What is the Engineered T Cells Market Size?
The global engineered T cells market size is expected to be valued at USD 47.5 billion in 2025 and is anticipated to reach nearly USD 616.91 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 32.96% from 2024 to 2034. The engineered T cells market is observed to grow with the expansion of advanced chemotherapy, synthetic biology, and automation in allogenic therapies. The market's expansion is supported by rising regulatory approvals for advanced therapies.
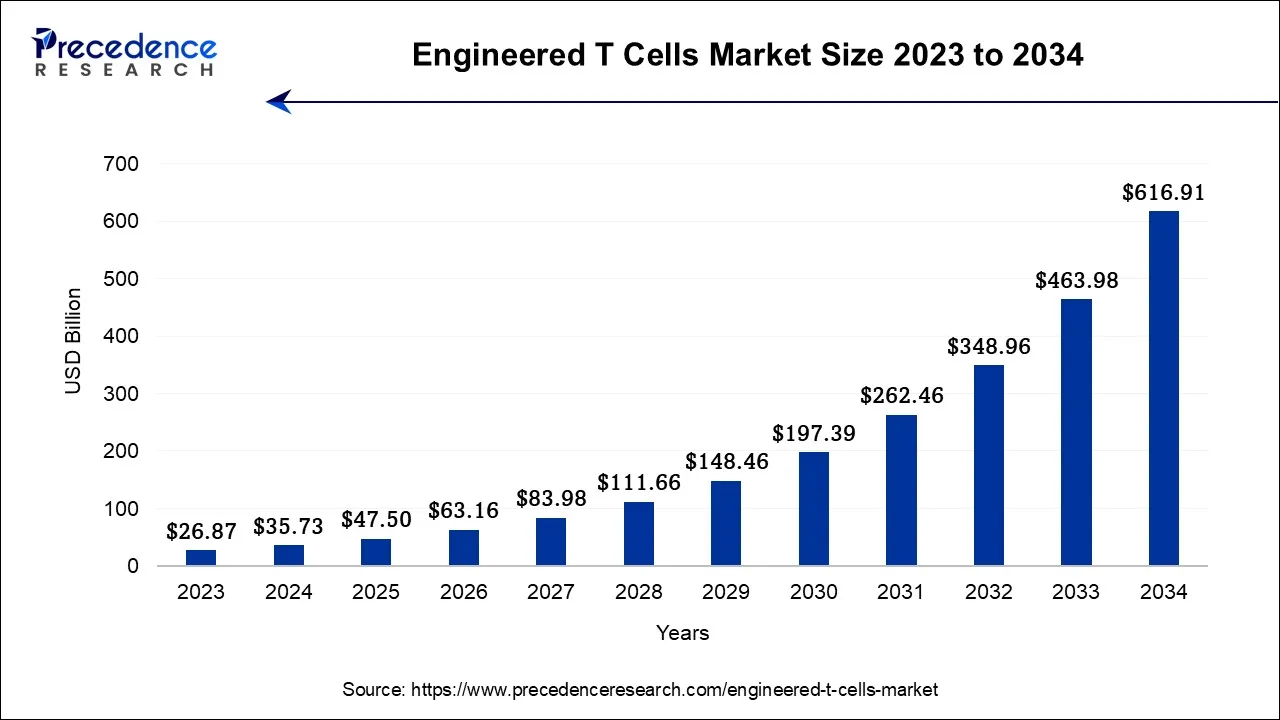
Engineered T Cells Market Key Takeaways
- North America accounted for the largest market share of the 46% in 2024.
- By Type, the chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) modified T cells segment led the market with the largest market share of 78% in 2024.
- By End-user, the hospitals segment contributed more than 58% of revenue share in 2024.
- By Application, the lung cancer segment is expected to grow at a significant CAGR from 2025 to 2034.
Market Overview
Redefining Cancer Therapy Through Cellular Engineering and Precision Medicine
The global Engineered T Cells Market is experiencing transformative growth, driven by rapid advancements in immuno-oncology, personalized medicine, and cellular engineering. Engineered T cell therapies, including CAR-T (Chimeric Antigen Receptor T cells), TCR-T (T Cell Receptor-modified T cells), and emerging allogeneic platforms, are revolutionizing the treatment landscape for hematologic malignancies and solid tumors by harnessing the body's immune system to selectively target and destroy cancer cells.
