Materials for Printed Flexible Electronics Market Size and Forecast 2025 to 2034
The materials for printed flexible electronics market is advancing next-generation technology with innovative conductive materials, flexible substrates, and scalable fabrication techniques that enable lightweight and bendable electronic devices. The growth of the market is driven by the increasing development of flexible electronics.
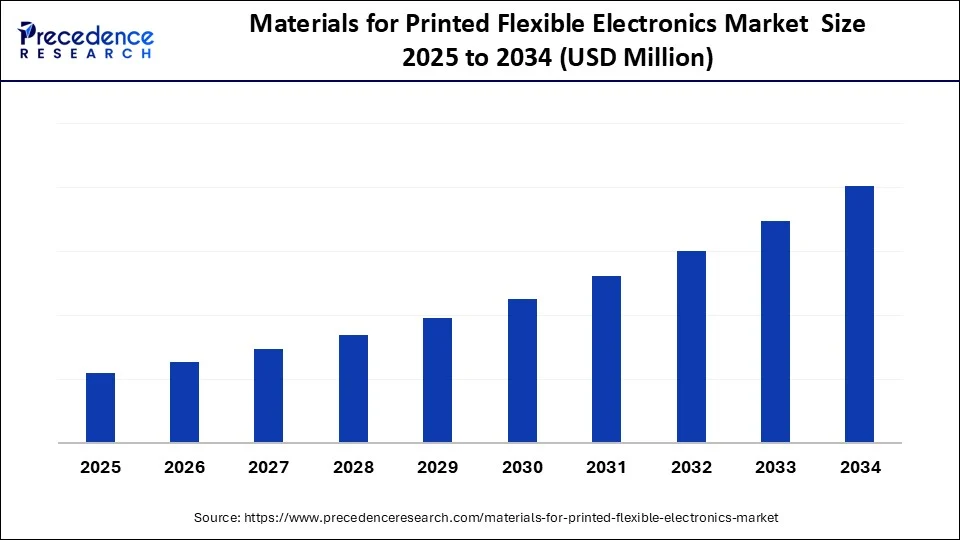
Materials for Printed Flexible Electronics Market Key Takeaways
- Asia Pacific dominated the materials for printed flexible electronics market with the largest market share of 47% in 2024.
- The Middle East and Africa is expected to expand at the fastest CAGR between 2025 and 2034.
- By material type, the conductive materials segment held the biggest market share in 2024.
- By material type, the semiconductive materials segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR between 2025 and 2034.
- By printing technique compatibility, the screen-printing-compatible materials segment generated the major market in 2024.
- By printing technique compatibility, the aerosol jet and 3D printable materials segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR between 2025 and 2034.
- By application, the displays (OLED, E-paper) segment contributed the highest market share in 2024.
- By application, the wearable electronics segment is expected to grow at the fastest rate between 2025 and 2034.
- By end-use industry, the consumer electronics segment captured the largest market share in 2024.
- By end-use industry, the energy and utilities segment is expected to grow at a remarkable CAGR between 2025 and 2034.
How is AI Impacting the Materials for Printed Flexible Electronics Market?
Artificial intelligence is becoming an integral force in advancing materials for printed flexible electronics, bridging the gap between innovation and scalability. AI-driven simulator tools are streamlining the design of flexible electronic circuits. By predicting the electric, mechanical, and thermal behavior of materials, AI reduces prototyping time and accelerates product development, allowing for faster market entry. Machine learning, on the other hand, is now being used to identify and optimize new materials with enhanced conductivity, durability, and flexibility. This predictive approach allows researchers to formulate better conductive inks or substrates that withstand repeated bending and wear. The inspection systems using computer vision enable real-time quality control during the printing process. These systems detect micro-defects, inconsistencies in ink distribution, and alignment issues with high precision, thus minimizing waste and improving yields.
Manufacturers can analyze user data and adjust production parameters in real time to cater to personalized, flexible devices. This includes wearables customized for specific health metrics or consumer preferences, enabled by smart, adaptive manufacturing lines. When embedded into printed flexible sensors, AI enables intelligent data processing at the edge. This is revolutionizing applications like smart textiles, medical diagnostics, and environmental monitoring by offering real-time, adaptive feedback mechanisms in ultra-thin formats. Moreover, AI accelerates the discovery of new materials with advanced properties.
Market Overview
The materials for printed flexible electronics market comprises a range of functional and structural materials used in the fabrication of electronic components on flexible substrates using additive or printing-based manufacturing techniques. These materials include conductive inks, semiconducting polymers, dielectrics, substrates, and encapsulation layers that enable the production of thin, bendable, and lightweight electronic devices for applications such as wearables, displays, sensors, RFID, photovoltaics, and automotive interiors. The market is experiencing robust growth, driven by the increasing demand for flexible electronic components across various industries. One of the primary sectors contributing to this growth is consumer electronics.
