Genetic Editing for ASCVD Market Size and Forecast 2025 to 2034
Market insights on genetic editing for ASCVD, featuring CRISPR based therapies targeting PCSK9 & ANGPTL3 to transform cardiovascular disease treatment. The genetic editing for ASCVD market is propelled by advanced research infrastructure, strong regulatory support, and growing demand for personalized cardiovascular therapies.
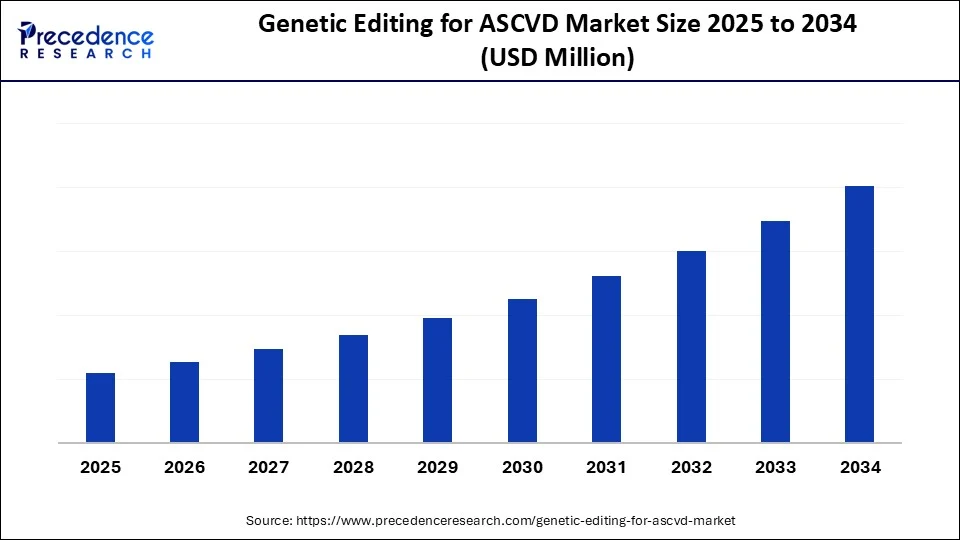
Genetic Editing for ASCVD MarketKey Takeaways
- North America dominated the genetic editing for ASCVD market with the largest market share 52% in 2024.
- Asia Pacific is anticipated to witness the fastest growth during the forecast years.
- By editing modality, the CRISPR/Cas9 gene knockout segment captured the biggest market share of 44% in 2024.
- By editing modality, the base editing segment is anticipated to show considerable growth over the forecast period.
- By therapeutic target, the PCSK9 segment contributed the highest market share of 38% in 2024.
- By therapeutic target, the ANGPTL3 segment is anticipated to show considerable growth over the forecast period.
- By delivery system, the AAV vectors segment held a significant market share in 2024.
- By delivery system, the lipid nanoparticles segment is anticipated to show considerable growth over the forecast period.
- By stage of development, the preclinical research segment held a significant market share in 2024.
- By stage of development, the phase I/II clinical trials segment is anticipated to show considerable growth over the forecast period.
- By end user, the pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies segment generated the major market share in 2024.
- By end-user, the specialty cardiology clinics segment is anticipated to exhibit the fastest growth over the forecast period.
How Is AI Integration Transforming Genetic Editing for ASCVD Market?
The integration of Artificial Intelligence is transforming the genetic editing for ASCVD by enhancing the efficiency, speed, and safety of gene therapies to a great extent. AI algorithms analyze vast genomic data to pinpoint optimal gene targets like PCSK9 or ANGPTL3, predicting off-target effects and minimizing unintended edits. This enhances the design and delivery of CRISPR treatments. AI also accelerates drug discovery, automates workflow optimization, and enables real-time editing and results monitoring.
Market Overview
The genetic editing for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) market refers to the application of next-generation gene editing technologies, such as CRISPR, base editing, and siRNA/ASO gene silencing, to prevent, treat, or reverse cardiovascular disorders caused by genetic dyslipidemia and inflammation, primarily familial hypercholesterolemia (FH), elevated Lp(a), PCSK9/LDLR mutations, and chronic vascular inflammation. The goal is to offer one-time or long-term disease-modifying treatments rather than lifelong lipid-lowering or anti-inflammatory drugs.