Key factors fueling market expansion include the increasing prevalence of cancer worldwide, growing clinical success of approved CAR-T therapies, expanding research pipelines, and strong investments from biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies. Moreover, continued innovation in gene editing technologies (such as CRISPR and TALEN), synthetic biology, and viral/non-viral vector design is enhancing the safety, efficacy, and scalability of engineered T cell products.
The field is also witnessing a paradigm shift toward next-generation, off-the-shelf allogeneic T cell therapies, designed to overcome manufacturing bottlenecks, reduce costs, and broaden patient access. Integration of advanced bioinformatics, AI-driven antigen discovery, and automated cell processing systems is further streamlining development and production, enabling greater precision and consistency in clinical outcomes.
In addition, collaborations among academic research centers, biotech startups, and major pharmaceutical companies are accelerating translational research and regulatory approvals. As the focus expands beyond oncology into autoimmune, infectious, and degenerative diseases, engineered T cells are poised to become a cornerstone of precision medicine, offering durable, targeted, and potentially curative treatment options for a broad range of patients.
What are Engineered T Cells?
The engineered T cells encompass advanced cell-based immunotherapies that modify a patient's or donor's T cells to recognize and eliminate diseased or cancerous cells with high specificity. Engineered T cells are created through genetic modification techniques, such as viral vector transduction or gene editing, to express synthetic receptors like Chimeric Antigen Receptors (CARs) or T Cell Receptors (TCRs) that enhance immune targeting and cytotoxic activity.
These therapies are at the forefront of precision oncology and cellular immunotherapy, offering groundbreaking treatment options for hematologic malignancies such as leukemia and lymphoma, and expanding into solid tumors, autoimmune diseases, and infectious disorders.
The adoption of automated cell processing systems, AI-based target discovery, and next-generation biomanufacturing technologies is enhancing scalability and reducing production timelines. The expanding network of clinical trials, regulatory approvals, and strategic collaborations between biotechnology firms, research institutions, and pharmaceutical companies continues to accelerate innovation and accessibility. Engineered T cells represent a transformative advancement in cell and gene therapy, driving a shift toward durable, personalized, and potentially curative treatments across a broad spectrum of diseases.
How Has AI Impacted the Engineered T Cells Market?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is having a significant impact on the engineered T cells market by improving the speed, precision, and efficiency of therapy development. AI algorithms are being used to identify optimal tumor-specific antigens, design safer and more effective CAR and TCR constructs, and predict patient responses to treatment. In manufacturing, AI-driven automation enhances process control, quality assurance, and scalability, reducing production time and costs. Additionally, the integration of AI in clinical trial design and data analysis is accelerating the discovery of next-generation engineered T cell therapies and supporting more personalized treatment strategies.
Industry Growth Overview
The global Engineered T Cells Market is growing steadily, driven by the rising incidence of cancer, the success of approved cell therapies, and rapid progress in gene and cell engineering technologies. Engineered T cell therapies, including CAR-T, TCR-T, and TIL-based products, are transforming the treatment landscape by enabling precise targeting of cancer and immune-related diseases.
Advances in gene editing, automation, and AI-assisted drug discovery are improving the safety, scalability, and accessibility of these therapies. The development of allogeneic, or “off-the-shelf,” engineered T cells is also helping to address high production costs and long manufacturing times associated with autologous therapies. With increasing regulatory approvals, strong clinical outcomes, and growing collaboration between biotechnology companies and research institutions, the market is expected to continue expanding over the next several years.
Sustainability Trends
Sustainability is becoming an important focus in the engineered T cells industry. Companies are working to make production more efficient and environmentally responsible by using closed, automated systems that reduce material waste and energy consumption. The shift toward non-viral gene delivery and transposon-based editing methods is improving safety and lowering the environmental impact of manufacturing.
