District Energy Services Market Size and Forecast 2025 to 2034
The district energy services market is gaining momentum with smart grid integration, efficient energy use, and eco-friendly infrastructure trends. The growth of the market is attributed to the rising demand for energy efficiency and increasing corporate sustainability goals.
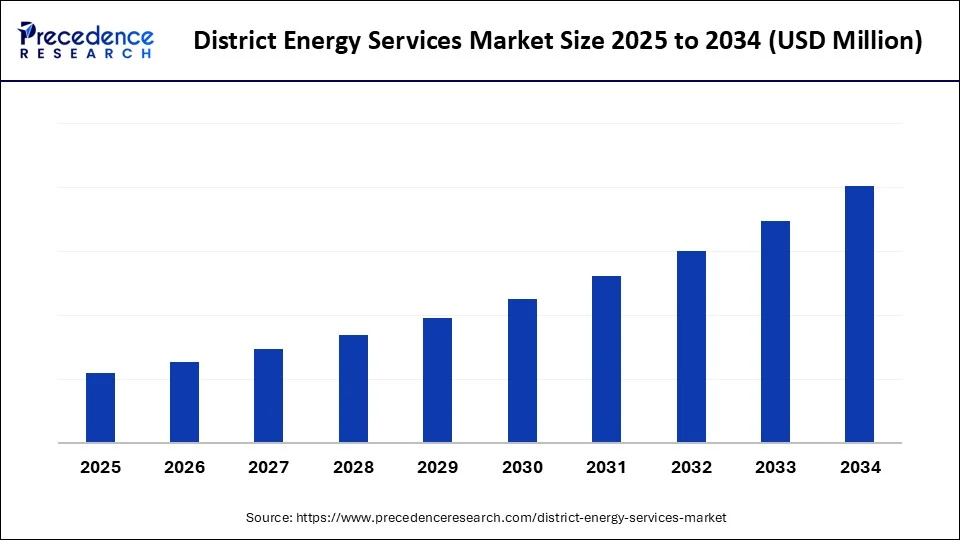
District Energy Services Market Key Takeaways
- Europe dominated the district energy services market in 2024.
- Asia Pacific is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR in the upcoming years.
- By service type, the district heating segment held the largest share in 2024.
- By service type, the combined heating and cooling (CHC) segment is observed to grow at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period.
- By technology, the combined heat and power (CHP) segment generated the major market share in 2024.
- By technology, the heat pumps segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period.
- By end-user, the residential segment dominated the district energy services market in 2024.
- By end-user, the institutional facilities segments segment is expected to grow at a solid CAGR during the forecast period.
- By energy source, the fossil fuels segment contributed the biggest market share in 2024.
- By energy source, the renewables segment is emerging as the fastest growing during forecast period.
- By distribution infrastructure, the hot water segment captured the highest market share in 2024.
- By distribution infrastructure, the chilled water segment is observed to grow at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period.
- By the ownership model, the public utility segment accounted for significant market share in 2024.
- By the ownership model, the public-private partnerships (PPPs) segment is emerging as the fastest-growing during forecast period.
How is Artificial Intelligence Enhancing the Operational Efficiency of District Energy Systems?
District energy systems are becoming much more efficient, thanks to artificial intelligence (AI) that makes network-wide decision-making smarter, quicker, and more accurate. AI algorithms optimize the distribution of heating and cooling loads based on demand patterns, weather, and occupancy trends by analyzing historical and real-time data from sensors, smart meters, and control systems. Better load balancing, less energy waste, and lower operating costs are the outcomes of this. AI also helps with predictive maintenance by anticipating possible equipment failures and reducing repair costs and downtime. To increase fuel efficiency and lower emissions, machine learning models can automatically modify system parameters in energy production facilities. Digital twins, which are virtual representations of physical systems driven by AI, enable operators to model scenarios and optimize performance without disrupting daily operations. AI aids district energy providers in improving cost-effectiveness, sustainability, and dependability while also enhancing real-time system adaptability and resilience.
