Albumin Market Size and Forecast 2025 to 2034
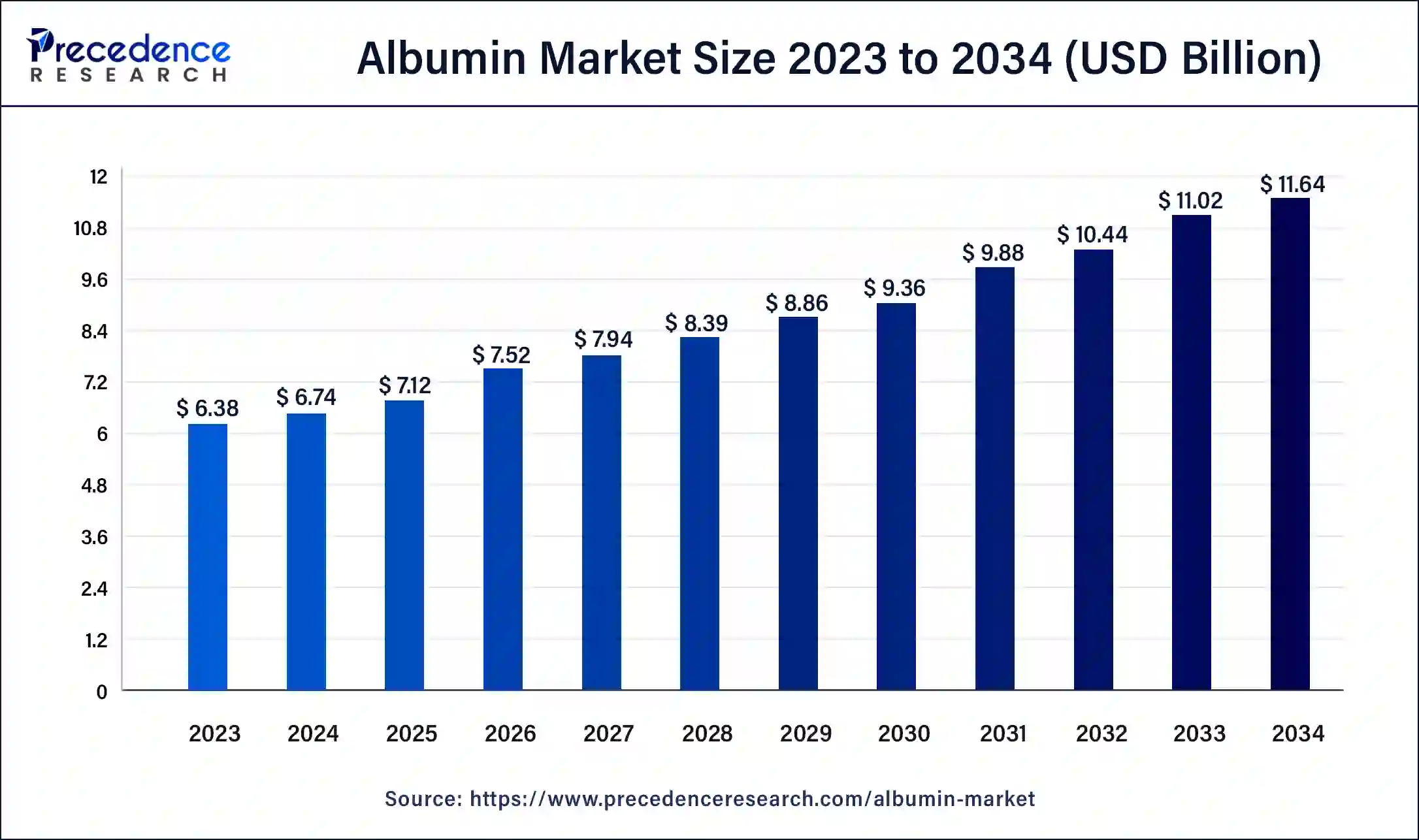
The global albumin market size was evaluated at USD 6.74 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 11.64 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 5.62% over the forecast period 2025 to 2034. The demand for albumin market is driven by increasing demand for albumin in emerging economies, advancements in biotechnology for albumin production, increasing plasma fractionation facilities, and the rising prevalence of chronic diseases that require albumin-based therapies.
Albumin Market Key Takeaways
- The global albumin market was valued at USD 6.74 billion in 2024.
- It is projected to reach USD 11.64 billion by 2034.
- The albumin market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 5.62% from 2025 to 2034.
- North America held the largest share of the albumin market in 2024.