In addition, the use of decentralized and modular production facilities is reducing transportation needs and carbon emissions. Many organizations are also emphasizing ethical sustainability by supporting equitable access to cell therapies and promoting transparent, data-driven development practices. These steps reflect a growing commitment to responsible and sustainable innovation in advanced cell therapy manufacturing.
Major Investors
The engineered T cells market is attracting strong investment from leading pharmaceutical companies, biotechnology firms, and venture capital groups. Major industry participants such as Novartis, Gilead Sciences (Kite Pharma), Bristol Myers Squibb, Johnson & Johnson (Janssen), and Bluebird Bio are investing heavily in research, clinical trials, and manufacturing capabilities.
Private equity and venture capital firms are also funding emerging companies that specialize in gene editing, allogeneic T cell development, and automated production technologies. Partnerships between academic institutions, contract manufacturing organizations, and large biopharmaceutical companies are accelerating innovation and helping to bring next-generation therapies to market faster. This growing investment landscape is supporting the continued evolution of engineered T cells as a key area of modern medicine.
What are the Trends in the Engineered T Cells Market?
International Growth
The engineered T cells market is expanding rapidly across both developed and emerging regions. North America and Europe continue to lead in terms of clinical adoption, research infrastructure, and regulatory approvals for CAR-T and TCR-T therapies. These markets are focused on expanding indications beyond hematologic cancers into solid tumors and autoimmune diseases, supported by advanced manufacturing facilities and strong biopharmaceutical pipelines.
Emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and the Middle East are also showing strong growth due to increasing investments in biotechnology, government support for cell and gene therapy research, and rising healthcare spending. Countries such as China, Japan, and South Korea are becoming key hubs for clinical trials and local manufacturing of engineered T cell therapies. Improved access to advanced healthcare and the establishment of regional production centers are helping to make these therapies more affordable and widely available to patients in developing markets.
Research and Development
Research and development are central to progress in the engineered T cells industry. Current R&D efforts focus on improving the safety, efficacy, and scalability of engineered T cell therapies. Scientists are developing next-generation CAR and TCR constructs with better tumor recognition, reduced toxicity, and enhanced persistence in the body.
There is also growing research into gene editing technologies such as CRISPR and TALEN to create universal or allogeneic T cells that can be used across multiple patients without immune rejection. Other areas of innovation include non-viral gene delivery systems, synthetic biology approaches for precise immune control, and automated, closed-system manufacturing to reduce production time and cost.
Engineered T Cells Market Growth Factors
Engineered T-cell therapies, particularly CAR-T cell therapies, have shown remarkable success in treating certain types of cancer. As these therapies illustrate positive outcomes in clinical trials and practical applications, their adoption is expected to rise. The shift towards personalized medicine in healthcare is anticipated to navigate the demand for CAR-T therapies.
The advancements in genetic engineering techniques, such as CRISPR-Cas9, have improved the precision and efficacy of engineering T-cells, facilitating the development of more effective and safer therapies. The increasing prevalence of cancer worldwide is a significant factor in the growth of engineered T-cell therapies, and these therapies offer a promising alternative for patients who have exhausted conventional treatment options.
The notable investments made by pharmaceutical companies, biotech firms, and research institutions in enhancing engineered T-cell therapies contribute to the market growth. This funding supports research, development, and clinical trials, accelerating the availability of these therapies to patients. These engineered T-cell therapies are being explored to treat rare diseases and conditions that were previously difficult to address with traditional treatments. This diversification of applications expands the market.
Market Scope
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 47.5Billion |
| Market Size in 2026 | USD 63.16 Billion |
| Market Size in 2030 | USD 197.39 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 616.91 Billion |
| Growth Rate from 2024 to 2034 | CAGR of 32.96% |
| Leading Region in 2024 | North America |
| Base Year | 20234 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | Type, Application, End-user, and Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Market Dynamics
Driver
Advancements in gene editing
The development of gene editing has expanded the potential of cell therapies by enabling more precise genetic manipulation to enhance T-cell engineering and function. Transposons, designer nucleases including CRISPR/Cas9, and zinc finger nucleases (ZFN) have all been investigated as gene editing techniques for T cell creation. These platforms' editing specificity, effectiveness, and capacity to reach T cells have their respective advantages. Thereby, advancements in gene editing are observed to act as a driver for the global engineered T cells market.
