Pan-Tumor Oncology Treatment Market Size and Forecast 2025 to 2034
The pan-tumor oncology treatment market is gaining momentum with the emergence of therapies targeting genetic mutations across cancer types, supported by advancements in companion diagnostics and personalized medicine approaches. The pan-tumor oncology market is rapidly gaining traction as researchers and clinicians recognize its potential to treat various cancers more effectively through targeted therapies. This approach's growing popularity reflects a shift toward personalized medicine, promising improved outcomes across multiple tumor types.
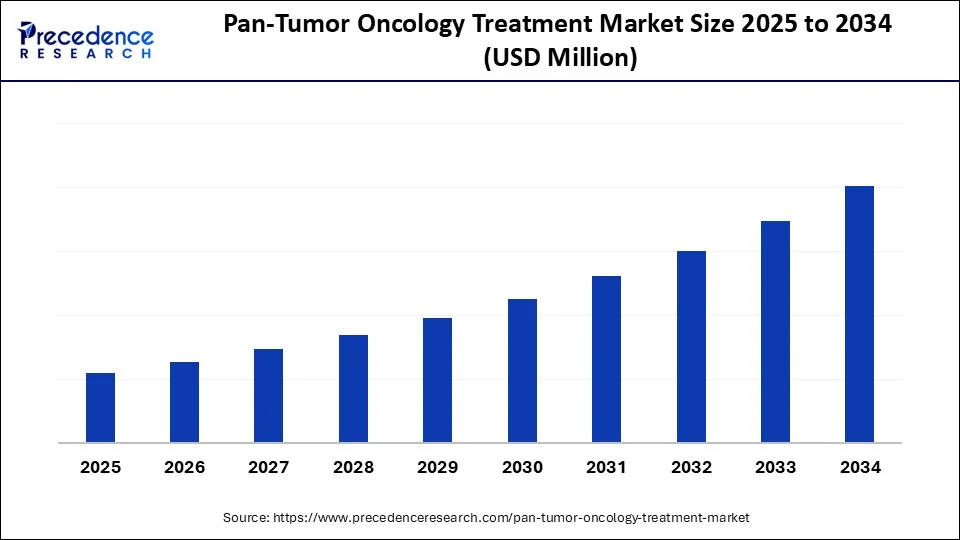
Pan-Tumor Oncology Treatment Market Key Takeaways
- North America dominated the pan-tumor oncology treatment market in 2024.
- Asia Pacific is expected to expand at the fastest CAGR in the market between 2025 and 2034.
- By therapy type, the targeted therapy segment held the largest market share in 2024.
- By therapy type, the RNA-based therapies segment is expected to grow at a remarkable CAGR between 2025 and 2034.
- By biomarker/genomic target, the NTRK gene fusions segment captured the largest market share in 2024.
- By biomarker/genomic target, the other rare targets (e.g., FGFR, MET, ALK) segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR between 2025 and 2034.
- By drug class, the small molecule inhibitors segment contributed the biggest market share in 2024.
- By drug class, the nucleic acid-based drugs (ASOs, siRNAs, mRNA) segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR between 2025 and 2034.
- By route of administration, the oral segment led market share in 2024.
- By route of administration, the subcutaneous (SC) segment is expected to grow at a remarkable CAGR between 2025 and 2034.
- By patient age group, the adult (18–64 years) segment held the major market share in 2024.
- By patient age group, the geriatric (65+ years) segment is expected to grow at a remarkable CAGR between 2025 and 2034.
- By end-user, the specialty cancer centers and hospitals segment generated the highest market share in 2024.
- By end-user, the homecare (for oral therapies) segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR during the projection period.
How is AI Impacting the Pan-Tumor Oncology Treatment Market?
Artificial intelligence is transforming the landscape of the market for pan-tumor oncology treatment by accelerating drug discovery and enabling personalized treatment plans. From molecular profiling to predicting treatment responses, AI is now an indispensable tool in oncology research and clinical practice. AI algorithms are adept at analyzing complex genomic and imaging data, enabling early detection of tumor-agnostic biomarkers. These tools can swiftly identify mutations such as NTRK fusions or MSI-H/dMMR, critical for pan-tumor therapies, thus reducing the diagnostic window and improving patient outcomes. Pharmaceutical companies are leveraging AI to model tumor behavior and predict drug efficacy across different tumor types. This has significantly shortened the R&D cycle, reducing the time-to-market for targeted therapies such as TRK inhibitors that show efficacy across multiple cancers.
