What is the Nuclear Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) Market Size?
The nuclear small modular reactors (SMRs) market is witnessing strong growth as nations adopt modular nuclear solutions for clean and reliable power. SMRs provide safety, scalability, and flexibility for diverse energy needs.The market is expanding rapidly, driven by modular designs, flexible deployment, and rising global clean energy demand.
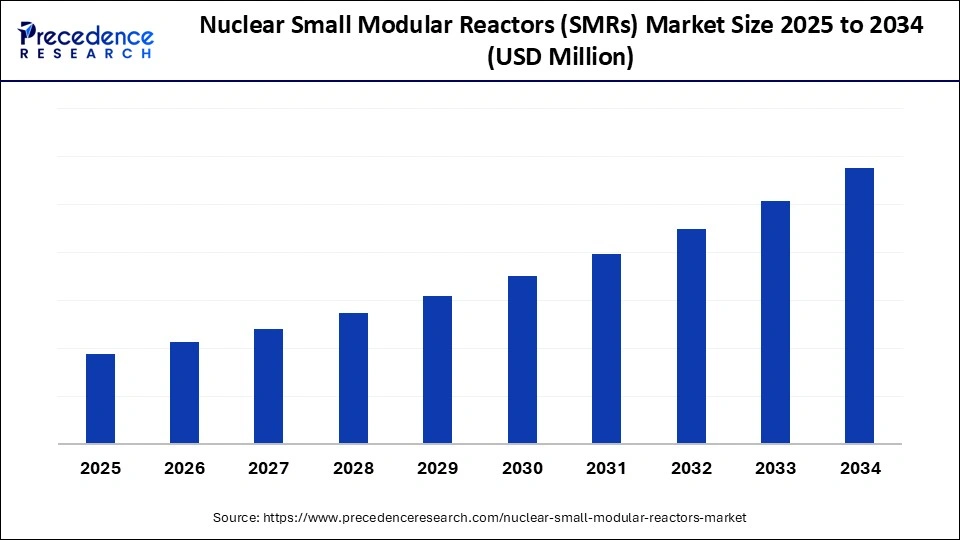
Nuclear Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) Market Key Takeaways
- North America dominated the nuclear small modular reactors (SMRs) market in 2024.
- Asia Pacific is estimated to expand the fastest CAGR between 2025 and 2034.
- By reactor/technology type, the light water reactor (LWR)/integral pressurized water reactor (iPWR) segment led the market in 2024.
- By reactor/technology type, the molten salt reactor (MSR) segment is anticipated to grow at a remarkable CAGR between 2025 and 2034.
- By power rating, the small (100–300 MWe) segment captured the largest market share in 2024.
- By power rating, the micro (<10 MWe) segment is expected to expand at a notable CAGR over the projected period.
- By coolant/moderator, the light water segment contributed the biggest market share in 2024.
- By coolant/moderator, the molten salt segment is expected to expand at a notable CAGR over the projected period.
- By application/ end-use, the grid power/baseload electricity segment held the highest market share in 2024.
- By application/end-use, the industrial heat segment is expected to expand at a notable CAGR over the projected period.
- By ownership/business and financing model, the utility-owned segment generated the major market share in 2024.
- By ownership/business and financing model, the vendor-financed (build-own-operate, BOO) segment is expected to expand at a notable CAGR over the projected period.
- By contract/delivery model, the EPC/turnkey contracts segment captured the maximum market share in 2024.
- By contract/delivery model, the power purchase agreement (PPA)-backed projects segment is expected to expand at a notable CAGR over the projected period.