Market Overview
The district energy services market encompasses the centralized production and distribution of thermal energy (heating and cooling) and, in some cases, electricity to multiple buildings through a network of insulated pipes. This system typically supplies district heating, district cooling, or combined heat and power (CHP) using sources such as waste heat, biomass, geothermal energy, solar energy, or natural gas. District energy systems enhance energy efficiency, reduce carbon emissions, and support urban decarbonization, making them integral to the development of sustainable, smart cities.
The district energy services market is experiencing robust growth, driven by the global push for low-carbon and sustainable energy systems, increasing urbanization, and rising energy demand in densely populated areas. District energy, which encompasses centralized power heating and cooling, leverages waste heat and renewable energy sources to deliver cost-effective energy, reduce emissions, and enhance efficiency. Furthermore, rising government support in the form of favorable laws, financial incentives, and smart city projects supports market growth. Smart metering, AI-powered controls, and digital monitoring are examples of technological innovations that improve system dependability and performance. District energy is becoming a crucial component of future-ready urban development, as cities prioritize environmentally friendly and resilient infrastructure.
Why is District Energy Becoming a Preferred Solution for Sustainable Urban Infrastructure?
District energy is gaining preference in urban planning due to its ability to deliver efficient, centralized heating and cooling while significantly reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Unlike traditional individual building systems, district networks optimize energy use by integrating renewables, capturing waste heat, and distributing it through a shared infrastructure. This model not only supports decarbonization goals but also improves energy reliability and long-term cost savings. As cities strive for net-zero emissions and climate-resilient infrastructure, district energy emerges as a scalable and future-proof solution.
District Energy Services MarketGrowth Factors
- Urbanization and Population Growth: Rapid urbanization, especially in developing nations, has increased demand for efficient, centralized heating and cooling systems. As cities expand vertically and horizontally, district energy systems offer scalable and space-saving solutions.
- Energy Efficiency and Emission Reduction Goals: Governments and industries are prioritizing low-carbon technologies to meet climate targets. District energy systems are significantly more efficient than individual systems and help reduce greenhouse gas emissions by using combined heat and power, waste heat, and renewable energy sources.
- Integration of Renewable Energy: The ability to integrate renewable sources like biomass, solar thermal, and geothermal energy into district networks is a major driver. This enhances energy security and supports the global transition to sustainable energy systems.
- Technological Advancements: Smart grid integration, AI-enabled control systems, and improved thermal storage solutions have increased the operational efficiency of district energy networks. These innovations lower operational costs and improve system responsiveness.
- Rising Demand from Commercial and Industrial Sectors: Large commercial complexes, hospitals, universities, and manufacturing units prefer district energy for a reliable and cost-effective energy supply. Their consistent demand ensures steady revenue for service providers.
Market Scope
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Dominating Region | Europe |
| Fastest Growing Region | Asia Pacific |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | Service Type, Technology, End-User, Energy Source, Distribution Infrastructure, Ownership Model and Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Market Dynamics
Drivers
Decarbonization and Climate Change Commitments
The rising decarbonization goals drives the growth of the district energy services market. District energy systems support decarbonization goals by integrating renewable sources and capturing waste heat from industrial or electricity generation processes. It is imperative to decarbonize heating and cooling since energy production and consumption account for more than 70% of global carbon emissions. Several countries have set their net-zero carbon targets, and many cities are pressuring utilities and developers to build clean energy infrastructure. Comparing district energy to traditional systems, emissions can be reduced by 30 to 50%. Additionally, it is essential to energy transition plans, particularly when it comes to updating and modernizing older streets. Leading the way in the use of district heating systems for carbon-neutral heating are nations like the Netherlands, Sweden, and Denmark.
