Power SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) Market Size and Forecast 2025 to 2034
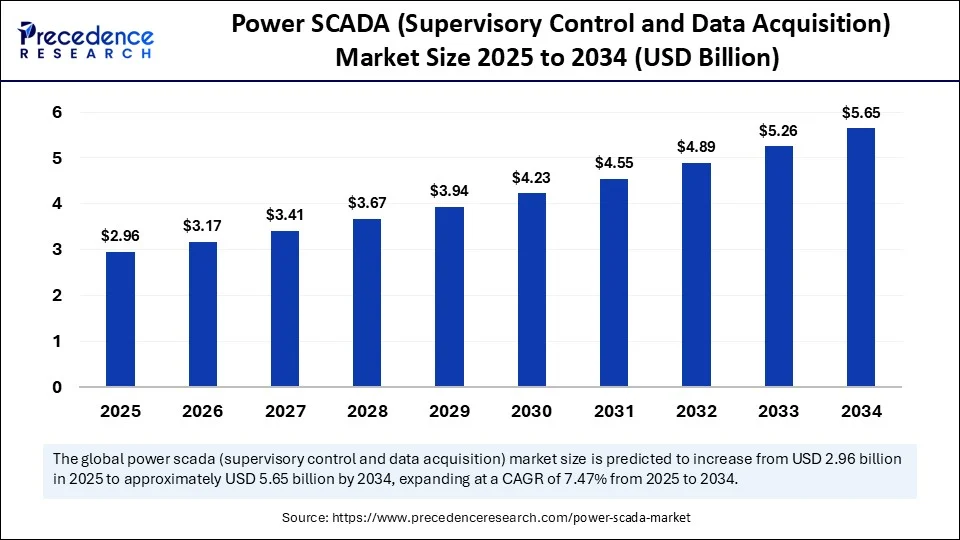
The global power SCADA (supervisory control and data acquisition) market size accounted for USD 2.75 billion in 2024 and is predicted to increase from USD 2.96 billion in 2025 to approximately USD 5.65 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 7.47% from 2025 to 2034. This market is growing due to the rising demand for real-time monitoring, control, and automation of power systems to enhance grid reliability and operational efficiency.
Power SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) MarketKey Takeaways
- In terms of revenue, the global power SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) market was valued at USD 2.75 billion in 2024.
- It is projected to reach USD 5.65 billion by 2034.
- The market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 7.47% from 2025 to 2034.
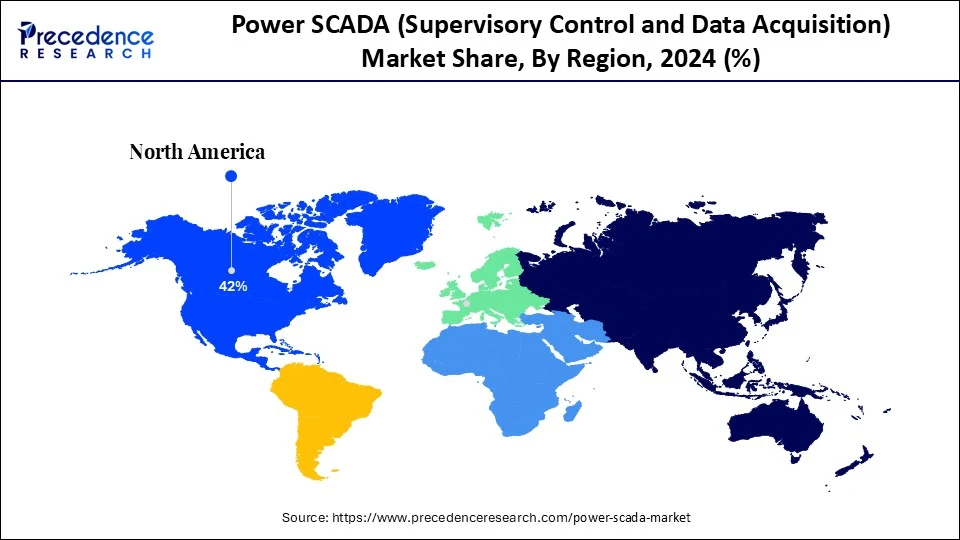
- North America dominated the power SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) market with the largest market share of 42% in 2024.
- Asia Pacific is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR in the upcoming years.
- By component, the hardware segment held the biggest share in 2024.
- By component, the software segment is observed to grow at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period.
- By architecture, the open system architecture (OSA) segment generated the highest market share in 2024.