How Artificial Intelligence is Impacting the Future of the Nuclear Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) Market?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is beginning to inform the nuclear small modular reactorsmaterial burdening efficiency on design, operation, and energy management. In February 2025, the Governments of India and France launched an AI plan for collaboration, specifying their focus on nuclear SMRs in improving efficiency, safety, and deploying low-carbon energy. This partnership highlights how AI could facilitate international cooperation on nuclear technologies. (Source:https://www.hindustantimes.com)
- In the United States, the start-up Aalo Atomics released a nuclear modular reactor called the Aalo-X that could directly power AI data centers in Austin, Texas. However, this example emphasizes AI's dual capability of improving the performance of SMRs while meeting the energy requirements of infrastructure, specifically AI systems. Together, these events highlight the impact of AI on providing a holistic view of SMRs as a sustained, scalable energy supply. (Source:https://www.msn.com)
Market overview: Understanding the Trends and Opportunities
The nuclear small modular reactor (SMR) market is building momentum as a flexible, scalable option to traditional nuclear plants that are typically large. SMRs, generating anywhere up to ~300 MWe per module, are produced in factory-controlled environments, are able to be transported, and are designed to allow flexibility or phased deployment, which provides a means to add capacity when demand increases. They utilize different technologies, such as light-water, molten salt, high-temperature gas, and liquid-metal-cooled reactors.
SMRs can be used for more than just electricity production; they are also being utilized for industrial heating, desalination, hydrogen production, or even off-grid power applications. An increasing focus on decarbonization, energy security, and reliable baseload power, together with government support to encourage development and the implication of private investors, is also encouraging global interest in SMRs' development and commercialization.
Nuclear Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) Market Growth Factors
- Increased Demand for Clean Energy: The global efforts to cut carbon emissions and their efforts are propelling the appetite for SMRs. They are unequivocably low-carbon and reliable sources of energy that can act as a complement to renewables and help achieve climate goals through reliable and low-carbon baseload generation.
- Flexible and Scalable Deploymen: SMR's modularized factory-built components allow for phased deployment, making them very cost-effective. All components supporting deployment can be dramatically adapted to a wide energy demand landscape, including remote locales and very demanding industrial sites in need of a secure, stable electricity supply.
- Supportive Policy and Investments: Intense supportive policy, funding initiatives, and public-private partnerships to support SMRs, through research, development, and commercialization, provide pathways to innovation and accelerate any possible worldwide commercial deployment.
- Growing Industrial Applications: In addition to powering electricity, SMRs are expected to find applications in desalination, hydrogen production, and other industrial heat applications, creating new revenue opportunities and expanding their commercialization role in diverse energy and industrial markets worldwide.
Market Outlook: Shaping the Future
- Industry Growth Overview: Increasing global demand for clean, reliable, flexible low-carbon energy solutions to meet the decarbonization goals and enhanced energy-intensive applications is responsible for the industry growth overview.
- Sustainability Trends: The sustainability trends focus on the development of reliable, dispatchable, and low-carbon baseload power sources to enhance passive safety features and reduce environmental risk.
- Major Investors: Venture capitalists, technology giants, and large industrial corporations are the major investors in the market. Bill Gates, Sam Altman, Amazon, Rolls-Royce SMR, and others are some of the major investors in the market.
- Startup Ecosystem: The startup ecosystem is focusing on accelerating the deployment and commercial viability of advanced reactor technologies. TerraPower, Oklo, Moltex Energy, and Kairos Power are the startups actively participating in the market.
Market Scope
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Dominating Region | North America |
| Fastest Growing Region | Asia Pacific |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | Reactor/Technology Type, Printing Method/Process, Power Rating, Coolant/Moderator, Application/End-use, Ownership/Business and Financing Model, Contract/Delivery Model, and Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Market Dynamics
Drivers
How are Data Centers Accelerating the Trend in Nuclear Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) Adoption?
Rising electricity needs from hyperscale data centers and the explosion of AI infrastructure are key drivers for the nuclear small modular reactor (SMR) market. SMRs offer clean, reliable, and consistent electric power to meet the staggering electricity demands from the next generation of technologies. In October 2024, Amazon signed an approximately $500 million deal with X-Energy to purchase SMRs, thereby securing new carbon-free energy dedicated to its operations.(Source: https://www.cnbc.com)
The urgency to initiate and secure SMR development projects shows how global technology companies are implementing SMRs as a long-duration, low-cost, scalable substitute for fossil fuels. In summary, it is the combination of the low carbon benefits and the modularity of deploying SMRs that are making it recognized as the next most important option to facilitate the power necessary for digital transformation and industrial activity.
