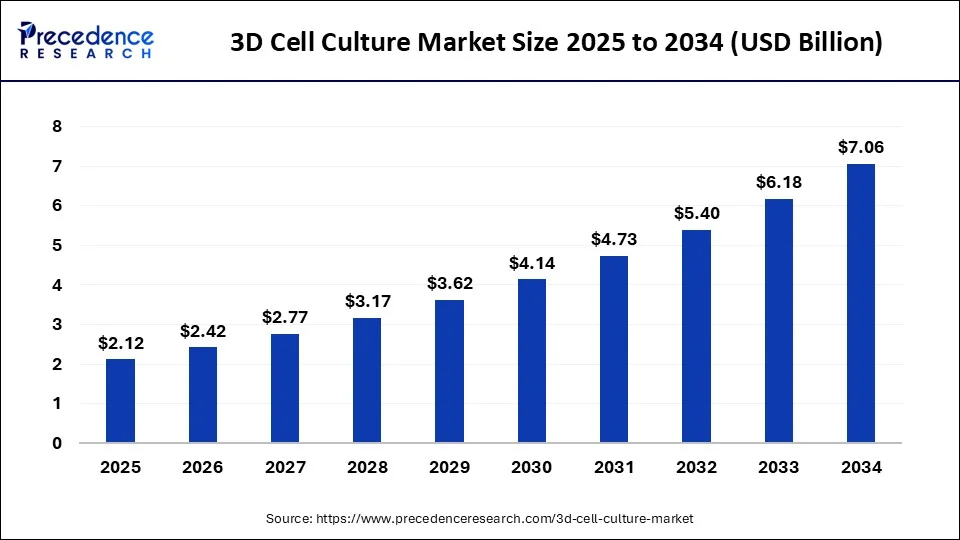
3D Cell Culture Market Size and Forecast 2025 to 2034
The global 3D cell culture market size accounted for USD 1.86 billion in 2024 and is expected to be worth around USD 7.06 billion by 2034, at a CAGR of 14.3% from 2025 to 2034. The North America 3D cell culture market size reached USD 730 million in 2023.
3D Cell Culture Market Key Takeaways
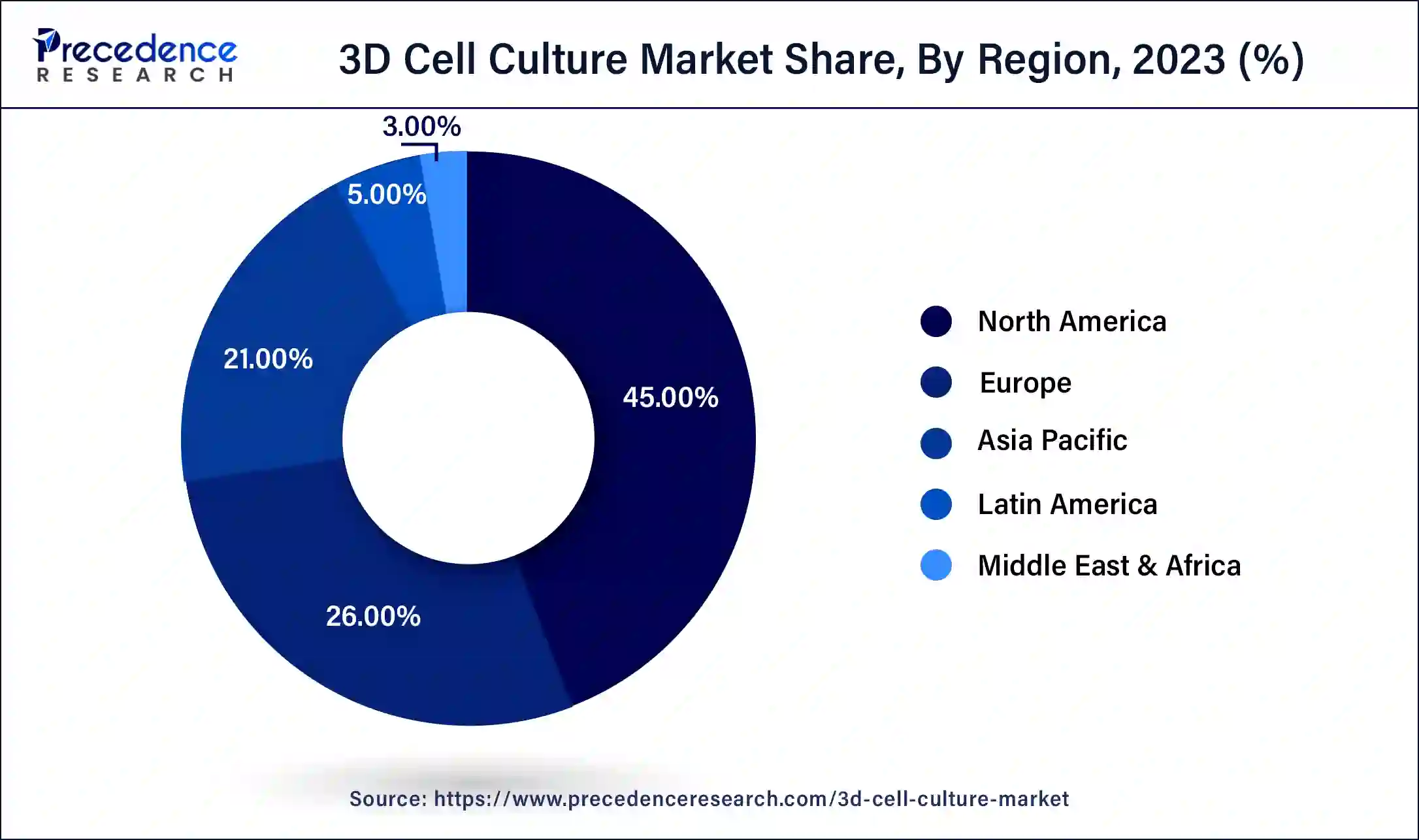
- North America generated more than 45% of the revenue share in 2024.
- Asia-Pacific is expected to expand at the fastest CAGR between 2025 and 2034.
- By Type, the scaffold-based 3D cell cultures segment captured the largest market share in 2024.
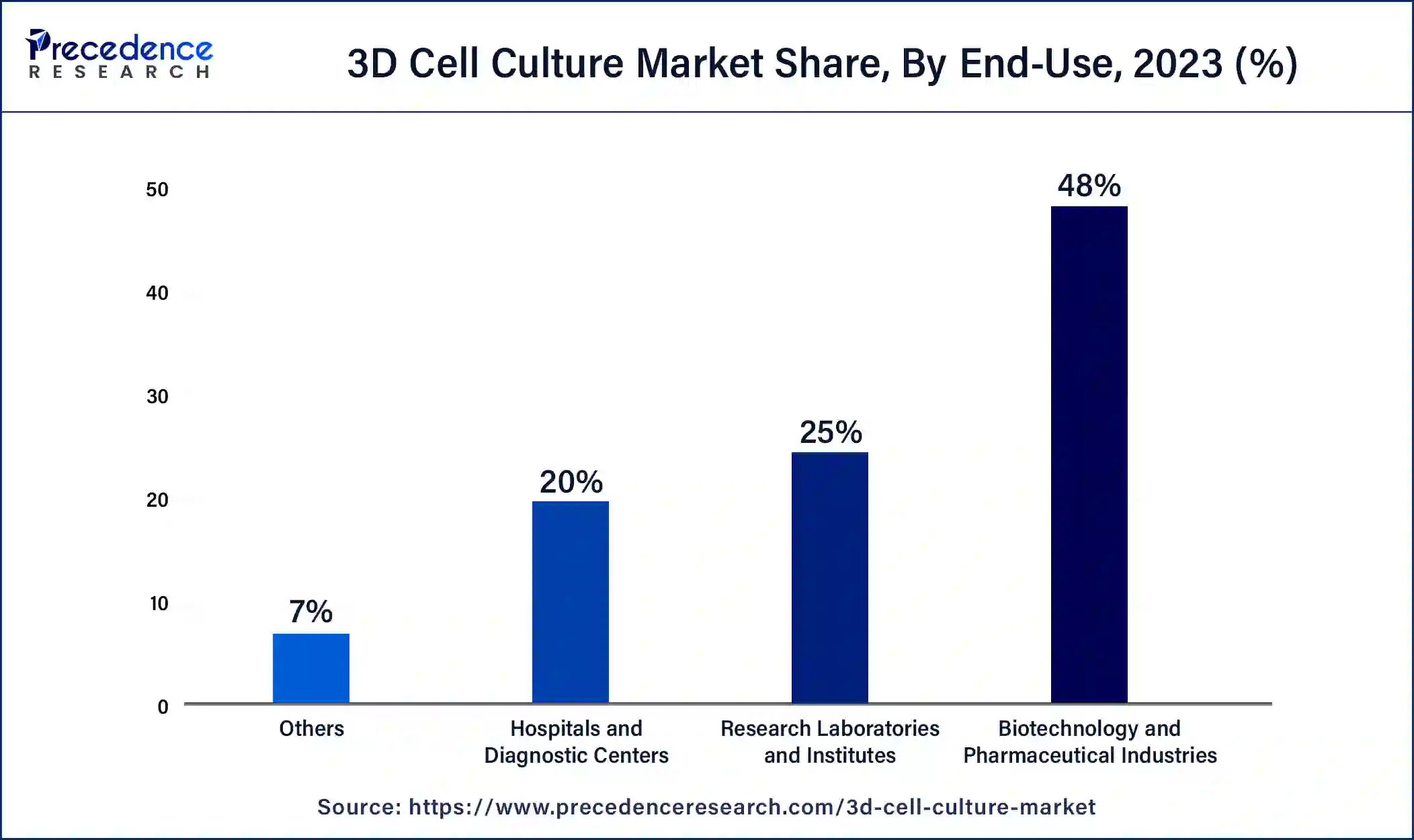
- By End-use, the biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries segment contributed more than 48% of revenue share in 2024.
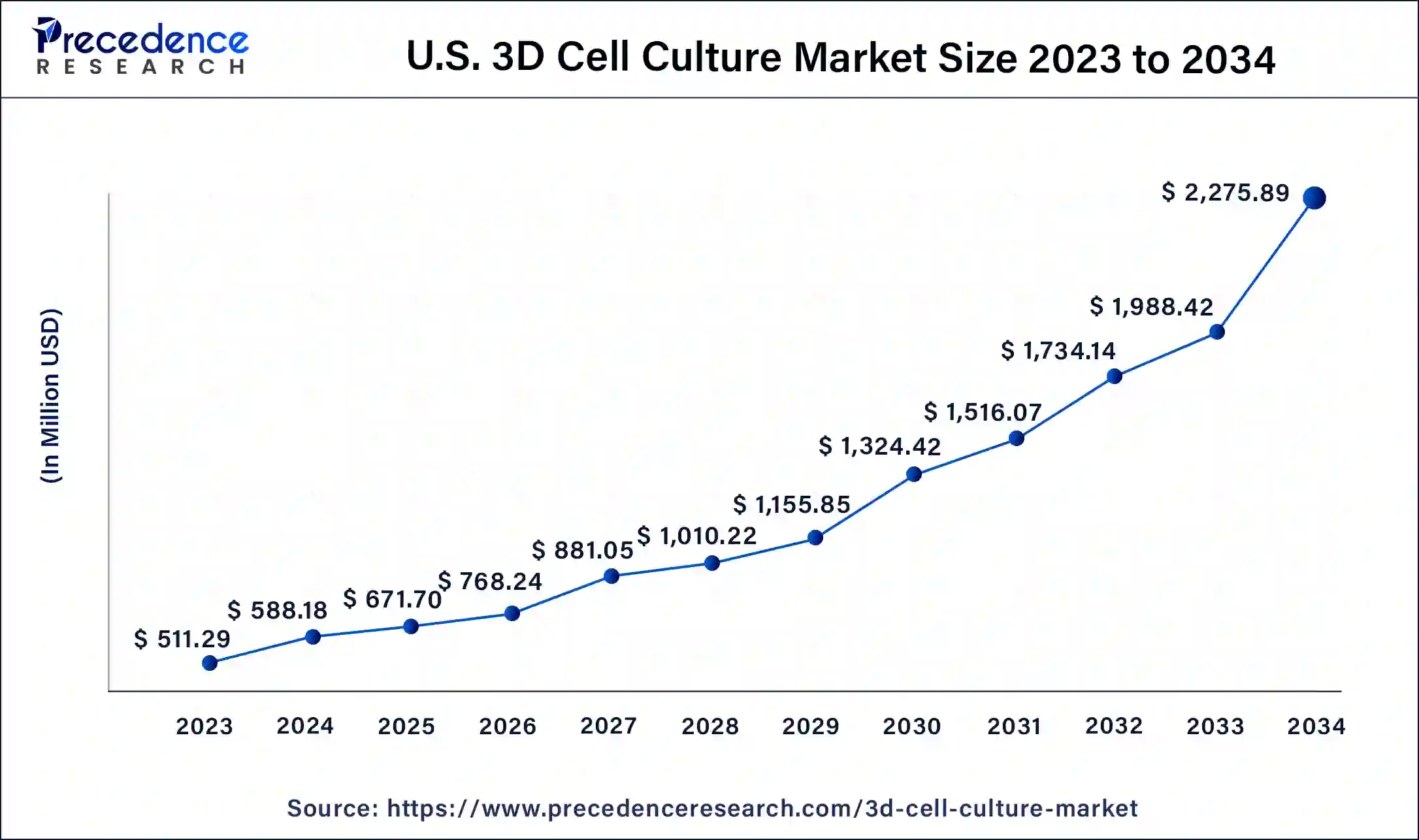
U.S. 3D Cell Culture Market Size and Growth 2025 to 2034
The U.S. 3D cell culture market size was estimated at USD 588.18 million in 2024 and is predicted to be worth around USD 2,275.89 million by 2034, at a CAGR of 14.40% from 2025 to 2034.