The genetic editing for ASCVD market is experiencing substantial growth, driven by advancements in CRISPR and gene therapy technologies. The rising prevalence of ASCVD, coupled with a growing demand for personalized medicine, is accelerating gene-targeted research. Increased funding for genomic research from government and private organizations, along with collaborations between biotech companies and healthcare networks, are further enhancing market growth. Moreover, the identification of genetic mutations, such as PCSK9 and ANGPTL3, linked to ASCVD, has opened up new avenues for therapeutic intervention.
What Factors are Fueling the Growth of the Genetic Editing for ASCVD Market?
- Innovations in Technology of Gene Editing: The discovery of gene editing tools such as CRISPR-Cas9, TALENs, and base editing has made gene editing easier, accurate, and less expensive. These technologies make it significantly easier to alter the genes implicated in ASCVD, including PCSK9 and ANGPTL3.
- Increment in the Frequency of ASCVD: Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease continues to be a cause of mortality and morbidity in the world. The rising burden of the disease leads to an immediate need for new and long-term treatment methods, such as gene editing, where investments and research speed are accelerated.
- Long-term Industry Partnerships and Investment:The drug companies, start-up companies in the biotechnological field, and the university research centers are forging strategic partnerships to speed up the implementation of gene treatments for ASCVD. Such alliances increase research and development, as well as streamline clinical testing.
Market Scope
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Dominating Region | North America |
| Fastest Growing Region | Asia Pacific |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | Editing Modality,Therapeutic Target, Delivery System, Stage of Development, End User, and Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Market Dynamics
Drivers
Focus on Personalized Medicine
The growing emphasis on personalized medicine is one of the major factrs driving the growth of the genetic editing for ASCVD market. With technologies such as CRISPR-Cas9, clinicians can directly edit the genes involved in lipid metabolism and cardiovascular risk, including PCSK9 and ANGPTL3. This individualized method enhances the success of therapy because it targets the underlying cause of the disease, rather than just the symptoms. Additionally, it will reduce the likelihood of negative reactions and improve the effectiveness of treatment. Genomic sequencing and bioinformatics can assist healthcare providers in identifying patients whose health conditions are most likely to be improved with the help of gene editing, reduce resource waste, and ultimately benefit patients.
Restraint
Ethical and Regulatory Challenges
One of the major inhibitors of the genetic editing market for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease is the complex ethical and regulatory framework. Methods, such as CRISPR-Cas9, which hold promise for revolutionizing the field of curing, raise significant ethical concerns related to safety, germ-line modification, and their potential unforeseen outcomes. Off-target effects, which result in the alteration of genes other than the intended target gene, are a significant risk to patient safety that regulators can not overlook. As a result, strict regulatory clearances and increased time to clinical trials hamper the commercialization process and their mass adoption.
Opportunity
Innovation of New Treatments
The continual evolution of new gene editing technologies and delivery systems presents a significant opportunity to enhance genetic therapy in the treatment of ASCVD. Most of the newer techniques, such as base editing, prime editing, and epigenome editing, find applications where ordinary CRISPR-Cas9 methods are not feasible. The second-generation tools are more precise, less likely to create off-target effects, and they may enable gene repair without introducing double-stranded breaks in the genome. This change might be safer and more effective. With the progress in research, it is now possible to correct multiple genetic risk factors simultaneously or modulate gene expression in adults using these new techniques.
Editing Modality Insights
Why Did the CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Knockout Segment Contribute the Most Revenue in 2024?
The CRISPR/Cas9 gene knockout segment held a 44% share of the genetic editing for ASCVD market in 2024 due to its proven efficacy. CRISPR/Cas9, a powerful gene-editing tool, induces specific DNA breaks, leading to insertions or deletions that disrupt disease-causing genes. This method is used in ASCVD to silence genes like PCSK9 and ANGPTL3, which are involved in lipid metabolism and high cholesterol, key factors in plaque formation. CRISPR/Cas9 gene knockout offers advantages such as a more established research foundation, lower development costs, and easier scalability compared to other methods.