Restraint
What is hindering the SMR market?
One significant slowing factor is that there is a long, complicated, and expensive regulatory and licensing process related to large-site reactors—not modular reactors. Even simple design approvals take many years; In the U.S., for example, Kairos Power applied for approval for its Hermes SMR design in 2021 and has yet to receive it in 2025; typical design reviews often take nearly a decade.
- In 2025, the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission started rolling out new microreactor licensing policies to streamline the process, but much SMR development continues to take a long time to review. Various projects worldwide, including India's SMR mission to Canada's GE Hitachi-led BWRX-300 at Darlington, need significantly adapted frameworks to proceed.
Opportunity
Can Decarbonization Policies Create Opportunities for SMRs to the Energy Mainstream?
The global shift to decarbonization mandates represents a major moment for the nuclear small modular reactor. More than 70 countries have pledged to achieve net-zero emissions by 2050, creating a demand for clean baseload power that can be relied upon. Nuclear has received renewed support from many policymakers — the EU officially classifies nuclear as "green" in its sustainable finance taxonomy (2022), which is expected to unleash billions of investment flows.
In the U.S., the Inflation Reduction Act has a production tax credit of up to $30/MWh provided for advanced nuclear, which will affect SMR economics directly. The UK's Great British Nuclear program (2023) placed Rolls-Royce SMRs on a shortlist for accelerated deployment. These specific policy moves show how SMRs are in a unique position as a flagship technology for powerful governments balancing decarbonization and energy security. (Source: https://www.spglobal.com)
Reactor/ Technology Type Insights
Why Light Water Reactor (LWR)/iPWR Have the Largest Nuclear Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) Market Share?
The light water reactor (LWR)/integral pressurized water reactor (iPWR) segment dominate the market due to their degree of technological maturity, authority familiarity, and established global supply chains. The LWR leverages decades of operational experience from conventional nuclear power plants with high margins of safety and reliability.
The molten salt reactor (MSR) segment is the fastest-growing technologies, which can use advanced applications to focus on hydrogen production, load-following power, and industrial heat. These designs have the potential for better thermal efficiencies, more inherent safety, and more flexible deployment than the current SMRs.
Power Rating Insights
Which Power Rating Dominates the Nuclear Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) Market?
The 100–300 MWe segment dominated the nuclear small modular reactors (SMRs) market in 2024, due to the need for grid-scale electrical generation within a compact modular plant to replace aging fossil fuel generation capacity. The 100-300 MWe rating includes compact modularity but has sufficient output to address urban centers and industrial demand.
The micro (<10 MWe) segment is the fastest-growing segment of the market, typically driven by demand for distributed capacity in remote locations, military bases, and off-grid industrial applications. Their small size, ease of deployment, and autonomous operational modes distinguish them from larger fixed nuclear installations. The current interest in developing resilient energy infrastructure with emergency backup supply is accelerating market interest.
Coolant/Moderator Insights
Which Material Type Dominated the Nuclear Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) Market?
The light water segment led the market in 2024 because it is an established technology with a proven safety radius and an international licensing status. Light water is benefiting from decades of deployed experience in large nuclear reactors, including supply chains, operational experience, and licensing experience.
The molten salt segment represents the fastest-growing segment. They can operate at higher temperatures with higher efficiencies, enabling them to be employed in advanced uses such as industry heat supply, hydrogen production, and cogeneration. Governments and private companies are investing heavily in demonstrations that highlight their potential for a coming generation of nuclear applications.
Application/End-use Insights
Why does the Residential Housing Dominate the Nuclear Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) Market?
