What is the Emission Control Technology Market Size?
The global emission control technology market size is calculated at USD 169.28 billion in 2025 and is predicted to increase from USD 182.20 billion in 2026 to approximately USD 350.26 billion by 2035, expanding at a CAGR of 7.54% from2026 to 2035.
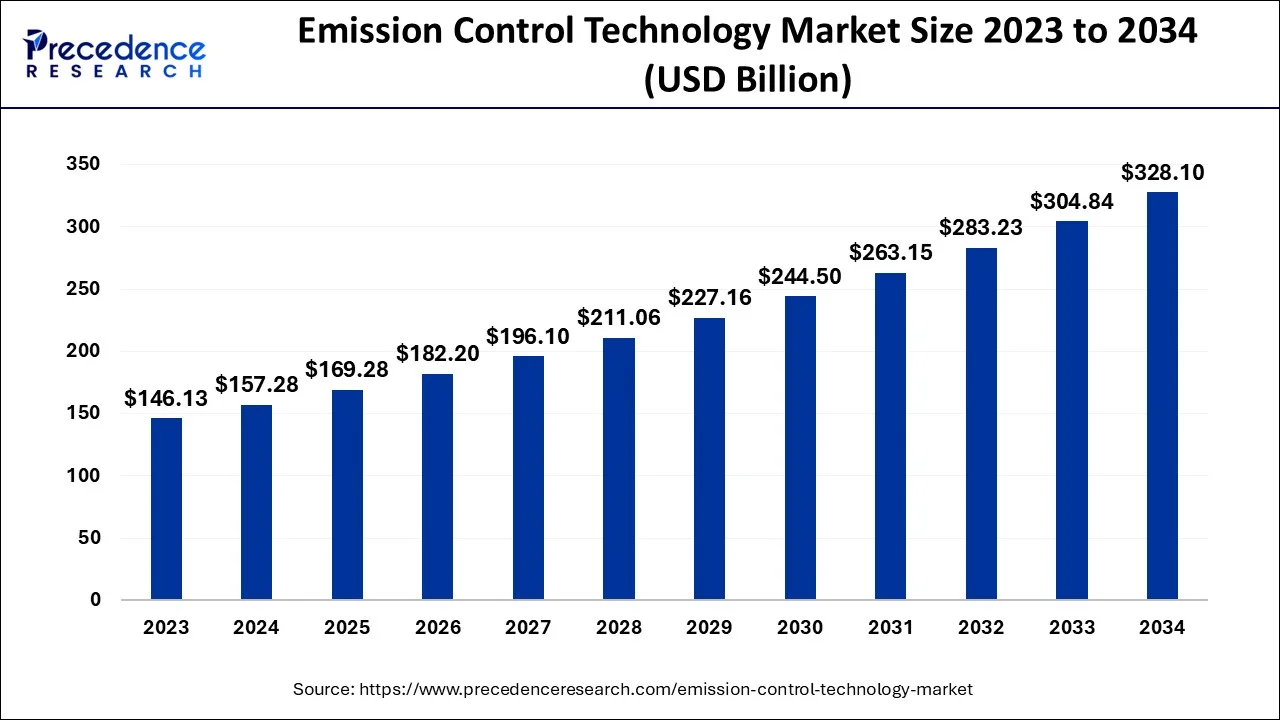
Emission Control Technology Market Key Takeaways:
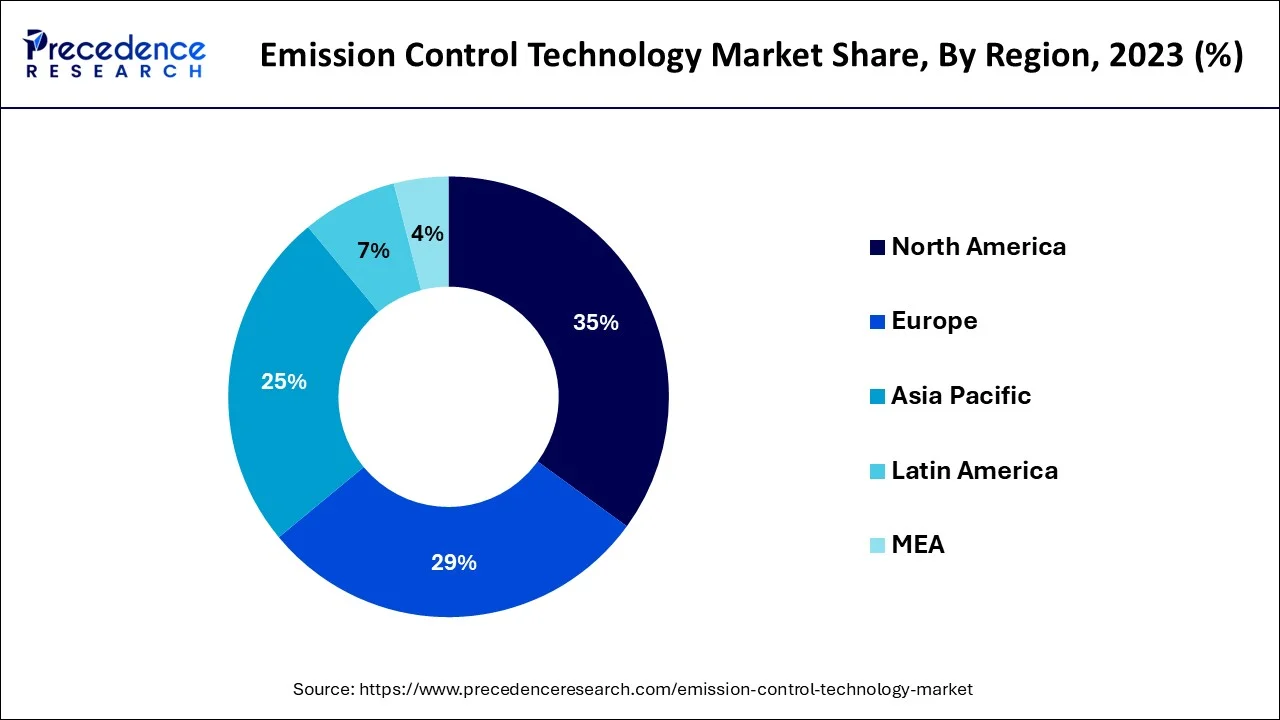
- North America region is predicted to dominate the global market between 2026 to 2035
- The Asia-Pacific region is expected to expand at the fastest CAGR from 2026 to 2035..
- By Technology, the diesel particulate filter (DPF) segment generating for the largest market share.
- By Fuel Type, the diesel segment contributes to the greatest market share.
- By End-user vertical, the automotive segment accounts for the highest market share.
Strategic Overview of the Global Emission Control Technology Industry
Emission control technology refers to a range of techniques, systems, and technologies designed to reduce or eliminate the release of harmful pollutants into the environment. These technologies are employed in various sectors, including industrial processes, transportation, and energy production, to mitigate air, water, and soil pollution. These technologies target different types of pollutants, such as greenhouse gases (e.g., carbon dioxide), nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulfur oxides (SOx), particulate matter (PM), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and other toxic substances. By implementing these technologies, the emission levels of these pollutants can be minimized or effectively treated before release, helping to protect human health, ecosystems, and the overall environment.
The emission control technology market is driven by government regulations and environmental policies aimed at reducing emissions and growing public awareness and demand for cleaner and sustainable solutions. With growing concerns over environmental pollution and the impact of greenhouse gas emissions on climate change, there has been an increased focus on implementing emission control measures across various sectors. As the need for emissions reduction continues to grow, the emission control technology market is expected to expand, providing opportunities for innovation and investment in cleaner and more sustainable solutions.
Furthermore, increasing concerns about climate change and its environmental impacts have led to a global focus on reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Governments, international agreements (such as the Paris Agreement), and sustainability initiatives drive the demand for emission control technologies. These technologies help industries, transportation, and energy sectors reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to global efforts in mitigating climate change.
