What is the Infectious Disease Diagnostics Market Size?
The global infectious disease diagnostics market size was accounted for USD 35.39 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach around USD 71.06 billion by 2035, expanding at a CAGR of 7.22% from 2026 to 2035.
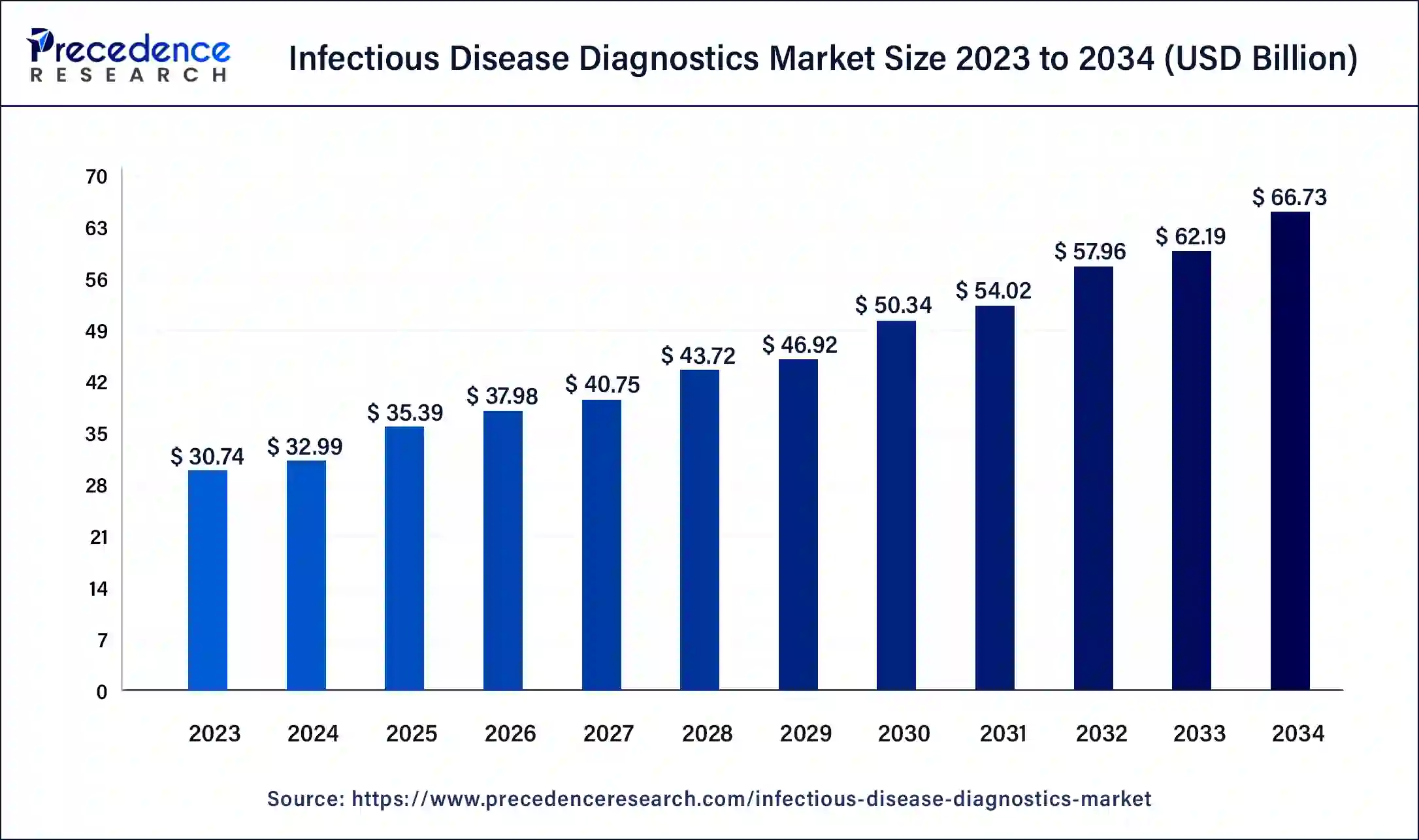
Infectious Disease Diagnostics Market Key Takeaways
