Military 3D Printing Market Size and Forecast 2025 to 2034
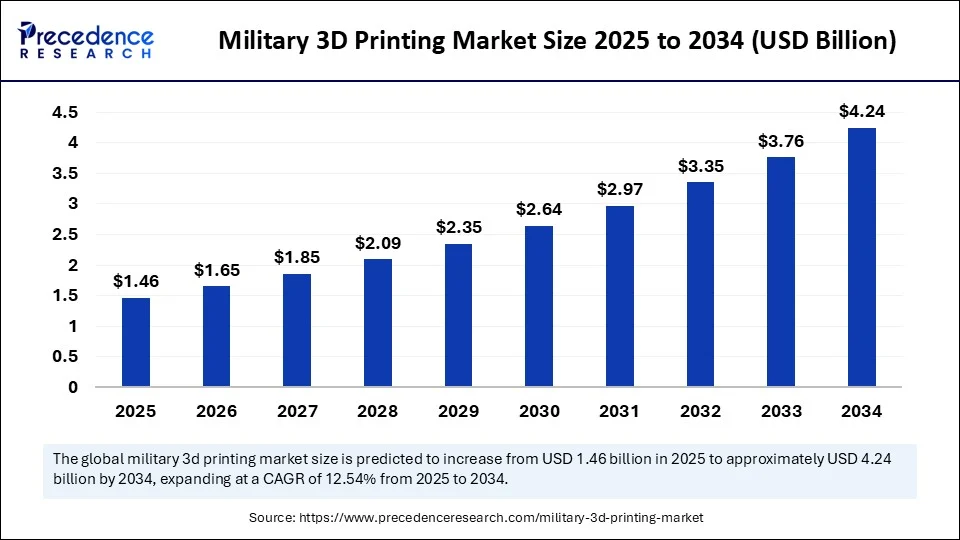
The global military 3D printing market size was calculated at USD 1.30 billion in 2024 and is predicted to increase from USD 1.46 billion in 2025 to approximately USD 4.24 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 12.54% from 2025 to 2034. The market for military 3D printing is emerging as a transformative force in modern defense strategies, reshaping how armed forces design, manufacture, and maintain equipment.
Military 3D Printing Market Key Takeaways
- In terms of revenue, the global military 3D printing market was valued at USD 1.30 billion in 2024.
- It is projected to reach USD 4.24 billion by 2034.
- The market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 12.54% from 2025 to 2034.
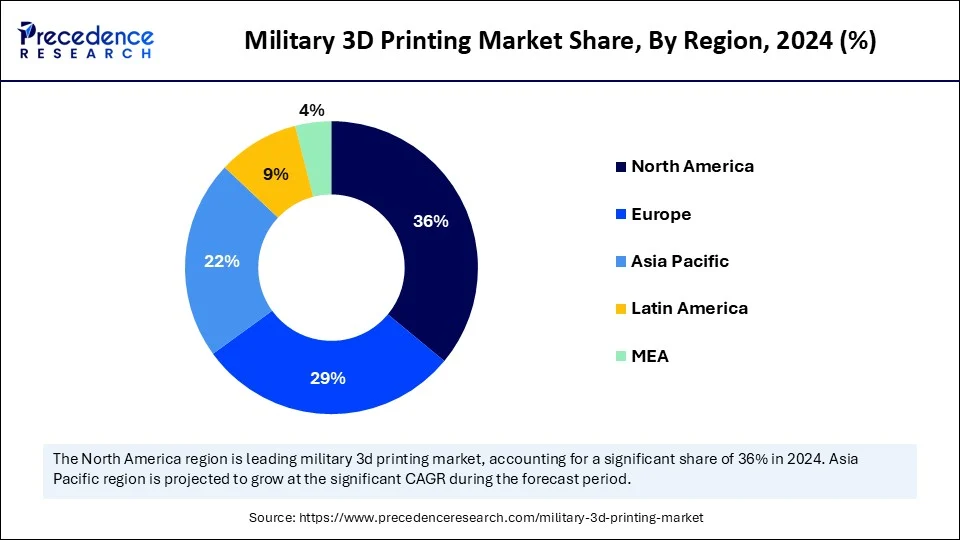
- North America dominated the military 3D printing market with the largest market share of 36% in 2024.