However, high implementation costs, technological complexity, and compatibility, limited awareness, and education are anticipated to impede the market growth. Emission control technologies often require integrating existing infrastructure, systems, or equipment. Compatibility issues may arise when retrofitting older facilities or vehicles with new emission control technologies. Technical complexities, such as the need for customizations or modifications, can pose challenges and increase implementation costs. Ensuring seamless integration and compatibility across different industries and sectors can restrain market growth.
The lockdown measures implemented by various governments in anticipation of the COVID-19 pandemic have disruptions in supply chains and manufacturing, leading to a slowdown in economic activity and delays or cancellations of planned emission control projects. Industries in aviation, tourism, and manufacturing sectors experienced reduced activity and financial constraints, which limited their capacity to invest in emission control technologies. As a result, the market for emission control technologies experienced a slowdown during the pandemic.
Artificial Intelligence: The Next Growth Catalyst in Emission Control Technology
AI is profoundly impacting the emission control technology industry by enabling more efficient, proactive, and precise solutions for monitoring and reducing pollutants. The technology drives the market through the development of advanced systems that can analyze vast amounts of data from sensors in real-time, leading to optimized industrial processes, improved energy efficiency, and enhanced regulatory compliance.
For instance, machine learning algorithms facilitate predictive maintenance of emission control equipment (like catalytic converters and oxygen sensors), preventing failures and associated emission spikes before they occur, which reduces costly downtime and environmental damage.
Emission Control Technology Market Outlook:
- Industry Growth Overview:
Between 2024 and 2034, the emission control technology market is projected to witness strong growth, driven by tightening global emission norms across automotive, industrial, and power generation sectors. The need to improve air quality in cities, particularly in the Asia-Pacific and Europe, has increased demand for diesel oxidation catalysts, selective catalytic reduction (SCR), and diesel particulate filters (DPFs). Market growth is also driven by rising environmental awareness and government incentives for clean technology. - Sustainability Trends:
Sustainability trends are transforming the emission control landscape, prompting companies to develop low-platinum and precious-metal-efficient catalysts that minimize environmental impact. Additionally, IoT and real-time monitoring have enhanced energy efficiency and lowered operational emissions in emission control systems. Innovations driven by sustainability are now a key differentiator among vendors in the global market. - Global Expansion:
Leading emission control technology vendors are strategically expanding their presence in emerging and high-growth regions to align with stricter environmental regulations and increasing industrialization. Firms such as Tenneco and CORMETECH are investing in local manufacturing and distribution channels to reduce costs and shorten delivery cycles. This international expansion allows vendors to gain a competitive edge while also addressing region-specific regulatory requirements. - Major Investors:
Private equity and strategic investors are increasingly entering the emission control technology market, attracted by regulation-driven demand and stable aftermarket revenue streams. Major firms such as KKR, Temasek, and The Carlyle Group have invested heavily in startups developing catalyst and emission technologies, with tightening global regulations ensuring sustained market growth and appealing long-term investment potential. - Startup Ecosystem:
The emission control technology startup ecosystem is rapidly expanding, with companies focusing on next-generation catalysts, hybrid systems, and IoT-enabled exhaust monitoring solutions. These startups are attracting significant venture capital by offering modular, scalable, and retrofit-compatible systems for automotive, industrial, and power-generation applications, while also exploring innovations in precious metal recovery, eco-friendly surface finishes, and weight-saving substrate technology to improve efficiency and reduce environmental impact.
Emission Control Technology Market Trends
- Stricter Global Environmental Regulations
Governments and international bodies worldwide are implementing and enforcing more rigorous emission standards (e.g., Euro 7, China VI, EPA standards) for both mobile (vehicles) and stationary (industrial plants) sources. - Development of Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS) Technologies
A significant trend is the expansion of emission control beyond traditional pollutants (like NOx and particulate matter) to include carbon dioxide (CO2). - Shift Towards Electrification and Hybrid Solutions
While the demand for traditional emission control systems for internal combustion engines remains strong, especially in emerging markets, the growing production and adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid systems is a major disruptive trend. - Focus on the Circular Economy and Sustainable Materials
There is a rising emphasis on sustainability, which includes the development of better ways to recover and recycle expensive precious metals (platinum, palladium, rhodium) used in catalysts from end-of-life products.