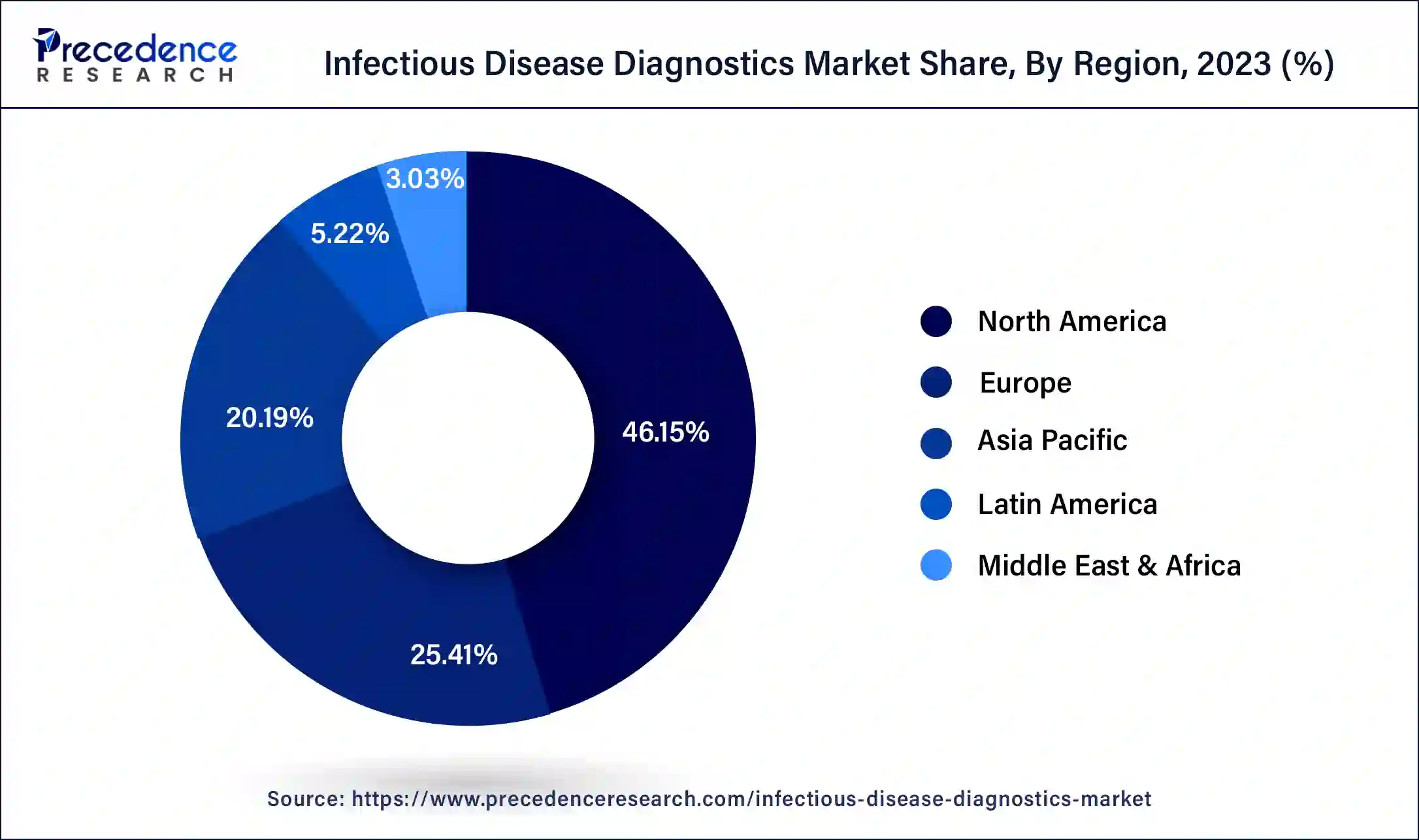
- North America led the global market with the highest market share of 46.15% in 2025.
- By Product, the assays & reagents segment generated more than 51% of revenue share in 2025.
- By Technology, the immunodiagnostics segment is estimated to record the highest market share from 2026 to 2035.
What is the Infectious Disease Diagnostics?
