Mosquito-Borne Infections Testing Market Size and Forecast 2025 to 2034
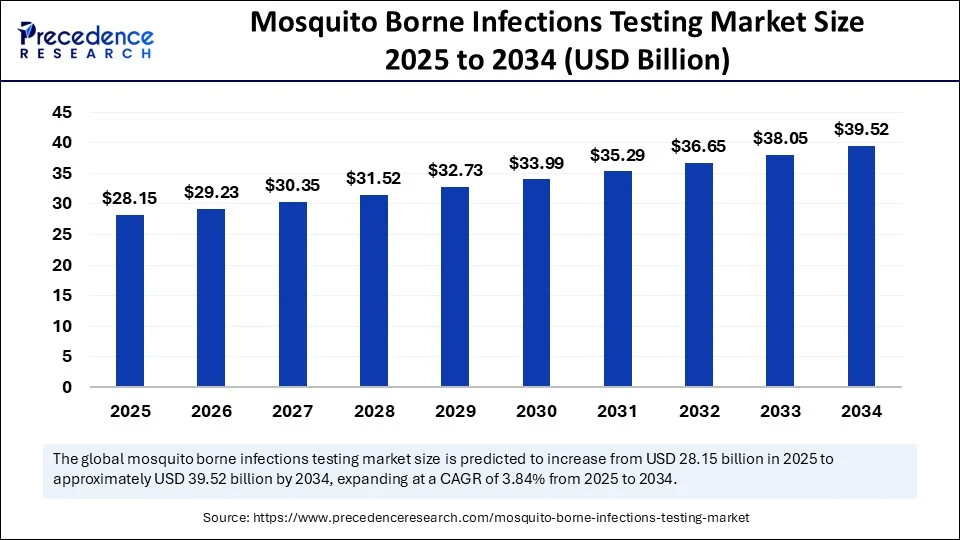
The global mosquito-borne infections testing market size was calculated at USD 27.11 billion in 2024 and is predicted to increase from USD 28.15 billion in 2025 to approximately USD 39.52 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 3.84% from 2025 to 2034. driven by increasing awareness of mosquito-borne diseases and advancements in diagnostic technologies.
Mosquito-Borne Infections Testing Market Key Takeaways
- In terms of revenue, the global disposable urine bags market was valued at USD 27.11 billion in 2024.
- It is projected to reach USD 39.52 billion by 2034.
- The market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 3.84% from 2025 to 2034.
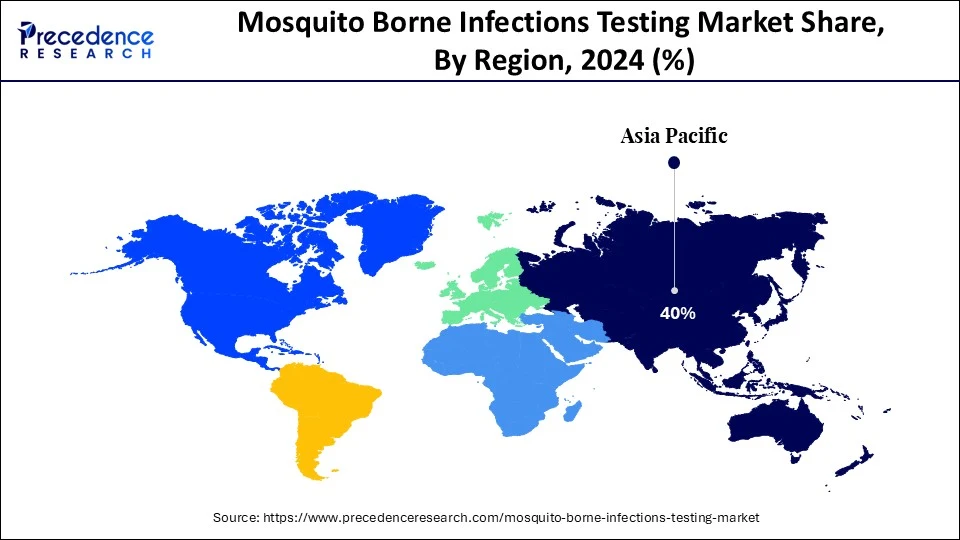
- Asia Pacific dominated the market, holding more than 40% of the largest market share in 2024.
- Latin America is expected to expand at the fastest CAGR in the market between 2025 and 2034.
- By disease type device type, the malaria segment held the largest of 34% market share in 2024.