- Asia-Pacific is anticipated to grow at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period.
- By technology, the fused deposition modeling (FDM) segment led the market in 2024.
- By technology, the direct metal laser sintering (DML) / selective laser melting (SLM) segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR in the market during the forecast period of 2025 to 2034.
- By material, the metal & alloys segment accounted for a considerable share of the market in 2024.
- By material, the ceramics & composites segment is projected to experience the highest growth CAGR between 2025 and 2034.
- By application, the functional parts manufacturing segment captured the biggest market share in 2024.
- By application, the medical & bioprinting segment is set to experience the fastest CAGR from 2025 to 2034.
- By end-user, the army segment contributed the highest market share in 2024.
- By end-user, the air force segment is anticipated to grow with the highest CAGR during the studied years.
- By distribution model, the direct procurement segment generated the major market share market in 2024.
- By distribution model, the additive manufacturing service providers segment is projected to expand rapidly in the coming years.
How Is AI Reshaping Military 3D Printing?
Artificial Intelligence is amplifying the potential of military 3D printing by enabling smarter design, predictive maintenance, and optimization of the manufacturing process. AI-powered algorithms can stimulate battlefield conditions to refine prototypes, ensuring equipment durability and performance before physical production. Machine learning models also streamline supply chain planning, enabling the precise prediction of spare part requirements. Additionally, AI enhances quality control by detecting flaws during production, thereby reducing waste and ensuring mission-critical reliability. The convergence of AI and 3D printing further supports autonomous manufacturing units capable of operating in remote or conflict zones. By accelerating production cycles and reducing human errors, AI is transforming military 3D printing into a highly intelligent, adaptive, and resilient technology.
- In January 2024, the Indian Army designated 2024 as the year of technology absorption, underscoring, underscoring.(Source: https://www.financialexpress.com)
U.S. Military 3D Printing Market Size and Growth 2025 to 2034
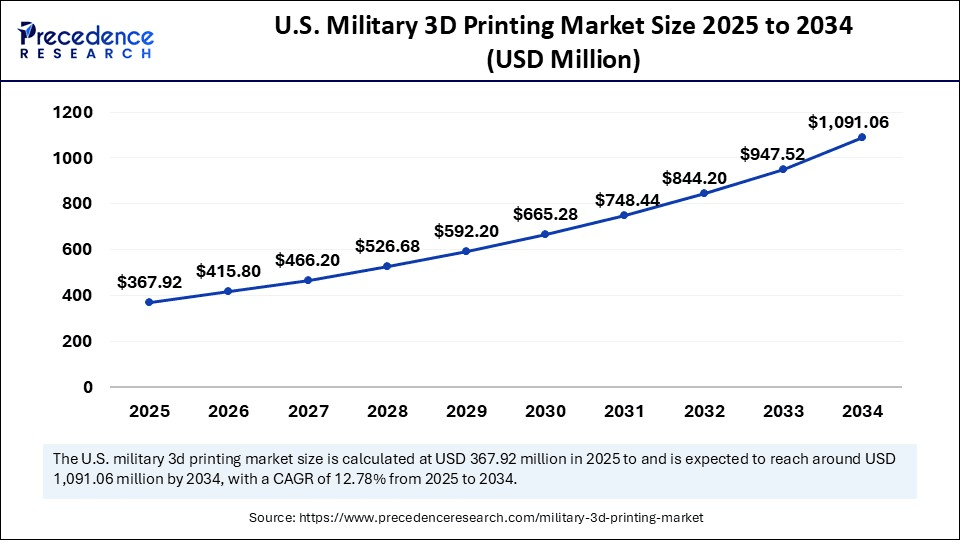
The U.S. military 3D printing market size was evaluated at USD 327.60 million in 2024 and is projected to be worth around USD 1,091.06 million by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 12.78% from 2025 to 2034.
Why Does North America Lead the Military 3D Printing Market?
By region, North America dominated the global market in 2024, driven by its advanced defense infrastructure and strong investment in research and development. The United States Department of Defense has been at the forefront of adopting additive manufacturing for critical applications, from aircraft maintenance to naval operations. Strong collaborations between defense contractors, startups, and academic institutions further accelerate innovation. In addition, the region benefits from a robust ecosystem of technology providers and advanced material manufacturers. The push toward greater defense self-reliance and modernization of legacy systems also supports market expansion. As North America continues to prioritize defense readiness, 3D printing remains central to its strategic initiatives.