Market Scope
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 169.28 Billion |
| Market Size in 2026 | USD 182.20 Billion |
| Market Size by 2035 | USD 350.26 Billion |
| Growth Rate from 2026 to 2035 | CAGR of 7.86% |
| Largest Market | North America |
| Fastest Growing Market | Asia Pacific |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 to 2035 |
| Segments Covered | By Technology, By Fuel Type, and By End-User Vertical |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Market Dynamics
Key Market Drivers
Government regulations and policies to brighten the market prospect
With increasing concerns about environmental sustainability and the need to mitigate climate change, governments worldwide have implemented stringent regulations to limit pollutant emissions and promote cleaner practices. These regulations create a market demand for emission control technologies as industries, vehicles, and power plants must adopt measures that reduce emissions and meet specific environmental standards. Governments set emission standards for various sectors, including industrial processes, power generation, transportation, and commercial buildings. These standards define the maximum allowable levels of pollutants that can be emitted, compelling industries and businesses to implement emission control technologies to meet the prescribed limits. For instance, in April 2023, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency announced new, more ambitious proposed standards to further reduce harmful air pollutant emissions from light-duty and medium-duty vehicles starting with the model year 2027.
In addition, governments provide financial incentives to encourage the adoption of emission control technologies. These incentives include tax credits, grants, subsidies, or favorable financing options, offset initial costs, and promote investment in cleaner technologies. Financial support programs encourage industries, vehicle manufacturers, and power plants to adopt emission control technologies and accelerate market adoption. Moreover, governments may establish market-based mechanisms such as emissions trading systems or carbon pricing schemes. These mechanisms create economic incentives for emissions reductions by putting a price on carbon emissions. Industries can reduce emissions and potentially lower compliance costs or generate revenue through emissions trading by implementing emission control technologies.
Climate change mitigation
The increasing recognition of the urgent need to reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and combat climate change, there is a growing demand for innovative solutions that can effectively control and minimize emissions across various sectors. Emission control technologies are vital in meeting these goals by enabling industries, transportation systems, and power generation facilities to reduce their environmental impact. The global commitment to climate change mitigation, as evidenced by international agreements like the Paris Agreement, has prompted governments and organizations to implement regulations and policies that encourage the adoption of emission control technologies. These technologies help industries transition to cleaner and more sustainable practices, significantly reducing GHG emissions.
In addition, the transition to a sustainable energy system is crucial to climate change mitigation. This transition involves a shift from fossil fuel-based energy sources to renewable energy systems. Emission control technologies, such as energy storage systems, grid optimization solutions, and advanced power generation technologies, are essential for integrating and efficiently utilizing renewable energy sources. The increasing demand for renewable energy and the need to decarbonize the energy sector further drive the demand for emission control technologies. In addition, the promotion of low-carbon transportation, the electrification of vehicles, and the development of sustainable transportation alternatives contribute to the demand for emission control technologies. Advanced emission reduction systems, charging infrastructure, and efficient transportation management solutions are necessary to support the widespread adoption of clean transportation options and reduce emissions from the transportation sector. Thus, climate change mitigation efforts and the global commitment to reduce GHG emissions are key drivers of the demand for emission control technologies.
Key Market Challenges
The high cost of emission control technology is causing hindrances to the market
The upfront investment required to install and integrate these technologies can be substantial, deterring businesses, industries, and governments from embracing them. The initial investment for emission control technologies often includes purchasing specialized equipment, retrofitting existing infrastructure, and upgrading processes. These costs can be especially burdensome for smaller businesses and organizations with limited financial resources. The high capital expenditure required upfront creates a barrier to entry, preventing many potential buyers from investing in emission control technologies. Furthermore, these technologies' return on investment (ROI) may take time to materialize. While emission control technologies can lead to long-term cost savings through reduced energy consumption, lower emissions, and improved operational efficiency, recouping the initial investment may take several years. This delayed ROI can deter organizations, particularly those focused on short-term financial goals, from prioritizing adopting emission control technologies.