North America held the largest revenue share of 45% in 2024.The US accounted for the largest share in the North American 3D cell culture market. In recent years, the United States has demonstrated a strong focus on research and development (R&D) in the field of 3D cell culture, making significant investments in this area. This emphasis has led to notable technological advancements within the country. The United States is prominently represented among the primary patent applicants in the domain of 3D cell culture. American applicants tend to develop their technologies both domestically and in Asian regions. Moreover, there has been a substantial increase in investments in the bioengineering sector within the United States over the past few years. These investments have significantly contributed to the growth of the US 3D cell culture market. Additionally, the presence of key competitors and a rise in research activities have further bolstered the market in the region. The United States benefits from the availability of advanced healthcare infrastructure, which also plays a vital role in supporting the regional growth of the 3D cell culture market throughout the forecast period.
In December 2024, MilliporeSigma, the U.S. and Canada Life Science business of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany, announced that the Life Science business of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany, has signed a definitive agreement to acquire HUB Organoids Holding B.V. (HUB) to advance the Next Generation Biology Portfolio. The acquisition assists in the expansion of MilliporeSigma's 2D and 3D cell culture portfolio. The transaction is expected to close at the end of December 2024.
In April 2023, the American Cancer Society (ACS), the largest non-government, non-profit funding source of cancer research in the United States, approved funding for 90 new Extramural Discovery Science (EDS) research and career development grants totaling more than $45 million. The grants will fund investigators at 67 institutions across the United States starting in 2023.
Asia-Pacific is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period.The increasing research and development activities in the field of tissue engineering along with rising investment in the healthcare infrastructure is anticipated to augment the regional growth of the 3D cell culture market during the forecast period. Furthermore, the growing demand forpersonalized medicinefor effective treatment increasing along with the aging population is also likely to support the regional growth of the market in the years to come. Additionally, the advancement and rising focus on the development of biotechnology is also expected to fuel market growth in the region.
Market Overview
The technique of 3D cell culture establishes an environment that facilitates the growth and interaction of cells in three dimensions, enabling them to engage with the surrounding extracellular matrix. In contrast, conventional 2D cell cultures confine cells to a flat monolayer on a plate. While 2D cultures have long been utilized as the standard for studying cellular and disease mechanisms due to their simplicity and cost-effectiveness, the popularity of 3D cell cultures has surged in the past decade. This is primarily because 3D cell cultures offer heightened physiological relevance and better represent the intricate structures of tissues found in vivo.