The grid power/baseload electricity segment was the dominant application segment in 2024, and remains the main application for SMRs and providing stable, reliable, and carbon-free energy to the national grids. From the utility perspective, SMRs help replace aging coal and gas plants and maintain a constant supply. SMRs can be modularly expanded over time, making them an excellent option for enhancing grid resilience and decarbonization commitments in the long term. As mentioned previously, despite the inherent potential of SMRs, deployment will rely on clear public policy signals and embracing SMRs as part of the energy landscape.
The industrial heat segment represents the fast-growing applications for SMRs as demand rises for clean energy for heavy industry and transportation. High-temperature SMRs can provide process heat to a range of applications, including refineries, chemical plants, and hydrogen electrolysis. SMRs can therefore be an important facilitator in hard-to-abate sectors where renewable energy may not provide consistent high-grade heat.
Ownership/Business and Financing Model Insights
Which Ownership/Business and Financing Model Segment Dominated the Market in 2024?
The utility-owned segment dominated the market in 2024, since well-established power companies are well-versed in the issues of siting, permitting, financing, and regulation. These utilities include SMRs in their long-term generation picture to diversify their generation resource, maintain a reliable supply of and provide affordable electricity, and comply with some level of required or voluntary carbon reductions. By being involved, the utility also provides comfort to governments and investors since utilities have shown their capability to deliver complex, regulated, large-scale energy projects.
The vendor-financed (build-own-operate, BOO) segment is growing at the fastest CAGR, as private developers and technology vendors now provide a route to market. By financing the projects, these models lower the barrier to entry, meaning less up-front costs for utilities or governments, and allow vendors to control operations and revenue in the interim. The growing interest in “non-traditional” financing solutions for smaller energy projects is accelerating SMR deployment, especially in developing nations and in the industrial end-user market.
Contract/Delivery Model Insights
Why EPC/Turnkey the Nuclear Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) Market in 2024?
The EPC/turnkey contracts segment was the dominant segment in 2024, because it provides the broadest, single-point solution to utilities and governments. EPC arrangements ameliorate complications by guaranteeing that the vendor or consortium will handle design, construction, and delivery. EPC contracts represent predictable timelines and costs. These factors make EPC contracts the optimal choice for large-scale nuclear projects, particularly those trying to reduce implementation risk.
The power purchase agreement (PPA)-backed projects segment is expected to expand at a notable CAGR over the projected period. Projects with PPAs as the funding model are supported by the benefits of sharing revenues and long-term stability, because in this model, end-users are reserving the right to buy power for the duration of that commitment. PPA arrangements encouraged private capital investment in SMRs, which is attractive to industrial facilities and other off-grid users who want low-carbon emissions smart power, without a significant upfront capital investment.
Regional Insights
Why is North America Poised to Lead in the Nuclear Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) Market?
North America is leading in SMR momentum because changes in policy, capital, and utility commitments are all converging to derisk the first-of-a-kind builds and create supply chains. Federal programs are providing direct incentives, as well as procurement signals (i.e., solicitations such as $900M, HALEU allocation, etc), and regulators have jumped through hoops to accelerate design reviews that have shortened the commercialization timeframes. Large utilities, as well as industrial off-takers, are realizing that SMRs can provide grid-stable, low-carbon capacity that can complement intermittent renewables, and they see pathways to commercialize factory-built modules and modules needed for modular construction methods.
Robust R&D Hubs Drive U.S.
U.S. is the hub for SMR scaling, given the concentration of R&D, the licensing active, the pilots by utilities, and the recent developments regarding NRC approvals and expedited plant-level design permitting - alongside DOE support for HALEU, and funding for competitive awards - to provide U.S. developers with a clear near-term runway to commercialization. Further, clear market signals from utilities and commercial partnerships allow for pragmatic deployment pathways - moving programs from prototyping to planning regulated assets and procurement strategies that would be bankable for institutional investors.
Why Is Asia Pacific the Fastest-Growing Region in the Nuclear Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) Market?