Moreover, Financial institutions may perceive emission control technologies as high-risk investments, resulting in stricter lending criteria or higher interest rates. This lack of affordable financing options further exacerbates the implementation cost challenge. It hampers the demand for emission control technologies, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) or organizations operating in regions with less developed financial markets. Uncertainty surrounding future regulations and policies also plays a role in hindering the demand for emission control technologies. If businesses are unsure about the stability or longevity of emission control regulations, they may hesitate to invest in technologies that address these regulations. The absence of regulatory clarity can create a wait-and-see approach, leading to delayed demand for emission control technologies. Therefore, the high implementation costs associated with emission control technologies significantly restrain their market demand.
Key Market Opportunities:
- Adoption of clean energy sources
- Industrial emission reduction
- Sustainable transportation solutions
Segment Insights
Technology Insights
On the basis of technology, the emission control technology market is divided into diesel particulate filters (DPF), gasoline particulate filters (GPF), diesel oxidation catalysts (DOC), selective catalytic reduction (SCR), and exhaust gas recirculation (EGR), with the diesel particulate filter (DPF) segment accounting for most of the market. Diesel particulate filters (DPFs) are specifically designed to capture and remove particulate matter (PM) or soot from the exhaust gases emitted by diesel engines. They play a crucial role in reducing emissions of harmful particles and ensuring compliance with stringent environmental regulations. DPFs trap and collect fine particles, preventing them from being released into the atmosphere. Periodic regeneration processes burn off the accumulated particles, maintaining the filter's efficiency.
Fuel Type Insights
On the basis of the fuel type, the emission control technology market is divided into gasoline and diesel, with diesel accounting for most of the market. This is because diesel engines are widely used in various sectors, including transportation, industrial applications, and power generation. These engines are known for their efficiency and high torque output, making them preferred in heavy-duty applications. However, diesel engines typically produce higher emissions of pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter (PM) than gasoline engines. Therefore, the demand for emission control technologies for diesel engines is significant.
End-User Vertical Insights
On the basis of the end-user vertical, the emission control technology market is divided into automotive, marine, aerospace, off-highway, rolling stock, and industrial, with automotive accounting for most of the market. This is because the automotive industry is a major consumer of emission control technologies. As governments implement stricter emission regulations to reduce air pollution and combat climate change, automakers must adopt effective vehicle emission control technologies. Technologies such as catalytic converters, diesel particulate filters (DPFs), selective catalytic reduction (SCR), gasoline particulate filters (GPFs), and exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) systems are widely used in vehicles to reduce emissions of pollutants like nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM), and greenhouse gases.
