RNA Editing Therapies Market Size and Forecast 2025 to 2034
The RNA editing therapies market is expanding as biotech firms and academic institutions invest heavily in clinical pipelines. These therapies hold potential to transform treatment landscapes for underserved diseases. The RNA editing therapies market has experienced significant growth in recent years, reflecting the increasing reliance on digital platforms for freelance and gig-based work. The RNA editing therapies market is a rapidly expanding sector driven by technological advancements and increasing demand for personalized medicine.
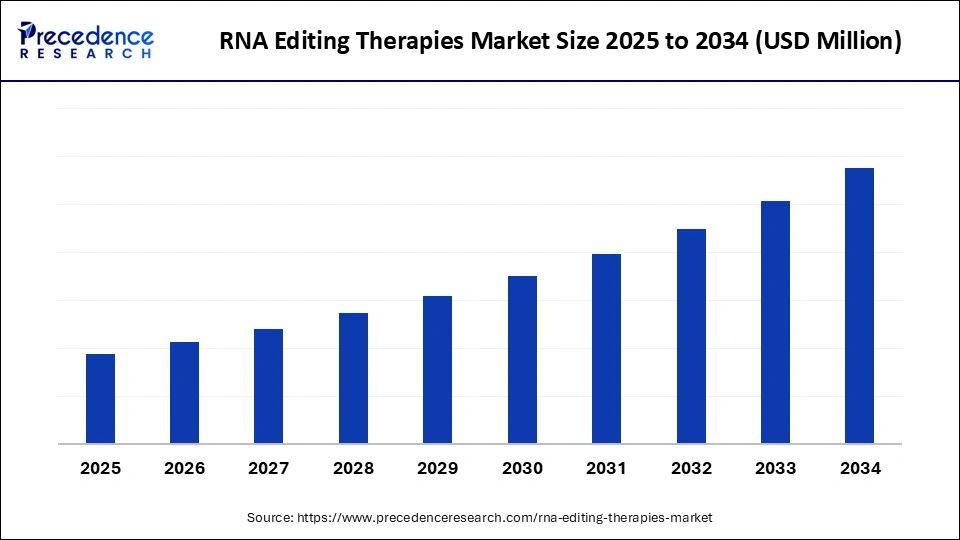
RNA Editing Therapies Market Key Takeaways
- North America held a major revenue share in the RNA editing therapies market in 2024.
- By region, Asia Pacific and Europe are anticipated to grow at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period.
- By editing modality/mechanism type, the ADAR-mediated base editing segment held the biggest market share in 2024.
- By editing modality/mechanism type, the RNA exon editing segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period.
- By therapeutic intent type, the repeat-dosed corrective editing segment accounted for a considerable share in 2024.
- By therapeutic intent type, the one-time durable RNA exon editors segment is projected to experience the highest growth CAGR between 2025 and 2034.
- By delivery platform, the LNP and conjugated oligo delivery for liver/systemic targets segment captured the highest market share in 2024.
- By delivery platform, the improved AAV serotypes and non-viral and LNP-based CNS-targeted delivery segment is set to experience the fastest CAGR from 2025 to 2034.
- By indication/disease area type, the rare genetic liver and ocular disorders led market share in 2024.
- By indication/disease area type, the neurological and multi-organ rare genetic diseases, as CNS delivery and exon editors mature. They are the fastest-growing from 2025 to 2034.
- By product type, the synthetic oligo editors segment contributed the maximum market share in 2024.
- By product type, vector-encoded exon editors and combination device-delivery offerings are the fastest-growing segments from 2025 to 2034.
- By mode of administration type, the intravenous/subcutaneous systemic dosing segment maintained the highest growth CAGR during the forecast period.
- By mode of administration type, the intrathecal and intravitreal routes are the fastest growing from 2025 to 2034.
- By distribution channel type, the hospital/specialty clinic administration is for initial launches. The segment accounted for a considerable share in 2024.
- By distribution channel type, the specialty pharmacies segment is projected to experience the highest growth CAGR between 2025 and 2034.
An Emerging Therapeutic Revolution
The RNA editing therapies market is in its early growth stage, but it is gaining momentum quickly. Multiple startups and pharmaceutical companies are investing heavily in the development of RNA-targeted drugs. Clinical pipelines focus on rare genetic disorders, neurological diseases, and oncology. Investors are attracted by the promise of treating conditions previously deemed undruggable. Although regulatory pathways are still evolving, the potential for breakthrough approval is strong. Overall, the market is poised for rapid expansion over the next decade.
