Rare Disease Small-Batch CDMO Market Size and Forecast 2025 to 2034
The rare disease small-batch CDMO market is driven by the rise of precision medicine and niche therapeutics. Specialized CDMOs support fast turnaround and high-quality production for rare conditions. The rare disease small-batch CDMO market has experienced significant growth in recent years, reflecting the increasing reliance on digital platforms for freelance and gig-based work. The small-batch CDMO market for rare diseases has seen remarkable growth recently, driven by the rising use of digital platforms for freelance and gig work. The market is valued with strong prospects for continued expansion.
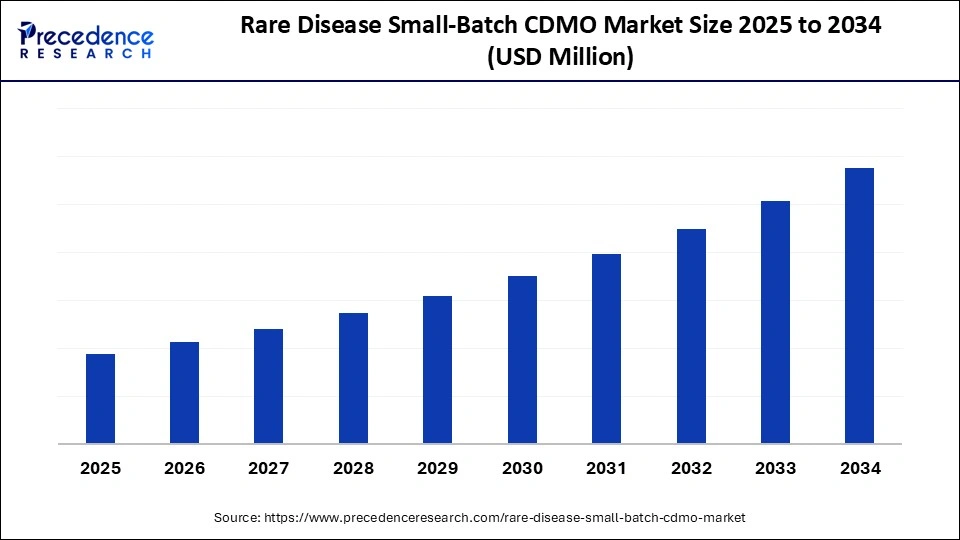
Rare Disease Small-Batch CDMO Market Key Takeaways
- North America dominated the rare disease small-batch CDMO market in 2024.
- Asia Pacific is anticipated to grow at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period.
- By service type, the clinical-scale API and drug product manufacturing segment led the market in 2024.
- By service type, the analytical development & specialized aseptic fill-finish segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period.
- By modality/technology, the small molecules segment accounted for a considerable share in 2024.
- By modality/technology, the viral-vector gene therapies segment is projected to experience the highest growth CAGR between 2025 and 2034.
- By batch/scale type, the clinical small-batch segment captured the biggest market share in 2024.
- By batch/scale type, the campaign & commercial small-batch segment is set to experience the fastest CAGR from 2025 to 2034.
- By development stage, the clinical supply segment contributed the highest market share in 2024.
- By development stage, the IND/CTA enabling services segment for advanced modalities are the fastest-growing from 2025 to 2034.
- By therapeutic area/indication, the genetic/neurological rare disease programs segment dominated the market in 2024.
- By therapeutic area/indication, the rare oncology & gene-editing indications are the fastest growing during the forecast period.
- By customer type, the small biotech/start segment generated the major market share in 2024.
- By customer type, the rare virtual biotechs are the fastest-growing in the CAGR from 2025 to 2034.
- By contract model, the fee-for-service & fixed-price segment held a maximum market share in 2024.
- By contract model, the strategic capacity reservation and hybrid risk-sharing deals segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period.
A Precision Driven Niche
Contract development & manufacturing services (CDMO) that provide small-batch, dedicated development and GMP manufacturing (drug substance, drug product, analytical/QC and regulatory support) specifically for rare-disease / orphan-drug programs, including small molecules, biologics, cell and gene therapies, and ATMPs where production runs are lower volume, require high flexibility, specialized technologies, and tight regulatory/quality support.
