companies such as B. Braun and Siemens Healthineers are leveraging nanoscale developments into imaging systems and medical coatings respectively, emphasizing the robustness of Germany's pathway to develop this field.
Asia Pacific's Growth in Market: What to Expect from China's Healthcare Sector?
The rapid growth of the nano healthcare medical equipment sector in the Asia-Pacific region has been driven by significant increases in medical investment and infrastructure. Countries across the region are expanding the adoption of advanced healthcare technologies, while also enhancing incorporation of nanotechnology research and innovation in diagnostics, wearable sensors, and surgical systems. Several government-dedicated initiatives, like India's National Mission on Nanoscience, and the Chinese focus on smart healthcare, fostered the urge to develop local front-end capabilities and facilitate partnerships between academia and industry.
China is leading the charge in the region through a strong and unified state commitment to facilitating the incorporation of nanotechnology in medical devices. China's “Made in China 2025” plan emphasizes a state commitment to improvement in healthcare delivery through advanced technologies, which include nanomedicine. Chinese companies and research institutions have become world leaders in creating nano-enabled surgical robots and diagnostic tools, and hospitals have started to adopt nano coatings and nanosensors to improve patient safety and care quality.
Market Overview
Nano healthcare technology in medical devices refers to the utilization of nanotechnology in developing unique and advanced tools and devices for individual diagnosis, treatment, monitoring, and delivery of drug therapy. Nano health technologies involve understanding and operating at the nanoscale, which is usually understood as below 100 nanometres and seeking to develop greater specificity and efficiency in the delivery of interventions to target a disease on the cellular or molecular level.
This market is expanding due to the global demand for less invasive investigations including targeted drug delivery, and the ability to diagnose diseases earlier with more reliable tools. Many of the smart materials developed in nanohealth are in the form of nanosensors, implantable devices, and on-demand drug delivery pathways that can positively affect healthcare management by allowing greater accuracy and reduced side effects. This market is supported by continuous research and development collaboration, a growing number of chronic diseases, and governmental options for acceptable avenues of funding new options to improve patient care. Globally healthcare systems are developing demands for faster, smarter, and more individualized solutions, and nano healthcare technologies are rapidly becoming a major component of the next generation of medical devices.
What are Major Trends in Nano Healthcare Technology for Medical Equipment Market?
- Demand for Precision Medicine: Nano-systems can harness the unique properties of nanomaterial structures to enable targeted drug delivery and/or personalized agents/processes that maximize beneficial effects while minimizing side effects, all very important features in many aspects of precision medicine across a variety of therapeutic indications.
- Progress in nanotechnology R&D: Continuing research in nanotechnology-based materials and nano-engineering are providing the foundation for developing more advanced diagnostic, biosensing, and therapeutic devices with improved sensitivity and functionality.
- Burden of chronic disease: The growing prevalence of cancer, heart disease, diabetes and other conditions, is heightening the need for 'nano-technology' based medical devices that can provide both early detection and effective treatment options.
- Investment in new technologies: Continued public and private sector investment in nanotechnology-based products and services in health care settings are speeding up development timeframes and market readiness of advanced medical devices.
- Shift to portable smart devices: The trend toward portable, smart devices in health care is driving demand for small (e.g. nano), discrete components that allow for signaling in real-time and for digital interpretation of the data readily.
Market Scope
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 14.63 Billion |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 5.99 Billion |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 5.42 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate from 2025 to 2034 | CAGR of 10.44% |
| Dominating Region | North America |
| Fastest Growing Region | Asia Pacific |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | Application, Medical Equipment, End-User, Material Type, and Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Market Dynamics
Drivers
Advance Nanobot Control Drives Breakthrough in Targeted Medical Treatments
One of the major drivers of nano-healthcare technology is the increasing demand for ultra-precise, minimally invasive treatment systems acting at the cellular level. Most standard therapies impact diseased and healthy tissues, requiring a change in the healthcare market for solutions that deliver drugs or interventions with precision targeting. Nanotechnology is ideal for applications of this nature, especially in combination with programmable control systems that take targeting to the next level.
In this situation, a study recently published by researchers at the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) was particularly noteworthy regarding individualized nanobot control. The researchers introduced a new technique called "intermittent randomization," where each individual nanobot in a swarm can be addressed independently rather than acting in parallel modality. This approach addresses a limiting factor in swarm robotics, where uniformity in control limited medical use cases.
For example, with the new individualized control model, a swarm of nanobots can transport multiple drugs to different sites, navigate unique biological conditions in the organism, or independently accomplish different tasks in parallel.
This enhanced nanoparticle control conceptually fits into the larger movement toward precision medicine, enhancing therapeutic outcomes and minimizing side effects. Additionally, it provides a more realistic representation of intelligent biological systems, thus positioning it as a key enabler of the next generation of adaptive nano-medical devices.