Regional Insights
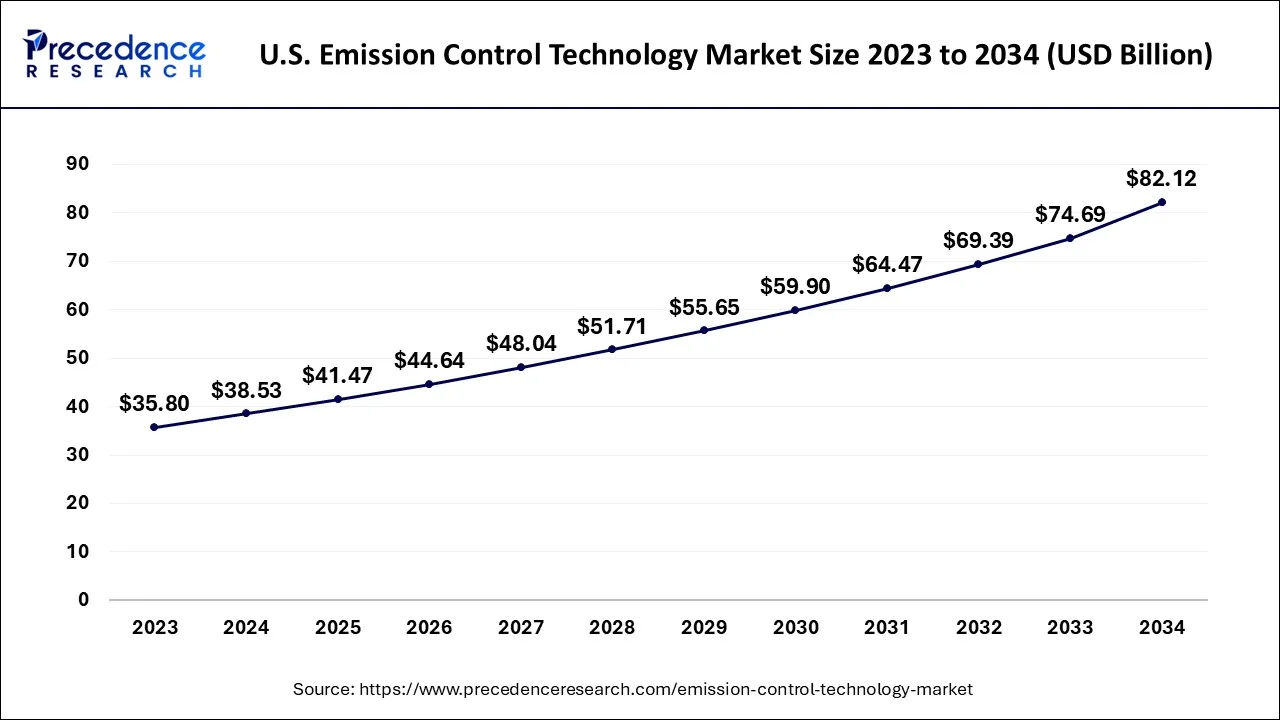
What is the U.S. Emission Control Technology Market Size?
The U.S. emission control technology market size is estimated at USD 41.47 billion in 2025 and is expected to be worth around USD 88.13 billion by 2035, expanding at a CAGR of 7.83% between 2026 to 2035.
North America
North America dominates the market, primarily driven by stringent emission regulations, technological advancements, a strong automotive industry, and the region's focus on environmental sustainability. North America has implemented stringent emission regulations to curb air pollution and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. These regulations have mandated using advanced emission control technologies in various industries, including automotive, marine, aerospace, and industrial sectors. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States and regulatory bodies in Canada have set emission standards that drive the demand for emission control technologies in the region.
U.S. Emission Control Technology Market Analysis
The U.S. is expected to lead the North American emission control technology market, driven by stringent federal and state regulations targeting power generation and the transportation sectors. The market is projected to grow rapidly due to increasing urbanization, rising environmental consciousness, and government pressure to improve industrial cleanliness, with additional demand driven by the need to retrofit older equipment and the growth of aftermarket services.
Why is Europe Considered a Significant Market?
Europe is a significant market for emission control technology, with Germany, the United Kingdom, and France being the major contributors to the market's growth. This is because Europe has significantly committed to reducing greenhouse gas emissions under the Paris Agreement and its climate targets. These commitments necessitate the adoption of emission control technologies across different industries. The European Green Deal and other sustainability initiatives promote the transition to cleaner technologies, driving the demand for emission control solutions.
Asia Pacific
The region in Asia-Pacific is anticipated to have the greatest CAGR due to its large population, expanding industries, and increasing environmental concerns. With governments' focus on air quality improvement and sustainability, the demand for emission control technologies is expected to grow significantly in the region. Furthermore, governments in the Asia-Pacific region are actively promoting environmental sustainability and low-carbon development. Initiatives such as the National Clean Air Program in India, the Green Growth Strategy in South Korea, and China's efforts to combat air pollution drive the demand for emission control technologies. Governments provide incentives and subsidies to encourage the adoption of clean technologies, creating opportunities for the emission control technology market.