Market Overview
The pan-tumor oncology treatment market refers to a category of cancer therapies that are tumor-agnostic, i.e., they target genomic or molecular alterations regardless of the anatomical location or tissue of origin of the tumor. These treatments act on common biomarkers (such as NTRK gene fusions, MSI-H/dMMR, BRAF mutations, RET fusions) rather than the traditional organ-specific approach (like breast, lung, colon). Pan-tumor therapies, which include targeted therapies, immunotherapies, and precision oncology drugs, are revolutionizing cancer treatment by enabling more personalized and biomarker-guided therapies.
The pan-tumor oncology treatment market is witnessing significant growth, driven by the rapid shift toward molecular-driven approaches rather than traditional organ-specific therapies. This approach focuses on shared genetic mutations or biomarkers found in various types of cancers, creating opportunities for treatment that span multiple indications. The market is primarily driven by the success of agnostic therapies such as NTRK and RET inhibitors, as well as immune checkpoint inhibitors that demonstrate efficacy across cancer types. Pharmaceutical companies are investing heavily in the development of such treatments, which are supported by regulatory frameworks that facilitate accelerated approvals and breakthrough therapy designations from agencies such as the FDA and EMA.
Key Trends in the Market
- Rise of tumor-agnostic drug approvals: There is a trend toward the regulatory acceptance of tumor-agnostic therapies. Landmark approvals, such as tumor-agnostic therapies. Landmark approvals such as those targeting NTRK gene fusions, MSI-H, and RET mutations have created a precedent for pan-cancer drug development.
- Integration of multi-omics and precision medicine: Multi-omics encompassing genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and epigenomics is becoming central to pan-tumor therapy development.
- AI and digital tools in clinical development: Artificial intelligence is no longer a futuristic concept but a present-day enabler of discovery. AI is helping identify new pan-tumor biomarkers, predict drug responses, and simulate treatment pathways. Additionally, digital health platforms and wearable devices are being used for real-time patient monitoring and data collection.
- Growth of companion diagnostics and NGS technologies: Next-generation sequencing has become a cornerstone in identifying candidates for pan-tumor treatments. The expansion of NGS-based diagnostic tools and companion diagnostics is increasing the precision of patient selection.
- Shift toward combination therapies: There is a growing focus on combining pan-tumor drugs with immunotherapies, chemotherapy, or radiotherapy to improve response rates am reduce resistance.
Market Scope
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Dominating Region | North Ameirca |
| Fastest Growing Region | Asia Pacific |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | Therapy Type, Biomarker/Genomic Target, Drug Class, Patient Age Group, End-User, and Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Market Dynamics
Drivers
Shift Toward Nutation-Based Oncology and Regulatory Support
A key driver of the pan-tumor oncology treatment market is the rapid shift from organ-based to nutation-based oncology. Unlike traditional therapies that are limited by tumor location, pan-tumor treatments target shared genetic mutations or molecular profiles, offering cross-cancer applicability. This enhances therapeutic reach and aligns with the growing need for personalized and efficient treatments. The increasing proliferation of genetic testing and next-generation sequencing is amplifying this shift. With a rising number of patients being tested for biomarkers like NTRK fusions, MSI-H, and RET alterations, the pool of eligible patients for tumor-agnostic drugs is expanding.
As testing becomes more routine and accessible, the demand for broad-spectrum therapies continues to rise. Regulatory support also plays a pivotal role. Agencies like the FDA and EMA are granting accelerated and breakthrough designations to therapies that demonstrate efficacy based on biomarkers rather than cancer type. These supportive policies are fast-tracking approvals and reducing time-to-market for innovators. Moreover, pharmaceutical and biotech companies are investing heavily in the development of novel molecules and drug platforms that can be applied across various tumor types.
