Genomics Market Will Grow at CAGR of 19.40% By 2032
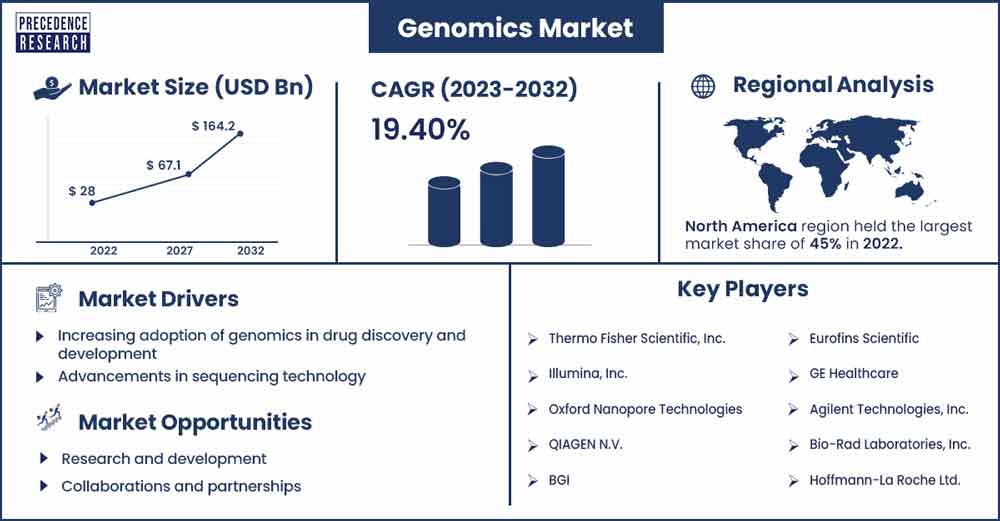
The global genomics market size accounted for USD 28 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach around USD 164.2 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 19.40% from 2023 to 2032.
Market Overview
Genomics is a branch of molecular biology that focuses on the study of genomes, which are the complete set of genetic material (DNA or RNA) within an organism. This field encompasses the analysis and interpretation of the structure, function, evolution, and mapping of genomes. Genomics involves the study of genes, their interactions, and how they influence the development and functioning of living organisms.
The genomics market was on a steady growth trajectory, driven by advancements in sequencing technologies, bioinformatics, and a deeper understanding of genomics' role in healthcare and research. The growth of the market is driven by increasing drug discovery, personalized medicines, and a surging need for gene therapy. An increasing number of collaborations and partnerships among key players is expected to drive the growth of the industry.
Regional Analysis
North America holds the largest share in the genomics market. In order to identify novel therapeutic targets, create tailored treatments, and comprehend the genetic causes of illnesses, numerous pharmaceutical and biotechnology firms in North America make significant investments in genomics research. The application of genomics in medical contexts has been growing. When it comes to identifying diseases, estimating risk, and developing treatment plans, genetic testing and genomic diagnostics are essential.
Genomic research is motivated by the idea of personalized medicine, which aims to customize medical care to each patient's unique features. Research on genomes has advanced because to ongoing developments in sequencing technology, including next-generation sequencing (NGS). Genomic regulations, including those pertaining to data privacy and ethics, are still developing. The development and commercialization of genomic goods and services are influenced by regulatory frameworks.
In the United States, the genomics industry has grown significantly because to technological developments, declining sequencing costs, and an increase in the use of genetics in a variety of industries, including research, healthcare, and agriculture. The advancement of genomics applications has been aided by government funding and efforts for genomics research and deployment, such as the US Precision Medicine Initiative. Direct-to-consumer genetic testing services have become more and more popular, giving people access to information about their traits, heritage, and health concerns. Genomic data is being utilized more and more to target medicines, forecast illness risk, and customize treatment regimens.
Canada has been a leader in the field of genomics research, having funded numerous projects to further the field of genetic medicine. The Canadian government has funded genomics research initiatives to learn more about diseases and create tailored health strategies through institutions like Genome Canada. Innovation and genetic research are highly regarded in Canada.
The use of genetic data to customize medical interventions, forecast illness risks, and enhance patient outcomes has gained popularity. Genomic technology is one of the many fields that make up Canada's biotechnology industry. The nation's genomics market may expand overall if more businesses concentrated on genetic testing, tailored medicine, and other applications connected to genomics were to emerge.
Genomics Market Report Scope
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Revenue in 2023 | USD 33.29 Billion |
| Projected Forecast Revenue by 2032 | USD 164.2 Billion |
| Growth Rate from 2023 to 2032 | CAGR of 19.40% |
| Largest Market | North America |
| Base Year | 2022 |
| Forecast Period | 2023 to 2032 |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Market Dynamics
Drivers
Advancements in sequencing technology
Continuous advancements in DNA sequencing technologies, such as next-generation sequencing (NGS), have significantly reduced the cost of sequencing, making genomic analysis more accessible. NGS technologies, such as Illumina's platforms, were widely used for their high-throughput capabilities and relatively low cost per base. They played a crucial role in various genomic applications, including whole-genome sequencing, exome sequencing, RNA sequencing, and epigenetic studies.