- By architecture, the closed system architecture segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR in the coming years.
- By deployment model, the on-premises segment captured the highest market share in 2024.
- By deployment model, the cloud-based is emerging as the fastest growing segment during the forecast period.
- By end-use industry, the power generation segment generated the major market share in 2024.
- By end-use industry, the non-renewables segment is emerging as the fastest growing.
How does artificial intelligence enhance operational efficiency of power SCADA systems?
Artificial intelligence significantly enhances the operational efficiency of power SCADA systems by enabling advanced data analysis, predictive maintenance, and real-time decision-making. AI algorithms process large volumes of SCADA-generated data to find trends, abnormalities, and inefficiencies that conventional monitoring might miss. This enables operators to minimize energy losses throughout the grid, thereby optimizing load distribution and predicting equipment failures. Moreover, AI facilitates automated control modifications and dynamic demand forecasting, enhancing system dependability and responsiveness. AI integration is transforming SCADA systems into more intelligent, self-optimizing platforms that enhance performance and cost efficiency by reducing manual intervention and enabling smarter automation.
U.S. Power SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) Market Size and Growth 2025 to 2034
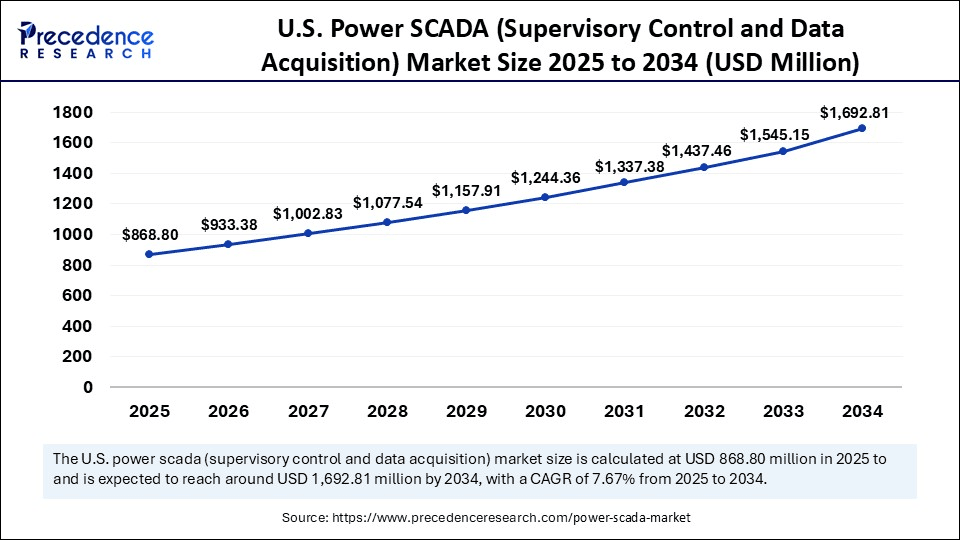
The U.S. power SCADA (supervisory control and data acquisition) market size was exhibited at USD 808.75 million in 2024 and is projected to be worth around USD 1,692.81 million by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 7.67% from 2025 to 2034.
Why factors contribute to North America's dominance in the market?
North America dominated the power SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) market with the largest share in 2024. The region is likely to sustain its growth trajectory in the coming years. With a strong emphasis on automation and grid reliability, the area boasts a sophisticated power transmission and distribution infrastructure. Early adoption of smart grid technologies, which rely on SCADA for fault detection, load balancing, and real-time monitoring, benefits local utilities. Government initiatives promoting energy digitization still provide funding for projects involving SCADA. Additionally, operators are being encouraged to implement sophisticated SCADA solutions due to a heightened awareness of cybersecurity and the convergence of IT and OT. Additionally, the area is home to several top SCADA technology suppliers, which promote innovation and local availability.
What opportunities exist in the power SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) market within Asia Pacific?
Asia Pacific is expected to witness rapid growth, driven by rising investments in smart grid projects, expanding urban infrastructure, and an increase in the demand for electricity. Utility operators in the area are adopting SCADA systems to improve operational visibility, automate power distribution, and reduce transmission losses. Through policy incentives and public-private partnerships, national governments are fostering digital transformation and an environment that is favorable to the adoption of SCADA. Demand is further increased by rural electrification and the growth of renewable energy. In this area of rapid growth, local manufacturing, and technological advancements are also enhancing the affordability and accessibility of SCADA systems.