Restraint
Complexity of Biomarker Identification and Limited Reimbursement Policies
The pan-tumor oncology market faces several challenges, particularly in identifying biomarkers. Not all mutations are equally well understood or easily actionable, making it difficult to develop universally effective tumor-agnostic treatments. This genetic heterogeneity across patients remains a significant scientific and clinical challenge. High treatment costs also pose a substantial barrier. Most approved or developing pan-tumor therapies are cutting-edge biologics or small molecules, which incur high R&D and production costs. As a result, access is often restricted to high-income countries or limited by insurance coverage, hampering equitable adoption across healthcare systems. Infrastructural gaps in diagnostic availability further slow the market growth.
Pan-tumor treatments rely heavily on advanced diagnostics, such as NGS and immunohistochemistry, but these tests are not uniformly available across regions or medical institutions. Limited access to diagnostics hinders accurate patient identification and limits the therapy's effectiveness. Regulatory ambiguity is another restraint. While some tumor-agnostic drugs have received landmark approvals, there is no uniform global regulatory framework for evaluating these therapies. The lack of harmonized guidance and inconsistent reimbursement policies can delay market entry and discourage investment. Clinical resistance and variability in patient response remain unresolved. While pan-tumor therapies show promise in clinical trials, real-world responses can be inconsistent, especially when mutations co-exist with other complex factors. These unpredictable outcomes raise concerns about efficacy, limit long-term confidence, and affect adoption rates.
Opportunity
Expanding Applications into Rare Cancer and Expansion into Emerging Markets
The pan-tumor treatment approach opens a universe of untapped opportunities across oncology. One of the most promising is the potential to serve rare cancer and orphan indications, where tumor-specific treatments are limited or non-existent. Pan-cancer therapies allow for meaningful intervention even when the cancer's origin is unknown or rare, filling a critical treatment gap. Another opportunity lies in pediatric oncology. Given the rarity and diversity of tumors in children, tumor-agnostic therapies can streamline pediatric drug development. Regulatory incentives and a growing focus on child-specific oncology care further open up new avenues for pan-tumor strategies.
Growing healthcare spending in emerging markets offers significant growth opportunities. As diagnostics like NGS become more widely adopted in emerging markets, a new wave of patient populations will become eligible for pan-tumor therapies. The integration of high-tech technologies, real-world data, and digital platforms offers yet another growth lever. From virtual trials to AI-assisted diagnostics, digital tools are reducing barriers to treatment-to-treatment development and deployment.
Therapy Type Insights
Why Did the Targeted Therapy Segment Dominate the Pan-Tumor Oncology Treatment Market in 2024?
The targeted therapy segment dominated the market with the largest share in 2024. This is mainly due to its precision-driven approach and proven success across multiple cancer types. Targeted therapies are designed to inhibit specific molecular pathways or genetic mutations responsible for cancer growth, offering highly personalized solutions that align perfectly with the pan-tumor model. In the case of pan-tumor treatments, targeted therapies focus on mutations such as NTRK, RET, and BRAF, which may be present across a spectrum of tumor origins. Their ability to bypass the need for tumor-site-specific treatment allows them to deliver results even in cancers that are rare or lack standardized therapies, making them indispensable in advanced oncology.
The high efficacy rates, reduced toxicity profiles, and longer progression-free survival benefits associated with targeted therapies make them the preferred choice among oncologists. Furthermore, their compatibility with companion diagnostics ensures that only patients with the relevant mutations are treated, maximizing therapeutic outcomes and resource efficiency. Pharmaceutical pipelines worldwide remain heavily skewed towards developing new targeted molecules and expanding the label indications of existing drugs.
Regulatory support, including accelerated approvals and breakthrough designations, has further propelled their dominance in the pan-tumor domain. Despite growing competition from emerging therapy classes, targeted therapy remains firmly established due to its mature technology, clinical track record, and adaptability to combination treatment strategies. It remains the bedrock of tumor-agnostic drug development.