Restraints
Limitations of clinical trials
Preclinical research, Phase I–III trials, and post–approval monitoring are some of the phases conducted during a clinical trial. The introduction of clinical trials for engineered T cells often covers a few years. As a result, further procedures can be delayed.
Clinical trial participants are frequently chosen using inclusion and exclusion criteria, which can result in a restricted representation of the patient population's diversity. To evaluate safety and dosage levels, phase I trials usually involve a small number of individuals. It may be challenging to forecast how the treatment will respond in the broader population given the small sample size's propensity for underrepresenting the complete range of responses and adverse effects. Thus, such limitations in clinical trials create a major restraint for the market.
Risk of adverse effects on health
The improper intervention of T cells can lead to major side effects. Neurological toxicity can include cognitive impairment, seizures, confusion, and life-threatening events like cerebral edema. These adverse effects occur due to the hyperactivity of the modified T cells, which can target healthy tissues in the nervous system or trigger an immune response that affects the brain and spinal cord and can lead to inflammation, disruption of the blood-brain barrier, and the release of cytokines, causing a cascade of neurological problems.
Further, the unpredictability of individual patient responses to these therapies makes it challenging to accurately assess and mitigate the risk of neurological toxicity. This leads to patients and healthcare professionals hesitating to adopt engineered T-cell therapies, limiting their market potential.
Opportunity
Advancement in the treatment of solid tumors
The Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) itself is undergoing modifications in terms of design. Scientists are creating more sophisticated CAR architectures with several signaling domains to improve T-cell activation and retention in the tumor microenvironment. The correct target antigen must be chosen. According to research, antigens that are specific to the tumor and are highly expressed diminish the danger of off-target effects and lessen the harm done to healthy cells.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors, radiation therapy, and small molecule inhibitors are some therapies that can be combined with CAR-T therapy to produce synergistic effects that enhance the overall response to treatment. Even though CAR-T therapy has demonstrated great success, it can also have serious adverse consequences. To render the treatment less toxic and safer for patients, researchers are investigating strategies to lessen its toxicities.
For instance, in January 2023, Researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania found in a preclinical study that CAR T cell therapy rewires patients' immune cells to target their blood malignancies, potentially improving the efficacy of surgery for solid tumors. Thus, such advancements in the treatment of solid tumors are observed to present multiple opportunities for the engineered T cells market in the upcoming period.
Segments Insights
Type Insights
The chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) modified T cells segment is expected to be dominant in the engineered T cells market during the predicted period. A cutting-edge tumor immunotherapy method for cancer treatment is CAR-T cell therapy. It is well known that CAR-T cells are effective in treating acute B lymphocytic leukemia, and there have been multiple published clinical trials using CAR-T cell therapy to treat different types of malignancies. This strategy is more specialized and adaptable because the antigen-binding region can be modified to focus on other tumor targets.