As consumers seek more portable, lightweight, and durable devices, manufacturers are turning to flexible electronic materials to innovate new products and enhance user experiences. The automotive industry is also rapidly adopting printed flexible electronics. These materials are crucial for developing flexible displays, sensors, and other components that can be integrated into vehicles, improving functionality and safety features. Healthcare is another significant sector benefiting from these advancements. Flexible electronic materials are being utilized in wearable health devices, medical sensors, and other healthcare applications, offering more comfort, adaptability, and improved performance.
Key Market Trends
- Increasing Adoption of Organic and Conductive Polymers: The market is witnessing a surge in the use of flexible, lightweight, and conductive polymers, such as PEDOT:PSS, for various electronic applications due to their excellent flexibility and conductivity.
- Growth in Silver and Copper Nanomaterials: Silver nanowires and copper inks are becoming popular substitutes for traditional materials, offering better electrical performance and cost efficiency for printed conductive layers.
- Advancements in Dielectric and Substrate Materials: Innovative dielectric materials with enhanced flexibility and stability are being developed to improve device durability and performance in flexible electronics.
- Environmental Sustainability and Eco-friendly Materials: There is a rising demand for sustainable materials, including biodegradable substrates and eco-friendly polymers, driven by environmental regulations and consumer preferences.
- Expansion of Hybrid Material Technologies: Integrating multiple materials such as nanocomposites and multilayer assemblies to enable multifunctional flexible electronic devices with improved performance.
- Customization Material Development: Material formulations are increasingly being tailored to meet specific requirements for applications like wearables, flexible displays, and medical devices.
Market Scope
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Dominating Region | Asia Pacific |
| Fastest Growing Region | Middle East and Africa |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered | Material Type, Printing Technique Compatibility, Application, End-Use Industry, and Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa |
Market Dynamics
Drivers
Rising Demand for Energy-Efficient Devices
The growing demand for lightweight, flexible, and energy-efficient electronic devices is a primary driver of the materials for printed flexible electronics market. Unlike traditional rigid circuits, flexible electronics can be conformed to curved surfaces or embedded into clothing, packaging, and even skin patches. This adaptability has opened a broad spectrum of applications, particularly in the healthcare and wearable tech industries. One of the most influential forces shaping this market is the rise in the adoption of wearable medical devices. With an aging global population and increasing awareness of personal health, consumers are turning to continuous monitoring solutions. Flexible biosensors, powered by advanced conductive inks and substrates, allow real-time health tracking in a non-intrusive manner, making them invaluable for preventive medicine.
In addition, the proliferation of smart packaging in consumer goods and pharmaceuticals is fueling market growth. Brands are incorporating flexible printed electronics in packaging to create interactive experiences or ensure product authenticity. These applications demand reliable, printable materials that are low-cost, durable, and environmentally resilient. The automotive sector is also playing a vital role. Flexible materials are being integrated into touch sensors, OLED displays, and in-vehicle health monitors, contributing to smarter, connected vehicles. As automakers shift toward electric and autonomous technologies, they require innovative solutions that are both space-saving and multifunctional.
Restraint
High Costs and the Lack of Standardization
Despite its promising trajectory, the materials for printed flexible electronics market face significant challenges that may hinder its full-scale adoption. Chief among these is the high cost of advanced materials, particularly conductive inks made from silver. These materials offer excellent performance but are expensive to produce, making them less viable for low-margin, mass-market products. Durability and performance consistency are also areas of concern. Flexible electronics must maintain performance even after repeated bending, stretching, or folding. However, some current materials show degradation over time, especially in harsh environments. This reduces their suitability for long-term industrial or outdoor applications, limiting their deployment.
Another issue lies in the lack of universal manufacturing standards. The printing processes and equipment used vary widely depending on the application, which can lead to inefficiencies and incompatibility. This fragmentation slows down adoption and increases production costs, especially for companies trying to scale up their operations. Environmental stability is yet another constraint. Some polymer-based substrates and organic semiconductors are sensitive to moisture and oxygen, requiring complex encapsulation layers. These added layers can increase weight, cost, and complexity, ironically counteracting the advantages of flexibility and simplicity.