Restraint
Safety and Commercialization Challenges due to Regulation Gaps
Though advances have been made in the use of nanomaterials in medicine, the majority of regulatory systems on a global level, such as those in India, the U.S., and EU countries, still evaluate nano-based medical devices and materials under existing regulatory frameworks that utilize the same evaluation criteria for all bulk materials Notably, the existing framework does not consider the unique properties of nanoparticles, such as their biological interactions, reactivity, and possible long-term toxicity based on the size and increased surface area of their nano-sized properties.
For example, in spite of assistance from bioengineering backgrounds, targeted delivery often is not currently being quantified as the nanoparticles can occlude biological barriers, and accumulate in organs like the liver and/or brain, yet no long-term biocompatibility studies are standardized or approved.
There are also no globally accepted standardized nano-specific clinical testing processes making the approval system fragmented. Since developers often have gaps in information relating to anticipated regulatory timelines, testing requirements, and post-market surveillance obligations, there is high uncertainty related to regulatory approval processes and frameworks which creates commercialization delays.
Additionally, they inhibit cross-border collaborative research, delaying the adoption of new technologies in a clinical environment. Until robust science-based, endorsed nanoparticle specific regulatory frameworks establish, new technologies face significant barriers and indicated technology may remain in a laboratory with further delay for innovations related to diagnostics, imaging and minimally invasive therapeutics reaching patients and positive outcomes.
Opportunity
Demand for Non‑destructive Cancer Diagnostics
Exciting new possibilities for nano‑healthcare are emerging from the development of nano‑needle patches for intraoperative diagnostics. Researchers at King's College London have recently developed nano‑needle patches composed of millions of silicon nano‑needles (each more than a thousand times thinner than a human hair) which can access single cells, and subsequently collect proteins, lipids, and genetic materials, without damaging the tissue . In initial trials in 23 brain tumour samples, the device produced results in less than 20 minutes, demonstrating the ability to discriminate tumour subtypes and provide real‑time recommendations to the surgeons, while they were performing the surgery .
Unlike a regular biopsy, which is invasive and time consuming, personalised treatment is possible with repeated minimally disruptive sampling, enabling the precise mapping of tumour heterogeneity; a new concept, related to spatial biology. The device technology utilises existing semiconductor fabrication methods that could help automated mass production and eventual integration into current surgical instruments. There are possible applications ranging from neurosurgery to oral and throat cancer cases and addresses critical unmet needs; speed, safety, and improved diagnostic accuracy. As spatially and temporally accurate diagnostics start to become increasingly utilized in oncology networks and surgical workflows, nano‑needle patches will be a paradigm shift in point‑of‑care nanotechnology.
Application Insights
Why Is Therapeutics the Leading in Application segment in Nano Healthcare Technology for Medical Equipment Market?
Therapeutics is the leading application segment based on multiple areas of its influence in the patient treatment modalities, particularly for targeted therapy and further precision medicine. Nanotechnology enables the delivery of therapeutic agents more directly to diseased cells while limiting the side-effects of those agents. For example, nanoparticle cancer treatment allows chemotherapy to be delivered to tumors while sparing healthy tissue. Recent advancements in therapeutics such as lipid nanoparticles in mRNA vaccines or nanorobotics for drug activation have bolstered this application even further. The on-going applications of nano based therapies in oncology, neurology or other autoimmune disorders eminently positions this application as the potential driving growth of the future.
Drug delivery is the fastest growing application, primarily due to demand for smart and targeted drug delivery systems. There are a number of approaches for drug delivery with the use of nan-delivery systems and nano-carriers include dendrimers, liposomes, and nanoshells that are seen as potential enhancements to bioavailability and precision dosing. There is also significant investment in nanobased delivery systems that can navigate biological barriers like the blood - brain barrier, providing therapeutic options that were not available before. Significant expansion of personalized medicines, and chronic disease management in Asia Pacific will spur near-term innovations and developments in drug delivery that are important to the future healthcare solutions in the nanomedicine space.
Medical Equipment Insights
What Made Nano Sensors the Most Prominent in 2024?
The nano sensors stand unrivalled in the medical equipment segment as they provide superior sensitivity and rapid detection of disease. Nano sensors have been integrated into diagnostic instruments to measure biomarkers at the molecular level, allowing for a faster and more precise diagnosis of cancer, infections, and metabolic disorders. Nano sensors are currently being widely deployed to monitor patients in real-time, and they increasingly enable lab-on-chip systems. The rise of nano sensors in portable diagnostic tools and wearables has accelerated the pace at which they are adopted by hospitals and diagnostic labs.