The rare disease small-batch CDMO market is gaining traction as the demand for highly specialized, low-volume manufacturing solutions increases, driven by the surge in orphan drug approvals and precision therapies. Unlike large-scale drug production, this niche segment thrives on flexibility, customization, and regulatory expertise, enabling biotech firms and pharmaceutical innovators to bring novel treatments for rare diseases to patients more quickly. With growing collaborations between biotechs and CDMOs, the market is evolving into a critical enabler of innovation in rare disease drug development.
AI's Touch- Transforming the Small Batch Landscape
Artificial intelligence has significantly impacted the rare disease small-batch CDMO market by transforming how small batches are designed, tested, and manufactured. AI-powered predictive analytics are helping manufacturers anticipate process bottlenecks and optimize resource allocation, ensuring faster and more reliable outcomes. Machine learning algorithms are being used to enhance quality assurance by detecting anomalies in small-batch runs, reducing batch failure risks where even a single dose is highly valuable. Digital twin technology is enabling virtual simulations of small-scale manufacturing environments, helping optimize process parameters before live execution. AI is also streamlining supply chain management, ensuring efficient coordination of raw materials for highly specialized projects. This technological adoption is reducing time-to-market for rare disease therapies, improving cost efficiency, and enhancing confidence in outcomes across the value chain.
- In April 2025, Digital health innovations and artificial intelligence (AI) are rapidly reshaping the landscape of rare disease management, offering new solutions for some of the sector's most persistent challenges. This was the central theme of a recent pharmaphorum-hosted webinar, supported by Chiesi Global Rare Diseases Chiesi GRD, featuring insights from leading experts, including Professor Maurizio Scarpa, MetabERN; Professor Alberta Spreafico, EVERSANA; and Alessandra Vignoli, Chiesi GRD.(Source: https://pharmaphorum.com)
Market Key Trends
- Rise of cell and gene therapies: Demand for small-batch CDMO services is surging as advanced therapies dominate the rare disease treatment pipeline.
- Flexible and modular facilities: CDMOs are investing in adaptive infrastructure that can quickly accommodate multiple small-scale projects.
- AI-driven manufacturing: Integration of AI tools for digital twins, predictive monitoring, and smart analytics is becoming mainstream.
- Patient-centric production models: Growing demand for ultra-personalized medicines is pushing CDMOs toward bespoke solutions.
- Strategic partnerships: Biotech startups are increasingly collaborating with CDMOs for end-to-end support, from R&D to commercialization.
- Global expansion of capacity: Emerging markets are seeing investments in small-batch facilities to balance affordability and access.
Market Scope
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Dominating Region | North America |
| Fastest Growing Region | Asia Pacific |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | Service Type, Modality/Technology, Batch/Scale Type, Development Stage, Therapeutic Area/Indication, Customer Type, Contract Model, and Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Market Dynamics
Drivers
Orphan Drugs as Catalysts
The market is propelled by the increasing prevalence of rare diseases and rising approvals of orphan drugs, which create sustained demand for niche CDMO services. Government-backed incentives such as tax credits, fee reductions, and extended market exclusivity for orphan drugs are providing a strong push for innovation. Biopharma companies are under pressure to accelerate speed-to-market for breakthrough therapies, and CDMOs with small-batch capabilities are filling this critical gap. Growing investment in advanced therapeutic modalities, including RNA-based and gene-editing technologies, further boosts demand for specialized CDMOs. Additionally, the shift toward personalized and precision therapies has amplified the need for agile manufacturing platforms.