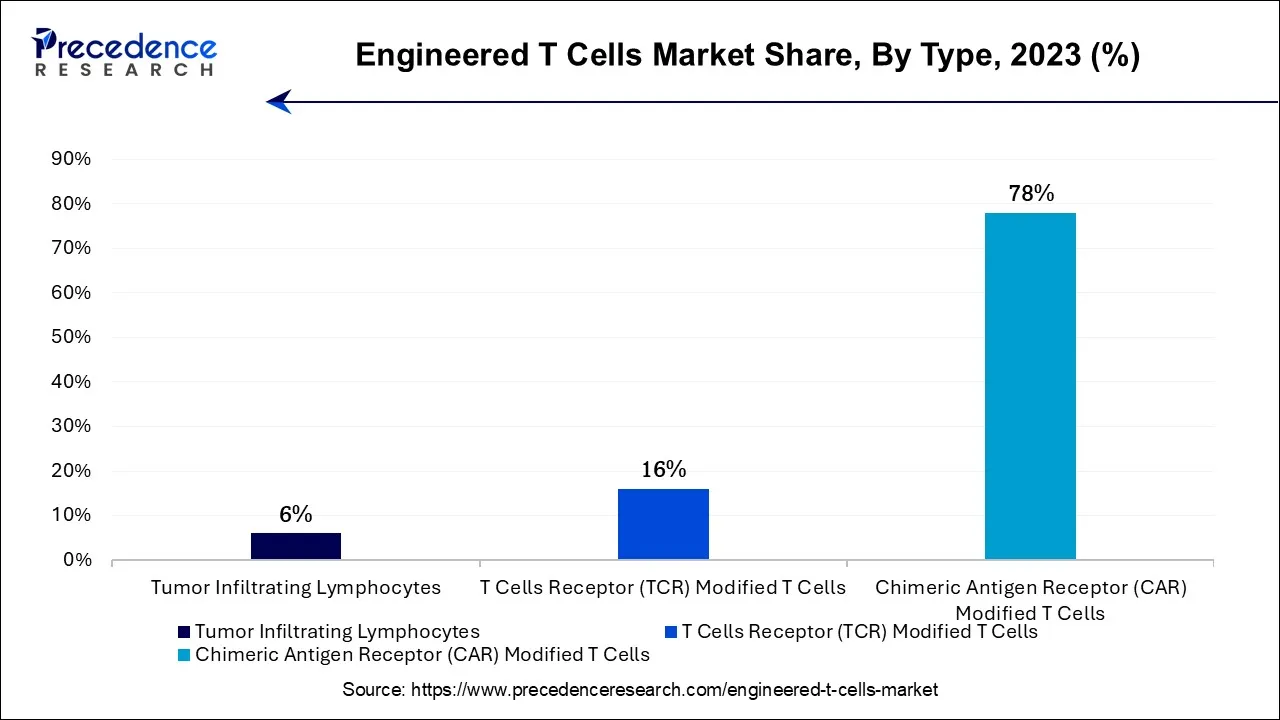
Furthermore, CAR-T cells can create memories in people with advanced leukemia. A CAR is a recombinant receptor that binds tumor antigens and activates T cells. Tumor-specific antigens can be recognized by and attached to CAR-T cells. Tumor surface antigens are recognized directly by CAR-T cells. CAR-T cells multiply and kill tumor cells when they bind to tumor surface antigens. Each patient can receive personalized CAR T-cell therapy. They are created by obtaining T cells from the patient and genetically modifying them to form chimeric antigen receptors, or CARs, on the surface of their cells. CARs identify and attach to antigens, or proteins, on the outermost layer of cancer cells.
The T cells receptor (TCR) modified T cells segment shows a significant growth in the engineered T cells market during the forecast period. TCR-modified T-cell treatment can be specifically adapted to a patient's malignancy by identifying particular tumor antigens. The efficacy of the medication is increased, and this tailored strategy decreases the likelihood of treatment resistance. TCRs are more specialized because they recognize intracellular antigens crucial to malignancy growth. This accuracy minimizes harm to healthy cells and lessens the possibility of off-target effects.
TCR-modified T-cells can be coupled with other treatments, such as checkpoint inhibitors, to increase their effectiveness. This synergistic potential creates possibilities for combination therapy that can focus on several elements of malignancy. TCR-modified T-cells may offer more significant, long-lasting responses because of their increased specificity and antigen recognition compared to previous therapies.
Tumor Infiltrating Lymphocytes (TILs) are a form of adoptive cell therapy that uses a patient's own immune cells, extracted directly from the tumor, to target and destroy cancer cells. This approach is gaining market momentum because it offers a personalized and highly targeted treatment, particularly for solid tumors where other engineered T cell therapies face challenges. Advances in cell expansion techniques, automation, and combination therapy strategies are improving efficacy and scalability, driving strong interest and investment in TIL-based therapies across the oncology landscape.
Application Insights
The lung cancer segment is expected to be dominant in the engineered T cells market during the predicted period. Lung cancer and other malignancies can be treated with engineered T cells, which can be created to target and fight cancer cells in the body. T-cell therapies have advanced because of research and development in this field, which could help patients with lung cancer and the general immunotherapy field.