- Asia Pacific is anticipated to witness the fastest growth in the market during the forecast period.
- By product, the human serum segment held the largest share of the market in 2024.
- By product, the bovine serum segment is expected to grow significantly in the market during the forecast period.
- By application, the therapeutics segment accounted for the dominating share of the market in 2024.
- By application, the drug formulation segment is observed to grow at a significant rate in the market during the forecast period.
- By end-use, the hospitals and clinics segment accounted for the dominating share of the market in 2024.
- By end-use, the pharmaceutical companies segment is observed to grow at a significant rate in the market during the forecast period.
Impact of AI on the Albumin Market
The increasing accuracy of artificial intelligence in recognizing albumin levels presents a significant opportunity in medical institutions, particularly in detecting early renal damage in diabetes through urinary microalbumin analysis. Serum albumin in machine learning-based prediction of cognitive function in the elderly using a basic blood test. In the albumin market, these advancements highlight artificial intelligence's role in improving diagnostic and detection capabilities and improving patient outcomes across diverse medical conditions.
Market Overview
Albumin is the predominant circulating protein found in plasma. It is a protein produced by the liver that plays a crucial role in maintaining oncotic pressure and supports various physiological functions in the body. It is administered in a wide spectrum of clinical scenarios including complications of volume resuscitation, cirrhosis, intradialytic hypotension, and priming of cardiopulmonary bypass circuit. It is used in hospitalized patients, as well as in outpatients with complications of cirrhosis.
Albumin Market Growth Factors
- Albumin is widely used in pharmaceuticals, primarily for therapeutic and diagnostic purposes such as treatment for shock, burns, liver disease, and a plasma volume expander.
- The albumin market is influenced by factors such as increasing demand for albumin in emerging economies, advancements in biotechnology for albumin production, and the rising prevalence of chronic diseases that require albumin-based therapies.
Market Scope
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 11.64 Billion |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 7.12 Billion |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 6.74 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate from 2025 to 2034 | CAGR of 5.62% |
| Largest Market | North America |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | Product, Application, End user, and Regions |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America and Middle East & Africa |
Market Dynamics
Drivers
Increasing demand for hypoalbuminemia treatment
Hypoalbuminemia is a common finding in both chronic and acute illnesses and is often associated with inflammation. Inflammatory processes can develop capillary permeability, leading to albumin leakage into the interstitial space and thereby increasing albumin's distribution volume. This, coupled with a shortened albumin half-life due to inflammation, results in reduced total albumin levels. Chronic hypoalbuminemia is recognized to reduce albumin synthesis from conditions like wasting and cachexia.
In hospitalized and critically ill patients, hypoalbuminemia may stem from declined production, increased loss via kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, skin, or extravascular spaces, or heightened catabolism. Understanding these mechanisms underscores the importance of managing hypoalbuminemia to mitigate infection risks and improve patient outcomes, thus driving the demand for albumin market.
- In 2022, the American Liver Foundation published data reported that more than 100 million people suffered from some form of liver disease in the U.S., and 4.5 million U.S. adults (1.8%) have been diagnosed with liver disease. However, it is estimated that 80-100 million adults in the U.S. have fatty liver disease. Albumin synthesis and secretion decrease due to liver failure. Thus, there is increased demand for albumin in the market.
Expansion of plasma fractionation facilities
The extraction of proteins from human plasma through fractionation remains key in biotechnology for producing lifesaving treatments for various diseases. Plasma-derived products include a variety of elements such as coagulation factors (e.g., factor VIII, factor IX, prothrombin complex, Von Willebrand factor, fibrinogen), polyvalent and hyperimmune immunoglobulins (e.g., anti-RhO, anti-hepatitis B, anti-rabies, anti-tetanus), protease inhibitors (e.g., alpha 1-antitrypsin, C1-inhibitor), anticoagulants (e.g., antithrombin), and albumin. It is essential to extract from human plasma by applying properly regulated industrial practices to ensure the best quality, safety, and recovery, as well as boost the albumin market growth.
- In March 2023, CSL opened a plasma fractionation facility in Marburg, Germany, which aims to make medicines for rare and serious diseases using donated human plasma. With optimized process flows, modern technologies, and automation.
- In December 2022, CSL opened a new plasma fractionation facility in Australia dedicated to fractionating human plasma. It can be used to treat hemophilia, immune system problems, burns, and other life-threatening medical conditions.