- In April 2025, The U.S. food and drug administration has introduced a new regulatory pathway designed to accelerate the approval of rare disease therapies by allowing pharmaceutical companies therapies by allowing pharmaceutical companies to rely on smaller, more targeted sets of clinical data. Developed as a joint initiative between the Center for Drug Evaluation and Research and the Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, the framework aims to address the significant clinical trial challenges associated with limited patient populations, ultimately facilitating the faster introduction of innovative treatments to the market.(Source: https://pharmaphorum.com)
Restraints
Scaling Challenges Ahead
Despite its strong growth trajectory, the rare disease small-batch CDMO market faces several barriers. Limited availability of expertise in rare disease manufacturing processes makes it challenging to scale capacity efficiently. High operational costs in maintaining small-scale GMP facilities reduce margins and limit widespread adoption. Regulatory scrutiny is particularly intense in this space, as rare disease drugs often have accelerated approval timelines that demand flawless compliance. Supply chain vulnerabilities for rare raw materials can cause bottlenecks, further straining CDMOs. Profitability is another hurdle, as small-batch projects yield lower commercial returns compared to large-scale pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Opportunity
Nurturing the Next Wave of Therapies
The rare disease small-batch CDMO market presents immense opportunities as the pipeline for rare disease therapies continues to expand. CDMOs that invest in advanced capabilities for gene therapies, RNA therapeutics, and personalized medicine will find themselves at a competitive advantage. Expansion into emerging economies offers significant potential, especially for cost-effective small-batch facilities that meet global quality standards. Incorporating AI-driven platforms, robotics, and automation will further strengthen operational efficiency, ensuring faster project turnaround times. Moreover, partnerships with academic institutions, biotech startups, and patient advocacy groups will open new avenues for collaborative innovation. As the focus shifts toward patient-centric and ultra-targeted treatments, CDMOs have the opportunity to establish themselves as indispensable innovation partners in shaping the future of rare disease drug development.
Service Type Insights
Why Is Clinical-Scale API and Drug Product Manufacturing Dominating the Rare Disease Small-Batch CDMO Market?
Clinical scale API and drug product manufacturing remain the backbone of the rare disease small-batch CDMO market, as most therapies entering the pipeline require small-scale but highly controlled production. Demand for this service is driven by the increasing number of orphan drug approvals and the need for CDMOs to provide both active pharmaceutical ingredient synthesis and final drug product preparation. Clients, especially early-scale biotechs, rely on integrated CDMOs to avoid complex supply chain fragmentation. These services are highly valued for their compliance with global regulatory standards, ensuring therapies advance seamlessly into trials. The dominance of this segment is further supported by strong demand for flexible, multipurpose facilities. As a result, clinical scale API plus drug product manufacturing continues to anchor the service portfolio.
The segment also benefits from the need for rapid turnaround times and quality consistency in small-batch production. Unlike large-scale programs, rare disease projects often cannot afford delays or production errors due to limited patient populations. CDMOs that offer end-to-end support, from synthesis through sterile fill, are positioned as strategic partners for biotechnology companies. Pharmaceutical innovators prefer this model as it reduces cost, time, and risk associated with outsourcing to multiple providers. The growing complexity of rare disease molecules further ensures this service type remains the most in-demand. Overall, clinical scale API and drug product manufacturing will continue dominating service offerings, supported by its critical role in translating research into clinical supply.
Analytical development & specialized aseptic fill-finish is the fastest growing segment in the rare disease small-batch CDMO market, driven by the reflecting increase in complexity of advanced rare disease therapies. Rare disease drugs, including increasingly complex and advanced therapies for rare diseases. Rare disease drugs, including biologics and gene therapies, require highly sensitive analytical methods to ensure quality, stability, and safety. CDMOs' offering specialized aspect fill-finish capabilities are becoming indispensable, as precision handling of small batches is critical for patient-specific therapies. The rise in injectable biologics and viral vector-based products has further elevated demand for advanced analytical and sterile finishing services. Clients increasingly prioritize CDMOs with specialized expertise in this area to mitigate risks associated with contamination or formulation instability.
Additionally, the integration of AI and digital analytics is enhancing the speed and reliability of quality testing in this segment. As regulatory authorities tighten requirements for rare disease drugs, robust analytical validation is non-negotiable. The growing adoption of innovative packaging formats, like pre-filled syringes and vials, has further expanded the fill-finish market. Emerging biotech's prefer outsourcing these capabilities due to the high capital investment needed to set up sterile facilities. CDMOs that combine analytical rigor with aseptic finishing efficiency are gaining a competitive edge. Consequently, this segment is projected to outpace traditional service offerings in growth, reshaping the value proposition of rare disease CDMOs.
Modality / Technology Insights
Why Are Small Molecules Dominating the Rare Disease Small-Batch CDMO Market?
Small molecules continue to dominate the rare disease small-batch CDMO market, owing to their long-standing therapeutic presence and proven development pathways. Many rare disease therapies, particularly for metabolic and neurological disorders, are still developed as small-molecule drugs due to their oral bioavailability and established regulatory precedent. CDMOs have significant expertise in scaling small molecules at the clinical scale, making them a reliable choice for biotech clients. The cost-efficiency of small molecule production compared to biologics also sustains its widespread use. Furthermore, existing infrastructure in most CDMOs is tailored to handle complex small molecule synthesis, ensuring this modality remains dominant. As orphan drug incentives expand pipelines, small molecules continue to anchor the commercial landscape for rare diseases.