Infectious diseases are caused by pathogenic microorganisms such as parasites, viruses, bacteria, & fungi, and they can be spread from one person to another person through various means such as breathing in an airborne virus, contact with blood and bodily fluids, or by being bitten by an insect. Infectious disease diagnostics is crucial for identifying the presence of specific pathogens in individuals, aiding healthcare professionals to make precise diagnoses, initiate appropriate treatments, and implement control measures to stop the transmission of infections.
Diagnostic tests for infectious diseases may include a range of techniques, such as immunoassays, microbiology cultures, molecular diagnostics , and serological testing. The market for infectious disease diagnostics includes various products and services, such as reagents and test kits, instruments and devices, software and systems, and laboratory services. These products and services are utilized in different settings, including hospitals, clinics, diagnostic laboratories, and research institutions.
The market is driven by several factors, such as the growing occurrence of infectious diseases globally, the emergence of new and drug-resistant pathogens, the necessity for accurate & rapid diagnostic methods, and the advancements in technology that led to the development of more specific and sensitive diagnostic tools. Infectious diseases pose a key threat to public health, and their prevalence has increased. This created a need for robust and efficient diagnostic tools to detect and manage these diseases effectively. Thus, the infectious disease diagnostics market is expected to grow as the burden of infectious diseases persists and as healthcare systems prioritize the early detection and effective management of these conditions.
Furthermore, increasing focus on early detection & prevention, increasing awareness and healthcare expenditure, and growing demand for rapid diagnostic tests have increased the demand for the infectious disease diagnostics market. There is rising recognition of the importance of early detection and prevention of infectious diseases. Timely diagnosis allows prompt treatment initiation, decreases disease transmission, and improves patient outcomes. Healthcare systems and policymakers are stressing the implementation of surveillance and screening programs, leading to increased demand for diagnostic tools in the infectious disease space, which may further drive demand in the infectious disease diagnostics market.
However, high costs, limited healthcare infrastructure, regulatory challenges and lack of awareness and education are anticipated to impede market growth. Limited awareness and understanding of the importance of diagnostic testing for infectious diseases can be a restraint. In several regions, healthcare professionals and the general public may lack awareness and education regarding the benefits of early diagnosis. Promoting awareness and providing educational initiatives can help address this restraint and drive market growth.
The lockdown measures implemented by various governments in anticipation of the COVID-19 pandemic have disrupted supply chains and manufacturing processes, leading to shortages of reagents, testing supplies, consumables, and logistical matters, obstructing diagnostic product distribution and availability. However, the pandemic led to an unprecedented global demand for diagnostic tests to identify SARS-CoV-2, the virus causing COVID-19. The necessity for mass testing to detect infected individuals and contacts, trace, and implement control measures resulted in a substantial rise in demand for diagnostic tools and testing supplies. This has led to increased interest in infectious disease diagnostics for these applications.
How is AI contributing to the Infectious Disease Diagnostics Industry?
AI enhances the diagnostics of infectious diseases by enhancing the detection of pathogens and also the diagnostic interpretation. Machine learning interprets scans and lab results as well as genomic sequences to detect the infection sooner and more accurately.
Artificial intelligence improves the speed of parasite and bacterial identification, and predictive analytics provides aid in the monitoring of outbreaks. The efficiency of laboratory workflow and the ability to identify patterns of antimicrobial resistance are also enhanced by AI.
Market Scope
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 35.39 Billion |
| Market Size in 2026 | USD 37.98 Billion |
| Market Size by 2035 | USD 71.06Billion |
| Growth Rate from 2026 to 2035 | CAGR of 7.22% |
| Largest Market | North America |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 to 2035 |
| Segments Covered | By Product, By Disease Type, and By Technology |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Market Dynamics
Drivers
Rising demand for rapid diagnostic tests to brighten the market prospect
Rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs) offer several advantages over traditional laboratory-based testing methods, including quicker results, ease of use, and the ability to perform testing at the point of care. The urgency to quickly detect and control infectious diseases has driven the demand for rapid testing solutions. In outbreaks or epidemics, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, timely identification of infected individuals is crucial for implementing appropriate containment measures and preventing further spread of the disease. RDTs provide results in minutes to hours, allowing for rapid decision-making and immediate initiation of treatment or isolation protocols. Furthermore, the convenience and simplicity of RDTs make them suitable for use in various healthcare settings, including resource-limited areas. These tests often require minimal infrastructure, specialized equipment, or technical expertise, making them accessible to a broader range of healthcare providers. RDTs are particularly valuable in remote or underserved regions where laboratory facilities may be limited, and transportation of samples to centralized labs can be challenging.