Restraint
High cost of production and regulatory challenges
Albumin, a protein derived from human blood plasma, is expensive to produce. The process involves extensive testing, purification, and fractionation methods to ensure safety and efficacy. Albumin is known as a human blood product, but it is also highly costly and has limited availability. Thus, limiting the albumin market growth.
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the voluntary standards of the Plasma Protein Therapeutic Association (PPTA) ensure the safety and quality of plasma fraction and the safety and health of the donor relative to the donation process.
Opportunity
Advancements in recombinant DNA technology
The rise in advancements in technology is projected to offer beneficial opportunities to the recombinant albumin market during the forecast period. Recombinant Albumin is produced using recombinant DNA technology, overcoming the limitations of plasma-derived human serum albumin (HAS), such as supply and quality variations. Recombinant human albumin (rHA) represents a significant advancement in biotechnological and pharmaceutical applications, providing a safe and consistent alternative to plasma-derived HAS.
Its role as a stabilizer in the formulation of therapeutic products, including vaccines, biologics, and drug-delivery systems, emphasizes albumin's utility in enhancing stability and improving yield. Recombinant DNA technology allows for the efficient production of human serum albumin (HAS) in large quantities. This reduces dependency on traditional methods of sourcing albumin from human plasma donors.
- In June 2024, Shilpa Medicare filed its first drug master file of recombinant human albumin 20% with the U.S. FDA, which is a completely environment-friendly, consistent, high-quality product, scalable to massive scales, and cost-competitive.
Product Insights
The human serum segment held the largest share of the albumin market in 2024. Human serum albumin (HAS) has widespread use in clinical and cell culture applications. It is the most prevalent protein in human blood and serves crucial roles in liver treatments, being widely recognized as advantageous for patients with liver damage. Within humans, serum albumin plays a key role in regulating plasma oncotic pressure and transporting both endogenous and exogenous ligands, including drugs.
In clinical practice, serum albumin levels are commonly evaluated through standard laboratory tests, aiding as an indicator of individual nutritional status. HAS offers several advantages, including a lengthy half-life, efficient recycling, and targeted accumulation capabilities. It features multiple binding sites where various ligands, such as fatty acids and ions, can attach non-covalently, facilitating drug delivery and potentially extending drug half-life while reducing renal clearance.
- In February 2024, Wuhan Healthgen Biotechnology Corp announced that it had completed phase III clinical trials for plant-derived recombinant human serum albumin for hypoalbuminemia patients.
The bovine serum segment is expected to grow significantly in the albumin market during the forecast period. Bovine serum albumin (BSA) is derived from cows and serves as a protein concentration standard in laboratory experiments. BSA is widely used in biochemical applications such as ELISAs (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays), immunoblots, and immunohistochemistry due to its small size, stability, and moderately non-reactive protein.
In immunohistochemistry, BSA commonly acts as a blocking agent. Serum albumin (SA) is the predominant plasma protein in mammals and is well-known for its remarkable capacity to bind ligands, facilitating it to transport a wide array of metabolites, drugs, nutrients, metals, and other molecules. Specified its ligand binding properties, albumins have broad applications in clinical, pharmaceutical, and biochemical fields.
- In August 2023, Dyadic International, Inc. announced that animal-free bovine serum albumin is structurally identical to commercial animal albumin, opening new commercialization opportunities. It has applications for human therapeutics, cell culture media, diagnostic test kits, PCR, vaccine development, and R&D.
Application Insights
The therapeutics segment accounted for the dominating share of the albumin market in 2024. Albumin, primarily synthesized in the liver, is a major plasma protein with essential physiological roles, especially in sustaining colloid oncotic pressure. Clinical scenarios where albumin therapy is indicated include conditions such as hypovolemia, shock, burns, hypoalbuminemia, surgery, trauma, cardiopulmonary bypass, acute respiratory distress syndrome, hemodialysis, and accumulation of protein-rich fluids, also used for expanding blood volume, potential therapeutic applications in liver diseases, and its role in nutrition are also areas of major importance. It serves roles in drug delivery, infusion therapy, accelerating wound healing, and acting as an antioxidant. Additionally, albumin injection treats hypoalbuminemia in patients with severe injuries, infections, or pancreatitis, especially when nutritional supplements prove inadequate.
- In July 2023, Kedrion Biopharma announced that China's National Institutes for Food and Drug Control (NIFDC) has approved BPL's human Albumin product for release to the Chinese market.
The drug formulation segment is observed to grow at a significant rate in the albumin market during the forecast period. Developing safe and stable drug formulations poses challenges in pharmaceutical development, where the selection of excipients plays a crucial role in formulation success. Albumin has established advantages over other excipients in formulating various active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), serving to address specific formulation obstacles.