Viral vectors gene therapy is the fastest-growing modality in the rare disease CDMO market, reflecting the shift toward curative treatments for genetic disorders. With more than half of rare diseases linked to genetic mutations, viral vectors are emerging as the delivery platform of choice. CDMOs with vector development and manufacturing expertise are experiencing unprecedented demand as biotech firms race to advance gene therapy pipelines. These therapies require small-batch production with stringent regulatory oversight, perfectly aligning with the capabilities of specialized CDMOs. As several gene therapies approach late-stage development, demand for viral vector capacity continues to surge. This makes viral vectors a central growth engine for the CDMO landscape.
Development Stage Insights
Why Is Clinical Supply Dominating the Rare Disease Small-Batch CDMO Market?
Clinical supply continues to dominate the rare disease small-batch CDMO market, as most therapies are still in early development or investigational stages. Small patient populations require limited quantities of clinical supply, making this batch type ideal for orphan drug pipelines. CDMOs excel at providing the precision, flexibility, and speed necessary to support clinical trial readiness. These batches ensure consistent quality while accommodating rapid changes in formulation and dosage, often required in early-stage programs. The emphasis on regulatory compliance for rare disease drugs further strengthens reliance on CDMOs for small-batch production. As a result, clinical small batches from the cornerstone of rare disease drug development.
Campaign and commercial small batch manufacturing is emerging as the fastest-growing segment as more rare disease therapies advance toward approval and commercialization. Unlike clinical batches, this category focuses on reproducibility, long-term consistency, and market distribution. CDMOs are increasingly scaling their small-batch capabilities to handle niche commercial volumes while meeting stringent GMP standards. With orphan drugs often granted market exclusivity, CDMOs play a critical role in sustaining commercial supply chains. This growth reflects the transition of rare disease therapies from research and development to market-ready treatments. The demand for reliable commercial supply is expected to expand significantly over the next decade.
Therapeutic Area / Indication Insights
Why Are Genetic/Neurological Rare Disease Programs Dominating the Rare Disease Small-Batch CDMO Market?
Genetic disorders dominant therapeutic area in the rare disease small-batch CDMO market, as most rare diseases have a genetic basis. Biotech firms are increasingly focusing on therapies targeting specific mutations, driving demand for specialized CDMO expertise. Gene replacement, RNA-based therapies, and enzyme replacement treatments are particularly prominent in this segment. CDMOs with the ability to produce small-batch, highly targeted therapies are essential in bringing these drugs to clinical trials. The high prevalence of rare genetic diseases in pediatric populations further fuels investment in this space. As a result, genetic disorder therapies remain the largest driver of CDMO activity. Represent the dominant therapeutic area in the rare disease small-batch CDMO market, as the majority of rare diseases have a genetic basis. Biotech firms are increasingly focusing on therapies targeting specific mutations, driving demand for specialized CDMO expertise. Gene replacement, RNA-based therapies, and enzyme replacement treatments are particularly prominent in this segment. CDMOs with the ability to produce small-batch, highly targeted therapies are essential in bringing these drugs to clinical trials. The high prevalence of rare genetic diseases in pediatric populations further fuels investment in this space. As a result, genetic disorder therapies remain the largest driver of CDMO activity.
Rare oncology is emerging as the fastest-growing therapeutic area within the rare disease CDMO market, fueled by breakthroughs in precision medicine and immuno-oncology. While oncology is a broad field, rare cancers often lack effective treatments, creating significant unmet medical needs. CDMOs are increasingly supporting small-batch oncology projects that focus on targeted therapies, antibody-drug conjugates, and cell-based approaches. Orphan drug incentives for rare cancers have further boosted activity in this space. The complexity of oncology drugs aligns with the capabilities of advanced CDMOs offering specialized manufacturing. As a result, rare oncology is the fastest-expanding therapeutic area in terms of CDMO demand.
Customer Type Insights
Why Are Small Biotech/Startups Dominating the Market?