Moreover, point-of-care testing allows immediate diagnosis and treatment initiation, eliminating the delays associated with sending samples to centralized laboratories and waiting for results. This approach is especially beneficial in emergency departments, ambulatory care settings, and low-resource healthcare settings, enabling faster clinical decision-making and improving patient outcomes. In addition, RDTs have gained popularity due to their cost-effectiveness and scalability. These tests are often less expensive than laboratory-based testing methods, making them more affordable for healthcare systems and patients. The scalability of RDTs allows for mass testing campaigns and surveillance efforts, which are crucial in managing outbreaks and pandemics. Thus, the rising demand for rapid diagnostic tests is a significant driver for the growth and demand across the infectious disease diagnostics market.
Emergence or re-emergence of infectious diseases
The emergence or re-emergence of infectious diseases creates a sense of urgency and highlights the need for accurate and efficient diagnostic tools. Diseases such as Ebola, Zika, and COVID-19 have demonstrated the devastating impact that novel pathogens can have on global health. Prompt detection and identification of these pathogens are essential for effective containment and management strategies. Diagnostic tests play a critical role in early detection, enabling timely interventions and preventing the further spread of these diseases. Furthermore, the emergence or re-emergence of drug-resistant strains of infectious agents further drives the demand for diagnostic solutions. Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) poses a significant threat to public health as it limits the effectiveness of traditional treatment options. Diagnostic tests that can identify specific pathogens and determine their resistance profiles are essential for guiding appropriate treatment decisions and preventing the spread of drug-resistant infections.
Moreover, the emergence or re-emergence of infectious diseases often triggers increased investments in research and development of diagnostic technologies. For instance, in May 2020, the Innovative Medicines Initiative provisionally selected eight projects for funding through its fast-track Call for Proposals on coronavirus diagnostics and treatments. Furthermore, the IMI funding pot has been increased from EUR 45 million to EUR 72 million. Furthermore, EFPIA companies, IMI Associated Partners, and other organizations may contribute more than EUR 45 million to support these projects.
The urgency to develop accurate and reliable diagnostic tools to detect and monitor these diseases leads to innovation and advancements in the field. These factors drive market growth as diagnostic companies strive to meet the evolving needs of healthcare systems and respond to emerging infectious threats. In addition, the emergence or re-emergence of infectious diseases stimulates collaborations between researchers, healthcare organizations, and diagnostic companies. These partnerships aim to develop and implement effective diagnostic solutions to combat the spread of these diseases. The shared goal of identifying, tracking, and controlling these infectious agents creates opportunities for cross-sector collaborations, leading to advancements in diagnostic technologies and expanded market presence.
Challenges
High cost causing hindrances to the market
The process of validating and developing diagnostic tests involves significant investment in research and development. This comprises the identification of appropriate biomarkers , formulation of assays, and optimization of testing protocols. Research and development costs can be substantial, especially when working with novel and complex infectious agents or developing innovative diagnostic technologies. In addition, manufacturing diagnostic tests involves several expenses. Producing high-quality test kits, reagents, and consumables requires specialized equipment, raw materials, and quality control processes. These manufacturing costs can be substantial, particularly for tests that involve sophisticated technologies or require precise calibration and quality assurance measures.
Moreover, executing diagnostic tests in healthcare settings comprises additional expenses. Healthcare facilities must invest in the infrastructure to execute tests, such as laboratory equipment, trained personnel, and quality management systems. The costs associated with establishing and maintaining testing laboratories, compliance with regulatory standards, and ensuring proper storage and transportation of samples can be significant. The high cost of diagnostic tests can also impact accessibility and affordability, especially in resource-limited settings or regions with inadequate healthcare infrastructure. Diagnostic companies need to consider the cost-effectiveness of their products and ensure that they are affordable for healthcare systems, patients, and payers. In some cases, the high cost of diagnostic tests can lead to limited access, delayed or restricted testing, and disparities in healthcare delivery.