The base editing segment is likely to grow at the fastest rate in the coming years due to its high precision and safety rates, making it a potentially valuable genetic editing and modification tool in managing ASCVD. This specificity reduces off-target effects and genomic instability, and base editing is especially appealing for correcting single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) associated with cardiovascular risks. Advances such as adenine base editors (ABE) and cytosine base editors (CBE) have been actively investigated as a method of curing pathogenic mutations in several genes involved in lipid metabolism. Due to the constantly increasing efficiency and safety data, base editing promises to transform the field of future ASCVD treatment, presenting extremely personalized and long-lasting treatment options.
Therapeutic Target Insights
How Does the PCSK9 Segment Lead the Genetic Editing for ASCVD Market in 2024?
The PCSK9 segment led the market while holding a 38% share in 2024 due to the clinical validation of PCSK9 as a demonstrable cholesterol-lowering target, specifically low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), a major risk factor for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. This leads to increased recycling of the LDL receptor and enhanced clearance of LDL-C from the blood. The long-term advantage of this strategy is that it is likely to reduce LDL-C levels throughout a person's life with a single intervention, thereby preventing the need for lifelong medication such as statins or injectable PCSK9 inhibitors. It has been found that PCSK9 is being focused on by both top biotech companies and research groups, as its biology is well understood and has high therapeutic potential.
The ANGPTL3 segment is expected to grow at a significant CAGR over the forecast period. ANGPTL3 plays a key role in regulating lipid metabolism. It works by blocking lipoprotein lipase and endothelial lipase, which are involved in breaking down triglycerides and LDL-C. This makes ANGPTL3 significant in managing high levels of lipids. Its therapeutic value is especially notable in rare lipid disorders like familial combined hyperlipidemia. Several biotech firms are working on gene editing therapies for ANGPTL3, aiming for a single, long-lasting treatment. Given its promising early results and increasing investment, ANGPTL3 is expected to experience significant growth, becoming a key component in future treatments for ASCVD.
Delivery System Insights
What Made AAV Vectors the Dominant Segment in the Genetic Editing for ASCVD Market in 2024?
The AAV vectors segment dominated the market, accounting for the largest revenue share in 2024, as AAV vectors are a favored method for delivering in vivo gene editing therapies, driven by their efficient gene transfer, lasting gene expression, and low immune response. In treating atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD), AAV vectors show promise for targeting the liver, which is crucial for lipid metabolism. By delivering CRISPR/Cas9 components directly to the liver, AAV's ability to target specific tissues and provide stable gene expression with a single dose makes it an ideal tool for correcting the disease.
The lipid nanoparticles segment is expected to grow at a significant CAGR over the forecast period because they are non-viral, repeatable, and extremely customizable. LNPs offer several advantages over viral vectors due to their higher safety and lower likelihood of causing immune responses, which is not always the case with viral systems. These benefits are especially important in cardiovascular treatments, where long-term safety, patient adherence, and precise targeting are critical. With increasing research and promising early results, LNP-based delivery is rapidly emerging as a leading approach for future genetic treatments for ASCVD.
Stage of Development Insights
Why did the Preclinical Research Segment Contribute the Most Revenue in 2024?
The preclinical research contributed the most revenue in 2024 and is expected to sustain its position throughout the projection period. Numerous pharmaceutical companies and research groups are actively working on gene-editing approaches for the PCSK9, ANGPTL3, and Lp(a) genes, which are strongly linked to elevated cholesterol levels and cardiovascular disease risk. To assess their effectiveness, delivery capabilities, and safety, these organizations are conducting in vitro and animal studies to evaluate various editing methods like gene knockouts, base editing, and prime editing.
Significant non-dilutive investments, including grants, government incentives, and early licensing opportunities, are supporting preclinical efforts. Promising results from animal models, indicating sustained control of LDL-C and triglycerides with a single treatment, are further driving interest. Because gene editing aims to provide lasting, single-dose cures for ASCVD, investments in this preclinical phase are expected to continue.