Market Overview
The power SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) market encompasses systems that provide real-time monitoring, control, data acquisition, and operational automation of electrical power infrastructure across generation, transmission, and distribution networks. These solutions enhance grid reliability, minimize downtime, and facilitate efficient power management, particularly in large or critical infrastructure facilities, including power plants, substations, and industrial installations. Power SCADA integrates hardware, software, communication protocols, and cyber security to provide centralized visibility and facilitate informed decision-making in electric power systems.
Why is the adoption of power SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems increasing across the energy sector?
With the increasing demand for effective real-time monitoring and control of complex power networks, power SCADA systems are gaining popularity in the energy sector. Utilities need smarter tools to manage load distribution, detect faults, and ensure grid stability as energy demand increases and power infrastructure becomes more decentralized with the integration of renewable sources. By facilitating remote access, predictive maintenance, and centralized data visualization, SCADA systems lower operating expenses and downtime. Furthermore, the growing trend toward digital transformation, smart grids, and government assistance in modernizing energy infrastructure is accelerating the industry's adoption of SCADA solutions.
Power SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) MarketGrowth Factors
- Rising Demand for Grid Reliability and Efficiency: Utilities and industries are increasingly deploying SCADA systems to enhance operational efficiency, reduce power outages, and ensure uninterrupted energy supply.
- Integration of Renewable Energy Sources: The growing adoption of solar, wind, and other renewable energy sources necessitates intelligent systems, such as SCADA, for real-time monitoring, load balancing, and seamless grid integration.
- Expansion of Smart Grid Infrastructure:Governments and utilities are investing heavily in smart grid projects, where SCADA plays a critical role in enabling communication, automation, and remote management.
- Need for Real-Time Monitoring and Remote Control: SCADA systems provide centralized visibility and control over geographically dispersed assets, which is crucial for making informed decisions and detecting faults in a timely manner.
- Industrial Automation and Digitalization: As power-intensive industries embrace Industry 4.0, the demand for SCADA systems rises to support predictive maintenance, system diagnostics, and overall process optimization.
- Government Support and Infrastructure Modernization: Many countries are launching initiatives to upgrade aging power infrastructure, with SCADA integration being a key component of modernization plans.
- Cybersecurity and Data Analytics Advancements: With enhanced cybersecurity protocols and advanced data analytics features, modern SCADA systems are safer and more insightful, promoting wider adoption across various sectors.
Market Scope
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 5.65 Billion |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 2.96 Billion |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 2.75 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate from 2025 to 2034 | CAGR of 7.47% |
| Dominating Region | North America |
| Fastest Growing Region | Asia Pacific |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | Component, Architecture, Deployment Model, End-Use Industry, and Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Market Dynamics
Drivers
Industrial Growth and Urbanization
One of the major drivers in the power SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) market is rapid industrialization and urbanization. The need for a steady and uninterrupted power supply rises as cities and industries grow. SCADA systems help control energy loads in commercial buildings, manufacturing facilities, and urban infrastructure. Large industrial users with complex energy requirements rely on them because they enable them to track usage, reduce waste, and improve efficiency. Street lighting, water treatment, and electric transportation systems are all managed by SCADA systems in smart cities. As automation and electrification increase, SCADA becomes essential for effectively controlling energy use.
Growing Need for Grid Modernization
With today's energy landscape heavily reliant on digital and renewable sources, outdated power infrastructure struggles to keep pace. SCADA systems facilitate digital communication, intelligent data logging, and automation of all crucial elements of a contemporary grid. As many nations transition to digital grids, SCADA provides the platform necessary for seamless integration of substation sensors and devices. To modernize the grid, legacy systems must also be replaced with interoperable platforms, with SCADA acting as the hub for in-the-moment decision-making. It makes integration with more recent technologies, such as AI and IoT, increasingly simpler.
Restraints
Cybersecurity Concerns
Growing concerns over cybersecurity hamper the growth of the power SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) market. SCADA systems play a vital role in the nation's energy infrastructure, making them extremely susceptible to cyberattacks. Data breaches, ransomware, and remote takeovers have become much more likely as connectivity and integration with IT/OT networks have increased. Power outages can damage property, and national security risks can result from a compromised SCADA system. As a result, some utilities are hesitant to digitize their operations fully. Employee training, firewalls, secure protocols, and regular software updates are all necessary to ensure cybersecurity, but they also increase operational complexity and expense.