Urbanization and Infrastructure Development
Rapid urban growth, especially in Asia Pacific and Africa, is creating demand for scalable and integrated utility infrastructure because it facilitates digital monitoring and automation and allows for effective resource management. District energy is a key component of smart city projects. The efficiency of centralized systems becomes even more alluring as cities grow more vertical with high-rise structures and mixed-use developments. To lessen the effects on the environment, construction complexity, and traffic on the roads, infrastructure planning bodies now favor integrated systems. To convert urban waste into useful power, district energy also facilitates the reuse of heat from metro stations, data centers, and industrial facilities. This is in line with global sustainable urban development plans.
Restraints
Complex Regulatory and Approval Processes
Setting up district energy systems involves navigating a complex web of local, regional, and national regulations, hampering the growth of the district energy services market. Zoning regulations, environmental clearances, and public utility commission approvals are a few examples of these. Delays and misunderstandings result from the lack of a clear regulatory framework for district heating and cooling in many areas. To lay underground pipes, utilities must also secure rights of way, which can be expensive and time-consuming. Project deployment is further slowed in developing markets by uneven policies and a lack of agency coordination. When utilities attempt to require user connections or retrofit existing infrastructure, they may also run into legal problems.
Limited Awareness and Market Penetration
Many stakeholders, such as building developers, small businesses, and residents, remain unaware of the benefits and working of district energy. During planning and execution, resistance may arise from misconceptions regarding expenses, dependability, and upkeep. Since they seem more recognizable and manageable, individual systems like boilers, heat pumps, or rooftop chillers are also culturally preferred in several areas. Acceptance is hampered by a lack of consumer education, particularly in residential sectors. Coordinated outreach is necessary to market district energy as a clever and environmentally friendly solution, but it is frequently lacking. Gaining enduring customer loyalty is challenging in the absence of robust public engagement.
Opportunities
Public Private Partnerships (PPPs) and Innovative Financing Models
To overcome high capital costs, municipalities are increasingly turning to PPPs and energy as the service model. With the help of energy performance contracts, these agreements enable private companies to make infrastructure investments while institutions or municipalities make payments gradually. This opens the market to new areas, including developing countries, and lowers barriers to entry. Through risk guarantees and low-interest loans, international institutions such as the World Bank and UNIDO are also assisting district energy expansion. Companies that provide turnkey solutions or design, build, operate, and maintain contracts are consequently discovering new sources of income. Long-term service agreements also guarantee the provider's steady cash flow.
Technological Advancements in Thermal Storage and Heat Pumps
Innovation in thermal energy storage, such as phase change materials, seasonal storage tanks, and underground aquifer systems, is enhancing load flexibility and cost-effectiveness. Additional advanced electric and hybrid heat pumps are gaining popularity, particularly in regions transitioning away from fossil fuels. By using these technologies, district energy systems can balance energy loads and incorporate more sporadic renewable energy sources. Electric-driven heat pumps help reduce carbon footprints as power grids become more decarbonized. This opens doors for tech companies' equipment producers and integrators who provide energy-enhancing next-generation thermal solutions.
Service Insights
Why Did the District Heating Services Segment Dominate the Market in 2024?
The district heating services segment dominated the district energy services market with the largest share in 2024 due to their efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and long-standing use in centralized thermal supply systems. High-density urban development greatly benefits from these services, which make it simple to integrate various heat sources such as waste heat and CHP. Their widespread use is further supported by the technology's maturity, dependability, and suitability for retrofitting older infrastructure. Furthermore, centralized heat supplies improve city-level energy planning and eliminate the need for individual maintenance.
The combined heating & cooling (CHC) services segment is expected to grow at the fastest rate in the upcoming period as they offer year-round thermal comfort with a single infrastructure setup. By meeting both heating and cooling requirements, these systems optimize both space and operational efficiency. Flexible energy solutions are needed for expanding commercial, institutional, and mixed-use developments, and CHC provides them. They are also appealing for contemporary infrastructure because of their compatibility with energy storage and smart controls.
TechnologyInsights
What Made Combined Heat and Power (CHP) the Dominant Segment in the Market in 2024?