- By disease device type, zika virus testing is expected to grow at a remarkable CAGR of between 2025 and 2034.
- By test type, the Serological Tests – ELISA segment held the largest of 38% market share in 2024.
- By test Type, diabetes Molecular Tests – RT-PCR are expected to grow at a remarkable CAGR between 2025 and 2034.
- By Sample Type, the blood segment held the largest market share of 51% in 2024.
- By Sample Type, saliva and urine segment is expected to grow at a remarkable CAGR between 2025 and 2034.
- By end user type, the diagnostic laboratories segment held the largest market share of 62% in 2024.
- By end user type, the point-of-care/field testing is expected to grow at a remarkable CAGR between 2025 and 2034.
- By technology type, the NAAT segment held the largest market share of 58% in 2024.
- By technology type, the microfluidics-based diagnostics is expected to grow at a remarkable CAGR between 2025 and 2034.
Role of AI in Smart Guardian of glucose control
Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing the blood glucose monitoring space by enabling predictive, personalized, and real-time management of blood sugar levels. Advanced algorithms can analyze continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) data to forecast fluctuations and suggest timely interventions. AI-powered apps offer dietary recommendations and insulin dosage alerts based on individual glucose trends.
Integrations with smartwatches and smartphones are making diabetic care more proactive than reactive. AI is also improving device accuracy and reducing false readings, enhancing user confidence. As AI gets embedded into CGMs and glucometers, it is turning devices from mere trackers into intelligent health companions.
Asia Pacific Mosquito-Borne Infections Testing Market Size and Growth 2025 to 2034
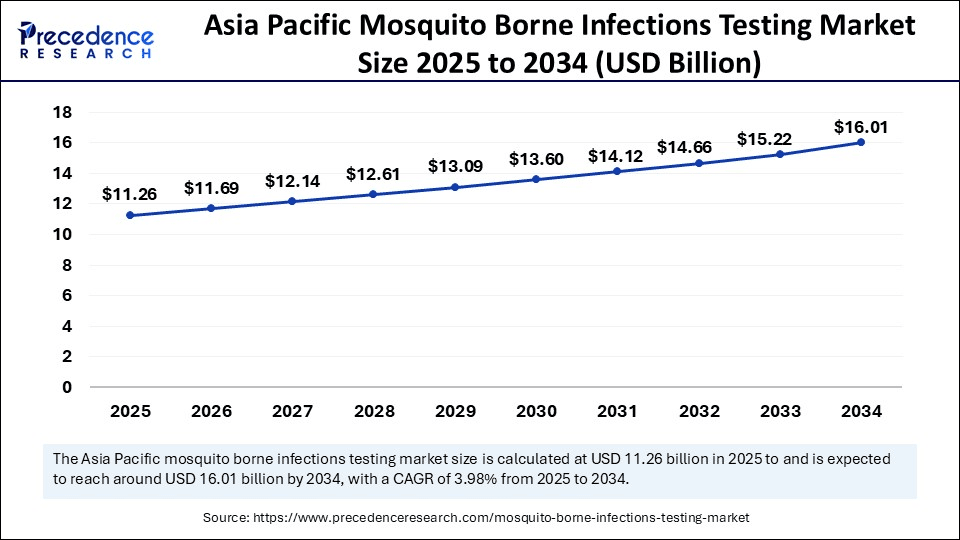
The Asia Pacific mosquito-borne infections testing market size is evaluated at USD 11.26 billion in 2025 and is projected to be worth around USD 16.01 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 3.98% from 2025 to 2034.
Is Asia Pacific the new powerhouse for glucose monitoring?
Asia Pacific continues to dominate the mosquito-borne infections testing market, driven by the rapid increase in diabetes cases, especially in urban populations. Government-led health initiatives are pushing for early detection and affordable glucose monitoring options. Rising disposable income and digital health awareness have accelerated the adoption of smart glucometers. Local manufacturers are innovating cost-effective solutions tailored to the region's diverse income segments. Countries like India, China, and Indonesia are investing heavily in healthcare infrastructure, including telehealth and diagnostics. This is enabling quicker access to glucose monitoring in semi-urban and rural areas as well.
India is dominating Asia Pacific, The region is also experiencing a surge in digital health adoption, with mobile apps and wearable devices gaining popularity. India's tech-forward healthcare startups are producing AI-powered, app-connected monitors at low prices. China's integration of glucose data into super apps (like WeChat health dashboards) is increasing user engagement. Meanwhile, public-private partnerships are enabling free or subsidized glucose monitors in certain areas. Regional customization, language localization, and compatibility with low-end smartphones are also accelerating adoption. As a result, Asia-Pacific is not only growing fast but shaping innovation patterns for global markets.