Growth in Asia-Pacific is being propelled by a combination of central energy demand from large populations, strong coordination by state governments, and concurrent investments in both large reactors and modular designs that speed learning curves. National energy strategies emphasize energy security and rapid decarbonization, making SMRs the preferred technology for new grids in remote locations, island provinces, and industrial clusters.
State-Coordinated Site Selection Boosts China
China's integrated approach, which includes state-coordinated site selection, domestic site manufacture, and tightly held project management, minimizes delivery risk (to be a more politically relevant benchmark) and compresses learning curves that allow Chinese firms to deploy scaled units domestically and also offer near turn-key export to most neighbouring markets. Coupled with this operational momentum could accelerate adoption across the region.
Demand for Clean and Low-Carbon Energy Propels Europe
Europe is expected to grow significantly in the nuclear small modular reactors (SMRs) market during the forecast period, due to growing demand for clean and low-carbon energy. The growth in investment initiatives and energy security concerns are also increasing their demand. Moreover, the companies are developing new nuclear SMRs, which are being supported by investment, encouraging the replacement of old reactors, and promoting market growth.
Government Initiatives Shape the UK
The growth in the government initiatives for the development of nuclear SMRs is increasing. At the same time, the growing focus on carbon net-zero goals is also increasing their use. Additionally, growing investments, R&D, and energy security concerns are also increasing their adoption rates.
Demand For Flexible Electricity Promotes South America
South America is expected to grow significantly in the nuclear small modular reactors (SMRs) market during the forecast period, due to growing demand for flexible and steady electricity. This is increasing their use across rural and remote areas, where their adoption in other regions is also increasing as a clean energy alternative. Their adoption is also being promoted by the government, which is driving the market growth.
Massive Industries Fuels Brazil
The presence of massive mining, manufacturing, and metallurgy industries in Brazil is increasing the use of nuclear SMRs. Moreover, their adoption is also driven by stringent regulations and the need for stable electricity. Additionally, the growing interest in low-carbon energy solutions is also increasing their use.
MEA's Decarbonization Drive
The Middle East and Africa (MEA) SMR market is expanding rapidly, driven by industrialization, population growth, and decarbonization goals. SMRs offer a flexible, low-carbon power solution for remote areas and industrial uses like desalination, making them an attractive option to diversify energy sources beyond fossil fuels.
UAE's Nuclear Futures
The UAE is a regional leader in nuclear energy with its large-scale Barakah plant, and it is now exploring SMR technology to meet growing power demands from sectors like data centers. Strategic investments and government support for clean, reliable power are key drivers for future SMR deployment in the Emirates.
Value Chain Analysis
- Reactor OEMs and Fuel Supply: Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) design and produce the SMR core, while fuel suppliers sell enriched nuclear fuel.
- Modular Fabrication and Assembly: Instead of building a reactor on-site, SMRs are fabricated in a factory as modular units, enabling standardized manufacturing. After being fabricated, the modules are shipped and assembled on-site, which allows for a reduced time frame, cost savings, and reduced risk to safety on the job site.
- EPC and Construction Services: Engineering, Procurement, and Construction (EPC) companies manage the integration of SMR modules by providing site preparation and infrastructure. They ensure that projects are delivered on time, maintaining quality and addressing regulatory requirements.
- Operations and Maintenance (O&M): Once the SMR is installed on-site, O&M services provide reactor monitoring, support to optimize performance, and undertake any ongoing maintenance. Together, effective O&M makes sure operations can continue for a long time and efficiently, while also sticking to safety regulations and environmental regulations.
- Licensing and Consulting: Consulting and licensing services can provide specialized professionals who can help in walking SMR projects through the regulatory approvals, compliance assessments, and safety certifications, to comply with safety regulations, while meeting regulations on a national and international scale related to nuclear policies and standards.
The Market Titans: Key Players' Offering
- NuScale Power: The company provides VOYGR and NuScale Power Modules.