Opportunities
- Integration of digital health technologies
- Increasing healthcare awareness
- Rising demand for point-of-care testing
Segment Insights
Product Insights
On the basis of product, the infectious disease diagnostics market is divided into assays & reagents, instruments, and software, with the assays & reagents segment accounting for most of the market. This is because assays and reagents are crucial to infectious disease diagnostics. These chemical or biological substances are used to detect specific infectious agents or markers in patient samples.
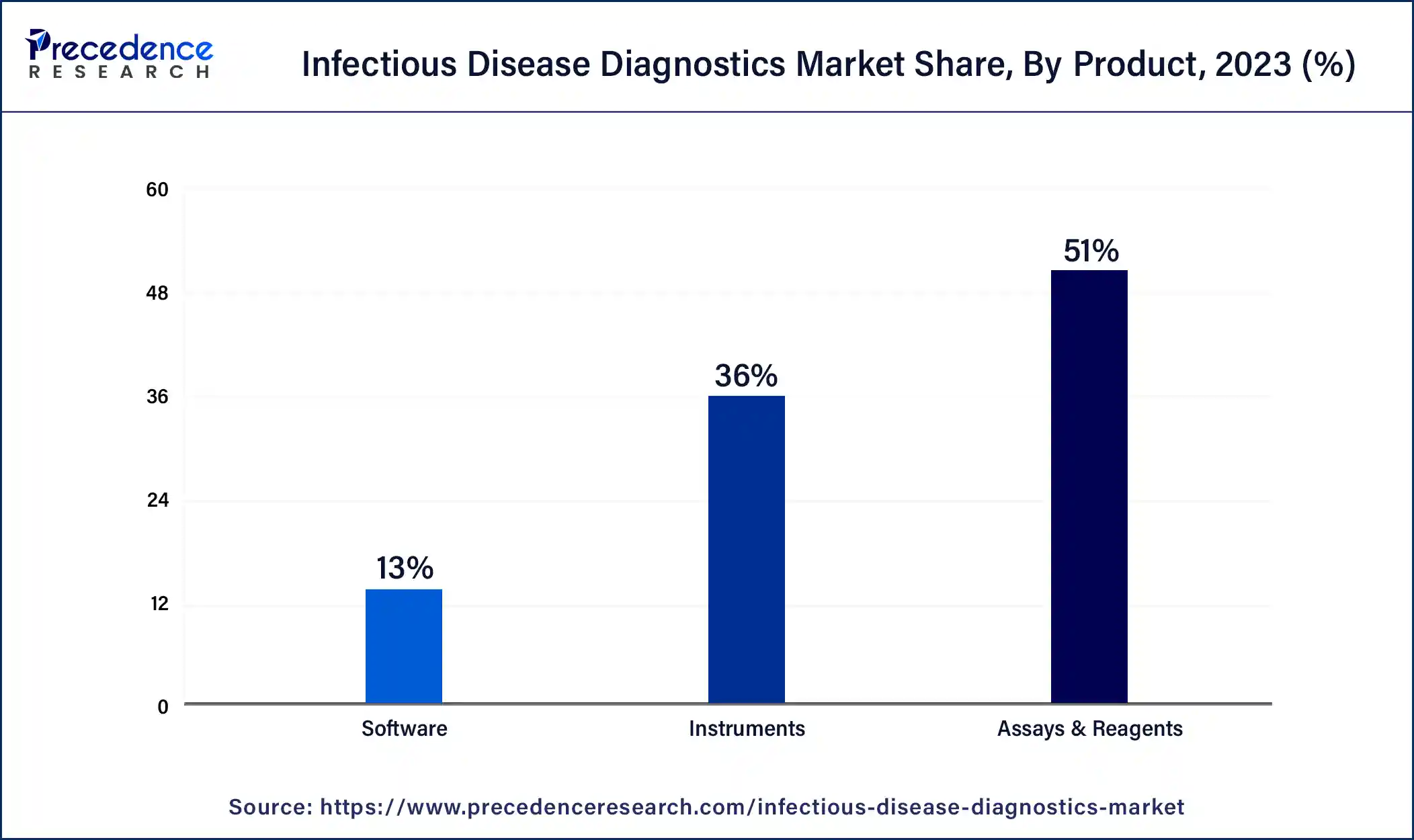
Assays may include immunoassays , molecular assays, serological tests, or culture-based tests. Reagents are the substances used in these assays to facilitate the detection and analysis of pathogens. Assays and reagents are developed and manufactured by diagnostic companies and are essential for accurate and reliable diagnosis of infectious diseases.