- For instance, according to the American Cancer Society's projections for lung cancer in the US in 2023, there will be around 117,550 new cases of the disease (117,340 in males) and 120,790 lung cancer deaths (59,910 in women).
Breast cancer is the fastest growing segment in the engineered T cells market during the forecast period. These cutting-edge treatments, such as CAR-T cell therapies, are demonstrating promising outcomes in clinical studies and have the potential to completely transform the way cancer is treated. The demand for more effective breast cancer therapies, rising investment, and research improvements are the main drivers of market expansion.
Colorectal cancer represents a significant application area for engineered T cell therapies due to its high global prevalence and unmet treatment needs. Researchers are actively developing CAR-T, TCR-T, and TIL-based approaches to overcome the challenges of targeting solid tumors and improving immune cell infiltration into the tumor microenvironment. Advancements in antigen identification, combination immunotherapy strategies, and next-generation cell engineering are supporting strong market growth for engineered T cell applications in colorectal cancer.
End-User Insights
The hospitals segment is expected to be dominant in the engineered T cells market during the forecast period. To administer and treat complicated designed T-cell therapy, hospitals frequently have a plethora of clinical knowledge and trained medical staff. These treatments entail complex procedures, meticulous patient observation, and risk management. Engineered T-cell therapies necessitate cooperation between oncologists, hematologists, immunologists, and geneticists, among other medical disciplines. The continuous interdisciplinary teamwork that hospitals provide improves patient care and therapeutic results. Patients with significant conditions seek treatment at hospitals as primary healthcare facilities.
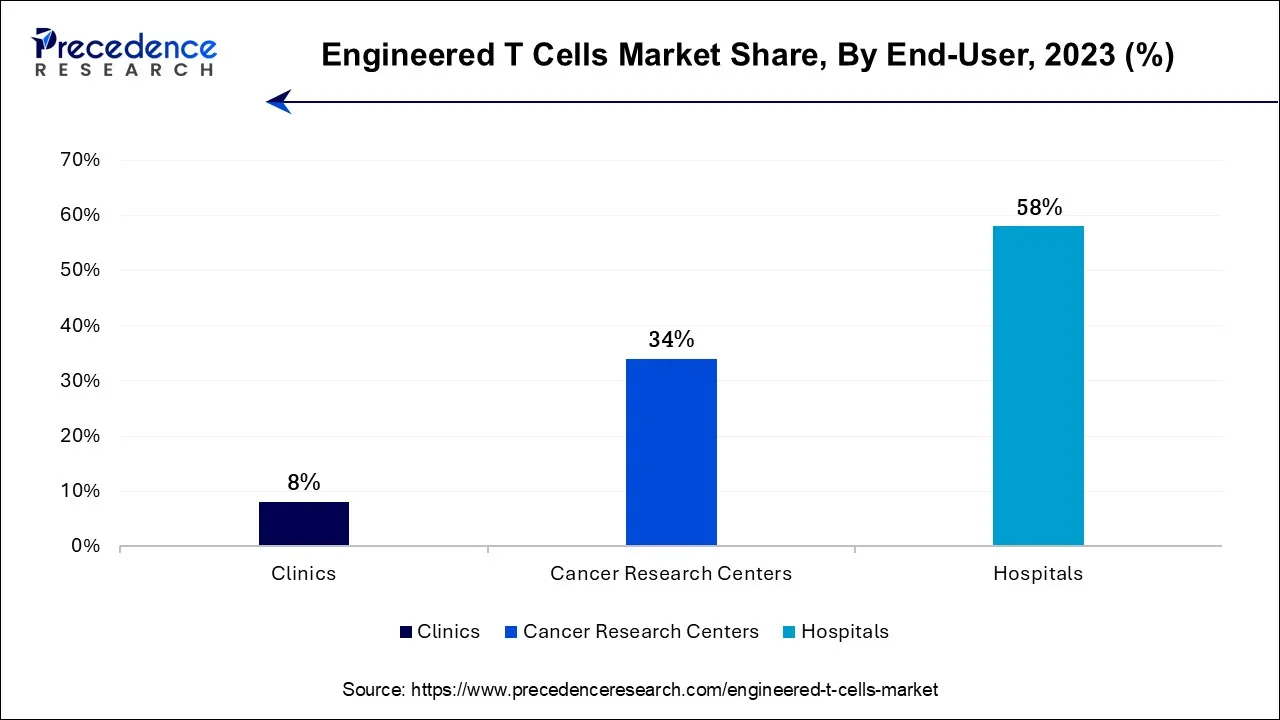
The cancer research centers segment shows an attractive growth in the engineered T cells market during the predicted period. Cancer research institutions can perform sophisticated research into modified T-cell treatments owing to their access to resources and knowledge. Improvements in treatment results are made possible by their research, which provides insightful information about these therapies' conception, creation, and optimization. These centers carry out rigorous clinical trials to assess the efficacy and safety of engineered T-cell treatments.