In blood, albumin acts as a transporter for several elements, such as metals, hormones, fatty acids, and toxins. These distinctive properties make albumin a functional choice for drug formulation processes. Leveraging albumin in formulation strategies can accelerate the development of challenging APIs through the pharmaceutical development pipeline.
- In October 2023, Panacea Biotec unveiled in the Canadian market Paclitaxel Protein-Bound Particles for Injectable Suspension (Albumin-Bound), which is indicated for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer, non-small cell lung cancer and adenocarcinoma of the pancreas.
End-user Insights
The hospitals and clinics segment accounted for the dominating share of the albumin market in 2024. Human albumin solution (HAS) is primarily utilized in hospitals and clinics for its adaptability in patient care. It is a crucial plasma-derived product, especially in fluid resuscitation for patients with septic shock, where alternatives like crystalloids are ineffective or unsuitable. Additionally, HAS demonstrates efficacy in managing severe complications in progressive liver cirrhosis patients. In its role as a plasma expander, HAS may possess additional therapeutic benefits due to its non-oncotic properties. In intensive care sceneries, HAS plays a vital role in the management of critically ill patients suffering from conditions like shock, sepsis, trauma, acute respiratory distress syndrome, burns, or instances requiring rapid correction of hypovolemia. These applications highlight its critical role in hospitals & clinics segments.
- In February 2024, NCBI published an article on albumin colloid-based products that are mostly utilized for hypovolemia & hypotension, sepsis & septic shock, and intradialytic hypotension treatments in hospitals.
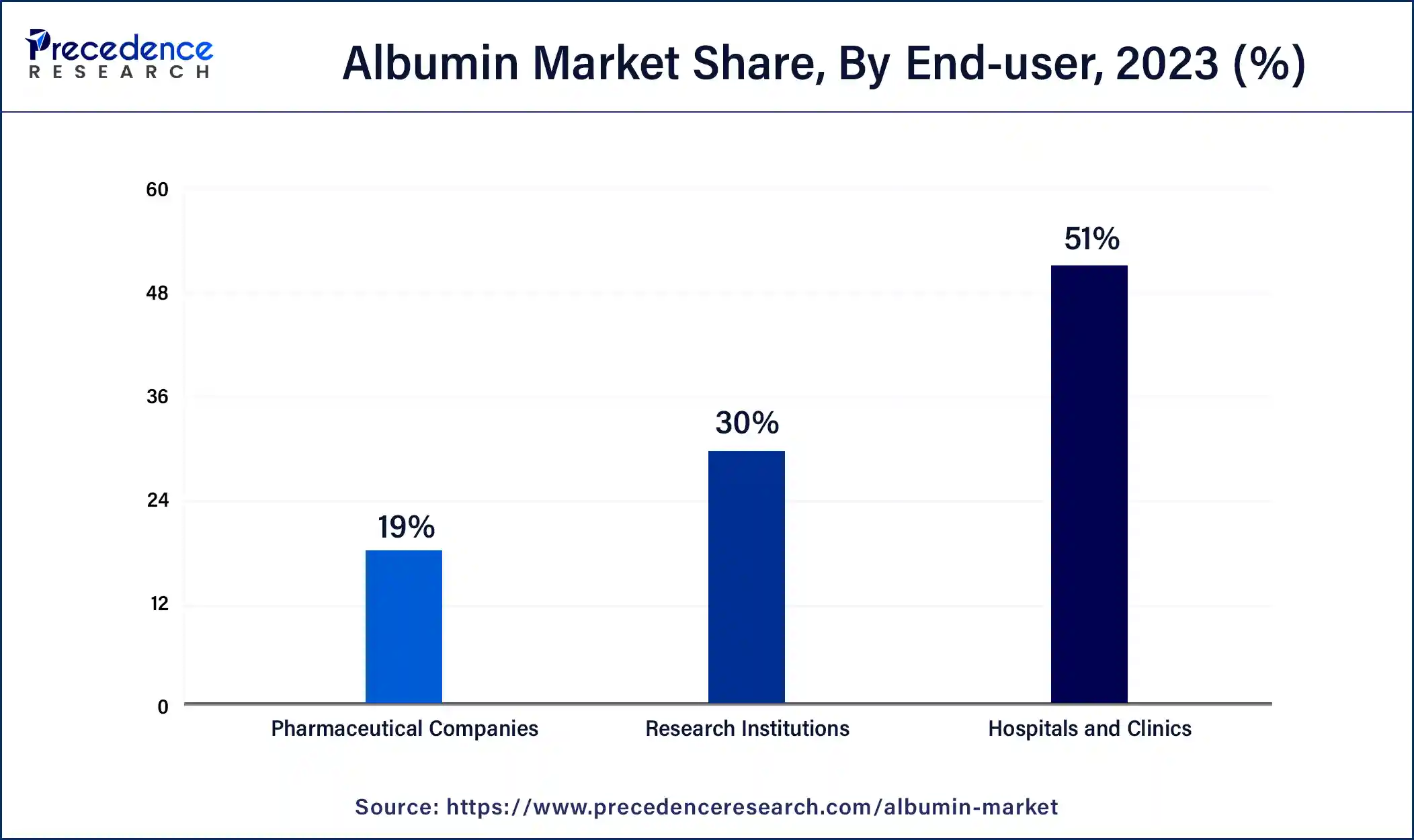
The pharmaceutical companies segment is observed to grow at a significant rate in the albumin market during the forecast period. Albumin, the predominant protein in mammalian blood serum, plays critical roles as a carrier molecule and in physiological processes. It is broadly employed in diverse molecular and cellular experiments and finds applications in emerging fields like cultured meat production.