On the other hand, the RNA-based therapies segment is expected to grow at the fastest rate in the upcoming period. The growth of the segment is attributed to the rising demand for targeted and personalized therapies. These therapies utilize RNA molecules such as siRNA, mRNA, and antisense oligonucleotides to modulate gene expression or repair genetic mutations, offering a new mechanism of action that complements and, in some cases, surpasses traditional small molecules. What makes RNA-based therapies exceptionally promising for pan-tumor application is their flexibility and specificity. They can be designed to silence oncogenic mutations, correct abnormal protein production, or even trigger immune responses, all tailored to the patient's unique tumor profile.
This modularity fits perfectly into the personalized, mutation-driven paradigm of pan-tumor care. The success of mRNA technology in vaccines has accelerated research into oncology-focused RNA treatments. Biotech firms are increasingly directing R&D toward developing RNA platforms that target cancer mutations present in multiple tumor types. These platforms are expected to produce faster, more scalable, and more cost-effective therapeutic solutions.
Moreover, RNA-based therapies are being explored for use in combination with immunotherapy or targeted drugs, enhancing their efficacy and overcoming resistance mechanisms. Their use in hard-to-treat or rare cancers, where few options exist, is another compelling reason behind their accelerated market growth. While the technology still faces challenges in delivery and stability, ongoing innovations in nanoparticle carriers and delivery systems are helping to overcome these limitations. As clinical trials progress and regulatory clarity improves, RNA-based therapies are poised to redefine the future of tumor-agnostic treatment.
Biomarker/Genomic Target Insights
How Does the NTRK Gene Fusions Segment Dominate the Market in 2024?
The NTRK gene fusions segment dominated the pan-tumor oncology treatment market with a major revenue share in 2024. NTRK gene fusions have become the poster child of pan-tumor oncology, serving as the first biomarker to earn FDA approval for tumor-agnostic treatment. Their discovery and clinical validation have marked a paradigm shift in how cancer is approached, prioritizing molecular identity over anatomical location. These gene fusions result in oncogenic TRK fusion proteins that drive cancer proliferation. While rare, they occur across a wide range of tumor types, including thyroid, lung, colon, and salivary gland cancers, making them an ideal candidate for tumor-agnostic intervention.
The FDA's approval of TRK inhibitors like larotrectinib and entrectinib has catalyzed this movement. What sets NTRK apart is not just its cross-cancer presence but also the exceptional response rates these patients demonstrate. Clinical trials have shown durable and deep responses, often with minimal side effects, establishing a new benchmark for tumor-agnostic drug performance. The success of NTRK-targeted therapies has accelerated efforts to identify and validate other fusion-driven cancers. There is greater adoption of comprehensive genomic profiling and NGS, helping oncologists uncover NTRK fusions in previously untargeted cancers.
Meanwhile, the other rare targets (e.g., FGFR, MET, ALK) segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period. This is mainly due to the rising focus on rare targets is the ability to serve niche patient populations that often lack standard treatment options. This approach aligns with the principles of precision medicine and orphan drug development, encouraging pharmaceutical innovation through regulatory and financial incentives. With the expansion of biomarker screening and advanced molecular diagnostics, these rare mutations are now being identified more frequently and at earlier stages of disease progression. This has opened new therapeutic possibilities and is reshaping how cancers with low incidence but high unmet need is approached.
Rare targets are increasingly being included in clinical studies that enroll patients based on genetic mutations rather than tumor type, thereby accelerating the clinical validation of tumor-agnostic therapies. As these trials yield promising results, more drugs targeting these uncommon alterations are expected to enter the pipeline. While challenges such as limited trial populations and commercial viability persist, the momentum is unmistakable. Rare targets, once overlooked, are now being recognized as powerful drivers of the next wave in pan-tumor oncology treatment.
Drug Class Insights
What Made Small-Molecule Inhibitors the Dominant Segment in the Pan-Tumor Oncology Treatment Market in 2024?
The small-molecule inhibitors segment dominated the market with a significant share in 2024, as they are the cornerstone of many therapeutic strategies due to their effectiveness in targeting specific biological pathways. Small-molecule inhibitors work by inhibiting enzyme activity or blocking receptor interactions, which can lead to improved outcomes in various diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disorders, and autoimmune conditions. Their ability to be administered orally, combined with well-established mechanisms of action, has solidified their presence in the treatment arsenal of healthcare providers.