How Latin America is raising awareness to turn the tide of diabetes?
Latin America is projected to be the fastest-growing in the mosquito-borne infections testing market, prompting urgent attention to glucose monitoring tools. Urbanization and lifestyle changes have increased the number of patients needing regular monitoring. Governments across the region are integrating glucose monitoring into primary healthcare services. Brazil, Mexico, and Argentina are leading in adoption, with initiatives promoting community-based testing and education. However, affordability remains a key concern, making low-cost glucometers and strips more popular than CGMs. The region is increasingly turning to mobile-connected devices to close the care gap, especially in remote areas.
Argentina is the fastest-growing in Latin America, Private clinics and wellness centers are offering bundled care packages, including regular monitoring. Local distributors are partnering with global manufacturers to increase the availability of cutting-edge solutions. Language-friendly mobile apps and real-time data visualization tools are enhancing the user experience. Investment in healthcare digitization is improving supply chains for diagnostic products. With the right mix of policy and technology, Latin America stands at the cusp of broader, more equitable access to blood glucose monitoring.
Market Overview
The mosquito borne infections testing market encompasses diagnostic solutions developed to detect infections transmitted through mosquito vectors such as Aedes, Anopheles, and Culex species. These infections include diseases such as malaria, dengue, Zika virus, chikungunya, yellow fever, West Nile virus, and others. The testing methods span molecular diagnostics (PCR, RT-PCR), serological testing (ELISA, rapid diagnostic tests), immunoassays, and next-generation sequencing (NGS). This market serves hospitals, diagnostic laboratories, research institutes, and point-of-care settings, particularly in endemic regions, and is expanding due to increasing outbreaks, climate change, and cross-border travel.
Market Trends
- Sugar in demand for non-invasive and pain-free monitoring devices.
- Increased adoption of CGM devices over traditional glucometers.
- Integration of glucose monitors with fitness trackers and smartphones.
- Growing preference for wearable and patch-based glucose sensors.
- Focus on pediatric and geriatric-specific monitoring solutions.
- Rise in telehealth-based glucose monitoring and remote patient management.
Market Scope
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 39.52 Billion |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 28.15 Billion |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 27.11 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate from 2025 to 2034 | CAGR of 3.84% |
| Dominating Region | Asia Pacific |
| Fastest Growing Region | North America |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | Disease Type, Test Type, Sample Type, End User, Technology, and Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Market Dynamics
Market Drivers
Rising Global Incidence of Mosquito-Borne Diseases
The increasing global prevalence of mosquito-borne diseases such as dengue, malaria, Zika virus, chikungunya, and West Nile virus is a major force driving the growth of the mosquito-borne infections testing market. As these diseases spread rapidly across both tropical and temperate regions, there's a growing demand for early, accurate, and accessible diagnostic testing. Increased International Travel and Migration have accelerated the cross-border transmission of infections, exposing new populations and heightening the need for surveillance and screening at points of entry.
Market Opportunity
Glucose monitoring reimagined: Where tech meets health
The Mosquito Borne Infections Testing Market encompasses diagnostic solutions developed to detect infections transmitted through mosquito vectors such as Aedes, Anopheles, and Culex species. These infections include diseases such as malaria, dengue, Zika virus, chikungunya, yellow fever, West Nile virus, and others. The testing methods span molecular diagnostics (PCR, RT-PCR), serological testing (ELISA, rapid diagnostic tests), immunoassays, and next-generation sequencing (NGS). This market serves hospitals, diagnostic laboratories, research institutes, and point-of-care settings, particularly in endemic regions, and is expanding due to increasing outbreaks, climate change, and cross-border travel.
The global blood glucose monitoring market is evolving rapidly due to technological progress and patient demand for ease and comfort. From traditional test strips to continuous glucose monitors, the market is expanding with diverse products catering to different needs. User-friendly interfaces, mobile syncing, and wearable technologies are transforming the way individuals track and manage their glucose levels. Innovations such as non-invasive glucose monitoring devices are gaining traction, offering more convenience, and reducing the discomfort associated with finger-pricking. The integration of AI and machine learning into these devices enhances not only the user experience but also the accuracy of readings, leading to better health outcomes. Additionally, ongoing research into advanced materials and sensor technologies is expected to pave the way for even more effective solutions in the future.