- Rolls-Royce SMR: 470Mwe Rolls-Royce SMR is provided by the company.
- Westinghouse Electric Company: The company offers AP300 and eVinci are provided by the company.
- GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy: BWRX-300 is developed by the company.
- TerraPower: The company is developing the Natrium reactor.
- X-energy: The Xe-100 reactor is being developed by the company.
- Oklo: The company is developing the Aurora microreactor.
Nuclear Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) Market Companies

- NuScale Power (U.S.)
- Rolls-Royce SMR (UK)
- Westinghouse Electric Company (U.S.)
- GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy (U.S./Japan)
- Holtec International (U.S.)
- TerraPower (U.S.)
- X-energy (U.S.)
- Kairos Power (U.S.)
- BWX Technologies/BWXT (Canada/U.S.)
- Rosatom (Russia)
- CNNC/CGN (China)
- KHNP/KAERI (South Korea)
- Oklo (U.S.)
- Newcleo (France)
- Ultra Safe Nuclear Corporation (USNC)
Recent Developments
- In February?2025, HD Korea Shipbuilding and Offshore Engineering (HD KSOE) unveiled a nuclear-powered containership model in Houston, receiving ABS approval. The design integrates a supercritical CO? propulsion system, enhancing thermal efficiency by approximately 5% over traditional steam-based systems. This innovation marks a significant step in decarbonizing maritime transport. (Source: https://www.offshore-energy.biz)
- In June?2025, Brenmiller Energy announced the development of a new bGen™ thermal energy storage system tailored for nuclear Small Modular Reactors (SMRs). The system aims to enhance flexibility and efficiency in SMR operations, addressing dynamic grid demands. A successful proof of concept was implemented with major utility Enel in Italy. (Source: https://www.stocktitan.net)
Segments Covered in the Report
By Reactor/Technology Type
- Light Water Reactor (LWR)/Integral Pressurized Water Reactor (iPWR)
- Pressurized Heavy Water Reactor (PHWR/HWR)
- High Temperature Gas Reactor (HTGR)
- Molten Salt Reactor (MSR)
- Fast Neutron Reactor (FNR)/Sodium-cooled Fast Reactor (SFR)
- Lead-cooled Fast Reactor (LFR)
- Gas-cooled Fast Reactor (GFR)
- Microreactors (<10–20 MWe)
- Transportable/Packaged Reactors
By Printing Method/Process
- Extrusion-based printing
- Powder/binder-jetting methods
- Hybrid/multi-material approaches
By Power Rating
- Micro (<10 MWe)
- Small (10–100 MWe)
- Medium (100–300 MWe)
By Coolant/Moderator
- Light Water
- Heavy Water
- Gas Coolant (Helium, CO?)
- Molten Salt
- Liquid Metal (Sodium, Lead)
- Graphite-Moderated
By Application/End-use
- Grid Power/Baseload Electricity
- Grid Support/Load-Following
- Industrial Process Heat (e.g., refining, petrochemicals)
- Desalination
- Hydrogen Production/Synthetic Fuels
- Remote/Off-grid Power
- Data Centers/AI Facilities
- Marine Propulsion/Floating SMRs
- Military and Defense
By Ownership/Business and Financing Model
- Utility-Owned
- Vendor-Financed (Build-Own-Operate, BOO)
- Independent Power Producers (IPPs)
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPP)
- Leasing and Service-based Models
By Contract/Delivery Model
- EPC/Turnkey Contracts
- Modular Factory Supply + Onsite Assembly
- Build-Own-Operate (BOO)/Build-Own-Transfer (BOT)
- Power Purchase Agreement (PPA)-Backed Projects
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Ask For Sample
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
 Get a Sample
Get a Sample
 Table Of Content
Table Of Content
 sales@precedenceresearch.com
sales@precedenceresearch.com
 +1 804-441-9344
+1 804-441-9344
 Schedule a Meeting
Schedule a Meeting