Opportunity
Sustainability Trend and Expanding Applications in Various Industries
The shift towards sustainability offers a unique opportunity for the materials for printed flexible electronics market. With industries under pressure to reduce their carbon footprint, materials that are biodegradable, recyclable, or derived from renewable sources are gaining interest. Companies investing in green alternatives to conventional inks and substrates are likely to attract eco-conscious consumers and regulatory support. Healthcare applications continue to present untapped potential, especially in personalized medicine and remote diagnostics. The increasing use of wearable devices for chronic disease management, pregnancy monitoring, and elderly care is expanding the need for skin-compatible, ultra-flexible sensors. These developments are pushing material scientists to explore biocompatible substrates and stretchable inks tailored for medical-grade devices.
Another promising opportunity lies in smart textiles and e-fashion. As technology becomes more discreet and seamlessly integrated into daily life, flexible electronics are being woven into fabrics to track fitness, control temperature, or even charge devices. This opens a new frontier for materials that are not only flexible but also washable, lightweight, and aesthetically compatible. Furthermore, the ongoing digital transformation of industrial processes, often referred to asIndustry 4.0, is driving the demand for flexible sensors in equipment and machinery. Predictive maintenance, asset monitoring, and factory automation are just some of the areas where printed electronics are emerging as key enablers, creating space for material innovations.
Material Type Insights
Why Made Conductive Materials the Dominant Segment in the Materials for Printed Flexible Electronics Market in 2024?
The conductive materials segment dominated the market with a major revenue share in 2024 as they are the essential backbone of printed flexible electronics, enabling the smooth transmission of electric current across flexible substrates. The segment's dominance is also attributed to its widespread use in core components such as sensors, antennas, interconnects, and printed circuits. Silver-based conductive inks are known for their high conductivity and reliability, making them a preferred choice across industries.
The surge in demand for flexible displays and wearable electronics has further reinforced the need for high-performing conductive materials with flexibility, stretchability, and printability traits that modern conductive inks are increasingly delivering. Carbon-based hybrid materials are also being explored to reduce costs while retaining conductive efficiency, thereby expanding applications. The versatility of these materials with multiple printing techniques, such as screen, inkjet, and gravure printing, allows easy integration into existing manufacturing lines. This reduces capital investment for adoption and enables widespread deployment.
On the other hand, the semiconductive materials segment is expected to grow at the fastest rate in the coming years due to its essential role in enabling active components like transistors, diodes, and sensors. As printed electronics move beyond passive functionalities, semiconductive materials become indispensable. The rapid development of organic semiconductors, including polymers like pentacene, has transformed the landscape. These materials offer flexibility, low-temperature processing, and compatibility with large-area printing, making them highly suitable for thin-film transistors used in displays and logic circuits.
Another growth factor is the increasing use of semiconductive materials in stretchable electronics. From smart bandages to bio-integrated devices, these materials are finding applications in the healthcare and wearable sectors, where traditional silicon cannot function effectively due to its rigidity. Researchers are also actively working on improving the charge mobility and environmental stability of these materials.
Printing Technique Compatibility Insights
Why Did the Screen-Printing-Compatible Materials Dominate the Market in 2024?
The screen-printing-compatible materials segment remains the most dominant technique in the printed flexible electronics space, primarily because of its scalability and cost-effectiveness. These materials are ideal for creating relatively thick, robust conductive traces, which are necessary for power lines and antenna structures in wearables and industrial sensors. Moreover, screen printing is well-suited for both high-volume manufacturing and prototype development, offering flexibility in production scale.
Another advantage is the ability to deposit materials on a wide range of substrates, including glass, ceramics, textiles, and plastics. Materials designed specifically for screen printing have optimized rheology, ensuring smooth flow through mesh screens and uniform layer formation on the substrate. Screen-printable materials are also durable and moisture-resistant, which are crucial for applications that must endure bending, stretching, or exposure to external elements. These characteristics make them highly attractive in automotive, medical, and industrial use cases.
Meanwhile, the aerosol jet & 3D printable materials segment is expected to grow at the fastest rate during the forecast period, as these materials enable the printing of ultra-precise, complex geometries, and high-resolution patterns that traditional techniques struggle to achieve. The materials compatible with aerosol jet and 3D printing, typically nano-based conductive inks and UV-curable polymers, are now gaining immense traction. Aerosol jet printing excels in depositing materials onto non-planar and irregular surfaces, which makes it perfect for producing antennas, interconnects, and microfluidic devices on curved or 3D structures. The demand for such high-precision components in aerospace, biomedical implants, and wearables is pushing the adoption of compatible materials.
Similarly, 3D printing is revolutionizing how devices are built layer by layer with multi-material integration. Materials tailored for this technique include photopolymers, thermoplastics, and stretchable inks that offer mechanical robustness along with electrical functionality. One of the main attractions of these materials is their ability to reduce material waste and simplify manufacturing processes by enabling direct-to-object printing. This reduces the need for complex assembly and offers a sustainable, design-flexible alternative.