Regional Insights
How Big is the U.S. Engineered T Cells Market?
The U.S. engineered T cells market size is projected to reach over USD 286.86 billion by 2034, increasing from USD 21.86 billion in 2025 with a healthy CAGR of 29.37% from 2025 to 2034.

North America dominated the market by holding more than 46% of market share in 2024 and is expected to sustain in the engineered T cells market throughout the predicted timeframe. North America is home to several of the world's top pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies. These businesses have made significant investments in the study of modified T cells, paving the way for the creation of ground-breaking treatments and tools. The healthcare system in North America is well-established and includes prestigious hospitals, clinics, and medical research facilities. This makes it easier to design and test new treatments in patients, such as modified T cells.
To fund biotech and medical research, North America has seen significant investments from venture capital firms, private equity, and government programs. This financial support has aided the expansion of new and established businesses engaged in the development of modified T-cell treatments.
According to the National Cancer Institute, breast cancer is the most common type of cancer, with 300,590 new cases anticipated in the US in 2023. Cellular therapies, such as modified T cells, have been developed and approved with the help of the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Due to the accelerated review procedures and simplified regulatory channels, companies have been encouraged to concentrate their research efforts on the region.

Asia Pacific is expected to be the fastest growing region in the engineered T cells market during the forecasted timeframe. Concerning modified T-cell therapies, the rising incidence of cancer and other chronic diseases in Asia has increased the need for novel and individualized therapies. The enormous and diversified population of Asia Pacific offers a sizable patient pool for clinical trials and the uptake of treatments. Furthermore, developed nations like China, Japan, South Korea, and India have created and market-engineered T-cell therapies thanks to improvements in healthcare infrastructure and biotechnology research capacity.
These countries have made significant R&D investments, encouraging partnerships between academic institutions, pharmaceutical firms, and research organizations to quicken development. With regulatory bodies shortening approval procedures and providing incentives for cutting-edge medicines, the regulatory environment in the Asia Pacific has also improved for cell-based therapies. This has permitted modified T-cell products to enter the market faster.
Why is Latin America Showing Notable Growth in the Engineered T Cells Market?
Latin America is showing notable growth in the engineered T cells market due to increasing investment in biotechnology and cancer research, along with the expansion of advanced healthcare infrastructure in countries such as Brazil, Mexico, and Argentina. Rising awareness of cell and gene therapies, coupled with supportive government initiatives and partnerships with international biopharmaceutical companies, is accelerating clinical adoption. In addition, growing participation in global clinical trials and improvements in regulatory frameworks are helping to make advanced immunotherapies more accessible across the region.
Brazil Engineered T Cells Market
The engineered T cells market in Brazil is growing rapidly, supported by the country's expanding biotechnology sector and increasing focus on advanced cancer therapies. Brazil's strong network of public and private research institutions, along with rising investments in cell and gene therapy infrastructure, is helping to establish it as a leading hub for immunotherapy development in Latin America.
Government initiatives to modernize healthcare, improve regulatory pathways, and encourage local clinical trials are accelerating the adoption of engineered T cell therapies, including CAR-T and TCR-T treatments. In addition, collaborations between Brazilian universities, hospitals, and international biopharmaceutical companies are enhancing technology transfer and clinical expertise.
With a large patient population, growing awareness of personalized medicine, and continued investment in biomanufacturing and innovation, Brazil's engineered T cells market is expected to experience strong growth over the coming years.