- In August 2025, the U.S. Army will have progressively incorporated the framework. This strategy not only enhances military capability but also opens up compelling career pathways for enlisted personnel. According to a report by the 3D printing industry, the army has launched a new lethality course, designed to equip participants with specialized skills in both drone technology and 3D printing.(Source: https://www.tomshardware.com)
Can Asia-Pacific Sustain Its Position As the Fastest-Growing Market?
Asia-Pacific is emerging as the fastest-growing region in the military 3D printing market, fueled by rising defense budgets and increasing technological adoption. Countries such as China, India, South Korea, and Japan are investing heavily in advanced manufacturing to strengthen their defense capabilities. The region is witnessing the rapid integration of 3D printing in naval, aerospace, and land-based defense projects. Local defense firms are collaborating with global players to establish indigenous manufacturing capabilities. Furthermore, geopolitical tensions and border security challenges are driving demand for quick, efficient, and cost-effective defense solutions. As governments push for military modernization and self-sufficiency, the Asia-Pacific is expected to sustain its growth momentum and become a pivotal hub for defense 3D printing.
Market Overview
The global military 3D printing market covers the adoption of additive manufacturing technologies for defense applications, including design, prototyping, and production of spare parts, weapons components, medical equipment, and lightweight structures. 3D printing in the military enables rapid manufacturing in remote or battlefield environments, reduces logistics burdens, lowers costs of spare part inventories, and supports customization of mission-critical equipment. Growth is driven by defence modernization programs, advancements in metal and polymer 3D printing, and the demand for on-demand, decentralized manufacturing for enhanced operational readiness.
The military 3D printing market is witnessing robust growth, primarily fueled by defense modernization programs and the need for agile manufacturing solutions. Governments are increasingly investing in additive manufacturing to reduce dependency on lengthy procurement cycles. 3D printing allows for the production of spare parts, prototypes, and mission-specific equipment directly at military bases or forward operating locations. This agility not only enhances operational readiness but also reduces downtime for critical equipment. Furthermore, Integration with advanced materials such as high-performance polymers and metals has expanded the scope of military applications. As militarians across the world aim for greater efficiency and self-reliance, 3D printing stands as a cornerstone technology reshaping defense manufacturing.
Market Key Trends
- Rising adoption of additive manufacturing for rapid prototyping and spare parts production.
- Integration of lightweight composite and mental materials of enhanced durability.
- Deployment of mobile 3D printing units in remote and battlefield environments.
- Increased collaboration between defense contractors, startups, and research institutions.
- Growing emphasis on cybersecurity for protecting digital design fit.
- Expansion of 3D printing applications beyond equipment into drones, vehicles, and weapon systems.
Market Scope
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size by 2034 | USD 4.24 Billion |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 1.46 Billion |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 1.30 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate from 2025 to 2034 | CAGR of 12.54% |
| Dominating Region | North America |
| Fastest Growing Region | Asia Pacific |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | Technology, Material, Application, End-User, Distribution Model, and Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Market Dynamics
Drivers
Redefining Military Logistics Through On-Demand Manufacturing
A major driver of this market is the pressing need to streamline military logistics and reduce reliance on vulnerable global supply chains. Traditional defense procurement is time-consuming and costly, often leading to delays in critical missions. 3D printing resolves this by allowing militaries to manufacture spare parts and mission-specific tools directly on-site, drastically reducing turnaround time. It also helps eliminate the risks associated with transporting bulky inventories across dangerous terrains. The technology empowers armed forces with flexibility, resilience, and operational independence. As defense organizations seek to achieve faster response times, the on-demand nature of 3D printing becomes a strategic advantage.