Disease Type Insights:
On the basis of the disease type, the infectious disease diagnostics market is divided into hepatitis, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), influenza, and others, with the others segment accounting for most of the market. This is due to the rise in the prevalence of healthcare-associated infection, the increase in surgical procedures and the surging demand for early diagnostics. The other segment includes diagnostic tests for infectious agents such as tuberculosis, malaria, sexually transmitted infections (STIs), respiratory infections, gastrointestinal infections, and emerging infectious diseases. Diagnostic tests for these diseases may include molecular assays, serological tests, culture-based methods, and rapid antigen detection tests. However, the hepatitis segment is anticipated to experience substantial growth throughout the forecast period. This growth can be attributed to the increasing prevalence of hepatitis, the rising demand for early diagnosis, and the development of advanced diagnostic laboratories in hospitals and clinics.
Technology Insights
On the basis of technology, the infectious disease diagnostics market is divided into immunodiagnostics, clinical microbiology , polymerase chain reaction, next-generation sequencing, and others, with the immunodiagnostics segment accounting for most of the market. Immunodiagnostics involves detecting and measuring specific antigens or antibodies present in patient samples. These tests rely on the interaction between antigens and antibodies to identify and diagnose infectious diseases. Immunodiagnostic tests include techniques such as enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA), lateral flow assays, and chemiluminescent immunoassays.
Regional Insights
What is the U.S. Infectious Disease Diagnostics Market Size?
The U.S. infectious disease diagnostics market size was estimated at USD 11.57 billion in 2025 and is predicted to be worth around USD 24.43 billion by 2035, at a CAGR of 7.76% from 2026 to 2035.
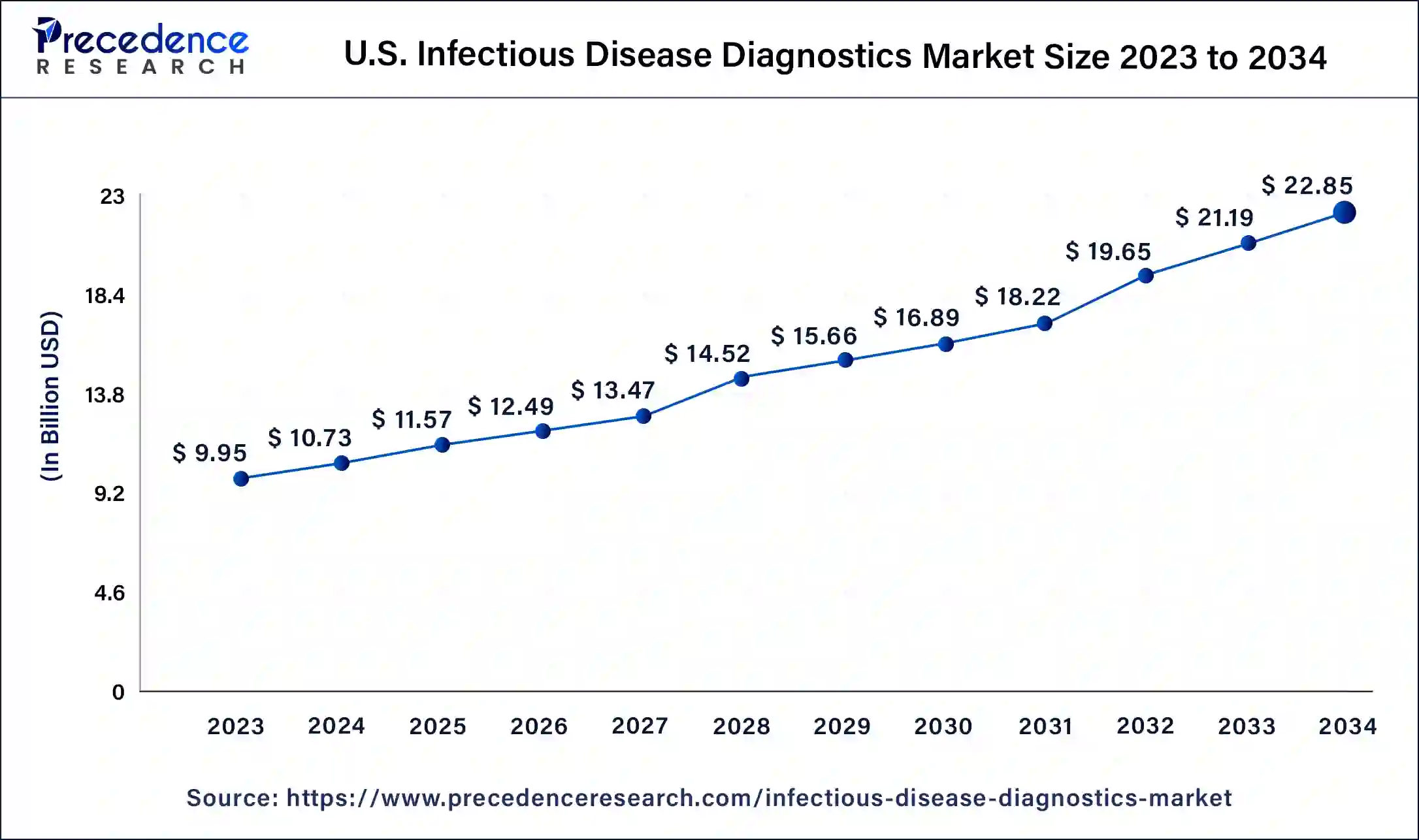
On the basis of geography, North America dominates the market, primarily driven by several factors. The region strongly focuses on infectious disease control and prevention, leading to a high demand for accurate and efficient diagnostic tests. Furthermore, North America faces a significant burden of infectious diseases, including HIV, hepatitis, influenza, sexually transmitted infections (STIs), and emerging infectious diseases. Accurate and timely diagnosis is crucial for effective disease management and public health interventions. This drives the demand for infectious disease diagnostic tests in the region.