Their established efficacy and safety profiles propel the demand for small-molecule inhibitors. For instance, many blockbuster drugs can be classified as small molecules, showcasing their importance in achieving therapeutic goals. The ongoing research into enhancing the potency and selectivity of these compounds has resulted in the continual emergence of new inhibitors, making this segment highly competitive. Additionally, the ease of development and cost-effectiveness of small molecules compared to biologics contribute to their sustained dominance in the market.
On the other hand, the nucleic acid-based drugs segment is expected to grow at the fastest rate during the projection period. Nucleic acid drugs, such as antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs), small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), and messenger RNAs (mRNAs), offer promising avenues for treating genetic disorders and diseases marked by defective protein expression. Unlike traditional small molecules, nucleic acid-based drugs can precisely target the root causes of diseases at the genetic level, providing a new dimension in the fight against a range of conditions. Their potential for personalized medicine is vast, further sparking interest and investment in this area.
Acid-based drugs present a fascinating counterpoint to small-molecule inhibitors. Progress in delivery mechanisms and stability has led to a surge in clinical trials and approvals for these treatments. Regulatory agencies are increasingly receptive to their potential, paving the way for groundbreaking therapies that were once deemed infeasible. As scientists uncover new methods to optimize nucleic acid structures for better performance, the speed at which these therapies reach the market is expected to increase, potentially altering the standard of care.
Route of Administration Insights
Why Did the Oral Segment Dominate the Pan-Tumor Oncology Treatment Market in 2024?
Oral administration remains the dominant route, driven by its convenience, patient compliance, and clinical efficacy. With targeted therapies and small-molecule inhibitors often developed in pill form, oral drugs have become the go-to option for tumor-agnostic treatments. They allow patients to manage treatment at home, reducing dependency on hospital infrastructure. The success of oral TRK inhibitors and kinase-targeting agents has demonstrated the viability of this route in delivering precise, systemic effects with relatively fewer side effects. These therapies not only cross tumor types but also offer flexibility in dosing schedules, which is particularly valuable in long-term cancer management.
Oral therapies help reduce the overall treatment burden. They lower hospitalization rates, minimize infusion-related complications, and reduce treatment delivery costs. This makes them highly desirable in both high-income and resource-constrained settings, contributing to their global dominance. Additionally, patient preference is shifting towards oral therapies for quality-of-life reasons. Cancer treatment is physically and emotionally taxing, and oral administration allows patients to retain a sense of normalcy and autonomy, especially for those managing chronic or rare tumors over extended periods.
On the other hand, the subcutaneous (SC) segment is expected to grow at the highest CAGR in the upcoming period. Subcutaneous delivery offers a favorable balance between efficacy, convenience, and control. This route involves injecting therapies under the skin, often allowing for quicker administration compared to intravenous infusions, with fewer complications and more comfortable patient experiences. With the expansion of biology and RNA-based formulations in tumor-agnostic care, subcutaneous delivery is gaining momentum due to its improved absorption and reduced administration time.
Biopharmaceutical companies are actively reformulating existing IV-administered therapies for subcutaneous use, capitalizing on this trend. This route is particularly suited for outpatient care and home-based treatment models. As healthcare shifts toward decentralized care, subcutaneous administration allows for self-injection or caregiver-assisted delivery, reducing the need for hospital-based visits and promoting treatment accessibility. From a pharmacological standpoint, subcutaneous therapies offer sustained drug release and more predictable pharmacokinetics, improving overall drug performance.
Patient Age Group Insights
What Made Adult the Dominant Segment in the Market in 2024?
The adult (18-64) segment led the pan-tumor oncology market while holding the largest share in 2024, primarily due to higher incidence rates of genetically targetable cancers within this age bracket. This age group often exhibits better physiological resilience, enabling broader eligibility for advanced therapies. Their higher likelihood of undergoing genetic screening and precision diagnostic procedures also plays a pivotal role in treatment uptake. Adults in this segment are more likely to pursue aggressive or experimental treatments, especially those promising long-term survival or improved quality of life across various cancer types. From a market perspective, this population group drives demand due to its size and higher rates of treatment adherence. Many within this age group are professionally active and socially engaged, leading them to seek treatments that allow faster recovery and minimal hospital dependency traits offered by pan-tumor therapies.