Small biotech companies dominate the customer base of the rare disease small-batch CDMO market, as they are the primary drivers of innovation in this field. With limited infrastructure and resources, these companies rely heavily on CDMOs to provide manufacturing, analytical, and regulatory services. Rare disease programs often begin in small biotech labs funded by venture capital or patient foundations. CDMOs provide these firms with cost-effective access to specialized facilities, eliminating the need for heavy upfront investment. Partnerships with CDMOs also allow small biotechs to focus on discovery and clinical strategy. This dynamic makes small biotechs the cornerstone customers of rare disease CDMOs.
Virtual biotech companies are the fastest-growing customer type in the rare disease CDMO market, representing a new model of drug development. These companies operate with minimal internal infrastructure, outsourcing nearly all activities—from discovery to manufacturing to specialized partners. For rare disease projects, where funding is often limited and speed is critical, virtual biotechs find CDMOs to be indispensable allies. This model allows them to remain lean while accessing world-class expertise and infrastructure. CDMOs with integrated service portfolios are especially attractive to virtual biotechs. As a result, demand from this customer type is expanding rapidly.
Contract Model Insights
Why Fee-for-Service & Fixed-Price Dominating the Rare Disease Small-Batch CDMO Market?
Fee-for-service and fixed-price models dominate the rare disease CDMO market due to their predictability and simplicity. Sponsors, especially small and mid-sized biotechs, prefer clear cost structures to manage limited budgets effectively. CDMOs offering fixed pricing ensure transparency and reduce financial risk for early-stage companies. This model aligns well with discrete, small-batch projects common in rare disease pipelines. Many CDMOs have built their business models around this arrangement, making it the most widely used contract type. As a result, fee-for-service continues to dominate the contractual landscape.
Strategic capacity reservation and hybrid risk-sharing contracts are emerging as the fastest-growing models in the rare disease CDMO market, because sponsors are increasingly securing manufacturing slots in advance to mitigate supply bottlenecks, especially for gene and cell therapies. Risk-sharing agreements, where CDMOs and clients share development or commercial risk, are also gaining traction. This model fosters deeper collaboration and aligns incentives between both parties. The complexity and high cost of developing treatments for rare diseases make these innovative contracts particularly attractive. As a result, this segment is experiencing rapid expansion.
Regional Insights
How Is North America Leading the Rare Disease CDMO Landscape?
North America holds the dominant position in the rare disease small-batch CDMO market, due to its advanced biotechnology ecosystem, strong regulatory framework, and robust funding for orphan drug development. The region benefits from a high concentration of pharmaceutical innovators and specialized CDMOs with deep expertise in gene and cell therapy manufacturing. Favourable policies such as the Orphan Drug Act have incentivized companies to invest heavily in rare disease pipelines. Additionally, the presence of well-established clinical trial networks accelerates the transition of therapies from research to commercialization. Partnerships between biotech startups and large pharmaceutical companies are further driving demand for smaller-batch CDMO capabilities. The focus on personalized therapies continues to strengthen North America's leadership in this space.
The region's dominance is also attributed to its early adoption of digital health and AI-driven manufacturing platforms. These technologies enhance quality control, streamline small-scale production, and reduce the time-to-market for rare disease drugs. Strong patient advocacy groups in North America play a pivotal role in shaping policy, raising awareness, and funding research initiatives. Furthermore, large venture capital investments and grants are fueling the growth of early-stage biotech companies that rely heavily on CDMO support. Regulatory agencies, such as the FDA, have been proactive in piloting new pathways that reduce clinical hurdles, giving North America a distinct advantage. Together, these factors ensure that the region remains at the forefront of innovation and commercial success in the rare disease CDMO market.
How Is the Asia Pacific Establishing Its Roots in the Rare Disease Small-Batch CDMO Market?
Asia Pacific is emerging as the fastest-growing region in the rare disease small-batch CDMO market, driven by the rising healthcare investment and expanding biotechnology capabilities. Governments across the region are increasingly prioritizing rare disease awareness, leading to stronger policy frameworks and funding for research. The growing burden of rare genetic disorders is also prompting demand for specialized therapies, thereby fueling CDMO collaborations. Pharmaceutical companies are setting up small-batch manufacturing facilities in key markets like China, India, Japan, and South Korea to capitalize on cost efficiencies. The region's expanding clinical trial capacity further supports the accelerated development of orphan drugs. Moreover, a rising middle-class population with increased access to healthcare is driving market growth.