Disease Type Insight
Is the rising incidence of malaria attributable to the proliferation of mosquito populations?
The malaria segment dominated the mosquito-borne infections testing market 2024, due to its high prevalence across tropical and subtropical regions. The disease's persistent burden in parts of Africa, Southeast Asia, and Latin America has fuelled consistent demand for rapid and reliable diagnostic tools. Governments and global health bodies prioritize malaria testing through national elimination programs and public health surveillance. Its diagnostic pipeline is also comparatively well-developed, incorporating both rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs) and advanced molecular techniques. Moreover, the established awareness about malaria symptoms encourages higher testing rates compared to other vector-borne diseases. These factors collectively sustain malaria's leading position in the market.
Frequent outbreaks, seasonal spikes, and drug resistance trends further support continual product innovation in malaria diagnostics. The push toward elimination by the WHO's 2030 goals has triggered massive investments in accurate, low-cost, and field-deployable testing kits. As a result, malaria-focused companies continue to lead sales volumes in endemic regions. Public-private partnerships in Africa and Asia are also streamlining last-mile diagnostic availability. From policy emphasis to technological maturity, malaria stands as a benchmark for other vector-borne diseases in terms of diagnostic infrastructure. The strong base it offers is hard to displace in the short term.
The Zika Virus is expected the fastest growth in the market during the forecast period, especially in the wake of increasing global travel and climate change-induced vector migration. Although once considered dormant, localized outbreaks and pandemic-level threats have reignited global interest in Zika diagnostics. Rapid advancements in serological and molecular technologies have made Zika testing more accessible and efficient. The virus's known link to birth defects and neurological disorders adds urgency to early diagnosis. Researchers are now developing multiplex assays to detect Zika alongside dengue and chikungunya for comprehensive surveillance. This multidimensional focus makes Zika diagnostics a high-potential growth area.
Governments and NGOs have stepped up surveillance protocols in at-risk areas, boosting procurement of Zika test kits. Diagnostic developers are also tapping into travel health and prenatal testing markets to address high-risk populations. The push for point-of-care solutions, especially for pregnant women in endemic zones, is shaping future market trajectories. Increasing diagnostic approvals from regulatory bodies indicate maturing commercial viability. Despite competition from better-established disease diagnostics, Zika is carving out a space thanks to innovation, awareness, and strategic targeting. It may not dominate in volume yet, but its growth momentum is undeniable.
Test Type Insights
How Serological Tests – ELISA is dominating the market?
The sserological tests – ELISA segment dominated the mosquito-borne infections testing market 2024, due to their ease of use, cost-effectiveness, rapid and accurate diagnostic testing allows for timely interventions, reducing the spread of infections. By utilizing advanced technologies, healthcare providers can identify outbreaks more efficiently, helping to allocate resources effectively. The market also fosters the development of innovative testing methods, improving the accessibility of diagnostics in remote and underserved areas. Increasing awareness of mosquito-borne diseases promotes education and prevention strategies, ultimately leading to healthier communities. Moreover, improved testing capabilities can support research efforts to develop vaccines and new treatments for mosquito-borne diseases.
The blood glucose monitoring market is witnessing transformative trends driven by technological advancements and consumer demand. The shift towards non-invasive and pain-free glucose monitoring devices reflects a growing appetite for comfort among users. Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices are becoming more prevalent, as they provide real-time data and insights for better diabetes management. Integration with smartphones and fitness trackers enhances user engagement and helps individuals monitor their health more proactively. Moreover, there's an increasing focus on developing monitoring solutions tailored for specific populations, such as pediatric and geriatric patients. As telehealth continues to rise, remote patient management is becoming an essential component of diabetes care, making it easier for patients to connect with healthcare providers.
The molecular tests – RT-PCR is expected the fastest growth in the market during the forecast period, driven by the need for higher accuracy and specificity. Techniques like PCR and isothermal amplification enable early detection of pathogen DNA/RNA, even during asymptomatic stages. This makes them ideal for tracking diseases like Zika and dengue where symptoms may overlap. Molecular diagnostics also reduce the risk of false positives and can differentiate between closely related pathogens. Their use in surveillance programs and clinical research further boosts their relevance. As costs decline, these tests are becoming more accessible beyond advanced labs.