Meanwhile, the geriatric (65+ years) segment is likely to grow at the fastest rate in the market. With cancer incidence rates sharply increasing in individuals aged 65 and above, this group presents both a challenge and a profound opportunity for the market. One key concern has been the frailty and comorbidity profile of geriatric patients, which often excludes them from clinical trials. However, the tumor-agnostic approach, especially using oral or subcutaneous therapies, offers a less invasive and more tolerable treatment option suitable for older patients. Precision medicine enables more accurate matching of treatments with a geriatric patient's genetic profile, reducing the risk of overtreatment and improving safety.
Tailored dosing and gentler treatment schedules can be developed based on molecular findings, enabling even the elderly to benefit from targeted interventions with minimal toxicity. In many developed countries, the healthcare system is evolving to be more inclusive of geriatric oncology. Geriatric assessment tools, specialized oncology clinics, and insurance models are being adapted to support tumor-agnostic treatment access for senior patients, reflecting their growing importance as a treatment demographic.
End-User Insights
How Does the Specialty Cancer Centers & Hospitals Segment Dominate the Market in 2024?
The specialty cancer centers & hospitals segment dominated the pan-tumor oncology treatment market, holding the largest share in 2024. These institutions are at the forefront of cancer treatment, offering patients access to advanced therapies and specialized care. With a focus on comprehensive cancer care, they integrate cutting-edge technologies and robust clinical practices, ensuring that patients receive the most effective and personalized treatment options. The demand for specialized oncology services is driving the growth of this segment as healthcare systems increasingly recognize the importance of targeted treatments and expert guidance in managing complex cancer cases.
Meanwhile, the homecare segment is poised to experience remarkable growth in the coming years. This is mainly due to the increased healthcare costs, which encourage patients to receive treatments in home settings. This trend is largely driven by the increasing adoption of oral therapies, which provide patients with the convenience and flexibility of administering treatment at home. The rising preference for homecare solutions reflects a shift toward patient-centered care, allowing individuals to manage their treatment schedules alongside their daily lives. As oral therapies gain regulatory approval and are incorporated into treatment regimens, the homecare segment is expected to flourish, offering both cost-effective and patient-friendly options for cancer treatment.
Regional Insights
What Factors Contribute to North America's Dominance in the Pan-Tumor Oncology Treatment Market?
North America registered dominance in the market by capturing the largest share in 2024. North America, particularly the U.S., stands as the global epicenter of pan-tumor oncology treatment development and adoption. With its robust healthcare infrastructure, advanced research capabilities, and strong investment environment, the region excels in both innovation and market penetration. Regulatory frameworks, such as the FDA's accelerated approval program, have played a crucial role in facilitating the early-stage approval of tumor-agnostic therapies.
The region also boasts high adoption rates of precision diagnostics, such as next-generation sequencing and biomarker testing. These technologies are readily integrated into clinical workflows, enabling oncologists to quickly identify patients eligible for pan-tumor therapies. This diagnostic readiness gives North America a significant advantage in pushing these therapies from the lab to besides faster than other markets. Research institutions and pharmaceutical companies in the region are consistently driving the boundaries of pan-tumor innovation.
With abundant funding, access to large clinical trial populations, and cross-collaborative ecosystems between academia, biotech firms, and big pharma, North America is setting the gold standard in tumor-agnostic treatment research and development. Furthermore, patient awareness and willingness to explore novel therapies are notably higher in North America. Coupled with supportive reimbursement systems for both testing and treatment, the market finds an engaged and responsive healthcare community. This environment significantly boosts uptake, especially for recently approved therapies with broad indications.
What are the Major Factors Driving the Growth of the Pan-Tumor Oncology Treatment Market Within Asia Pacific?