AI's Impact: Intelligent Acceleration of RNA Editing
Artificial Intelligence is reshaping how key players in the RNA editing therapies market are discovered and developed. Machine learning algorithms accelerate the identification of optimal RNA targets with higher precision. AI-driven platforms also help predict off-target effects, reducing trial-and-error in preclinical stages. These tools shorten development timelines and improve success rates in clinical trials. Furthermore, AI enhances personalized therapy design by matching editing strategies to patient-specific mutations. As a result, AI is becoming an indispensable catalyst for RNA editing's market growth.
Market Key Trend
- One major trend is the rise of programmable RNA editors with improved accuracy. Another is the growing collaboration between biotech firms and academic institutions. Investors are increasingly funding startups focused on RNA tools beyond CRISPR.
- There is also a trend toward combining RNA editing with delivery technologies such as lipid nanoparticles. Personalized RNA therapies tailored to specific patient mutations are gaining traction. Together, these trends highlight the market's strong momentum and innovative edge.
Market Scope
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Dominating Region | North America |
| Fastest Growing Region | Asia Pacific |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | Editing Modality / Mechanism, Therapeutic Intent, Delivery Platform, Indication / Disease Area, Product Type, Mode of Administration, Distribution & Commercial Channel, and Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Market Dynamics
Drivers
Forces Powering Growth
The primary driver of the RNA editing therapies market is the growing demand for precision medicine that targets root genetic causes. Advances in RNA biology have expanded the range of diseases considered treatable. Strong venture capital interest and pharma partnerships are fueling early-stage development. The increasing prevalence of genetic and rare disorders is expanding the addressable market. Regulatory agencies are also showing openness toward novel RNA-based therapies. These factors collectively drive strong momentum for RNA editing therapies.
Restraints
Barriers to Breakthrough
Despite its promise, the RNA editing therapies market faces significant scientific and commercial hurdles. Off-target editing and safety concerns remain major challenges for clinical adoption. Delivery of RNA editors into specific tissues is technically complex. High development costs and long timelines also strain smaller biotech firms. Uncertain regulatory frameworks add additional risks to commercialization. These restraints may slow widespread adoption in the near term.
Opportunities
Unlocking Untapped Potential
Rare diseases represent the most immediate opportunity for RNA editing therapies. Neurological disorders, where reversible editing could offer safer alternatives, are another promising area. Expansion into oncology opens new therapeutic possibilities. Partnerships with AI and delivery technology firms enhance innovation capacity. Global demand for cutting-edge genetic therapies provides a significant growth runway. Together, these opportunities suggest RNA editing could become a cornerstone of next-gen medicine.
Editing Modality / Mechanism Insights
Why Does ADAR-Recruiting RNA Editing Remain Dominant in the RNA Editing Therapies Market?
ADAR-recruiting RNA editing remains the dominant sub-segment in the RNA editing therapies market modality due to its ability to harness naturally existing enzymes within the body. This approach provides higher safety margins compared to synthetic systems, as it leverages endogenous cellular machinery. Biopharmaceutical companies prefer this method for its scalability and regulatory familiarity. Additionally, ADAR recruitment has shown significant promise in correcting point mutations linked to rare genetic disorders. Its ease of integration with oligonucleotide delivery platforms also strengthens adoption. As a result, ADAR-based therapies continue to set the benchmark in clinical pipelines.
Another factor that secures ADAR recruiting's dominance is its lower immunogenicity compared to engineered systems. By working with natural enzymes, the therapy reduces the risk of immune rejection, a critical factor in long-term treatments. Researchers have optimized guide RNAs to enhance specificity, minimizing off-target edits. This makes ADAR recruiting especially attractive for diseases requiring precision. Established pharma players are also expanding partnerships with biotech firms to advance ADAR-based platforms. With robust clinical validation on the horizon, ADAR recruiting is expected to remain a cornerstone of RNA editing.
RNA exon editing is rapidly gaining traction as the fastest-growing modality in the market. Unlike base editing approaches, exon editing allows for broader correction of larger RNA segments, opening opportunities in complex diseases. Its flexibility makes it attractive for disorders where single-base corrections are insufficient. Emerging biotech startups are aggressively pursuing exon editing pipelines due to their transformative potential. Advances in delivery technologies are accelerating its translation from preclinical research into clinical testing. This positions RNA exon editing as a key future growth driver.
RNA exon editing also benefits from growing computational support, with AI models now predicting splice patterns and improving editing accuracy. This convergence of biology and computation accelerates its path toward commercialization. Startups specializing in exon correction are attracting strong venture capital, indicating confidence in this modality. The potential to address multi-gene disorders sets it apart from base editing approaches. As delivery improves, exon editing could achieve transformative outcomes in neurology and metabolic diseases. These advantages ensure it continues to outpace other modalities in growth.