Data Overload and Mismanagement
Large volumes of real-time data are generated by SCADA systems, which can overwhelm operators and hinder prompt decision-making if not properly handled. Identifying important alarm trends or patterns can become challenging in the absence of efficient data analytics and filtering systems. Operational errors and a lack of situational awareness can result from inadequate data visualization tools. Large dataset processing and storage also necessitate cloud infrastructure and high-capacity servers, which raises system costs. Compliance and auditing issues are also brought on by improper SCADA data management.
Opportunities
How do smart city initiatives expand the scope of SCADA systems?
The key opportunity for the power SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) market lies in the rising development of smart cities. Smart city projects are accelerating the demand for SCADA systems that can manage diverse infrastructure components, such as electricity, water, and transportation, through a unified control interface. As cities modernize, they require energy-efficient systems that offer automation, data analytics, and remote monitoring. SCADA supports the backbone of smart infrastructure by enabling responsive, real-time decision-making across utilities. This creates a significant opportunity for vendors offering integrated urban SCADA platforms. Urbanization and funding for smart infrastructure continue to fuel this opportunity.
How are government incentives and infrastructure investments driving SCADA adoption?
Smart grid policies, grants, and financial incentives are being utilized by governments worldwide to support enhancements to power infrastructure. To update outdated grids and boost efficiency, these programs encourage the use of automation and control technologies such as SCADA systems. Regulatory requirements for real-time monitoring of energy efficiency and emission reduction further encourage the adoption of SCADA. Businesses that provide scalable, secure, and compliant SCADA solutions now have a competitive advantage. Additionally, especially in emerging economies, public-private partnerships are opening new areas of growth.
Component Insights
Why did the hardware segment dominate the power SCADA market in 2024?
The hardware segment continues to dominate the power SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) market due to its vital role in field data collection, input/output management, and substation control center communication. For real-time operations and prompt grid disruption response, hardware like sensors, remote terminal units (RTUs), and programmable logic controllers (PLCs) are essential. These devices have low latency and high durability and are frequently made for harsh environments. For continuous operation in the event of emergencies or power outages, utility companies favor robust hardware. Global demand for hardware is also being fueled by ongoing investments in transmission upgrades and smart substations. Additionally, hardware offers the structural underpinnings needed for software to be implemented successfully.
The software segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period as utilities move from static control systems to intelligent, analytics-driven platforms. Cloud-based SCADA software enables real-time monitoring and control from remote locations, enhancing responsiveness and flexibility. Integration of AI, machine learning, and big data analytics enhances grid forecasting, fault detection, and load management. Modular software also enables seamless scalability, supporting expansion without requiring system overhauls. The increasing demand for cybersecurity solutions is driving the need for software with advanced threat detection and encryption features. Overall, the software allows for smarter grid operations, which is becoming a strategic necessity across both developed and emerging markets.
Architecture Insights
How does the open system architecture (OSA) segment dominate the market in 2024?
The open system architecture (OSA) segment dominated the power SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) market with a major revenue share in 2024 due to its adaptability and compatibility with cutting-edge technologies and devices from multiple vendors. Because open systems are easier to integrate with current infrastructure and allow for more affordable upgrades rather than complete replacements, utilities favor them. By combining new digital equipment with legacy components, these architectures enable operators to prolong the life of their assets. Additionally, Open SCADA makes it possible to communicate with new technologies such as DERs, EV charging stations, and Internet of Things devices. Open standards encourage competition among vendors, which in turn lowers procurement costs and stimulates innovation and creativity. Because of this, they are the preferred option for utilities looking to develop flexible, future-ready grid systems.
The closed system architecture is experiencing rapid growth due to increasing concerns about data integrity, cybersecurity, and regulatory compliance. Security comes before adaptability in high-risk settings like nuclear power plants and national grid control centers. Closed systems are less susceptible to outside threats because they provide greater control over the system architecture and communication channels. Utility companies seeking dependable solutions with minimal customization find OEMs' integrated, pre-validated solutions appealing. As the number of cyberattacks targeting vital infrastructure rises, many operators are turning to closed platforms to improve operational security. Closed systems also lessen the need for third-party updates and the complexity of maintenance.
Deployment Model Insights
What made on-premises the dominant segment in the power SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) market in 2024?
The on-premises segment continues to dominate the market because it offers high levels of control, privacy, and data protection. These systems are typically preferred by utility companies managing sensitive power infrastructure and mission-critical assets. On-premises models enable uninterrupted operations even in areas with poor or unstable internet connectivity. They also ensure compliance with data residency regulations in many regions, especially in government-controlled utilities. Operators can fully customize hardware and software configurations to meet their operational demands. Additionally, many legacy utilities have already invested heavily in on-premises systems, which discourages sudden shifts to cloud models.