The phase I/II clinical trials segment is expected to grow at a significant rate in the upcoming period, fueled by the development of promising therapies into human trials. Specifically, several companies are advancing in vivo gene-editing programs targeting PCSK9, with some having already initiated patient recruitment and released preliminary safety and efficacy data. These studies evaluate the use of CRISPR/Cas9 therapeutics in humans for the first time, potentially leading to long-term reductions in LDL-C following treatment. The benefits for participating companies include increased investor confidence, enhanced public visibility, and the opportunity to establish leadership in a dynamic, competitive market.
End User Insights
Why Did the Pharmaceutical & Biotechnology Companies Segment Dominate the Genetic Editing for ASCVD Market in 2024?
The pharmaceutical & biotechnology companies segment dominated the genetic editing for ASCVD market, holding the largest revenue share in 2024. These companies heavily utilize reagents and tools, such as CRISPR/Cas9, base editing, and prime editing, to develop groundbreaking therapies that address the genetic origins of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. These companies possess significant R&D resources, advanced infrastructure, and collaborative ventures, positioning them as leaders in preclinical research, clinical trials, and commercialization strategies. Furthermore, venture capitalists, government agencies, and strategic partners are prepared to make substantial investments in these companies, generating revenue through licensing, milestone payments, and technology platforms. Many of the leading gene-editing companies have partnered with major pharmaceutical companies to scale delivery systems, optimize clinical performance, and prepare for commercialization.
The specialty cardiology clinics segment is expected to experience rapid growth during the forecast period, fueled by the increasing clinical application of novel genetic treatments. As CRISPR-based interventions transition from research to patient treatment, these clinics will play a crucial role in delivering gene-editing therapies, particularly for conditions with complex cardiovascular risk factors, such as elevated LDL-C and triglycerides. These centers are also better equipped to address the ethical, technical, and logistical challenges associated with one-time gene-editing therapies, including patient eligibility, genetic counseling, and informed consent. Additionally, as patients and physicians become more aware of the potential of personalized medicine, the adoption of genomic-based ASCVD treatments may be more prevalent in specialty clinics compared to general hospitals or primary-care settings.
Regional Insights
What Made North America the Dominant Region in the Genetic Editing for ASCVD Market in 2024?
North America led the market, holding a 52% share in 2024. This is mainly due to its well-established genetic therapy ecosystem and robust biomedical innovation infrastructure. Strong financial support from venture capitalists, government organizations like the NIH, and the private sector fuels preclinical and clinical development, ensuring the development of innovative therapies. Coupled with increased awareness of personalized medicine and greater access to genetic testing, North America is poised to remain a key driver of growth in the global market. The U.S. is a major contributor to the market. An aging population, rising rates of obesity and hyperlipidemia, and growing healthcare costs are driving investments in gene editing by healthcare stakeholders. Furthermore, the U.S. regulatory framework, led by the FDA, has shown increasing support for genetic therapies by providing expedited classifications and guidance on genome-editing procedures. The country also hosts the most active Phase I/II trials focused on cardiovascular gene editing, solidifying its leading role in clinical advancements.
Why Is the Asia Pacific Region Expected to Grow at the Fastest CAGR?
Asia Pacific is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period. This is primarily due to increased investment in biotechnology, growing awareness of genetic diseases, and advancements in healthcare infrastructure. Nations such as Japan, India, South Korea, and Singapore are actively establishing regulatory frameworks for gene editing and genomic medicine. Japan, in particular, has introduced accelerated approval pathways for regenerative and genetic treatments, fostering innovation in precision cardiovascular therapies. This progress is further supported by the increasing affordability of genetic testing and the expansion of partnerships between stakeholders.
China is a major player in the market. China's biotech sector is heavily engaged in developing CRISPR-based treatments for cardiovascular and metabolic disorders, with several projects already in early-stage clinical trials. The country benefits from a rapidly expanding genome data pool and a strong talent base in molecular biology and biomedical engineering. Despite ongoing discussions regarding ethical and regulatory challenges, China is working to improve its regulatory system to align with international standards, thereby improving clinical governance.
What Factors Are Influencing Europe's Genetic Editing for ASCVD Market?