Therapeutic Intent Insights
What Therapeutic Segment Led the RNA Editing Therapies Market?
The repeat-dosed corrective editing segment led the market for RNA editing therapies in 2024, reducing patient burden. They are particularly attractive for severe genetic diseases where lifelong therapy is impractical. Investors and researchers see this as a game-changer for healthcare economics and patient quality of life. As delivery platforms improve, durable editing strategies are gaining regulatory and clinical confidence. This makes them a critical area for near-future expansion.
Repeat dosing also aligns with existing treatment models for chronic conditions, making it more familiar to clinicians. Patients who require long-term monitoring are already accustomed to repeat injections or infusions. This reduces the barrier to adoption for RNA editing therapies that follow a similar schedule. Pharma companies benefit from predictable revenue streams, further incentivizing development. Safety monitoring is also easier with repeat dosing, as adjustments can be made between cycles. This pragmatic alignment with healthcare systems cements its dominance.
One-time durable editing approaches are the fastest-growing therapeutic intent. These therapies promise long-lasting benefits with a single administration, reducing patient burden. They are particularly attractive for severe genetic diseases where lifelong therapy is impractical. Investors and researchers see this as a game-changer for healthcare economics and patient quality of life. As delivery platforms improve, durable editing strategies are gaining regulatory and clinical confidence. This makes them a critical area for near-future expansion.
Repeat dosing also aligns with existing treatment models for chronic conditions, making it more familiar to clinicians. Patients who require long-term monitoring are already accustomed to repeat injections or infusions. This reduces the barrier to adoption for RNA editing therapies that follow a similar schedule. Pharma companies benefit from predictable revenue streams, further incentivizing development. Safety monitoring is also easier with repeat dosing, as adjustments can be made between cycles. This pragmatic alignment with healthcare systems cements its dominance.
Delivery Platform Insights
Why Did LNPs and Conjugated Oligo Delivery Systems Dominate the RNA Editing Therapies Market?
The lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) and conjugated oligo delivery systems dominate the RNA editing therapies market due to their proven success in targeting the liver. The liver is a favorable organ for RNA therapies because of its accessibility and metabolic functions. Decades of experience with LNP delivery from siRNA and mRNA therapies bolster confidence in this route. Pharma pipelines are heavily concentrated on liver-related genetic conditions due to delivery reliability. This dominance is further supported by scalable manufacturing and familiarity with regulations. Together, these advantages ensure the liver remains the prime focus for RNA editing therapies.
The maturity of LNP technology also reduces regulatory hurdles, as agencies have built frameworks from prior mRNA approvals. Conjugated oligos, such as GalNAc-linked systems, further enhance precision by targeting hepatocytes directly. These platforms are cost-effective to manufacture at scale, reinforcing commercial viability. Industry leaders are investing in expanding LNP facilities worldwide to meet rising demand. The established safety record in humans adds to their clinical appeal. This entrenched infrastructure makes liver delivery the dominant platform.
The fastest growth sub-segment in the RNA editing therapies market is seen in improved AAV serotypes and non-viral approaches for CNS delivery. These platforms aim to overcome the challenge of delivering therapies across the blood-brain barrier. Breakthroughs in serotype engineering and non-viral vectors are opening possibilities for treating neurological diseases. Their ability to target previously inaccessible tissues makes them highly disruptive. Biopharma investment in CNS-targeted editing is accelerating rapidly. This positions CNS delivery as the next major frontier in RNA editing.
The field is also witnessing hybrid approaches, combining viral and non-viral technologies for optimized CNS penetration. Next-generation AAV serotypes are engineered to reduce immunogenicity while improving tissue targeting. Non-viral nanoparticles are being refined to minimize toxicity and maximize crossing efficiency. These advancements open doors for tackling ALS, Parkinson's, and other debilitating neurological conditions. Strategic partnerships between academia and industry are accelerating innovation in this space. With these rapid advances, CNS delivery is on a steep growth trajectory.
Indication / Disease Area Insights
Which Disease Treatments Were the Most Popular in the RNA Editing Therapies Market?
Rare liver and ocular diseases currently dominate as leading therapeutic targets for RNA editing. These conditions provide strong proof-of-concept due to localized pathology and accessible tissues. Early clinical successes in these areas have validated RNA editing's potential. Moreover, patient advocacy and regulatory incentives accelerate development in rare disease spaces. The relative ease of delivery to the liver and eye further consolidates dominance. These advantages make liver and ocular disorders the most commercially viable starting points.