Asia Pacific is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period, driven by increasing healthcare investments and the rising burden of cancer. With the world's largest population of cancer patients, the region represents a vast and underpenetrated market. One of the key catalysts for growth is the increasing adoption of precision diagnostics and genetic testing in countries such as China, India, Japan, and South Korea. Governments and private healthcare players are investing in infrastructure to make NGS and biomarker testing more affordable and accessible. This diagnostic revolution enables the identification of mutation-driven cancers across diverse tumor types.
Asia Pacific is also witnessing a growing wave of local biotech and pharmaceutical firms investing in oncology innovation. These companies are forming partnerships with global leaders to co-develop or distribute tumor-agnostic treatments tailored for regional populations. Regional clinical trial centers, along with growing regulatory clarity, further support collaborative research efforts. Additionally, the rising awareness of personalized medicine among physicians and patients is driving the adoption of advanced therapies. Urban healthcare centers in countries such as Singapore, Australia, and South Korea are already integrating tumor-agnostic drugs into their treatment pathways, with others following suit quickly. While challenges persist around pricing, insurance coverage, and rural healthcare access, the Asia-Pacific's sheer market potential, supported by increasing digital and diagnostic maturity, positions it as a powerful engine for future growth in the pan-tumor oncology landscape.
Pan-Tumor Oncology Treatment Market Comapnies

- Roche Holding AG
- Bristol Myers Squibb
- Merck & Co., Inc.
- Eli Lilly and Company
- Bayer AG
- Novartis AG
- Pfizer Inc.
- AstraZeneca plc
- Seagen Inc.
- Blueprint Medicines Corporation
- Genentech Inc.
- Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
- GlaxoSmithKline plc
- BeiGene, Ltd.
- Mirati Therapeutics, Inc.
- Loxo Oncology (Eli Lilly)
- Array BioPharma (Pfizer)
- Amgen Inc.
- F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
- Gilead Sciences, Inc.
Recent Developments
- On June 2025, in a pathbreaking medical feat, a 17-year-old boy suffering from relapsed Neuroblastoma, an aggressive form of paediatric cancer, was given a new lease of life through an experimental nuclear therapy conducted at ACTREC (Advanced Centre for Treatment, Research and Education in Cancer), R&D wing of the Tata Memorial Centre in Navi Mumbai.
(Source:https://www.hindustantimes.com)
- In December 2024, Servier India introduced its oncology portfolio with the launch of Onivyde (nanoliposomal irinotecan) for metastatic pancreatic cancer. This launch demonstrates Servier's commitment to providing therapies for hard-to-treat cancers, with an emphasis on improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
(Source: https://www.business-standard.com)
Segments Covered in the Report
By Therapy Type
- Targeted Therapy
- TRK inhibitors (e.g., larotrectinib, entrectinib)
- RET inhibitors
- BRAF/MEK inhibitors
- Immunotherapy
- Checkpoint Inhibitors (PD-1/PD-L1, CTLA-4)
- T-cell engaging therapies
- Gene Therapy / Gene Editing
- Cell Therapy (CAR-T, TILs)
- RNA-based Therapies
By Biomarker/Genomic Target
- NTRK Gene Fusions
- Microsatellite Instability-High (MSI-H) / dMMR
- RET Fusions
- BRAF V600 Mutations
- KRAS Mutations
- Other Rare Targets (e.g., FGFR, MET, ALK)
By Drug Class
- Small Molecule Inhibitors
- Monoclonal Antibodies
- Biologics (Fusion Proteins, ADCs)
- Nucleic Acid-based Drugs (ASOs, siRNAs, mRNA)
By Route of Administration
- Oral
- Intravenous (IV)
- Subcutaneous (SC)
By Patient Age Group
- Adult (18–64 years)
- Pediatric
- Geriatric (65+ years)
By End-User
- Specialty Cancer Centers & Hospitals
- Academic Research Institutes
- Ambulatory Infusion Centers
- Homecare
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- South America
- Middle East & Africa
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Ask For Sample
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
 Get a Sample
Get a Sample
 Table Of Content
Table Of Content
 sales@precedenceresearch.com
sales@precedenceresearch.com
 +1 804-441-9344
+1 804-441-9344
 Schedule a Meeting
Schedule a Meeting