The combined heat and power (CHP) segment dominated the district energy services market, holding a significant share in 2024. This technology is widely preferred for its ability to generate both electricity and heat from a single fuel source, significantly increasing overall energy efficiency. By guaranteeing optimal resource utilization, this dual output system lowers operating expenses and its negative impact on the environment. It is more appealing because it can offer energy independence and grid resilience in distributed applications. The extensive use of CHP in institutional and industrial areas bolsters its market dominance.
The heat pumps are the fastest-growing segment due to their efficiency and ability to operate on electricity, aligning with global decarbonization trends. They are suitable for both retrofitting existing installations and performing well in networks with low temperatures. They are perfect for integrated systems because they can be used for both heating and cooling. Adoption is also accelerating in both residential and commercial applications due to increased R&D and policy incentives.
End-User Insights
How Does the Residential Segment Dominate the District Energy Services Market in 2024?
The residential segment dominated the market by capturing the largest revenue share in 2024 as it represents a large and stable demand base for heating services. For buildings with multiple units, centralized systems streamline the energy supply and eliminate the need for separate equipment maintenance. District energy promotes constant indoor comfort and helps achieve building efficiency goals. Because of their scalability and social impact, residential areas are frequently given priority when governments and service providers expand their networks.
The institutional segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR during the projection period. Institutional facilities such as schools, hospitals, and government buildings are making efforts to modernize infrastructure and achieve sustainability goals. These users usually work on campuses that are perfect for systems that use centralized energy. To increase financial viability, they also provide long-term energy contracts. Investments in district energy upgrades are also motivated by the need to set an example in environmental initiatives.
Energy SourceInsights
Why Did the Fossil Fuels Segment Dominate the District Energy Services Market in 2024?
The fossil fuels segment continues to dominate the market because many existing systems were initially designed around natural gas, coal, or oil due to historical availability and low costs. Making the shift away from these sources requires significant capital investment and an overhaul of the infrastructure. Furthermore, some systems integrate cleaner technologies while using fossil fuels as backup or transitional sources. Their supremacy is maintained by the presence of well-established supply chains and legal authorization.
Renewables such as biomass, solar thermal, and geothermal are the fastest growing due to environmental regulations and their capacity to lower emissions. These sources are becoming increasingly attractive while producing reliable, clean thermal energy. More renewable energy sources are being incorporated into the design of modern district systems from the beginning. Adoption rates are increasing in both public and private developments due to technological advancements and supportive funding.
Distribution InfrastructureInsights
What Made Hot Water Distribution the Dominant Segment in the Market?
The hot water distribution segment dominated the district energy services market in 2024 because they are simpler to operate, safer, and use less energy than high-temperature steam systems. In addition to lowering thermal losses, they work well with contemporary energy-saving technologies and renewable heat sources. They operate at a lower temperature, extending the life of equipment and enabling flexible control. Additionally, these networks make maintenance simpler and are simpler to scale for future increases in demand.
The chilled water distribution is the fastest-growing segment because large residential and commercial developments are experiencing a surge in demand for district cooling. The replacement of separate cooling systems promotes increased building energy efficiency. Through the reduction of dependency on peak-load cooling devices, chilled water networks aid in managing electricity demand. They also play a key role in the integration of smart buildings and improving climate control in office parks, malls, and data centers.
Ownership ModelInsights
How Does the Public Utility-Owned Model Dominate the Market?
The public utility-owned segment dominated the district energy services market with the biggest share in 2024 because it ensures equitable energy access, long-term planning, and system-wide coordination. Public organizations often fund major infrastructure initiatives with an eye toward environmental sustainability and the overall well-being of the community. They could issue bonds, obtain government funding, and implement policies to facilitate the transition to clean energy. Stable pricing and consistent service quality are made possible by their centralized management approach.
The public-private partnership (PPPs) segment is expected to expand at the fastest rate, as this model enables innovation, private investment, and shared risk in infrastructure projects. PPPs enable modern energy solutions to be implemented more quickly without placing an undue strain on the public budget. Governments provide user bases and regulatory support, while private companies contribute operational efficiency. For large mixed-use or institutional developments that call for flexible service agreements, this model works particularly well.