These indications also benefit from strong orphan drug incentives, providing extended market exclusivity and pricing power. Patient advocacy groups are actively supporting clinical trials, boosting awareness and recruitment. The liver and eye are relatively immune-privileged sites, further enhancing treatment safety. Early clinical results demonstrate measurable biomarkers, making trial outcomes clearer. This helps developers move faster through regulatory pathways. Together, these dynamics secure dominance for liver and ocular disorders.
Neurological and multi-organ rare disorders are the fastest-growing targets as CNS delivery and exon editors mature. These diseases represent large unmet medical needs with limited treatment options. Advances in intrathecal and non-viral delivery methods are expanding access to these indications. Multi-organ rare disorders also benefit from systemic approaches to RNA editing. Biopharma companies are increasingly building pipelines targeting ALS, Huntington's, and multi-systemic genetic syndromes. This category is expected to become a major growth driver in the next decade.
Product Type Insights
Why Did Synthetic Oligonucleotide Editors Dominate the RNA Editing Therapies Market?
Single-molecule RNA editors/synthetic oligonucleotide editors dominate the RNA editing therapies market due to their maturity and adaptability across various therapeutic applications. They are easier to manufacture, scale, and modify compared to complex vector-based systems. Oligo editors integrate seamlessly with LNP and conjugated delivery platforms. Their regulatory track record also supports smoother clinical progression. Biopharma companies prefer synthetic oligos for early-stage clinical testing due to lower risk profiles. These strengths ensure their current market dominance.
Vector-encoded exon editors and device-assisted delivery approaches are the fastest-growing product types. They enable precise and durable interventions while allowing delivery to complex tissues, such as the CNS. Combination device delivery is especially valuable for localized applications in neurology and ophthalmology. Although technically complex, these approaches promise higher efficacy and longer-term outcomes. Investment in these products is rising sharply as proof-of-concept data strengthens. Their disruptive potential positions them as a leading segment of the future.
Mode of Administration Insights
How Did Intravenous Administration Dominate the Market for RNA Editing Therapies?
Intravenous administration dominates as the most established and reliable route for the RNA editing therapies market. It offers systemic delivery, which is ideal for liver and multi-organ targets. Pharma companies prefer this route due to its familiarity with both clinicians and regulators. IV administration also supports flexible dosing strategies, from single-dose to repeat cycles. Manufacturing and distribution infrastructures are well-aligned with this approach. These factors collectively anchor IV administration as the dominant mode.
Intrathecal and intrauterine administration are the fastest-growing routes for RNA editing therapies. Intrathecal delivery allows direct access to the CNS, bypassing the blood-brain barrier. Intrauterine approaches hold promise for in-utero correction of severe genetic diseases. Both methods are being explored for high-impact indications where systemic routes fall short. Advances in minimally invasive techniques are boosting their feasibility. Together, these routes represent the most innovative growth frontier.
Distribution & Commercial Channel Insights
Why Did Hospitals Remain the Dominant Distribution Channel for the RNA Editing Therapies Market?
Hospitals and specialty clinics remain the dominant distribution channel for RNA editing therapies market. These settings provide the infrastructure and expertise required for advanced genetic treatments. Patients trust these centers for novel and high-risk therapies. Pharma companies also prefer hospital-based launches due to controlled administration and monitoring. Specialty clinics enable focused delivery for rare diseases. This ensures hospitals and specialty centers retain dominance in distribution.
Specialty pharmacies are emerging as the fastest-growing distribution channel. They provide improved access for chronic and repeat-dose RNA therapies. Their expertise in rare disease management enhances patient adherence and outcomes. Digital platforms and telehealth integration expand their role in therapy support. Payers are increasingly collaborating with specialty pharmacies to streamline reimbursement. As RNA editing scales, specialty pharmacies will play a central role in patient accessibility.
Regional Insights
How Is North America Leading the Charge in RNA Editing Therapies Market?
North America dominates the RNA editing therapy market due to its robust biotech ecosystem. The region hosts pioneering startups and established pharma giants investing heavily in RNA tools. Strong funding pipelines from venture capital and government initiatives boost innovation. Academic research institutions also contribute to cutting-edge discoveries in RNA biology. The U.S. regulatory framework, while evolving, provides pathways for breakthrough designations. These advantages ensure North America remains the market leader.