Meanwhile, nano carriers are growing overall at the fastest rate of growth, as they represent a very important aspect of smart nano solutions, primarily for their ability to facilitate delivery of therapeutic agents with great specificity while controlling release. Nano carriers, including polymeric nanoparticles and nanoliposomes, help with enhancing solubility and stability of drugs, allowing for reduced systemic toxicity. There are also critical applications of nano carriers in applications including gene therapy and immunotherapy. The demand for multifunctional nanocarriers, that may include therapy as well as imaging, is also an important aspect of the growth, particularly for the management of cancer and rare diseases.
End User Insights
Which End-user Segment Dominated the Market in 2024?
Hospitals are the largest end-user segment for nano healthcare technologies based on their infrastructure capability, trained workforce, and access to sophisticated equipment. These characteristics greatly facilitate the use of nano-based diagnostics, therapeutic devices, and monitoring solutions in these settings. Hospitals were early adopters of nano-enabled tools or devices for cancer detection, surgical precision, and infection control, and the use of nano implants and nano-coated instruments during surgeries are becoming increasingly routine and accepted in urban, tertiary care centres.
Home care is the fastest growing end-user segment, because of increased market demand for portable, wearable, and remote-monitoring devices enhanced with nanotechnology. In particular, nano sensors included in home use diagnostic kits and smart wearables can assist patients in conducting real-time health monitoring of their vital signs, glucose, and other parameters. Demographic factors, such as a growing aged population, combined with increased incidences of chronic diseases, are playing a key role in accelerating decentralized care, while government initiatives and telemedicine service providers, particularly in places like India and China, are increasing the adoption rate in the home care segment.
What Makes Nanoparticles the Dominant Sub-segment in Material Type?
Nanoparticles dominate the material type segment primarily because of their flexibility and efficacy in many medical applications. They have been utilized in imaging, diagnostics, and drug delivery systems, often with increased permeability and retention in localized therapies. Metal-based nanoparticles including; gold and silver are commonly used in cancer diagnostics, and antimicrobial coatings, whereas polymeric nanoparticles are often used more broadly for controlled release of drugs. They can easily be manipulated at their surface to enhance biological interactions, increasing their value across the therapeutic pipeline.
Nanocomposites are also expected to grow the fastest because of their superior mechanical, thermal, and bio-functional properties. Nanocomposites take the form of nanoparticles embedded into polymeric or ceramic materials to improve the biocompatibility and durability of the material, making them efficient material use for long-term implementation like implants, sensors, and prosthetics. There is much ongoing research and development with nanocomposites specifically relating to bone regeneration, and wound healing abilities.
Nano Healthcare Technology for Medical Equipment Market Companies

- Abbott Laboratories
- CureMetrix
- GE Healthcare
- Honeywell
- Medtronic
- NantHealth
- Nanobiotix
- Philips
- Siemens Healthineers
- Stryker
- Thermo Fisher Scientific
- Royale Healthcare
- Johnson & Johnson
- Becton Dickinson
- Nanosys
Recent Developments
- In May 2025, BioVaxys Technology Corp. and Sona Nanotech Inc. announce that they have entered into a Research Agreement to collaborate on the development of new cancer therapeutics based on BioVaxys' DPX™ Immune Educating Platform in combination with Sona's Targeted Hyperthermia Therapy™, a photothermal cancer therapy that uses highly targeted infrared light to treat solid tumors.
(Source:https://www.prnewswire.com)
- In June 2025,Cardinal Health announced the U.S. launch of its multi-parameter, single-patient use monitoring cable and lead wire system that enables the continuous monitoring of cardiac activity, blood oxygen level and temperature with one point of connection. The new Kendall DL™ Multi System is designed to travel with the patient from admission to discharge for smooth transport. It helps improve clinician workflows, provides reliable monitoring to help determine the best course of care, and maximizes value across the hospital.
(Source: https://www.prnewswire.com)
- In October 2024, UPM Biomedicals, the forerunner in producing high quality nanofibrillar cellulose for medical and life science applications, announces the launch of FibGel™—a natural injectable hydrogel for permanent implantable medical devices. Designed and manufactured under ISO 13485 standards in Finland and designed for medical applications, FibGel is poised to transform the fields of soft tissue repair, orthopedics, regenerative medicine and more.
(Source: https://www.azom.com)
Segments Covered in the Report
By Application
- Diagnostics
- Therapeutics
- Drug Delivery
- Imaging
- Monitoring
By Medical Equipment
- Nano Sensors
- Nano Tools
- Nano Carriers
- Nano Implants
By End-User
- Hospitals
- Clinics
- Research Institute
- Home Care
By Material Type
- Nanoparticles
- Nanotubes
- Nanocomposites
- Nanofilms
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Ask For Sample
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
 Get a Sample
Get a Sample
 Table Of Content
Table Of Content
 sales@precedenceresearch.com
sales@precedenceresearch.com
 +1 804-441-9344
+1 804-441-9344
 Schedule a Meeting
Schedule a Meeting