Germany Emission Control Technology Market Analysis
Germany is expected to dominate the European emission control technology market, driven by stringent environmental regulations like Euro 7 and robust sustainability policies. The country's strong automotive manufacturing base and industrial sector, coupled with cross-border trade agreements within the EU, are expected to accelerate technology adoption and market penetration throughout the region.
What Makes Asia Pacific the Fastest-Growing Area in the Emission Control Technology Market?
China is expected to lead the Asia-Pacific emission control technology market, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and the strict enforcement of emission standards across manufacturing, energy, and transportation sectors. Collaborations between local and foreign suppliers are enhancing access to emission control products and services, while growing demand for sustainable industrial practices in India, Japan, and South Korea is expected to drive further market growth across the region.
What Potentiates the Growth of the Market in Latin America?
The emission control technology market in Latin America is expected to grow at a steady rate in the upcoming period, driven by increasing industrialization, urban pollution challenges, and regulatory pressure from key countries in the region. The market's growth is further supported by emerging private sector financing for environmental compliance projects, while partnerships with foreign technology suppliers are likely to enhance product accessibility and foster greater competition in the market.
Brazil Emission Control Technology Market Analysis
Brazil leads the market in Latin America, supported by increasing industrialization, urban air quality concerns, and stricter emission regulations. The market is expected to grow further through investments in upgrading power stations, manufacturing facilities, and transportation infrastructure. Environmental sustainability efforts and government incentives are likely to boost adoption in the industrial and automotive sectors.
What Opportunities Exist in the Middle East and Africa for Market Expansion?
The Middle East and Africa (MEA) present significant opportunities for expanding the emission control technology market due to increasing industrialization, energy production, and government efforts to reduce air pollution. Growing output in the manufacturing, energy, and transportation industries creates a demand for emission control measures. International vendors are partnering with domestic companies to transfer technology and implement products. Further growth in the market is expected from economic incentives and policies focused on sustainability.
UAE Emission Control Technology Market Analysis
The UAE is projected to lead the Middle East and Africa emission control technology market, driven by significant industrial expansion, energy production, and the government's focus on reducing emissions. The rapid expansion of the energy, manufacturing, and transport sectors also contributes to the market growth.
Value Chain Analysis of the Emission Control Technology Market
- Raw Material Sourcing
The foundation of emission control technology lies in the sourcing of specialized raw materials such as precious metals (platinum, palladium, rhodium), ceramic substrates, stainless steel, and advanced coatings. These materials are critical for manufacturing catalysts, filters, and other emission-reducing components.
Key Players: Johnson Matthey, Umicore, BASF SE, Albemarle Corporation - Component Fabrication
Raw materials are processed into functional components, including catalytic converters, diesel oxidation catalysts (DOCs), selective catalytic reduction (SCR) catalysts, diesel particulate filters (DPFs), and adsorbers. Precision manufacturing and coating techniques are applied to ensure optimal chemical activity and durability.
Key Players: Corning Incorporated, Clariant AG, DCL International Inc., CORMETECH - Emission Control Device Manufacturing
Catalyst-coated substrates are integrated into full emission control devices, including automotive catalytic converters, industrial SCR systems, and stationary source scrubbers. This stage focuses on engineering devices to meet strict emission standards and regulatory compliance.
Key Players: Tenneco Inc., Clean Diesel Technologies Inc., AeriNOx Inc., Johnson Matthey - System Integration & Testing
Devices are installed in automotive exhaust systems, power plants, and industrial equipment. Advanced testing ensures performance under real-world operating conditions, including temperature extremes, engine load variability, and fluctuations in pollutant concentrations.
Key Players: Tenneco Inc., DCL International Inc., AeriNOx Inc. - Distribution to OEMs and Industrial Clients
Finished emission control systems are delivered to automobile manufacturers, industrial plants, power generation companies, and heavy equipment OEMs. Aftermarket solutions are also supplied for retrofitting older engines to comply with updated regulations.