U.S. Infectious Disease Diagnostics Market Trends
The demand in the U.S. has increased due to the use of advanced molecular testing and automated diagnostic laboratories. There is an uptake of multiplex testing panels and decentralized diagnostic solutions in hospitals. The AI-based interpretation of images and laboratory automation can enhance the turnaround in diagnostics. The further growth of diagnostic technologies within the healthcare systems is supported by industry consolidation and the strengthening of the supply chains.
Europe is a significant market for infectious disease diagnostics, with Germany, the United Kingdom, and France being the major contributors to the market's growth. This is due to Europe's well-established healthcare infrastructure, technological advancements, high disease burden, favorable regulatory environment, collaborative approach, presence of key market players, and focus on personalized medicine contribute to the growth and advancements in the infectious disease diagnostics market in the region. Europe remains a prominent market for innovative diagnostic technologies and solutions, driving improvements in patient care, disease management, and public health outcomes.
Germany Infectious Disease Diagnostics Market Trends
Germany's demand is increasing due to the high use of molecular diagnostic tools in hospitals. Healthcare systems focus on precise pathogen identification and monitoring of antimicrobial resistance. Automated laboratory systems and digital pathology are better investments to enhance efficiency. Data control and regulatory systems influence the implementation of integrated digital diagnostic reporting systems.
The region in Asia-Pacific is anticipated to have the greatest CAGR. This is because Asia-Pacific is home to a large and densely populated region with diverse healthcare needs. The region experiences a high burden of infectious diseases such as tuberculosis, malaria, dengue, hepatitis, and emerging infectious diseases. The need for accurate and timely diagnostic tests to control and manage these diseases drives the region's demand for infectious disease diagnostics. Thus, driving the growth of the Asia-Pacific infectious disease diagnostics market.