North America's dominance is further reinforced by clinical trial concentration in the U.S. and Canada. Many biotech firms strategically launch therapies in this region due to favorable reimbursement structures. Collaborative research hubs like Boston and San Francisco accelerate innovation cycles. Patient advocacy groups also drive awareness and early adoption of genetic therapies. The high prevalence of rare diseases creates a strong demand base. Altogether, these factors anchor North America's dominant role.
How Asia Pacific & European Rising Stars of the RNA Editing Therapies Market?
Asia Pacific and Europe are the fastest-growing markets for RNA editing therapies. Europe benefits from strong academic research, particularly in Germany, the U.K., and Switzerland. Asia Pacific, led by China, Japan, and South Korea, is rapidly scaling biotech investments. These regions also offer large patient populations for clinical trials. Governments are supporting genomics and precision medicine initiatives aggressively. As a result, both regions are emerging as growth engines for RNA editing.
Their growth is also fuelled by expanding biotech clusters and cross-border collaborations. Europe's regulatory frameworks are supportive of innovation while ensuring safety. Asia Pacific benefits from lower trial costs and faster patient recruitment. The increasing prevalence of genetic disorders in these regions creates significant unmet medical needs. Local biotech firms are also entering global partnerships to advance RNA therapies. Together, these dynamics make Asia Pacific and Europe the fastest-growing regions.
RNA Editing Therapies Market Companies

- ADARx Pharmaceuticals
- Amber Bio
- Ascidian Therapeutics
- Beam Therapeutics
- Catalent
- GSK
- Korro Bio
- Moderna
- ProQR Therapeutics
- Regenxbio
- Roche
- Shape Therapeutics
- Wave Life Sciences
- ADAPTABLE CDMO / specialized oligo CDMOs
- Smaller specialist startups & platform players
Recent developments
- Yale researchers created a new, safe family of RNA-editing tools in September 2025. They found a "hidden" RNA-targeting activity within a widely used gene editing tool called CRISPR-Cas9. According to the study, senior author Ailong Ke, a professor of molecular biophysics and biochemistry at Yale School of Medicine, the solution was surprisingly straightforward. "We uncovered robust RNA-targeting activity within IscB, an enzyme related to CRISPR-Cas9, and tapped into its potential to target RNA.(Source: https://phys.org)
Segments Covered in the Report
By Editing Modality / Mechanism
- ADAR-recruiting RNA base editing (A→I/G)
- RNA exon editing / RNA trans-splicing (multi-kilobase exon replacement)
- Programmable oligonucleotide editors (guide oligos that recruit endogenous editors)
- RNA-guided deaminases / engineered RNA editors (protein-RNA editor fusions)
- Transient RNA knockdown + re-write hybrid approaches
- ADAR-recruiting AI-based editing
- RNA exon editing (kilobase-scale replacement)
By Therapeutic Intent
- One-time durable/edit-permanent-feeling RNA interventions (long-lasting exon edits)
- Repeat-dosed corrective editing (ASO-like dosing to sustain edits)
- Symptom-modifying RNA edits (modulate expression or splicing)
- Combination regimens (RNA edit + supportive biologic)
- Repeat-dosed corrective editing
- One-time durable RNA exon editors
By Delivery Platform
- AAV-mediated delivery (viral vectors for in vivo CNS / ocular / systemic)
- Lipid nanoparticle (LNP) delivery (systemic, liver-focused)
- Conjugated oligo delivery (GalNAc, peptide conjugates for tissue targeting)
- Localized/intrathecal delivery (CNS-targeted administration)
- Non-viral nanoparticle / novel carriers
By Indication / Disease Area
- Rare genetic liver diseases (e.g., AATD)
- Rare retinal & ocular genetic diseases
- Neurological rare diseases (SMA subtypes, ataxias)
- Metabolic & systemic genetic disorders
- Common chronic diseases
By Product Type
- Single-molecule RNA editors (synthetic oligos recruiting endogenous enzymes)
- Vector-encoded RNA editor constructs (AAV/LV delivered editor expression)
- Combination drug-device (editor + intrathecal delivery implant)
- Platform-licensed programs (partnered IP)
By Mode of Administration
- Intravenous systemic dosing
- Subcutaneous/conjugated subcutaneous dosing
- Intrathecal/intraventricular injection for CNS
- Intravitreal ocular injection
- Localized tissue injection / catheter-based delivery
By Distribution & Commercial Channel
- Hospital & specialist clinic administration (infusion/injection sites)
- Specialty pharmacy + manufacturer hub logistics
- Direct-to-clinic manufacturer logistics for complex vector deliveries
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
 Get a Sample
Get a Sample
 Table Of Content
Table Of Content