The European genetic editing for ASCVD market is expected to grow at a notable rate, driven by sustained biomedical innovation, robust public research and development funding, and a well-established healthcare infrastructure. The presence of major pharmaceutical and biotech firms, alongside leading academic institutions, fuels continuous research into CRISPR-based treatments targeting ASCVD-related genes, such as PCSK9, ANGPTL3, and Lp(a). Furthermore, Europe faces a substantial ASCVD burden, largely due to an aging population and lifestyle factors, creating a need for innovative, long-term treatment solutions such as gene editing.
The UK plays a central role in the development of the European market for genetic editing for ASCVD. With a strong presence in life sciences and genomic medicine, the UK boasts an ecosystem rich in institutions, including the Francis Crick Institute, the Wellcome Sanger Institute, and the UK Biobank, which contribute extensive genomic data to cardiovascular disease research. UK-based biotech companies and universities are actively developing CRISPR-based solutions for lipid metabolism and inflammatory pathways in ASCVD. Additionally, the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) in the UK supports the adoption of innovative therapies in clinical practice through streamlined mechanisms.
Genetic Editing for ASCVD Market Companies

- CRISPR Therapeutics
- Intellia Therapeutics
- Editas Medicine
- Beam Therapeutics
- Verve Therapeutics
- Sangamo Therapeutics
- Vertex Pharmaceuticals
- Novartis
- Allogene Therapeutics
- Crispr BioPharma
- Alnylam Pharmaceuticals
- Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals
- Precision BioSciences
- BlueRock Therapeutics (Bayer)
- Acuitas Therapeutics
- Moderna Therapeutics
- Pfizer
- Amgen
- BioNTech
- Evotec
Recent Developments
- In June 2025, Eli Lilly disclosed that it will acquire Verve Therapeutics in a transaction valued at around $1.3bn, representing a major augmentation to cardiovascular disease (CVD) capacity at the firm. The transaction will provide Lilly with access to a pipeline of single-course gene editing therapies that Verve is developing to treat the causes of atherosclerotic CVD (ASCVD), which contributes to approximately 85 percent of all cardiovascular fatalities and is brought on by the formation and proliferation of plaques in the innermost layer of the arteries. (Source: https://pmlive.com)
- In May 2025, Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Inc. announced positive topline data of olezarsen in the Essence study of individuals with moderate hypertriglyceridemia (fasting triglycerides 150 mg/dL to less than 500 mg/dL) and with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) or at risk of the disease. Almost all the participants were using the present standard of care lipid-lowering medications. (Source: https://ir.ionis.com)
- In April 2025, Verve Therapeutics, a clinical-stage company building a new class of genetic medicines to treat cardiovascular disease, announced positive initial data from the Heart-2 Phase 1b clinical trial of VERVE-102. The Heart-2 Phase 1b Investigation is measuring patients having heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HeFH) and/or premature coronary artery disease (CAD), who necessitate profound and sustainable low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels in the blood.(Source:https://ir.vervetx.com)
Segments Covered in the Report
By Editing Modality
- CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Knockout
- Base Editing (e.g., BE, ABE)
- Prime Editing
- siRNA/ASO Gene Silencing
- Zinc Finger & TALENs (legacy / niche)
- Epigenome Editing
By Therapeutic Target
- PCSK9 – lifelong LDL-C lowering via knockout
- ANGPTL3
- ApoC3 – triglyceride reduction
- Lp(a) – emerging target for residual risk
- LDLR Gene Repair – monogenic hypercholesterolemia
- Inflammatory Cytokines (e.g., IL-1β)
By Delivery System
- AAV Vectors
- Lipid Nanoparticles
- Ex Vivo Edited Cell Therapies (e.g., HSCs)
- Nanoparticle-Conjugates
- Electroporation / Physical Methods
By Stage of Development
- Preclinical Research
- Phase I/II Clinical Trials
- Phase III / Pivotal
- Regulatory Review / Approval
By End User
- Pharmaceutical & Biotechnology Companies
- Academic & Research Institutes
- Contract Development & Manufacturing Organizations
- Specialty Cardiology Clinics
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Ask For Sample
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
 Get a Sample
Get a Sample
 Table Of Content
Table Of Content
 sales@precedenceresearch.com
sales@precedenceresearch.com
 +1 804-441-9344
+1 804-441-9344
 Schedule a Meeting
Schedule a Meeting