China Infectious Disease Diagnostics Market Trends
China is expected to grow at a significant rate during the forecast period due to the high investments in diagnostic infrastructure and surveillance programs. There is an increase in domestic production of quick diagnostic tests and handheld equipment. E-health systems bridge the gap between distant areas and labs. The emphasis on early screening initiatives and test technologies that can be scaled up to assist in the greater population health surveillance.
Infectious Disease Diagnostics Market Companies
- Abbott Laboratories : offers quick point-of-care and molecular diagnostic systems such as ID NOW and Alinity systems that concentrate on respiratory infections and clinical laboratory tests.
- Becton Dickinson and Company : Invents automated microbiology systems such as BACTEC blood culture systems and Veritor antigen testing to aid pathogen identification and antimicrobial resistance control.
- bioMerieus SA: focus on clinical diagnostics of microbiology, such as BIOFIRE syndromic testing, and VITEK automated pathogen identification to support the detection of sepsis and monitoring of antimicrobial resistance.
Other Major Key Players
- Bio-Rad Laboratories
- Danaher Corporation
- F Hoffman-La Roche
- Hologic Inc.
- Luminex Corporation
- Qiagen Inc.
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
Technological Advancement
Technological advancements in the infectious disease diagnostics market feature point-of-care (POC) testing, next-generation sequencing, and molecular diagnosis. The molecular diagnostics consist of technologies such as nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs), polymerase chain reaction (PCR), and next-generation sequencing (NGS). This technology detects pathogens' genetic materials to provide a quick diagnosis. NGS enables a detailed view of the pathogen's genome. It identifies drug resistance and other factors.
Clinical biology in the infectious disease diagnostics market helps utilize traditional laboratory methods and techniques to cure infectious diseases. The healthcare sector is expanding with the disease rate, so technological advancements are an important factor in preventing and curing diseases quickly. POC testing helps with rapid diagnostic results directly at the patient's location, enabling access to care.
Recent Developments
- In January 2025, BMCRI announced its plans to establish South India's first infectious disease research and diagnostic laboratory. The facilities will focus on diseases caused by fungi, bacteria, and parasites to contribute to the management of such conditions with quick diagnosis.
- In January 2025, India's CDSCO issued guidance on validating rapid infectious disease diagnostics in Asia Pacific. This will help companies to understand the requirement to validate the laboratory to prepare a validation process for the same.
- In October 2024, Haystack Analytics expanded its infexn test for infectious disease test. The NGS test provides clinicians with a more streamlined approach to diagnosing infections. It enables screening for major RNA viruses.
- In February 2023, Thermo Fisher Scientific announced that its Applied Biosystems TaqPath PCR kits for infectious diseases such as multi-drug-resistant tuberculosis (MTB MDR), M. tuberculosis complex (MTB), hepatitis B virus (HBV), hepatitis C virus (HCV), human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), and for genetic analysis (HLA B27). These kits have received licensing rights from the Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO) and will be manufactured in India in collaboration with Mylab Discovery Solutions.
- In February 2023, the Centre for Cellular and Molecular Platforms (C-CAMP) launched a program to enhance India's readiness for present and future pandemics and expand the diagnostics sector for infectious diseases. The National Diagnostics Catapult (C-CAMP InDx 2.0) was officially launched with the esteemed presence of Dr. Parvinder Maini, Scientific Secretary at the Office of the Principal Scientific Adviser to the Government.
Segments Covered in the Report
By Product
- Assays & Reagents
- Instruments
- Software
By Disease Type
- Hepatitis
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus
- Influenza
- Others
By Technology
- Immunodiagnostics
- Clinical Microbiology
- Polymerase Chain Reaction
- Next-generation Sequencing
- Others
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Ask For Sample
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
 Get a Sample
Get a Sample
 Table Of Content
Table Of Content




 sales@precedenceresearch.com
sales@precedenceresearch.com
 +1 804-441-9344
+1 804-441-9344
 Schedule a Meeting
Schedule a Meeting