Application Insights
How Does the Displays Segment Dominate the Materials for Printed Flexible Electronics Market in 2024?
The displays (OLED, E-paper) segment dominated the market in 2024 due to the increased production of high-resolution displays. As consumers and industries gravitate toward lightweight, bendable, and even rollable screens, the demand for high-quality materials to support these innovations is booming. OLED technology, in particular, benefits from printed organic semiconductors and transparent conductive materials. These enable ultra-thin, energy-efficient displays with brilliant color reproduction. OLED panels are increasingly used in smartphones, TVs, wearables, and automotive dashboards.
E-paper displays, known for their low power consumption and sunlight readability, are also on the rise. They require flexible substrates, barrier films, and reflective inks that can operate with minimal energy input, making them ideal for e-readers and smart labels. Materials used in display applications must offer not only electrical performance but also optical clarity, flexibility, and environmental stability. This complexity has led to the creation of highly engineered, multi-layered material systems that can support long-term display use without degradation.
The booming consumer electronics and automotive infotainment markets further strengthen this segment. As flexible displays move toward mainstream adoption, especially in foldable phones and digital signage, they will continue to be the primary driver for advanced printed electronic materials.
On the other hand, the wearable electronics segment is expected to expand at the highest CAGR during the projection period. The growth of the segment is attributed to the rising demand for temperature sensors, pressure sensors, RFID tags, and biosensors. These are designed to adapt, monitor, or react to environmental and user-specific conditions in real-time. Materials for these applications must be highly responsive, flexible, and sensitive to changes in physical or chemical conditions. Innovations in nanomaterials and hybrid polymers have made it possible to produce printed sensors that are not only stretchable but also accurate and cost-effective.
Wearable healthcare devices are a significant contributor to this growth. Flexible ECG patches, hydration sensors, and glucose monitors are becoming increasingly common, particularly in remote or home-based healthcare setups. These rely on variable electronics that can bend, breathe, and move with the body. Smart packaging is another area where variable electronics are rising. Packages equipped with printed sensors can track product freshness, temperature variations, or tampering, enhancing supply chain visibility and consumer trust.
End-Use Industry Insights
What Made Consumer Electronics the Dominant Segment in the Materials for Printed Flexible Electronics Market in 2024?
The consumer electronics segment dominated the market while holding the largest revenue share in 2024, driven by the increased demand for compact, lightweight, and multifunctional gadgets. From foldable smartphones and smartwatches to AR/VR devices and fitness bands, the integration of flexible materials is reshaping how consumers interact with technology. Materials used in these devices must balance performance, aesthetics, and flexibility. High-resolution conductive inks, transparent electrodes, and ultra-thin barrier films allow manufacturers to build sleeker, more durable devices that can fold, stretch, or bend as needed.
The wearable tech revolution is especially significant. Fitness trackers, smart rings, and health-monitoring headbands rely on sensors and circuitry that need to be durable. This fuels the demand for skin-safe, stretchable, and waterproof materials in both casual and medical-grade consumer wearables. Consumer expectations for smarter, personalized, and aesthetically pleasing gadgets are pushing the limits of materials. The rising demand for wireless charging and responsive touch interfaces also supports segmental growth.
Meanwhile, the energy & utilities is the fastest-growing segment. As the world shifts toward sustainable and decentralized energy solutions, the need for flexible electronic components is rising. Flexible printed solar panels are gaining momentum for both urban and rural deployment. The energy & utility sector requires specialized conductive and barrier materials that can withstand outdoor conditions while maintaining efficiency. These materials are helping extend clean energy to places where conventional panels are impractical.Printed sensors are being widely adopted in grid monitoring, pipeline management, and smart metering. These flexible devices must be rugged, low-cost, and durable, pushing demand for specialized polymers and inks that can function reliably in industrial environments. Moreover, the rise of smart grids and energy-efficient buildings is boosting the need for printed lighting and energy-storing materials. This includes flexible OLED lighting panels and printed supercapacitors, requiring innovative organic and inorganic material combinations.
Regional Insights
Why Did Asia Pacific Dominate the Market in 2024?
Asia Pacific dominated the materials for printed flexible electronics market by capturing the largest revenue share in 2024. This is mainly due to its massive manufacturing capabilities and strong supply chain ecosystem. Countries such as China, Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan host some of the world's most advanced electronics production hubs, where large-scale printing, fabrication, and testing facilities coexist seamlessly. A key driver for the region's dominance is the presence of leading display and semiconductor manufacturers. Giants like Samsung, LG, BOE, and Panasonic are continually innovating in flexible displays, sensors, and circuits, creating a constant demand for high-quality conductive inks, substrates, and organic semiconductors.