The growth momentum is amplified by the region's rapid adoption of AI, automation, and digital platforms in pharmaceutical manufacturing. Asia-Pacific CDMOs are increasingly forming partnerships with global biotech firms to provide cost-effective yet high-quality solutions for rare disease therapies. Local governments are also offering tax incentives and policy support to attract foreign investments in advanced manufacturing. Rising collaborations between academia, hospitals, and private players are strengthening research pipelines and clinical readiness. The focus on expanding capabilities for next-generation therapies, such as RNA-based and gene therapies, is positioning the Asia-Pacific as a global innovation hub. With its combination of affordability, scale, and technological adoption, the region is set to become a critical growth engine for the rare disease small-batch CDMO market.
Rare Disease Small-Batch CDMO Market Companies

- Lonza.
- Catalent.
- Thermo Fisher Scientific / Patheon.
- WuXi Biologics / WuXi AppTec.
- Samsung Biologics.
- FUJIFILM Diosynth Biotechnologies.
- Ajinomoto Bio-Pharma Services (ABP)
- BioVectra
- Alcami.
- CordenPharma
- Charles River Laboratories
- Novasep / Combi-blocks
- Aenova / Vetter
- PCI Pharma Services
- Jubilant Biosys / Jubilant HollisterStier
Recent developments
- In July 2025, Charles River Laboratories International entered into a plasmid DNA contract development and manufacturing agreement. With Elly's team, a parent-led foundation dedicated to finding a cure for a neurodevelopmental disorder with regression, abnormal movements, loss of speech, and seizures, a rare genetic condition. Through Charles River's cell and gene therapy accelerator program, Elly's team leveraged the company's established CDMO expertise and advisory services to produce essential starting materials in support of an upcoming Phase I clinical trial.(Source: https://www.morningstar.com)
- In May 2025, Primal Pharma expects modest single-digit growth in its contract development and manufacturing business in FY2026, as near-term uncertainties weigh on performance. The company noted that clients are delaying key decisions due to ongoing concerns surrounding U.S. pricing pressures and tariff policies.(Source: https://www.livemint.com)
Segments Covered in the Report
By Service Type
- Process development & optimization
- Analytical development & QC (stability, method validation)
- Clinical-scale API / drug substance manufacturing (GMP)
- Commercial-scale API manufacturing (GMP)
- Formulation development & drug product (oral, sterile, transdermal)
- Aseptic fill-finish / sterile terminal fill
- Packaging & secondary packaging
- Regulatory affairs & CMC consulting
- Supply chain & cold-chain logistics
By Modality/Technology
- Small molecules (API + finished dosage)
- Biologics (mAbs, proteins)
- Cell Therapies (Autologous/Allogeneic)
- Viral-Vector Gene Therapies (AAV, Lentiviral)
- Oligonucleotides & ASOs/siRNA
- mRNA therapeutics & vaccines
- Conjugates (ADC, Radioconjugates)
By Batch/Scale Type
- Micro/Bench Scale (Preclinical)
- Clinical Small-Batch (Phase I/II) — Single-Lot Supply For Trials/Compassionate Use
- Commercial Small-Batch (Or Niche Commercial)
- Campaign Manufacturing (Multiple Small Runs)
By Development Stage
- Discovery / Preclinical Support
- IND/CTA Enabling (toxicology, GMP batches)
- Clinical Supply (Phases I–III)
- Tech Transfer & Scale-Up To Commercialization
- Post-Approval/ Commercial Supply (Limited Volumes)
By Therapeutic Area/Indication
- Genetic/Neurodegenerative Rare Diseases
- Rare Oncology / Hematologic Disorders
- Metabolic & Enzyme-Replacement Indications
- Ophthalmology, Rare Cardiomyopathies, And Rare Pulmonary Diseases
By Customer Type
- Small Biotech / Orphan-Drug Startups
- Virtual Biotechs / Academic Spinouts
- Mid-Sized Pharma/Specialty Pharma
- Large Pharma (Outsourcing Niche Programs)
By Contract Model
- Fee-For-Service (Time & Materials)
- Fixed-Price Project / Milestone-Based
- Risk/Reward (Revenue-Share, Royalty)
- Long-Term Strategic Supply Agreements/Capacity Reservation
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Rest of World
 Get a Sample
Get a Sample
 Table Of Content
Table Of Content