Albumins used in research and biotechnological contexts often originate from animal serum, raising ethical and reproducibility concerns, or are produced through recombinant methods in organisms such as yeast or rice. This highlights ongoing efforts to enhance production methods while addressing concerns about scientific consistency.
- In July 2023, Grifols announced that it completed the enrollment in the phase-3 trial of Albutein (albumin-human injection) for the treatment of patients with decompensated cirrhosis.
Regional Insights
North America held the largest share of the albumin market in 2024 and is observed to sustain its position throughout the forecast period. North America has been a pioneer in adopting recombinant DNA technology for protein production, including albumin, and is known for its strong biotechnology and pharmaceutical sectors. The region benefits from advanced research facilities, strong regulatory frameworks, and high healthcare expenditure, contributing to a significant market presence for albumin products.
Government organizations, such as the National Institutes of Health (NIH) in the United States and the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) in Canada, provide significant funding to support discoveries and innovations that enhance our health and reinforce our healthcare system. This funding supports research projects focused on recombinant DNA technology, including the production and applications of proteins like albumin. Thus driving the albumin market in the region.
- According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), published data about 1 in 400 adults are living with cirrhosis in the United States.
Asia Pacific is anticipated to witness the fastest growth in the albumin market during the forecast period. Asia Pacific is expected to have rapid growth in the biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries, driven by increasing healthcare spending and rising demand for advanced medical treatments that driven the market growth. Countries such as China, India, and South Korea have developed as key players in the production and consumption of recombinant albumin.
Progressive liver disease is a leading indication for albumin in China, which not coincidentally has the world's highest chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection burden. Of an estimated 240 million people globally living with chronic HBV, some 90 million live in China, of whom an estimated 28 million require treatment and seven million require urgent, intensive treatment for advanced liver disease.
Albumin Market Companies
- Octapharma AG
- Albumedix Ltd.
- Biotest AG
- Grifols SA
- HiMedia Laboratories
- Medxbio Pte Ltd.
- CSL Limited
- Merck KGaA
- Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited
- Ventria Bioscience Inc.
Recent Developments
- In May 2023, American Regent, Inc. announced the launch of Paclitaxel Protein-Bound Particles for Injectable Suspension (Albumin-Bound), an alternative to Abraxane.
- In August 2022, Sartorius AG acquired Albumedix, Ltd., a manufacturer of recombinant human albumin-based products. This acquisition will help Sartorius AG strengthen its product portfolio in recombinant-based products.
- According to Aadi Bioscience, Fyarro (sirolimus protein-bound particles [albumin-bound]) was available in February 2022 to treat adult patients with metastatic malignant perivascular epithelioid cell tumors.
Segments Covered in the Report
By Product
- Human Albumin
- Bovine Albumin
- Recombinant Albumin
By Application
- Drug Formulation
- Therapeutics
- Others
By End-user
- Hospitals and Clinics
- Pharmaceutical Companies
- Research Institutions
By Geography
- North America
- Asia Pacific
- Europe
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Ask For Sample
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
 Get a Sample
Get a Sample
 Table Of Content
Table Of Content
 sales@precedenceresearch.com
sales@precedenceresearch.com
 +1 804-441-9344
+1 804-441-9344
 Schedule a Meeting
Schedule a Meeting