Regional Insights
What Made Europe the Dominant Region in the Global District Energy Services Market?
Europe dominated the district energy services market by capturing the largest revenue share in 2024. This is mainly due to its dependable infrastructure, enduring legislative backing, and carbon neutrality guidelines. European countries have been investing heavily in centralized heating and cooling systems for decades, resulting in expanding networks with low emissions and high efficiency. The integration of waste heat, CHP, and renewable energy sources into district systems has been facilitated by robust regulations. Furthermore, Europe's leadership in sustainable district energy development is strengthened by ongoing innovation in smart grid and thermal storage technologies. There is a rapid shift toward renewables, bolstering the regional market growth.
Asia Pacific is expected to grow at the fastest rate during the forecast period. The growth of the market within Asia Pacific is attributed to growing urbanization, increased energy consumption, and a greater emphasis on environmentally friendly infrastructure. Large-scale urban planning initiatives and rapid population growth are driving up demand for centralized heating and cooling systems. Modern energy networks are being deployed more quickly thanks to public-private investments and smart city initiatives. In district systems, the region is also witnessing an increase in the use of clean energy sources, such as geothermal and solar thermal, which contribute to achieving energy access and climate goals. Additionally, the increasing focus on smart grid integration and government regulations aimed at reducing carbon emissions are supporting regional market growth.
District Energy Services Market Companies

- ENGIE SA
- Veolia Environnement S.A.
- Fortum Corporation
- Vattenfall AB
- Emirates Central Cooling Systems Corporation (Empower)
- Ramboll Group
- Keppel Infrastructure Holdings Pte Ltd
- Tabreed (National Central Cooling Company)
- Goteborg Energi AB
- Helen Ltd
- Logstor A/S
- Shinryo Corporation
- Statkraft AS
- NRG Energy, Inc.
- Ørsted A/S
- Babcock & Wilcox Enterprises, Inc.
- Therma Holdings LLC
- Dalkia (EDF Group)
- Korea District Heating Corp.
- Siemens Energy AG
Recent Developments
- In June 2025, Caterpillar Inc. announced the results of a fuel flexibility project with District Energy St. Paul that successfully demonstrated a 2.0 MW combined heat and power (CHP) system with a Cat G3516 gas generator set using 100% hydrogen fuel. The CHP system demonstrated maximum efficiency consistent with high-performance generator sets operating entirely on natural gas.
(Source: https://www.cat.com) - In March 2025, Adani Energy Solutions Ltd (AESL) expanded its district cooling services (DCS) business. The company has been developing this segment for the past few years and is now setting up large-scale cooling facilities across industrial, commercial, residential, and mixed-use projects.
(Source: https://www.angelone.in)
Segments Covered in the Report
By Service Type
- District Heating Services
- District Cooling Services
- Combined Heating & Cooling (CHC) Services
By Technology
- Combined Heat and Power (CHP)
- Boiler-Based Systems
- Chiller-Based Systems
- Heat Pumps
- Solar Thermal
- Geothermal
- Waste-to-Energy
By End-User
- Residential
- Commercial
- Office Buildings
- Hotels & Hospitality
- Retail Centers
- Healthcare Facilities
- Industrial
- Institutional
- Government Buildings
- Universities & Schools
- Military Bases
By Energy Source
- Fossil Fuels (e.g., Natural Gas, Oil, Coal)
- Renewables
- Biomass
- Solar Thermal
- Geothermal
- Waste Heat Recovery
By Distribution Infrastructure
- Hot Water Distribution
- Steam Distribution
- Chilled Water Distribution
By Ownership Model
- Public Utility-Owned
- Privately Owned
- Public-Private Partnership (PPP)
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Ask For Sample
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
 Get a Sample
Get a Sample
 Table Of Content
Table Of Content
 sales@precedenceresearch.com
sales@precedenceresearch.com
 +1 804-441-9344
+1 804-441-9344
 Schedule a Meeting
Schedule a Meeting