The realm of 3D cell models consists various types, including spheroids, organoids, bioprinted cell models, and organs-on-chips. Spheroids arise from the growth and aggregation of cells within a 3D culture, retaining the inherent characteristics of the original cells while assuming a spherical configuration. In contrast, organoids exhibit greater complexity as they are derived from stem cells or progenitor cells, displaying higher levels of differentiation. Organs-on-chips, characterized as microfluidic devices, replicate the cellular structure of organs, allowing for the dynamic flow of media. Collectively, these models serve as in vitro representations of tissues or organs that closely mimic their in vivo counterparts.
3D Cell Culture Market Growth Factors
The shortage of donor organs and the need for alternatives have fueled the demand for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine approaches and this is anticipated to augment the growth of the 3D cell culture market during the forecast period. Additionally, the 3D cell culture models offer a more physiologically relevant environment for drug screening, toxicity testing, and evaluation of drug efficacy. The ability to better predict drug responses and toxicity in human tissues drives their adoption in the pharmaceutical industry, leading to market growth. Ongoing research and technological advancements are augmenting the development of more potent 3D cell cultures, contributing to the growth of the market in the years to come.
The development of novel scaffold materials and fabrication techniques has expanded the possibilities for scaffold-based 3D cell cultures. Advances in biomaterials, such as natural polymers, synthetic polymers, hydrogels, and decellularized matrices, provide more options for designing scaffolds with tailored properties. Also, the increasing adoption in cancer research has facilitated the development of effective 3D cell culture and opened up new avenues for market growth in the years to come.
Market Scope
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 7.06 Billion |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD $2.12 Billion |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 1.86 Billion |
| Growth Rate from 2025 to 2034 | CAGR of 14.3% |
| Largest Market | North America |
| Fastest Growing Market | Asia Pacific |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | Type, Application, End-Use, and Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Market Dynamics
Drivers
Increasing focus on precision medicine
The increasing focus on precision medicine is anticipated to augment the growth of the 3D cell culture market within the estimated timeframe. The utilization of 3D cultures, particularly organoid cultures, opens up possibilities for developing personalized therapies tailored to each patient. For instance, considering the variations in cancer cells due to mutations among different individuals, the ability to grow small tumor explants from individual patients and evaluate their response to treatment has been employed in numerous studies to identify novel drugs.
In the realm of respiratory medicine, researchers cultivated organoids from two cystic fibrosis patients to determine their responsiveness to the drug ivacaftor. Encouragingly, the organoid cultures accurately predicted the subsequent positive responses observed in the patients. Similar findings have been observed in cancer research, wherein patient-derived pancreatic cancer tumoroids exhibited a correlation in drug sensitivity with the original tumors. Given that organoid cultures can be generated from adult tissues, this approach holds significant promise for tailoring treatment approaches on an individual basis for various diseases. Thus, this is likely to contribute to the growth of the 3D cell culture market during the forecast period.
Restraints
Difficulties in assay development for cells in 3D environments
The majority of cell-based assays have been developed and improved using 2D monolayers in old cell culture settings. Consequently, when transitioning to a 3D cell spheroid model, assay conditions optimization becomes necessary. The development of assays for 3D environments presents specific challenges, such as the ability of reagents to effectively penetrate and lyse the spheroid, as well as concerns about signal quenching when lysing larger spheroids.
Numerous examples demonstrate the need for assay optimization to achieve success in 3D culture systems. Potential solutions include the utilization of stronger detergents specially reformulated for usage in 3D cultures and the extension of incubation times to address these challenges effectively. Tackling this obstacle is a crucial focus as it has the potential to impede market growth during the forecast period.
Opportunities
Increasing collaborations & partnerships among key players
The increasing collaborations and partnerships among various organizations for the development and advancement of 3D cell cultures are anticipated to create growth opportunities for the market in the years to come. For instance, in June 2020, Lonza, in collaboration with the Swedish company CELLINK, joined forces to provide a comprehensive solution for 3-dimensional (3D) bioprinting. The aim of this partnership is to enhance and facilitate complete 3D cell culture workflows. This collaboration ultimately seeks to optimize and expand access to advanced 3D cell culture technologies. Also, in April 2022, Manchester BIOGEL and Cell Guidance Systems Ltd. have formed a collaboration to introduce PODS-PeptiGels.