Engineered T Cells Market Companies
- Amgen Inc. – Amgen is a global biotechnology company engaged in developing engineered T-cell therapies targeting cancer and autoimmune diseases. The company focuses on bispecific T-cell engager (BiTE) technology, which redirects T cells to attack cancer cells, with products like Blincyto paving the way for next-generation immuno-oncology treatments.
- Bellicum Pharmaceuticals Inc. – Bellicum specializes in cellular immunotherapies, including engineered T cells with switch-control technology. Its proprietary GoCAR-T and CaspaCIDe platforms enhance T-cell performance, persistence, and safety, particularly in targeting solid and hematologic cancers.
- Bristol-Myers Squibb – Bristol-Myers Squibb is a major player in cell and gene therapy, focusing on CAR-T and TCR-T therapies for hematologic malignancies. The company's pipeline includes Abecma and Breyanzi, developed in collaboration with bluebird bio and Juno Therapeutics, expanding access to advanced T-cell therapeutics.
- Precision BioSciences Inc. – Precision BioSciences develops engineered T-cell therapies using its ARCUS genome editing platform. The company's allogeneic CAR-T candidates target hematologic cancers and solid tumors, focusing on scalable, off-the-shelf immunotherapy solutions.
- Eli Lilly and Company – Eli Lilly has entered the engineered T-cell therapy space through strategic acquisitions and collaborations. The company invests in cell-based immuno-oncology platforms, leveraging precision engineering to enhance T-cell receptor targeting and anti-tumor activity.
- Gilead Sciences, Inc. – Through its subsidiary Kite Pharma, Gilead Sciences leads in CAR-T cell therapy development, producing treatments such as Yescarta and Tecartus for lymphoma and leukemia. The company continues to expand its T-cell therapy research to solid tumors and allogeneic approaches.
- Novartis AG – Novartis is a global leader in CAR-T cell therapy, having launched Kymriah, the world's first FDA-approved CAR-T treatment for leukemia and lymphoma. The company continues to advance next-generation T-cell engineering, focusing on solid tumors and manufacturing innovation.
- Athenex Inc. – Athenex develops T-cell receptor (TCR) and CAR-T therapies for oncology, emphasizing scalable production and improved safety profiles. Its pipeline includes allogeneic and autologous T-cell therapies, supported by proprietary cell engineering and cryopreservation technologies.
- Oxford Biomedica Plc – Oxford Biomedica is a pioneer in viral vector manufacturing for engineered T-cell therapies, supporting global partners developing CAR-T and TCR therapies. The company plays a key role in process optimization and gene-delivery technologies essential to clinical-scale T-cell production.
- Pfizer Inc. – Pfizer is advancing T-cell immunotherapy platforms through strategic partnerships and in-house R&D. The company collaborates with biotech innovators in CAR-T and TCR-T technologies, focusing on treating solid tumors and hematologic cancers with enhanced efficacy and safety.
Recent Developments
- In January 2025, Immuneel Therapeutics (India) announced the launch of “Qartemi”, described as India's first global CAR‑T cell therapy for adult relapsed/refractory B‑cell Non‑Hodgkin's Lymphoma (B‑NHL).
- In January 2025 – CellFE launched T-Rest™ Resting T Cell Kit, a manufacturing tool for gene-edited, resting T-cell workflows in CAR-T therapy production.
- In July 2025 – Legend Biotech launched a CAR-T therapy for multiple myeloma in the US and Europe, aiming to expand commercial availability beyond China. This launch represents a major step in making advanced cell therapies accessible globally and highlights the company's commitment to addressing unmet needs in multiple myeloma treatment.
Segments Covered in the Report
By Type
- Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) Modified T Cells
- T Cells Receptor (TCR) Modified T Cells
- Tumor Infiltrating Lymphocytes
By Application
- Lung Cancer
- Colorectal Cancer
- Melanoma
- Breast Cancer
- Leukemia
By End-user
- Hospitals
- Cancer Research Centers
- Clinics
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa
 Get a Sample
Get a Sample
 Table Of Content
Table Of Content