- In April 2025, amid the historic settings for Perl Harbor's Ford Island, the U.S. Army conducted a landmark demonstration showcasing autonomous ship-to-shore resupply operations during Project Convergence Capstone. The exercise highlighted a forward-looking vision where logistics become smarter, faster, and safer, driven by autonomous platforms functioning seamlessly across vast distances.(Sources: https://www.army.mil)
Restraint
Security and Standardization Hurdles in Defense Additive Manufacturing
Despite its potential, the military 3D printing market faces challenges related to cybersecurity, regulatory frameworks, and quality standardization. Digital blueprints used for additive manufacturing are highly vulnerable to cyber threats, making intellectual property protection a critical concern. Moreover, the lack of uniform standards in 3D printed components raises questions about safety and reliability in combat conditions. High initial costs of deployment, combined with the need for a skilled workforce, further restrict widespread adoption. Additionally, geopolitical restrictions on material supply chains could hinder consistent production. Until these barriers are addressed, full-scale adoption across militaries may progress at a measured pace.
Opportunity
Fueling Defense Modernization With Additive Innovation
The military 3D printing market presents vast opportunities in line with global defense modernization programs. The ability to customize equipment and upgrade legacy systems with minimal resources aligns with the evolving needs of modern warfare. Emerging opportunities lie in printing advanced weapon components, unmanned aerial vehicles, and lightweight armored structures. Additionally, 3D printing supports sustainable initiatives by minimizing material waste and reducing carbon footprints in defense manufacturing. The expansion of battlefield-ready mobile printing units also opens new frontiers for real-time innovation. With continuous research into advanced materials and bioprinting, the market is poised to unlock futuristic opportunities that redefine defense capabilities.
- In August 2025, Mr. Deasy is steering the Pentagon's modernization agenda, particularly its drive to integrate commercial, enterprise-level cloud capabilities. Yet, cloud adoption is only one element of a broader, AI-driven vision. The Department of Defense seeks to move beyond treating computers as mere tools and instead regard them as true partners in warfare. “As artificial intelligence advances, we must redefine the role of computers in warfighting. How will they become our partners? Through reasoning, enhanced performance robustness, and even applications such as brain-controlled systems or prosthetic limbs,” Mr. Deasy explained during the DoDIIS Worldwide Conference in Omaha, Nebraska, as reported by FedScoop.(Source: https://www.beckershospitalreview.com)
Technology Insights
Why Is Fused Deposition Modeling Dominating the Military 3D Printing Market?
The fused deposition modeling (FDM) segment held a dominant presence in the military 3D printing market in 2024, driven by its cost-effectiveness and ease of use. The technology enables rapid prototyping and the creation of durable parts, making it a reliable choice for defense applications. Its widespread adoption stems from the ability to produce lightweight components with significant material efficiency. The relative simplicity of the process also reduces operational risks and maintenance challenges. Defense units prefer FDM for quick on-site part replacement, ensuring operational continuity in remote or combat zones. As a result, FDM remains the cornerstone of military additive manufacturing strategies.
Fused deposition modeling dominance is also strengthened by its compatibility with multiple thermoplastic materials. This flexibility allows military engineers to customize parts for various applications, from field tools to structural components. The affordability of printers and materials ensures accessibility across different defense branches. Moreover, the scalability of FDM makes it viable for both small-scale and large-scale projects. Training personnel in FDM technology is relatively straightforward, further increasing its adoption. Thus, its balance of practicality, versatility, and cost-efficiency cements FDM's leadership in the market.
The direct metal laser sintering (DML) / selective laser melting (SLM) is the fastest-growing in the military 3D printing sector. Its ability to produce high-strength, complex metal parts is revolutionizing defense manufacturing. Unlike conventional processes, DMLS allows for intricate geometries and lightweight designs without sacrificing durability. This capability is particularly vital in aerospace and armored vehicle applications. The demand for precision and high-performance equipment is accelerating the adoption of this technology. Consequently, DMLS is gaining prominence as a transformative force in modern defense logistics.
Material Insights
Why Metals & Alloys Account for a Large Share of the Military 3D Printing Market?
The metal & alloys segment accounted for a considerable share of the market in 2024, due to its unmatched strength and performance characteristics. These materials are essential for manufacturing structural components, weapons parts, and aerospace-grade equipment. Their durability ensures reliability in extreme battlefield conditions. The defense sector relies on metal-based printing to replace parts that must withstand high stress and heat. This makes metals indispensable in ensuring operational readiness across diverse environments. Accordingly, metals and alloys form the backbone of defense-related additive manufacturing.