Governments around the region are also heavily investing in infrastructure development, boosting the need for flexible electronic devices. China's Made in China 2025 plan, Japan's innovation-driven economy, and South Korea's “Digital New Deal” provide funding, tax benefits, and policy support to both established players and start-ups working on flexible electronics. These initiatives ensure technological leadership and domestic demand growth. Additionally, Asia-Pacific benefits from a growing tech-savvy consumer base with a high desire for smart gadgets, wearables, and flexible screens. Urban populations in countries like South Korea and Singapore are adopting emerging technologies quickly, encouraging continuous innovation in healthcare and consumer electronic devices.
How is the Middle East & Africa Emerging as the Fastest-Growing Region?
The Middle East & Africa is emerging as the fastest-growing market for materials for printed flexible electronics. One of the driving forces is the increasing investment in smart infrastructure and digital healthcare across the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries. Governments in the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Qatar are actively pushing for technological diversification beyond oil. Through large-scale initiatives like Saudi Vision 2030 and Dubai's Smart City program, there is a growing focus on smart packaging, wearable health monitoring, and environmental sensing, all of which require advanced, flexible electronic components. Healthcare modernization is also playing a crucial role.
In many African nations, where access to traditional healthcare infrastructure is limited, the demand for wearable medical devices and remote diagnostic solutions is rising. This creates the need for bio-compatible and flexible materials. In addition, the region is becoming a hotspot for solar energy and sustainable technologies. Printed flexible solar panels, which are lightweight and adaptable to varied terrains, are gaining traction in remote areas and smart buildings. These applications require durable conductive materials and weather-resistant substrates, thus expanding the market.
Materials for Printed Flexible Electronics Market Companies

- DuPont de Nemours, Inc.
- Henkel AG & Co. KGaA
- Agfa-Gevaert N.V.
- NovaCentrix
- Heraeus Holding GmbH
- Polymer Vision
- Sun Chemical Corporation
- Merck KGaA
- Intrinsiq Materials Ltd.
- NANOGAP
- Cambrios Technologies Corporation
- Nitto Denko Corporation
- Daicel Corporation
- Applied Nanotech Inc.
- Nano Dimension Ltd.
- Creative Materials Inc.
- FlexEnable Ltd.
- C3Nano Inc.
- TOYO INK SC Holdings Co., Ltd.
- Johnson Matthey Advanced Materials
Recent Development
- In July 2025, Scientists at KAIST and Seoul National University developed an electronic ink” that can be printed into circuits that switch between hard and soft, simply by changing the temperature. This breakthrough could lead to a new generation of flexible electronics - gadgets that aren't just bendy, but can change how stiff or soft they are, depending on where and how they are used.
(Source:https://www.msn.com)
Segments Covered in the Report
By Material Type
- Conductive Materials
- Silver inks
- Copper inks
- Carbon-based inks
- Nanoparticle inks
- Dielectric Materials
- Semiconductive Materials
- Organic semiconductors
- Hybrid nanomaterials
- Substrate Materials
- Polyethylene terephthalate (PET)
- Polyimide (PI)
- Polyethylene naphthalate (PEN)
- Paper & biodegradable films
- Encapsulation Materials
- Barrier films
- Parylene coatings
- Adhesives & Interface Materials
By Printing Technique Compatibility
- Inkjet-Compatible Materials
- Screen-Printing-Compatible Materials
- Gravure/Flexographic-Compatible Materials
- Aerosol Jet & 3D Printable Materials
By Application
- Displays (OLED, E-paper)
- Sensors (biosensors, strain, pressure)
- RFID & Smart Labels
- Energy Storage (Printed batteries, supercapacitors)
- Photovoltaics (Printed solar cells)
- Wearable Electronics
- Lighting (Flexible OLED lighting)
By End-Use Industry
- Consumer Electronics
- Healthcare & Medical Devices
- Automotive
- Retail & Logistics
- Industrial IoT
- Aerospace & Defense
- Energy & Utilities
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
For inquiries regarding discounts, bulk purchases, or customization requests, please contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Ask For Sample
No cookie-cutter, only authentic analysis – take the 1st step to become a Precedence Research client
 Get a Sample
Get a Sample
 Table Of Content
Table Of Content
 sales@precedenceresearch.com
sales@precedenceresearch.com
 +1 804-441-9344
+1 804-441-9344
 Schedule a Meeting
Schedule a Meeting