Governments and diagnostic companies are investing in portable molecular testing platforms for decentralized use. New innovations are targeting rapid results within 30–60 minutes with minimal technical training. The integration of AI and machine learning to interpret molecular data is enhancing diagnostic speed and accuracy. Their utility in confirming ambiguous serological test results adds a layer of validation. As precision medicine and outbreak control demand better tools, molecular testing is emerging as the gold standard. This growth trajectory shows no signs of slowing down.
Sample Type Insights
How is Blood leading the league?
The blood segment dominated the mosquito-borne infections testing market 2024, Due to its easy recognition of the disease through a blood sample, this method has gained popularity. A blood sample can determine whether the disease is present in the bloodstream. This approach allows for early detection, which can lead to more effective treatment options. Additionally, blood tests are often less invasive than other diagnostic methods. The results can usually be obtained quickly, providing patients with timely information. As a result, healthcare providers can make informed decisions and initiate necessary interventions sooner. This advancement in medical testing showcases the importance of technology in improving patient outcomes.
The mosquito-borne infections testing market is poised for significant growth, driven by a rising awareness of diseases transmitted by mosquitoes and advancements in diagnostic technologies. Asia Pacific is leading the market, holding a substantial share, while Latin America is expected to experience the fastest growth between 2025 and 2034. In terms of disease types, the malaria segment currently dominates the market, whereas zika virus testing is projected to see remarkable expansion in the coming years. Testing methods, particularly serological tests such as ELISA, are most prevalent, but molecular tests like RT-PCR are gaining traction. The blood sample type represents the majority of the market.
The saliva/urine is expected the fastest growth in the market during the forecast period, The detection of disease biomarkers and accurate diagnoses are increasingly facilitated by the collection of saliva and urine samples, which require no specific equipment. This method has emerged as one of the fastest-growing segments in the market. A recent study published by Science Direct highlights that both saliva and urine can effectively detect a variety of Plasmodium nucleic acids and antigens, which is crucial for the early detection of malaria. While blood samples have traditionally been used for these purposes, the roles of saliva and urine are becoming increasingly significant.
Furthermore, many plasma or serum proteins can be identified in urine at low molecular weights, making urine an advantageous medium for investigating not only kidney diseases but also systemic health issues. This growing recognition of alternative sample sources reflects a broader trend towards more accessible and efficient diagnostic methods. Governments are showing growing interest in deploying them in school-based and mobile health programs. As testing decentralizes and moves toward home-based models, saliva and urine samples offer a promising alternative. These trends are likely to shape future testing strategies, particularly in remote and underserved regions.
End User Insight
Why diagnostics laboratory still a powerhouse in the market?
The diagnostics laboratory segment dominated the mosquito-borne infections testing market 2024, These labs offer the infrastructure needed for complex testing like PCR, ELISA, and culture-based assays. Their capacity to process high volumes of samples makes them indispensable during epidemics. Centralized labs also enable confirmatory testing and serve as reference points for regional health data. They are often the first recipients of government-supplied diagnostic kits. Clinical accuracy, traceability, and reporting capabilities further solidify their lead in the market.
Accredited laboratories are often part of national disease surveillance programs, especially for diseases like malaria and dengue. They maintain the quality standards required for regulatory compliance and data reporting. Ongoing digitization efforts are enhancing workflow efficiency and reducing turnaround times. Additionally, partnerships between public health labs and private diagnostic chains are increasing testing coverage in urban and semi-urban areas. While emerging point-of-care models are growing, the central role of laboratories in complex and batch testing remains unmatched. Their dominance will likely continue through government-funded health initiatives.
The point-of-care/field testing is expected the fastest growth in the market during the forecast period, due to their real-time application and accessibility. These tests are crucial during outbreaks in rural or remote areas where lab infrastructure is limited. Their portability and ease of use make them ideal for rapid mass screenings. Newer PoC tools are leveraging lateral flow assays, isothermal amplification, and microfluidics for on-site accuracy. In emergencies, they offer critical early detection capabilities that can curb disease transmission. Their time-saving nature enhances both public health response and clinical outcomes.
The rise in government-backed mobile health units and NGO-led rural health initiatives has boosted demand for PoC solutions. These platforms are now being integrated with mobile apps for real-time data logging and disease tracking. Innovations are reducing reliance on cold chains and specialized storage conditions. In low-income regions, PoC tests serve as the first and sometimes only diagnostic line. Public-private partnerships are also channeling funds into community-based diagnostics with real-time reporting features. With their user-centric design and rapid action, PoC diagnostics are reshaping how vector-borne diseases are monitored and managed.
Technology Insights
How NAAT is dominating the market?