This innovative kit integrates the advantages of two established cell culture technologies that are synthetic peptide hydrogels, known as PeptiGels, and a collection of constant-release growth factors called PODS. The purpose of this collaboration is to offer a reliable and flexible platform for the 3D cell culture by leveraging the unique features of both technologies. The resulting PODS-PeptiGels kit provides researchers with a reproducible and highly adaptable environment for conducting their 3D cell culture experiments. Therefore, this is likely to accelerate the growth of the market in the years to come.
Type Insights
The scaffold-based 3D cell cultures segment held the largest market share in 2024. Scaffold-based cell culture involves providing support to cells in all dimensions using either an artificial structure or a hydrogel, which is a polymer network. Hydrogels, known for their high water content (up to 90%); can be composed of either animal-derived extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins or synthetic formulations that are free from animal components.
The purpose of embedding cells in hydrogels is to mimic the natural extracellular matrix found in living organisms. Alternatively, "hard" scaffolds can be created using specialized culture ware that possesses fibrous or sponge-like structures. These scaffolds are typically made from biodegradable materials such as optically-transparent polystyrene or polycaprolactone, allowing for optimized imaging. Although these engineered supports may differ from the in vivo ECM, they offer advantages such as improved reproducibility and simplified cell retrieval from the culture. These factors are likely to support the segmental growth of the market during the forecast period.
End-Use Insights
On the basis of end-use, the biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries segment held a revenue share of 48% in 2024. 3D cell culture offers several significant benefits due to its ability to provide a more realistic representation of cell interactions, division, and morphology, closely resembling the natural cellular environment. As a result, gene expression and morphology in 3D cell culture systems are more representative of the human body.
Additionally, one key advantage is the creation of environmental niches and microenvironments where cells experience varying levels of oxygen, nutrients, metabolites, and signaling molecules. This stands in contrast to 2D cell culture, where cells have unrestricted and equal access to these factors. These aspects drive the growth of the biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries segment during the forecast period.
3D Cell Culture Market Companies
- Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.
- Merck KGaA
- Corning Incorporated
- Lonza
- PELOBIOTECH GmbH
- Iwai North America Inc.
- Lena Biosciences
- REPROCELL Inc.
- Synthecon
- InSphero AG
- Promocell GmbH
Recent Developments
- In August 2021,Amerigo Scientific broadened its range of cell culture offerings by introducing a new 3D Cell Culture system for various scientific applications. This innovative system is designed to be utilized in research fields including drug discovery, medicine, nanomaterial evaluation, and fundamental life science studies.
- In December 2021,Inventia Life Science successfully concluded a Series B funding round, securing a total of US $25 million. The funding round was led by Blackbird Ventures. In conjunction with this milestone, Inventia has initiated its operations in the United States and has appointed Dwayne Dexter as the Director of US Sales. With the proceeds from the Series B financing, Inventia intends to globally market its RASTRUM 3D cell culture platform and expand its workforce from 36 to 150 employees by the end of 2024. The company's primary objective is to establish a strong presence in the United States, a market valued at over US $40 billion in biomedical research and drug discovery. Including the Series B funding, Inventia has amassed a total funding of US $32 million to date. Notably, Skip Capital also reinvested significantly in this funding round.
Segments Covered in the Report
By Type
- Scaffold-based 3D Cell Cultures
- Scaffold-free 3D Cell Cultures
- Microfluidics
- Bioreactors
By Application
- Cancer
- Tissue Engineering & Immunohistochemistry
- Drug Development
- Stem Cell Research
- Others
By End-Use
- Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical Industries
- Research Laboratories and Institutes
- Hospitals and Diagnostic Centers
- Others
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Ask For Sample
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
 Get a Sample
Get a Sample
 Table Of Content
Table Of Content
 sales@precedenceresearch.com
sales@precedenceresearch.com
 +1 804-441-9344
+1 804-441-9344
 Schedule a Meeting
Schedule a Meeting