The cloud-based segment is expected to expand at the fastest CAGR during the projection period because cloud-based SCADA systems are affordable, scalable, and simple to use. Since they do not require a large hardware infrastructure, startups and small-to-mid-sized utilities find them appealing. Managing dispersed energy resources requires remote operation, centralized data analysis, and cross-site coordination, all of which are made possible by cloud deployment. Without requiring physical assistance, utilities are able to apply security patches, analytics, and real-time updates. Additionally, it facilitates data redundancy and disaster recovery, strengthening systems' resilience. Cloud-based SCADA is becoming more and more popular as 5G and edge computing become more widely available.
End-Use IndustryInsights
Why did the power generation segment dominate the market in 2024?
The power generation segment dominated the power SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) market with the largest share in 2024 because power generation equipment like boilers, transformers, generators, and turbine monitoring requires SCADA systems. In large-scale plants, these systems support load balancing, voltage stability, and operational safety. Generation scheduling, automatic fuel supply control, and real-time performance analytics are all supported by SCADA. SCADA ensures maximum efficiency in thermal, hydro, and renewable plants while minimizing human intervention. To guarantee a demand-supply balance, SCADA is also essential for connecting grid operators and generating plants. Operators value accuracy and control, which SCADA systems provide due to the high capital intensity of power generation.
The non-renewables (Coal, nuclear, gas) segment is experiencing the fastest growth due to increasing demand for safety automation and emission control. There is growing pressure on these plants to update their operations to increase efficiency and comply with more stringent environmental regulations. Complex parameters such as fuel consumption, emissions, turbine performance, and combustion efficiency can be monitored with the aid of SCADA systems. SCADA is being integrated into digital retrofits for legacy thermal plants to increase efficiency and reduce manual error rates. For redundant system checks, safety controls, and radiation monitoring, nuclear plants use SCADA. Investments in updating outdated power plants are another factor driving the adoption of SCADA in non-renewable power plants.
Power SCADA Market Companies

- Siemens AG
- ABB Ltd.
- Schneider Electric SE
- General Electric Company
- Emerson Electric Co.
- Eaton Corporation plc
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- Honeywell International Inc.
- Rockwell Automation, Inc.
- Hitachi Energy
- Toshiba Corporation
- Yokogawa Electric Corporation
- Larsen & Toubro Limited
- Open Systems International (OSI)
- Indra Sistemas S.A.
- ETAP (Operation Technology Inc.)
- ZIV Automation
- Ingeteam
- SCADAfence
- Advantech Co., Ltd.
Recent Developments
- In May 2025, Solargik Ltd introduced SOMA Pro, an AI-powered integrated SCADA platform for solar trackers, offering real-time visibility, diagnostics, and control. The system enhances yield by up to 6% through AI-driven performance optimization.
(Source: https://www.globenewswire.com) - In April 2025, State power utility Madhya Pradesh Power Transmission Company Ltd (MPPTCL) has established a new SCADA system housed in a newly constructed control room located at Navagaon in Jabalpur. The old SCADA system now stands upgraded in conformity with the latest guidelines issued by Central Electricity Authority (CEA). Operations from the new SCADA control room were recently initiated.
(Source: https://www.tndindia.com)
Segments Covered in the Report
By Component
- Hardware
- RTU (Remote Terminal Unit)
- PLC (Programmable Logic Controller)
- HMI (Human-Machine Interface)
- Communication Systems
- Other Control Units
- Software
- Real-Time Monitoring Software
- Energy Management Systems
- Automation and Control Software
- Services
- Consulting
- Integration & Implementation
- Support & Maintenance
- Training & Education
By Architecture
- Open System Architecture (OSA)
- Closed System Architecture
By Deployment Model
- On-Premises
- Cloud-Based
- Hybrid
By End-Use Industry
- Power Generation
- Renewable Power Plants (Solar, Wind, Hydro)
- Non-Renewable (Coal, Nuclear, Gas)
- Transmission
- Distribution
- Oil & Gas
- Utilities
- Metals & Mining
- Transportation
- Manufacturing
- Others (Commercial, Data Centers, etc.)
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East & Africa
- South America
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Ask For Sample
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
 Get a Sample
Get a Sample
 Table Of Content
Table Of Content
 sales@precedenceresearch.com
sales@precedenceresearch.com
 +1 804-441-9344
+1 804-441-9344
 Schedule a Meeting
Schedule a Meeting