The NAAT segment dominated the mosquito-borne infections testing market 2024, NAAT provides unmatched sensitivity and specificity. It's especially vital for early detection of low viral or parasitic loads in asymptomatic patients. NAAT platforms are being miniaturized for portable use in outbreak scenarios. The ability to target multiple pathogens in a single run increases diagnostic value. NAAT has become essential in both confirmatory diagnostics and epidemiological surveillance.
Global health agencies are integrating NAAT into their advanced diagnostic toolkits for malaria elimination and arboviral surveillance. Although cost and infrastructure requirements remain high, innovation is gradually reducing barriers. Automated sample processing, AI-assisted analysis, and cloud-based result sharing are enhancing NAAT scalability. Several nations are prioritizing NAAT in their pandemic preparedness frameworks. As regulatory bodies continue approving NAAT-based kits for vector-borne diseases, market penetration is accelerating. In terms of diagnostic certainty and clinical confidence, NAAT continues to lead.
The microfluidics-based diagnostics is expected the fastest growth in the market during the forecast period, due to their real-time application and accessibility. These lab-on-a-chip platforms enable the integration of sample collection, processing, and detection on a single device. They require minimal reagents, small sample sizes, and offer rapid results. In resource-constrained environments, these tools are proving transformative. Microfluidics also supports multiplex testing, allowing simultaneous detection of several vector-borne diseases. This is especially useful in regions where coinfections are common.
Startups and research institutions are leading innovation in this space, often with funding from global health foundations. Portable microfluidic devices are being piloted in field settings to validate their usability. Integration with smartphones and IoT is enhancing real-time reporting and remote diagnostics. Unlike bulky lab equipment, microfluidic platforms can be deployed in schools, homes, and field clinics. Their cost-effectiveness and ease of use are catching the attention of national disease control programs. With a blend of innovation and accessibility, microfluidics could redefine frontline diagnostics in endemic regions.
Mosquito-Borne Infections Testing Market Companies
- Abbott Laboratories
- Thermo Fisher Scientific
- Bio-Rad Laboratories
- F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG
- Siemens Healthineers
- Becton, Dickinson and Company (BD)
- bioMérieux SA
- Qiagen N.V.
- Danaher Corporation (Cepheid)
- Merck KGaA
- Ortho Clinical Diagnostics
- GenMark Diagnostics
- QuidelOrtho Corporation
- LumiraDx
- InBios International
- Hologic Inc.
- Atlas Genetics
- Fast Track Diagnostics (Siemens)
- Diasorin S.p.A
- Molbio Diagnostics Pvt Ltd
Recent Development
- In August 2025, With the advances in CRISPR gene-editing technology, this vision could soon become a reality. In significant breakthroughs, researchers have discovered a method to genetically alter mosquitoes so they are unable to penetrate human skin, rendering them incapable of biting, drawing blood, or breaking through the skin. CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) is a potent gene-editing tool that enables scientists to make accurate cuts in DNA. Consider it as a molecular pair of scissors that can deactivate specific genes or introduce new ones.
(Source: https://www.news18.com)
Segments Covered in the Report
By Disease Type
- Malari
- Plasmodium falciparum
- Plasmodium vivax
- Others
- Dengue
- NS1 Antigen Detection
- IgM/IgG Antibody Detection
- Zika Virus
- Chikungunya
- Yellow Fever
- West Nile Virus
- Others (Japanese encephalitis, Rift Valley fever, etc.)
By Test Type
- Molecular Tests
- RT-PCR
- qPCR
- Isothermal Amplification
- Serological Tests
- ELISA
- Lateral Flow Assay (RDT)
- Immunoassays
- Next Generation Sequencing (NGS)
- Others (e.g., CRISPR-based diagnostics)
By Sample Type
- Blood
- Serum/Plasma
- Saliva/Urine
- Others (e.g., cerebrospinal fluid)
By End User
- Hospitals & Clinics
- Diagnostic Laboratories
- Public Health Agencies
- Research Institutes
- Point-of-Care/Field Testing
- Others
By Technology
- Nucleic Acid Amplification Techniques (NAAT)
- Immunochromatographic Techniques
- Microfluidics-based Diagnostics
- Biosensor Platforms
- Others
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Ask For Sample
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
 Get a Sample
Get a Sample
 Table Of Content
Table Of Content
 sales@precedenceresearch.com
sales@precedenceresearch.com
 +1 804-441-9344
+1 804-441-9344
 Schedule a Meeting
Schedule a Meeting