The ceramics & composites are the fastest-growing in the military 3D printing sector. Their unique combination of lightweight properties and heat resistance makes them attractive for specialized applications. These materials are particularly suited for protective armor, thermal shielding, and high-performance aerospace components. The versatility of composites enables tailored designs that balance strength and weight. Military research is increasingly focused on exploiting these advantages. As a result, ceramics and composites are carving out a critical role in future defense manufacturing.
Application Insights
Why Functional Parts Manufacturing Led the Military 3D Printing Market?
The functional parts manufacturing segment led the military 3D printing market, driven by its ability to produce mission-critical components on demand, ensuring continuous operations in combat and remote environments. Parts such as weapon handles, vehicle spares, and structural elements drastically reduce dependency or customize traditional supply chains. It also enhances flexibility by allowing the military to customize components for unique requirements. Thus, functional parts manufacturing remains at the forefront of defense applications.
The dominance of this application is also linked to its role in extending equipment lifecycles. By producing replacement parts on-site, downtime is significantly minimized. It reduces the logistical costs of transporting spares across long distances. Additionally, the military gains independence from external suppliers during emergencies. The adaptability of 3D printing in producing diverse functional parts further strengthens this segment. As a result, it continues to dominate the defense application landscape.
The medical & bioprinting segment is set to experience the fastest rate of market growth from 2025 to 2034, driven by the technology that enables the creation of customized implants, prosthetics, and even tissue models for battlefield medical care. This advancement is particularly significant for treating soldiers injured This advancement is particularly significant for treating soldiers injured in combat zones. Bioprinting supports personalized medicine by tailoring solutions to individual needs. Its potential to revolutionize trauma management and recovery is driving rapid growth. Consequently, medical bioprinting is gaining momentum as a critical defense application.
The growth of this field is also propelled by advancements in biomaterials. On-site printing of medical solutions reduces the time required to deliver emergency care. It enhances battlefield survival rates by offering immediate treatment capabilities. The long-term vision includes printing organs and complex tissues for rehabilitation. Partnerships between defense and medical research bodies are accelerating adoption. Therefore, medical bioprinting is set to be the most dynamic segment in the coming years.
End-User Insights
Why is the Army registering a lead in the Military 3D Printing Market?
The army segment is leading the military 3D printing market, driven by its vast requirements for vehicle components, field equipment, and combat tools drive large-scale adoption. The Army relies heavily on additive manufacturing to ensure operational readiness in diverse terrains. Quick replacement of parts in forward bases significantly enhances efficiency. Moreover, the Army's emphasis on cost-effective maintenance fuels further demand. Thus, the Army remains the largest stakeholder in defense additive manufacturing.
This dominance is reinforced by the Army's focus on tactical innovation. The branch continues to integrate 3D printing into both combat and support roles. Its large troop size amplifies the need for consistent and reliable parts availability. The ability to produce lightweight and durable materials contributes to enhanced mobility. In addition, the Army's large budget allocation sustains its leadership in this sector. Consequently, the Army continues to dominate as the primary end user.
The air force segment is the fastest-growing in the military 3D printing sector, owing to the demand stemming from the need for lightweight, high-performance components in aerospace applications. Aircraft require parts that the Air Force is the fastest-growing end user of military 3D printing. Its demand stems from the need for lightweight, high-performance components in aerospace applications. Aircraft require parts that balance durability with fuel efficiency. 3D printing offers a solution by enabling complex geometries and optimized designs. The Air Force also leverages additive manufacturing for rapid prototyping of aerospace technologies. This focus has positioned it as the most dynamic growth segment.
The air force adoption is further boosted by its pursuit of next-generation aviation systems. On-demand part production reduces downtime for critical aircraft. This directly enhances mission readiness and cost efficiency. Its strong alignment with advanced material technologies accelerates implementation. The Air Force's emphasis on precision and innovation aligns perfectly with additive manufacturing. As a result, it is emerging as the fastest-growing defense user segment.
Distribution Channel Insights
Why Is Direct Procurement Dominating the Military 3D Printing Market?