Key Players: Tenneco Inc., Johnson Matthey, Umicore, Clean Diesel Technologies Inc.
Emission Control Technology Market Companies
- DCL International Inc.: A global provider of advanced emission control systems for stationary and mobile engines, including diesel particulate filters (DPFs), SCR systems, and catalytic mufflers.
- Umicore: Provides industrial and automotive emission control catalysts and materials, supporting power generation, refining, and mobility sectors with advanced catalyst technologies.
- Tenneco Inc.: Designs and manufactures exhaust after treatment systems and emission control solutions for light vehicles, commercial trucks, and off-highway vehicles, meeting stringent global standards.
- CORMETECH, Inc.: Manufactures SCR catalysts, adsorbers, and full lifecycle catalyst management services for power, industrial, and hydrogen applications to reduce NOâ‚“, CO, and VOCs.
- Clean Diesel Technologies, Inc.: Develops and supplies retrofit emission control devices and catalyst systems for heavy-duty and light-duty diesel vehicles, reducing PM, HC, and CO emissions.
- Clariant AG: Offers speciality emissions control catalysts for industrial off gases (e.g., EnviCat series) that remove harmful substances including NOâ‚“, Nâ‚‚O, and VOCs from chemical plants and stationary sources.
- Corning Incorporated: Supplies ceramic substrates and emission control devices for automotive catalytic converters, supporting tighter diesel and gasoline emission standards.
- AeriNOx Inc.: Specializes in turnkey Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) systems for large stationary diesel and natural gas engines, achieving up to ~98% NOâ‚“ reduction.
- BASF SE: It provides advanced catalysts and materials that improve vehicle emissions performance and industrial air quality.
- Johnson Matthey: It plays a key role in the market with its innovative emissions reduction technologies, including catalysts for automotive and industrial applications, focused on reducing harmful pollutants and supporting regulatory compliance.
Recent Developments
- In March 2024, Intangles Lab unveiled an AI-powered Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) solution for commercial vehicles. These vehicles are providing advanced insights into DPF regeneration quality to enhance fuel efficiency and engine performance.
(Source:www.intangles.ai/) - In September 2024, Light Path Technologies launched the Mantis high-temperature monitoring camera system. The system is designed for accurate monitoring across a broader range of temperatures in industrial burn processes to optimize operations and reduce COâ‚‚ emissions. (Source:finance.yahoo.com/)
- In December 2021,the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) approved and implemented federal greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions standards for passenger cars and light trucks, covering Model Years (MY) 2023 through 2026. These finalized standards capitalize on advancements in clean car technology, resulting in many benefits for the American population. Notably, they are projected to yield net benefits of approximately $190 billion. These benefits encompass reducing climate pollution, enhancing public health, and cost savings for drivers at the fuel pump.
- In June 2023,Chart Industries, Inc., a leading engineering design and manufacturing company specializing in clean energy and industrial gas applications, revealed its collaboration and contract agreement with Kathairos Solutions, a Calgary-based cleantech startup. This partnership aims to assist Kathairos in meeting the methane reduction targets set by the oil and gas industry. Over the next few years, Kathairos plans to deploy tens of thousands of its proprietary nitrogen systems across North America, and the partnership with Chart Industries ensures they will have the necessary capacity to achieve this goal.
Segments Covered in the Report:
By Technology
- Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF)
- Gasoline Particulate Filter (GPF)
- Diesel Oxidation Catalyst (DOC)
- Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR)
- Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR)
By Fuel Type
- Gasoline
- Diesel
By End-User Vertical
- Automotive
- Marine
- Aerospace
- Off-highway
- Rolling Stock
- Industrial
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Ask For Sample
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
 Get a Sample
Get a Sample
 Table Of Content
Table Of Content




 sales@precedenceresearch.com
sales@precedenceresearch.com
 +1 804-441-9344
+1 804-441-9344
 Schedule a Meeting
Schedule a Meeting