Increased investments in genomics research and development by both public and private sectors have propelled the growth of the genomics market. This includes initiatives focused on understanding the genetic basis of diseases, drug discovery, and personalized medicine.
Government initiatives
The government is also taking various initiatives and policies in order to support genomics research. The development of precision medicine initiatives and funding for large-scale genomic projects are driving the market growth. Many governments have been investing in precision medicine programs that leverage genomics data to tailor medical treatments to individual patients. These initiatives aim to improve healthcare outcomes and reduce overall healthcare costs.
Governments also encourage collaborations between academia, industry, and healthcare providers to promote the translation of genomic research findings into practical applications, such as diagnostics and therapeutics.
Restraints
High cost of sequencing
High costs associated with genomic sequencing technologies have been a significant restraint. While the costs have been decreasing over time, they still pose a barrier to widespread adoption, especially in resource-limited settings. The initial research and development costs for creating advanced sequencing technologies can be substantial, and these costs may be reflected in the overall pricing of sequencing services.
The massive amount of data generated by sequencing requires significant computational power and storage capacity for analysis. Moreover, the costs associated with managing and interpreting this data contribute to the overall expense. Maintaining the necessary infrastructure, such as specialized laboratories and equipment, contributes to the overall cost of sequencing.
Interpretation and clinical utility
The examination and comprehension of genomic data is referred to as interpretation in the field of genomics. This entails interpreting the genetic code to find changes, mutations, or other pertinent data in a person's DNA. The interpretation encompasses comprehending the functional consequences of detected genetic variants as well. This entails determining the potential impact of particular genetic alterations on the emergence of illnesses or ailments.
In the field of genomics, "clinical utility" refers to the usefulness and implementation of genetic data in a therapeutic context. It evaluates the efficacy of using genetic information from genomic data to inform medical decisions and enhance patient outcomes. The success of the genomics business depends on efficient methods and tools for interpreting large genetic datasets in order to extract relevant information.
Opportunities
Research and development
To customize care for each patient, researchers are attempting to find genetic variants linked to certain diseases. In genomics research, the ground-breaking CRISPR-Cas9 gene-editing technique has received a lot of attention. In an effort to address genetic abnormalities and create new therapeutic strategies, scientists are constantly improving and broadening its uses. The cost and time needed for genome sequencing have been drastically lowered thanks to developments in next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies. The study of genomics is widely used in cancer research to determine the genetic causes of various diseases. The roles of genes and how they interact with biological systems are being studied by researchers.
Collaborations and partnerships
Pharmaceutical companies and genomics companies frequently work together to use genomic data for drug development and discovery. The goal of these partnerships is to find possible therapeutic targets and biomarkers. Technology businesses that specialize in genomics may collaborate with other tech companies to improve their platforms or incorporate complementary technologies. Large-scale genomic investigations are often conducted in partnership with genomics firms by academic institutions and research groups.
Companies that specialize in genomics frequently work with providers of clinical and diagnostic services to integrate personalized medicine and genomic testing into the mainstream of healthcare. Contributions from different nations and organizations are made to international projects and collaborations like the Human Genome Project. Genomic start-ups may partner with more established businesses to obtain resources, knowledge, and distribution channels.
Recent Developments
- In July 2023, DRAGEN 4.2, the most recent version of the program for analyzing data from next-generation sequencing, was just released, according to a recent announcement from Illumina, Inc. (ILMN). It is anticipated that DRAGEN 4.2 will increase accuracy while maintaining flexibility and scalability to facilitate effective workflows and derive significant insights from genomic data.
- In June 2023, leading genomics and precision health investment business Illumina Ventures announced today that Illumina® Ventures Labs will be launched. Illumina Ventures Labs will operate and provide access to fully equipped genomics labs in the US and the UK, mentorship, and seed capital to attract a wide range of genomics-related start-ups, building on the success of the Illumina Accelerator program.
Key Market Players
- Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.
- Illumina, Inc.
- Oxford Nanopore Technologies
- QIAGEN N.V.
- BGI
- Eurofins Scientific
- GE Healthcare
- Agilent Technologies, Inc.
- Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.
- Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
- Others
Market Segmentation
By Product and Services
- Consumables
- Systems and software
- Services Equipment
By Technology
- PCR (polymerase chain reaction)
- Sequencing
- Microarray
- Nucleic acid extraction and purification
- Other technologies (branched DNA analysis, single-cell genomics analysis, and flow cytometry)
By Application
- Drug discovery and development
- Diagnostics
- Precision medicine
- Agriculture and animal research
- Other applications
By End-Users
- Hospitals & clinics
- Research centers and academic & government institutes
- Pharmaceutical & biotechnology companies
- Other end users
Buy this Research Report@ https://www.precedenceresearch.com/checkout/1204
You can place an order or ask any questions, please feel free to contact at sales@precedenceresearch.com | +1 650 460 3308