The direct procurement has become a dominant force in the military 3D printing applications, and defense organizations prefer maintaining full control over sensitive manufacturing processes. This approach ensures confidentiality and security in producing classified components. On-site production also eliminates delays linked to outsourcing. It gives the military greater flexibility and adaptability in responding to immediate needs. Consequently, in-house production also eliminates delays linked to outsourcing. It gives the military greater flexibility and adaptability in responding to immediate needs. Consequently, in-house production remains the dominant mode in defense additive manufacturing.
The additive manufacturing Service Providers are the fastest-growing in the military 3D printing sector, given the fact that they offer specialized expertise and advanced facilities to defense organizations. Outsourcing to these providers reduces the need for heavy in-house investments. It also allows access to cutting-edge technologies and materials not always available internally. With defense agencies seeking flexible partnerships, service providers are rapidly gaining traction. Therefore, they represent the fastest expanding channel in the market.
Military 3D Printing Market- Value Chain Analysis
- Raw Material Sourcing
Raw materials for 3D printing span plastics, metals such as aluminum, steel, titanium, and their alloys, along with ceramics and other specialized substances, typically available in powders, filaments, or resin forms. These materials are generally sourced through conventional supply chain models, though there is a rising emphasis on demand procurement and recycling military waste, such as packaging materials and bullet castings. This approach aims to create a secure, sustainable, and localized supply of essential parts directly on the battlefield, thereby minimizing lead times, enhancing operational agility, and reducing logistical burdens.
- Component Manufacturing
Component manufacturing in military 3D printing is carried out through a structured yet highly flexible process that blends advanced additive manufacturing technologies with strict defense-grade standards. Like for example, design and digital modeling in every component begin with a CAD or digital blueprint. Engineers often use AI-driven simulations to test stress points, aerodynamics, or thermal resistance before actual production.
- Testing and Certifications
Testing and certification of military 3D printed components is a critical phase to ensure that every part meets stringent defense and battlefield requirements. Once a component is manufactured, it undergoes mechanical testing such as tensile, fatigue, and impact strength assessments to validate durability under combat stress. Specialized thermal and environmental evaluations are performed to confirm that the part can withstand extreme temperatures, humidity, corrosion, and even chemical exposure.
Military 3D Printing Market Companies

- 3D Systems Corporation
- Stratasys Ltd.
- EOS GmbH
- ExOne (Desktop Metal)
- GE Additive
- SLM Solutions Group AG
- Renishaw plc
- Materialise NV
- HP Inc.
Recent Development
- In August 2025, Deputy Prime Minister Mai Van Chinh announced that the upcoming national exhibition, themed 80-Year Journey of Independence, Freedom, and Happiness, will celebrate the nation's remarkable achievements across diverse fields, including defence, security, economy, diplomacy, science and technology, healthcare, education, culture, sports, and tourism. Scheduled to take place at the Vietnam Exposition Centre from August 28 to September 5, the exhibition will serve not only as a major cultural and political event but also as a meaningful occasion for the Party, military, and people to reflect on the nation's proud and glorious historical journey, Chinh told the Vietnam News Agency.(Source: https://en.vietnamplus.vn)
Segments Covered in the Report
By Technology
- Stereolithography (SLA)
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
- Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DML) / Selective Laser Melting (SLM)
- Electron Beam Melting (EBM)
- Binder Jetting & Others
By Material
- Metals & Alloys (Titanium, Aluminum, Steel)
- Polymers (PLA, ABS, Nylon, High-Performance Polymers)
- ceramics & composites
- Hybrid Materials
By Application
- Prototyping & Concept Modeling
- Functional Parts Manufacturing (spare parts, weapons components)
- Tooling & Fixtures
- medical & bioprinting (field hospitals, prosthetics)
- Unmanned Aerial / Ground Vehicle Components
- Customized Protective Gear & Equipment
By End-User
- Army
- Navy
- Air Force
- Special Forces & Defense R&D Units
By Distribution Model
- Direct procurement (OEMs to the Defense Force
- Defense Contractors & Integrators
- Additive Manufacturing Service Providers
- Research Collaborations with Academia/Defense Labs
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Ask For Sample
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
 Get a Sample
Get a Sample
 Table Of Content
Table Of Content
 sales@precedenceresearch.com
sales@precedenceresearch.com
 +1 804-441-9344
+1 804-441-9344
 Schedule a Meeting
Schedule a Meeting